Alcohols
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
State and explain the bond angel of H-C-H and C-C-O in an alcohol (3)
109.5
4 bonding pairs of electrons
Repelling to a position of minimum repelling
State and explain the bond angle in H-O-C in an alcohol (4)
104.5
2 bonding pairs and 2 lone pairs
Repelling to a position of minimum repulsion
Lone pairs repel more than bonding pairs so angle is reduced
Explain the boiling points of alcohols
High
Due to relatively low volatility
And ability to form hydrogen bonds between alcohol molecules
What are the conditions for the partial oxidation of primary alcohols (2)
Reagent : potassium dichromate (VI) and dilute sulphuric acid
Conditions : warm and distil aldehyde as if forms
What is the reaction in the partial oxidation of primary alcohols (1)
Primary alcohol to aldehyde and water molecule
What is the reaction for the full oxidation of primary alcohols (1)
Primary alcohol to carboxylate acid and water molecule
What are the conditions for the full oxidation of primary alcohols (2)
Reagant: potassium dichromate (VI) and dilute sulfuric acid
Conditions ; heat under reflux
What is the reaction of the oxidation of secondary alcohols
Secondary alcohol to ketone and water molecule
What are the conditions for the oxidation of secondary alcohols (2)
Reagent : potassium dichromate (VI) and diluted sulfuric acid Conditions
Conditions: heat under reflux
Why can’t tertiary alcohols be oxidised (1)
There is no hydrogen atom bonded to the carbon with the -OH group
Explain the process for testing for aldehydes using tollens Reagant (5)
Form tollens reagent by mixing aqueous ammonia and silver nitrate
Heat gently
Aldehydes are oxidised into carbolxylic acid
And silver ions are reduced to silver atoms
Forming a silver mirror coat
What is the chemical formula for tollens reagent (1)
[Ag(NH3)2]+
Explain the process for testing for aldehydes using Fehlings solution (4)
Heat gently
Aldehydes are oxidised into carboxylic acid
Copper (II) ions are reduced to copper (I) oxide
which produces a colour change from blue to red
How can you test for the presence of a carboxylic acid (2)
Add sodium carbonate
It will fizz and produce carbon dioxide
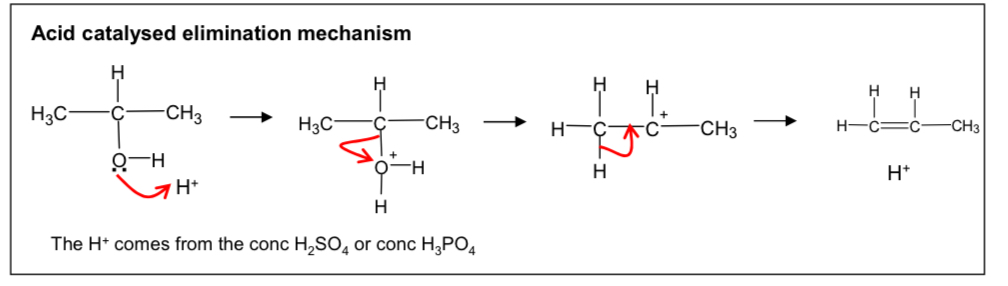
What are the conditions for converting an alcohol into an alkene
Reagant : conc sufuric acid
Conditions : warm under reflux
What is a dehydration reaction (1)
Removes a water molecule from a molecule
What type of reaction if the conversion of alcohol to alkene (1)
Acid catalysed elimination
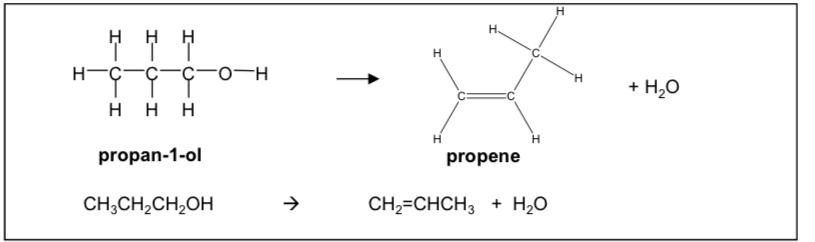
Draw out the displayed formulas for the reaction of converting an alcohol into an alkene
Draw out the acid catalysed elimination mechanism to form alkene from alcohol
What is the word equation for the fermentation of glucose (2)
Glucose to ethanol and carbon dioxide
What is the chemical equation for the fermentation of glucose (3)
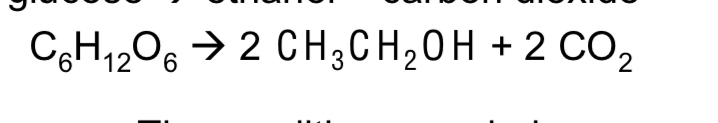
What are the conditions needed for fermentation of glucose (3)
Yeast
No air
38 degrees Celsius
Why is 38 the temperature used for fermentation (2)
At lower, the reaction is too slow
At higher, the yeast dies and enzymes denature
Why is fermentation done in the absence of air (1)
Because air can oxidise the ethanol to ethanol acid
What are the advantages of fermentation (3)
Sugar is renewable resource
Production uses low technology
Production uses cheap equipment
What are the disadvantages of fermentation (3)
Batch process is slow and gives high production costs
Ethanol made is not pure and needed purification by fractional distillation
Depletes land is used for growing food crops
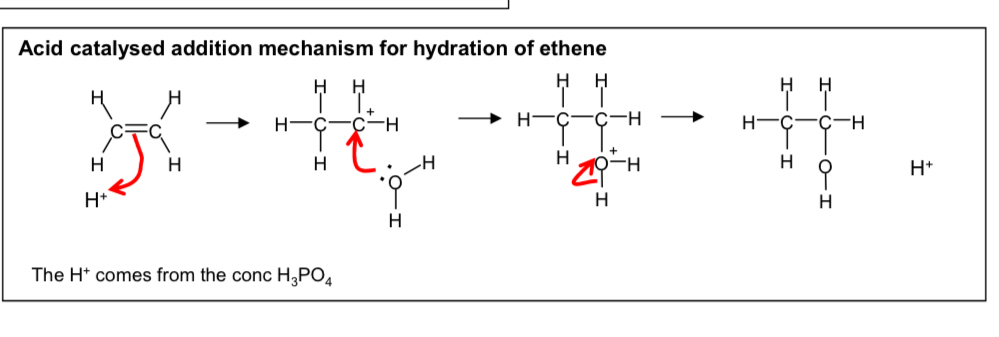
Explain the conditions required to form ethanol from ethene (3)
300 c
70 atm
H3PO4
What are the advantages of producing ethanol from ethene (3)
Faster reaction
Purer product
Continuous process
What are the disadvantages of producing ethanol from ethene (3)
High tech equipment costs
Ethene is non renewable resource
High energy costs to produce high pressures
Draw the mechanism for the hydration of ethene to form ethanol
What does the term carbon neutral mean (1)
An activity that has no net annual carbon emissions to the atmosphere
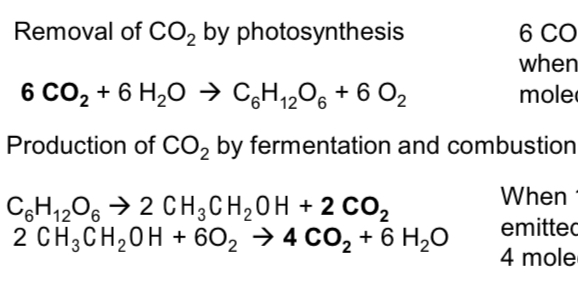
Write out the equations that show no net contribution to CO2 through photosynthesis and fermentation (4)
What is the mechanism for the greenhouse effect (6)
UV wavelength radiation passes through the atmosphere to earth surface
and heats up earths surface
Earth radiates our infrared long wavelength radiation
C=O bonds in carbon dioxide absorb infrared radiation so the IR radiation does not escape from atmosphere
This energy is transferred to other molecules in atmosphere by collision
Therefore atmosphere is warmed
How can you test for primary and secondary alcohol (2)
Add potassium dichromate and sulfuric acid
Colour change from orange to green