A&P 2 EXAM 1 CH 16 & 17
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/182
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
183 Terms
1
New cards
Produces the hormones that promote the development of the female secondary sexual characteristics at puberty.
Ovaries
2
New cards
Storehouse for the hormones produced by the hypothalamus of the brain.
Pituitary
3
New cards
Produces the hormones that direct the production of the secondary male sex characteristics.
Testes
4
New cards
Produce steroid hormones and glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids
Adrenal Glands
5
New cards
Produces hormones and is considered a neuroendocrine organ.
Hypothalamus
6
New cards
An autoimmune problem involving the thyroid gland.
Graves' disease
7
New cards
Hyposecretion of growth hormone.
Pituitary dwarfism
8
New cards
Hyposecretion of the pancreas.
Diabetes mellitus
9
New cards
Hyposecretion of the adrenal cortex.
Addison's disease
10
New cards
Hypersecretion of growth hormone.
Acromegaly
11
New cards
Hyposecretion of the thyroid in adults.
Myxedema
12
New cards
Hypersecretion of the adrenal cortex.
Cushing's disease
13
New cards
Hyposecretion of the the thyroid in infants.
Cretinism
14
New cards
The size and shape of a pea; produces hormones that stimulate other endocrine glands.
Pituitary
15
New cards
Produces hormones that regulate glucose levels in the body.
Pancreas
16
New cards
Produces a hormone that controls blood levels of calcium and potassium by their removal from bone tissue.
Parathyroid
17
New cards
Produces the body's major metabolic hormones.
Thyroid
18
New cards
Produces glucocorticoids.
Zona fasciculata
19
New cards
Produces epinephrine.
Adrenal medulla
20
New cards
Produces aldosterone.
Zona glomerutosa
21
New cards
Excess hormone levels result in Cushing's syndrome.
Zona fasciculata
22
New cards
Hormones mimic sympathetic nervous system neurotransmitters.
Adrenal medulla
23
New cards
Produces androgens.
Zona reticularis
24
New cards
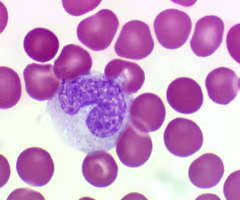
Monocyte.
25
New cards
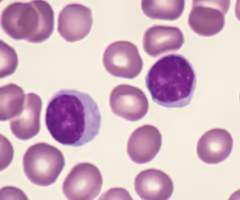
Lymphocyte.
26
New cards
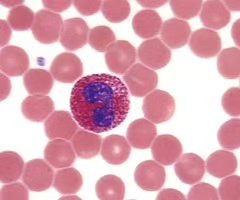
Eosinophil.
27
New cards
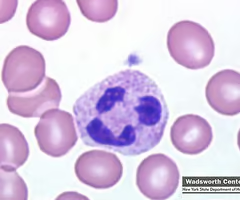
Neutrophil.
28
New cards
Most common white blood cell found in whole blood.
Neutrophil
29
New cards
Mounts an immune response by direct cell attack or via antibodies.
Lymphocyte
30
New cards
Kills parasitic worms.
Eosinophil
31
New cards
Becomes a macrophage.
Monocyte
32
New cards
Main bacteria killer during acute infections.
Neutrophil
33
New cards
Nucleus has two lobes; contains granules of lysosomal enzymes; functions in attacking parasitic worms.
Eosinophil
34
New cards
Nucleus is multilobed; functions as a phagocyte; contains fine indistinct granules.
Neutrophil
35
New cards
Transports CO2 and oxygen.
Erythrocyte
36
New cards
Contains a U- or and S- shaped nucleus; granules stain very dark; releases histamine and heparin.
Basophil
37
New cards
Largest of the WBCs; crucial in defense against viruses; associated with chronic infections.
Monocyte
38
New cards
The major contributor to plasma osmotic pressure.
Albumin
39
New cards
Thrombin catalyzes the activation of these molecules present in plasma.
Fibrinogen
40
New cards
Forms the structural framework of a blood clot.
Fibrinogen
41
New cards
Makes up most of plasma protein.
Albumin
42
New cards
Antibodies released by plasma cells during immune response.
Gamma globulins
43
New cards
Transport proteins that bind to lipids, metal ions, and fat-soluble vitamins.
Alpha and beta globulins
44
New cards
Produced by platelets.
Prostaglandin derivatives such as Thromboxane A2
45
New cards
A fibrous protein that gives shape to an RBC plasma membrane.
Spectrin
46
New cards
Hormone that stimulates productions of RBCs.
Erythropoietin
47
New cards
Stimulates WBC production.
Interleukins and CSFs
48
New cards
Natural anticoagulant found in basophils.
Heparin
49
New cards
Cancerous condition involving white blood cells.
Leukemia
50
New cards
Condition in which blood has abnormally low oxygen-carrying capacity.
Anemia
51
New cards
Abnormal excess of erythrocytes resulting in an increase in blood viscosity.
Polycythemia
52
New cards
Free-floating thrombus in the bloodstream.
Embolism
53
New cards
The antagonistic hormones that regulate the blood calcium level are calcitonin and parathyroid hormone. (T/F)
True
54
New cards
The hormone that raises blood sugar levels is insulin. (T/F)
False- The hormone that raises blood sugar levels is glucagon.
55
New cards
Addison's disease is due to a deficient output of glucocorticoids only. (T/F)
False- Addison's disease is due to a deficient output of glucocorticoids and mineralocorticoids (cortisol and aldosterone).
56
New cards
Both "turn on" factors (hormonal, humoral, and neural stimuli) and "turn off" factors (feedback inhibition and others) may be modulated by the activity of the nervous system. (T/F)
True
57
New cards
ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone) stimulates the adrenal cortex to release corticosteroid hormones. (T/F)
True
58
New cards
LH (luteinizing hormone) is also referred to as a gonadotropin. (T/F)
True
59
New cards
Chronic stress increases blood levels of cortisol and appears to contribute to memory deterioration. (T/F)
True
60
New cards
Oxytocin is a strong stimulant of uterine contractions. (T/F)
True
61
New cards
Follicle cells of the thyroid gland produce thyroglobulin, while follicles of the parathyroid produce calcitonin. (T/F)
False- Follicle cells of the thyroid gland produce thyroglobulin, while parafollicular cells of the thyroid produce calcitonin.
62
New cards
Type 2 diabetics may reflect declining receptor sensitivity to insulin rather than decreased insulin production. (T/F)
True
63
New cards
The prime metabolic effect of cortisol is gluconeogenesis. (T/F)
True
64
New cards
The beta cells are the pancreatic islet cells that produce insulin. (T/F)
True
65
New cards
Most type 2 diabetics do not produce insulin. (T/F)
False- Most type 1 diabetics do not produce insulin.
66
New cards
Aldosterone is the most potent mineralocorticoid produced in the adrenals but the least abundant. (T/F)
False- Aldosterone is the most potent mineralocorticoid produced in the adrenals and the most abundant.
67
New cards
Atrial natriuretic peptide (ANP) is a hormone that controls blood pressure in part by increasing the urinary excretion of sodium. (T/F)
True
68
New cards
Although glucagon is a small polypeptide, it is nevertheless very potent in its regulatory effects. (T/F)
True
69
New cards
The thyroid gland is a large gland that controls metabolic functions throughout the life of an individual. (T/F)
True
70
New cards
Many hormones synthesized in the gastrointestinal tract are chemically identical to brain neurotransmitters. (T/F)
True
71
New cards
All of the following hormones are secreted by the anterior pituitary: ACTH (adrenocorticotropic hormone), FSH (follicle-stimulating hormone), and LH (luteinizing hormone). (T/F)
True
72
New cards
Iodine is an essential element required for the synthesis of thyroxine. (T/F)
True
73
New cards
The endocrine gland that is probably malfunctioning if a person has a high metabolic rate is the parathyroid. (T/F)
False- The endocrine gland that is probably malfunctioning if a person has a high metabolic rate is the thyroid.
74
New cards
Growth hormone always exerts its influence by targeting other endocrine glands to produce hormones. (T/F)
False- Growth hormone always exerts its influence by targeting other endocrine tissues to produce hormones.
75
New cards
Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that usually enhance the immune response when an individual is suffering from severe stress. (T/F)
False- Glucocorticoids are steroid hormones that usually do not enhance the immune response when an individual is suffering from severe stress.
76
New cards
Direct gene activation involves a second-messenger system. (T/F)
False- Direct gene activation does not involve a second-messenger system.
77
New cards
All peptide hormone synthesis requires gene activation that produces mRNA. (T/F)
True
78
New cards
All anterior pituitary hormone except GH (growth hormone) affect their target cells via a cyclic AMP (adenosine monophosphate) second messenger. (T/F)
True
79
New cards
The primary source of RBCs in the adult human being is in the bone marrow in the shafts of the long bones. (T/F)
False- The primary source of RBCs in the adult human being is in the bone marrow in flat bones.
80
New cards
The immediate response to blood vessel injury is clotting. (T/F)
False- The immediate response to blood vessel injury is vascular spasm.
81
New cards
The process of fibrinolysis disposes of bacteria when healing has occurred. (T/F)
False- The process of fibrinolysis disposes of unneeded blood clots when healing has finished.
82
New cards
The RBC "graveyard" is the liver. (T/F)
False- The RBC "graveyard" is the spleen.
83
New cards
Hemorrhagic anemias result from blood loss. (T/F)
True
84
New cards
White blood cells are produced through the action of colony-stimulating factors (CSF). (T/F)
True
85
New cards
Hemoglobin is made up of the protein heme and the red pigment globin. (T/F)
False- Hemoglobin is made up of the red pigment heme and the protein globin.
86
New cards
Each heme contains an atom of iron and can transport one molecule of oxygen. (T/F)
True
87
New cards
Each hemoglobin molecule can transport two molecules of oxygen. (T/F)
False- Each hemoglobin molecule can transport four molecules of oxygen.
88
New cards
Diapedesis is the process by which red blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries. (T/F)
False- Diapedesis is the process by which white blood cells move into tissue spaces from the interior of blood capillaries.
89
New cards
Positive chemotaxis is a feedback system that signals leukocyte migration into damaged areas. (T/F)
True
90
New cards
A condition of leukocytosis indicates over 11,000 white blood cells per cubic millimeter in the blood. (T/F)
True
91
New cards
Basophils increase in number when parasitic invasion occurs. (T/F)
False- Eosinophils increase in number when parasitic invasion occurs.
92
New cards
Leukopenia is an abnormally low number of leukocytes. (T/F)
True
93
New cards
A person with type B blood could receive blood from a person with either type B or type O blood. (T/F)
True
94
New cards
Leukocytes move through the circulatory system by amoeboid motion. (T/F)
False- Leukocytes move through the circulatory system by going with the flow of the blood.
95
New cards
Granulocytes called neutrophils are phagocytic and are the most numerous of all white blood cell types. (T/F)
True
96
New cards
All lymphocytes are leukocytes, but not all leukocytes are lymphocytes. (T/F)
True
97
New cards
Gluconeogenesis occurs in the liver due to the action of _____.
A) aldosteron
B) insulin
C) secretin
D) cortisol
A) aldosteron
B) insulin
C) secretin
D) cortisol
D) cortisol
98
New cards
Normal development of the immune response is due in part to hormones produced by the _____.
A) adrenal medulla
B) pancreas
C) thyroid gland
D) thymus gland
A) adrenal medulla
B) pancreas
C) thyroid gland
D) thymus gland
D) thymus gland
99
New cards
Virtually all of the protein or amino acid-based hormones exert their effects through intracellular _____.
A) ions
B) deactivators
C) nucleotides
D) second messengers
A) ions
B) deactivators
C) nucleotides
D) second messengers
D) second messengers
100
New cards
Which of the following is not a category of endocrine gland stimulus?
A) enzyme
B) humoral
C) neural
D) hormonal
A) enzyme
B) humoral
C) neural
D) hormonal
A) enzyme