Electrical Stimulation and TENS
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
What are some contraindications for NMES and TENS?
Pacemaker or implanted defibrillator, unstable arrhythmia, over a thrombosis, pregnancy (over trunk), over recent tendon repair or tear
What are some precautions for NMES and TENS?
Cardiac disease, impaired sensation, malignancy, or open wounds
What is a direct current (DC)?
A continuous stream of charged particles in one direction
When would you use direct current?
Used with Iontophoresis and stimulating contractions in denervated muscles
What is alternating current (AC)?
Continuous flow of charged particles in two directions (flowing back and forth)
When should you use alternating current?
For pain management and muscle contraction
What is a pulsed current?
Interrupted flow of charged particles, pulses with periods of no current flow
When should you use pulsed currents?
Pain control, tissue healing, or muscle contraction
What is monophasic pulsed current and when should you use it?
A pulsed current that flows in one direction only
For tissue healing and edema management
What is biphasic pulsed current and when should you use it?
Pulses that go back and forth, can be symmetrical or asymmetrical
For muscle contractions and modulates pain
Most commonly used setting
What is an interferential current?
Uses 4 electrodes to produce two slightly different AC frequencies that meet in the middle and target that middle spot (like an X)
More comfortable and targets deeper tissue
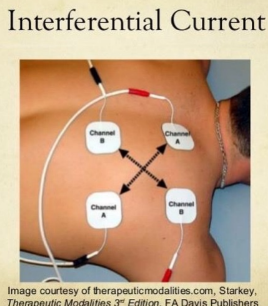
What frequency should an interferential current be set to?
1,000-10,000 Hz
What is a premodulated current?
Sequentially increases and decreases the current amplitude with a single circuit, not as deep as IFC, good for pain management, edema, and slow muscle contractions
2 electrodes total
What frequency should a premodulated current be set to?
1,000-10,000 Hz
What is a Russian protocol current?
Used for muscle re-education, 10 ms-long bursts with 50 bursts per second
What frequency does a Russian protocol current have to be used at?
2,500 Hz
What is a phase?
The period when a current flows in one direction
What is phase duration?
How long a phase lasts (time the phase occurs for) in microseconds
What is a pulse?
The period when electrical current flows in any direction (biphasic)
What is a pulse duration?
How long a pulse lasts from start of first phase to end of the last phase
What is frequency?
The number of cycles or pulses that occur in one second, measured in Hz or pulses per second (pps)
What is amplitude?
the magnitude or strength of the current flow (measured in amps or volts)
What is the interpulse interval?
The time no pulse or phase is occurring
How does TENS modulate pain?
Activates non-nociceptor A-beta fibers to stop the transmission of pain signals (tricks the brain)
Can also release the body’s opioid (endorphins) that are the body’s natural Tylenol
How long can low-rate TENS help release endorphins in the body for?
4-5 hours post treatment
When do you use neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES)?
Use in innervated muscles, with AC or PC current (Russian or pulsed biphasic)
When do you use electrical muscle stimulation (EMS)?
Use on denervated muscles with DC current
What type of muscle fiber is activated with physiologically initiated contraction?
Slow twitch type 1 fibers first, then type 2 fibers
What type of muscle fiber is activated with electrically stimulated contraction?
Fast twitch type 2 first, then type 1 fibers
When should you use a biphasic frequency of < 30 pps?
To stimulate motor nerves and for smaller muscles
When should you use a biphasic frequency of 35-50 pps? *Recommended frequency
Twitches are closer together and form a smoother contraction for larger muscles
When should you use a biphasic frequency of 50-80 pps?
For stronger contractions and can increase muscle strengthening and increase fatigue
What is galvanotaxis?
Movement of cells in response to the electrical fields. Use a negative electrode to promote healing of inflamed or infected wounds (cathode). Use positive electrode to promote healing of wounds w/o inflammation (anode)