Computer Science 0478 IGCSE C1
1/62
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Why do computers use binary?
Computers only understand ON (1) and OFF (0) states.
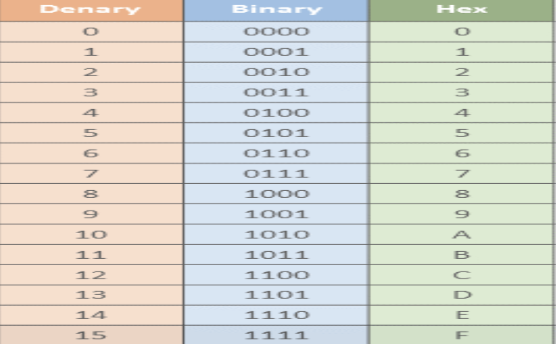
What number systems must we know?
Binary (base 2), Denary (base 10), Hexadecimal (base 16).
Why is binary used in computers?
It enables fast calculations and efficient data storage.
What is hexadecimal used for?
MAC addresses, IPs, HTML colours, error codes.
Convert binary 00111110 to hexadecimal.
3E
Convert denary 94 to binary.
01011110
Convert binary 01100110 to denary.
102
Convert denary 63 to hexadecimal.
3F
Convert hexadecimal A7 to binary.
10100111
Why is hexadecimal useful?
Fewer digits, easier to read/debug than binary.
Add binary: 01011001 + 00110010
10001011 (no overflow)
What is overflow in binary addition?
When result exceeds available bits and data is lost.
Convert denary 22 to binary, shift left 1 place.
00010110 → 00101100 (×2 = 44)
What does a left binary shift do?
Multiplies by 2 for each shift.
What does a right binary shift do?
Divides by 2 for each shift.
What is two’s complement used for?
Representing positive and negative binary integers.
Convert -12 to binary using two’s complement.
11110100

Convert 10110011 to denary (two’s complement).
-77
What is ASCII?
7-bit code for English characters.
What is Unicode?
16-bit+ code supporting many languages.
Difference between ASCII and Unicode?
Unicode supports more characters; ASCII is smaller.
How is sound represented in binary?
Analogue is sampled and converted via ADC.
What is sample rate?
Number of samples per second (Hz).
What is sample resolution (bit depth)?
Number of bits per sample.
Effect of increasing sample rate or resolution?
Better quality, larger file size.
How is an image stored in binary?
As pixels with binary values for colour.
What is image resolution?
Total number of pixels (width × height).
What is colour depth?
Bits used per pixel to represent colour.
Higher resolution/colour depth = ?
Sharper image, larger file size.
What is a bit?
A single binary digit (0 or 1).
How many bits in a nibble?
4
How many bits in a byte?
8
How many bytes in 1 KiB?
1024
Image file size formula?
width × height × colour depth
Sound file size formula?
sample rate × duration × bit depth × channels
Benefits of data compression?
Saves space, faster transfers, lower cost.
Lossy vs Lossless compression?
Lossy removes data; Lossless keeps all data.
Example of lossy file type?
.mp3, .jpeg
Example of lossless file type?
.png, .txt
What is Run Length Encoding (RLE)?
Compresses repeated data into count + value.
RLE example: AAAABBBCCDAA
4A3B2C1D2A
Why do computers use binary to represent data?
Because computers have two states, ON (1) and OFF (0), which binary represents.
What is ASCII used for?
Representing English characters with 7-bit binary codes.
What is Unicode?
A character set using 16 or more bits that supports many languages and symbols.
State one advantage of Unicode over ASCII.
Unicode supports multiple languages and more characters.
Compare ASCII and Unicode in terms of size and language support.
ASCII uses 7 bits and supports English only; Unicode uses 16+ bits and supports multiple languages.
What does sample rate mean in sound representation?
The number of sound samples taken per second.
How does sample rate affect digital sound quality?
Higher sample rate means better quality and larger file size.
What does sample resolution (bit depth) control in sound?
The number of bits per sample, affecting accuracy and file size.
How does increasing sample resolution affect sound quality?
It increases accuracy and file size.
Calculate the file size in bits of an image with resolution 640×480 and colour depth 24 bits.
640 × 480 × 24 = 7,372,800 bits.
Calculate the file size of a 800x600 image with 24-bit colour depth.
800 × 600 × 24 = 11,520,000 bits or 1,440,000 bytes.
Calculate the file size of a 3-minute stereo audio with sample rate 44,100 Hz and sample resolution 16 bits.
44,100 × 180 × 16 × 2 = 254,016,000 bits.
Give one example of a file type that uses lossy compression.
JPEG for images or MP3 for audio.
Give one example of a file type that uses lossless compression.
PNG for images or WAV for audio.
What is overflow in binary addition?
When the result exceeds the number of bits available to store it.
Give an example of overflow with an 8-bit register adding 255 + 1.
255 (11111111) + 1 = 00000000 (overflow occurs).
Explain what happens when a binary number is shifted left by one bit.
It is multiplied by 2; all bits move left, a 0 fills the right.
Explain what happens when a binary number is shifted right by one bit.
It is divided by 2; all bits move right, a 0 fills the left.
Explain what happens when a binary number is shifted right by two bits.
It is divided by 4 (ignoring remainder).
What is the size of 1 KiB in bytes?
1024 bytes.
Represent the decimal number -12 in 8-bit two’s complement.
11110100.
Explain why two’s complement is used.
To represent positive and negative integers in binar