Life history
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
Fecundity
The potential reproductive capacity of an individual organism or population
★ cohort
group of individuals in a population that were all born at around the same time
★ kin selection
a process whereby natural selection favours a trait due to its positive effects on the reproductive success of an organism's relatives
★ clutch size fast facts
clutch size increases with increasing latitude and day length
lay less than expected so that more can survive
★ survivorship curve
plots survivorship against age and characterizes the pattern of mortality
★ age specific fecundity
charcterizes fecundity at a particular age
★ net reproductive rate
average number of female offspring that a female is expected to have in a life time
★ life table parameters
age class, number surviving, number of births, survivorship, fecundity
Fecundity rate
The average number of offspring per reproductive female per year
★ Life history
The sequence, time in, and nature of events in an organism's life, from birth to reproduction to death
★ Life history strategy
Pattern of life history traits that has evolved by natural selection over time in a population in response to particular ecological and environmental conditions
Life history trait
A heritable trait that determines some aspect of life history of an organism or species
Age and size at maturity, number of offspring
★ Key life history questions
How long and how big to grow
When sexually mature and how long reproductively active
How many offspring and how much to invest in each
How much to invest in growth and survival vs. reproduction
Life history trade offs
Arise because resources allocated to one trait cannot be used for another
Every life history strategy comes with both costs and benefits
Constraints
Limit how an individual can invest in survival and reproduction
Can be imposed by environment
Some are imposed by physiology
if allocation to survival and growth increases
The allocation to reproduction must decrease
The allocation to each offspring must decrease
Growth rate
r = b - d
r > 0 : pop is growing
r = 0 : pop is stable
r < 0 : pop is shrinking
Age structure
Pre-reproductive: 0-20
Reproductive: 20-50
Post-reproductive: 50+
★ successful life history
stable or growing populations
Demographic parameters
Quantitative values that characterize the life history of a species
Birth rate
Death rate
Fecundity
Age of first reproduction
Life table
Summarizes how fecundity and mortality vary with age
Estimate population growth more accurately
★ Survivorship
The fraction of the initial cohort that survives to start an age class
Divide the live individuals by initial cohort size
Type 1
Human, elephant
High survivorship in early and middle ages, quick decline at old age
Type 2
Squirrel, birds
Constant mortality rate throughout life. Same proportion survive each age class
Type 3
Barnacle, trees
Very low survivorship for young individuals, high for those who reach middle and old age
Many offspring
Fecundity schedule
Set of age specific fecundities of a population
Net reproductive rate
Average number of female offspring that a female has in her lifetime
Depends on how many offspring she has at each age and her survival to that age
R0 = Σlxmx
If R0 is greater than 1, then the population is growing
Generation time
The average time that elapsed from the birth of a female until the birth of her daughters
Unit of G is in years
Shorter generation time = larger population growth rate
★ Per capita population growth rate
r = b - d
The average number of individuals added to the population per individual per unit time
Depends on how many daughters a typical female produces and how long it takes her to produce daughters
Exponential growth equation
Estimate the size of a population that has been growing for a time period from an initial size
Demographic transition
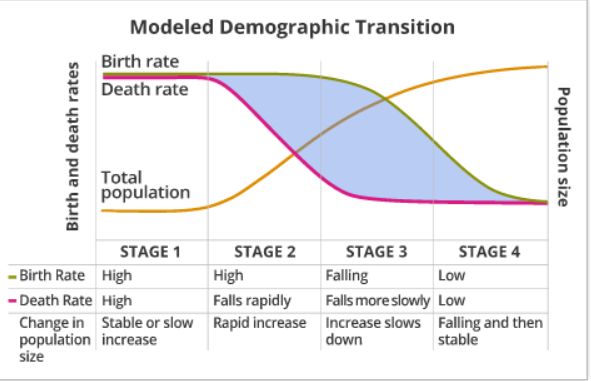
Stage one
High birth
High death
Stable population
Stage two
High birth
Falling death
Rapid increase in population size
Stage three
Falling birth
Falling death, slower
Slower increase in population size
Stage four
Low birth
Low death
Falling then stable population
Trade offs with age of first reproduction
The age at which a fish reaches sexual maturity can affect its fecundity
Fish that mature early spec into reproduction and spec out of growth and survival
Fish that delay reproduction can spec into growth
Fish they delay reproduction are more fecund when they start reproducing
Have more gametes
Maintain this advantage through life
They can reproduce early but remain less fecund or they can delay reproduction and remain more fecund for longer
Principle of allocation
Any resource used for one function reduces the amount of energy available for another function
Iteroparity
Multiple bouts of reproduction during an individual's lifetime
Iteroparous
Reserve resources during each reproductive bout to invest in growth, maintenance, and future reproduction
Semelparity
A single bout of reproduction in a lifetime
Semelparous
Produce a huge number of offspring
Benefit by delaying reproduction until they are grown big, can invest heavily in reproduction
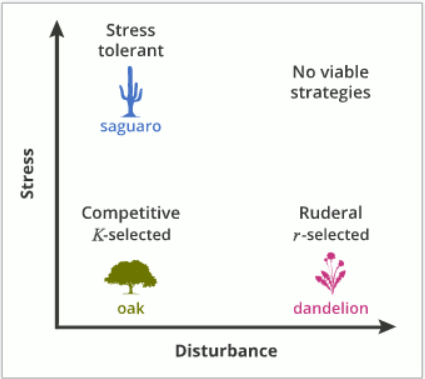
Species are classified as r or K selected based on how they respond to disturbances which reduce population densities and make resources more readily available
r-selected
Reproduce early and often
Invest lightly in each offspring
More successful in environments where disturbances are regular
Competition isn’t important
K-selected
Highly competitive
More successful in stable environments
Perform well when population size is close to K
Grow larger, live longer, reproduce later, invest resources into offspring
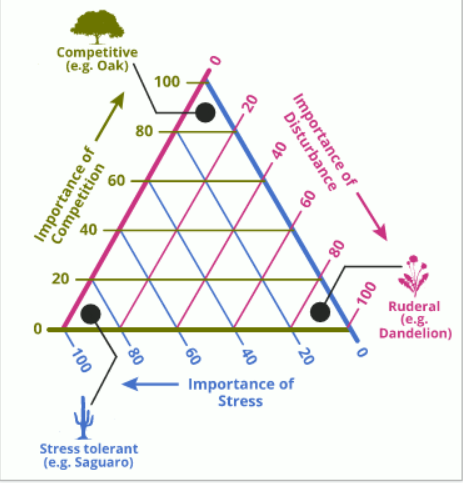
Ruderal
r-selected plants stay small, reproduce early, invest heavily in seed production
Seed survive long periods of dormancy
Grass, dandelions
Competitive
K-selected plants have low mortality, efficiently take up water and nutrients, live long, devote more energy to growth and survival and reproduction
Do best environments what are low stress and low disturbance
Oak, hickory
Stress tolerant
Have adaptations for tolerating periods of scarcity and exploiting ephemeral resources
Water after a storm
Slow growth rates, evergreen, long-lived tissues, storage of nutrients and water
High reproductive rates, low juvenile survivorship, long lifespans
Cacti, arctic lichens
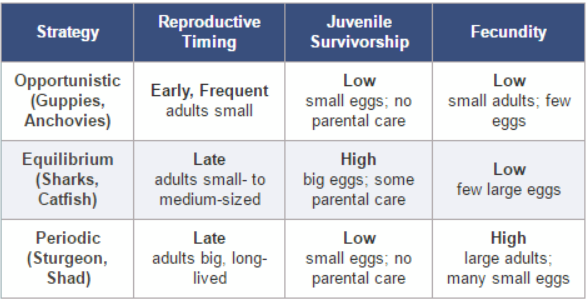
Opportunistic
Early, frequent
Low Juvenile survivorship
Low Fecundity
Guppies, anchovies
Equilibrium
Late
High Juvenile survivorship
Low Fecundity
Sharks, catfish
Periodic
Late
Low Juvenile survivorship
High Fecundity
Sturgeon
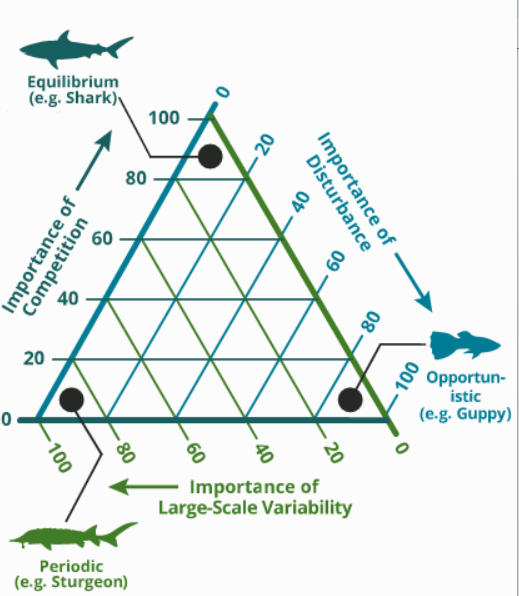
Large scale variability
Response to strong seasonality or special variability