Exam 3 Study Guide
4.5(2)
Card Sorting
1/61
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biology
norris
kennedy norris
JSU
DNA
DNA structure
DNA function
haploid
diploid
chromosomes
nucleotides
DNA replication
DNA polymerase
DNA mutation
mutation
neoplasms
malignant
benign
mutagen
transcription
translation
DNA transcription
DNA translation
RNA
mitosis
telomere
telomeres
meiosis
allele
sexual reproduction
asexual reproduction
genetics
codominance
incomplete dominance
punnett square
punett square
evolution
charles darwin
macroevolution
microevolution
University/Undergrad
Last updated 7:33 PM on 11/30/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
62 Terms
1
New cards
RNA
transcription is the process of genes being transcribed into ( )
2
New cards
thymine
Which is NOT one of the nucleotides found in RNA: adenine, guanine, thymine, cytosine
3
New cards
cytoplasm
where does translation take place within the cell
4
New cards
tRNA
which type of RNA brings amino acids to the ribosomes to make proteins
5
New cards
malignant
which type of neoplasms grow fast, spread, and are dangerous to the organism's health
6
New cards
single
RNA molecules are ( ) stranded
7
New cards
double
DNA molecules are ( ) stranded
8
New cards
nucleus
where does transcription take place within the cell
9
New cards
metaphase
which phase of mitosis involves the chromosomes lining up in the middle of the cell
10
New cards
introns
( ) are removed from newly made mRNA strands because they do not code for proteins
11
New cards
meiosis
halves the number of chromosomes
12
New cards
fertilization
restores the number of chromosomes
13
New cards
if fruit flies have a diploid chromosome number of 8 then how many chromosomes do their gametes have?
4
14
New cards
Gregor Mendel
the father of modern genetics
15
New cards
sexual reproduction in animals requires ( )
meiosis, fertilization, gametes
16
New cards
ff
if an individual is homozygous recessive for a trait, what would their allele combination look like?
17
New cards
haploid
this type of cell has one set of chromosomes
18
New cards
diploid
this type of cell has two sets of chromosomes
19
New cards
the four nucleotides that make up DNA
Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), Thymine (T)
20
New cards
chromosomes
tightly packed DNA, two sister chromatids that are joined together
21
New cards
What does DNA polymerase do?
assemble new strands of DNA at primers using nucleotides. Like a printer, catch mistakes during DNA replication
22
New cards
mutations can be..
beneficial, neutral, or harmful
23
New cards
mutation
permanent change in the DNA sequence of a chromosome
24
New cards
how mutations happen
Nucleotide may be moved or deleted, Extra nucleotide may be added, Replicated DNA that isn’t like parent strand
25
New cards
common causes of mutations
Chemical exposure, infectious agents, direct damage to DNA
26
New cards
mutagen
chemical that permanently changes DNA
27
New cards
transcription
Process of copying a gene into RNA form
28
New cards
what does transcription do?
this process makes 3 types of RNA (rRNA, tRNA, mRNA)
29
New cards
translation
Using mRNA to build proteins from amino acids
30
New cards
what does translation do?
this process makes a protein
31
New cards
rRNA
ribosomal RNA
32
New cards
tRNA
transfer RNA
33
New cards
mRNA
messenger RNA
34
New cards
genes
segments of DNA that contain information about certain traits
35
New cards
where does transcription occur?
nucleus
36
New cards
where does translation occur?
cytoplasm
37
New cards
intron
segments of genes that are removed from newly made mRNA strands because they do not code for proteins
38
New cards
exon
segments of genes that code for proteins
39
New cards
telomere
regions of noncoding DNA at the ends of chromosomes
40
New cards
telling age with telomeres
They act as a cushion to protect genes in DNA, they shorten when cells divide and when they’re too short the cell dies, causes organisms to get weak with age
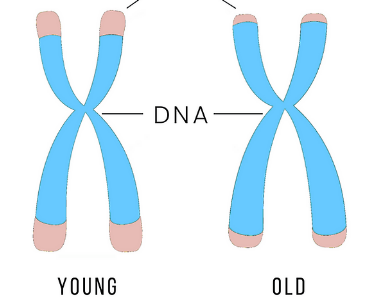
41
New cards
chromosomes number of parent and daughter cells..
is the same
42
New cards
malignant neoplasms
grow fast, spread, and are dangerous to the organism's health
43
New cards
benign neoplasms
don’t spread, grow slowly, don’t negatively affect health.
44
New cards
apoptosis
Major mistakes that can’t be fixed by checkpoint genes can trigger this; Self destruct button that starts cell death
45
New cards
asexual reproduction uses..
mitosis only
46
New cards
sexual reproduction uses..
meiosis and mitosis
47
New cards
what does meiosis do to chromosome number?
halves the number of chromosomes
48
New cards
what does fertilization do to chromosome number?
restores chromosome number
49
New cards
allele
different forms of the same gene
50
New cards
sexual reproduction
reproduction with offspring from two parents, creates genetically unique offspring
51
New cards
asexual reproduction
single parent copies itself to make offspring, genetically identical offspring
52
New cards
codominance
two dominant alleles, often see a mix of the two traits, both traits are present

53
New cards
incomplete dominance
both alleles aren’t fully dominant or recessive, often get a combo of the two traits

54
New cards
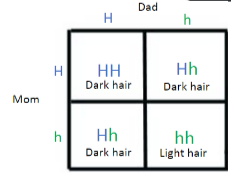
punnett square
55
New cards
four principles of evolution
Variation in traits, inheritance of traits, selection (encourage, discourage) of traits, time
56
New cards
macroevolution
large scale evolutionary changes over a long period of time, most controversial part of evolution
57
New cards
microevolution
evolutionary change within a species over a short period of time (like the croatian lizards)
58
New cards
mutations create..
new alleles
59
New cards
Charles Darwin
studied finches on the Galapagos Islands, best known for the understanding of evolutionary biology, natural selection
60
New cards
speciation
the formation of new and distinct species during evolution, ancestral population splits up and form new species
61
New cards
fitness
how well a species is suited for a particular environment
62
New cards
evolution
a process of gradual change that takes place over many generations, during which species of animals, plants, or insects slowly change some of their physical characteristics, change of population