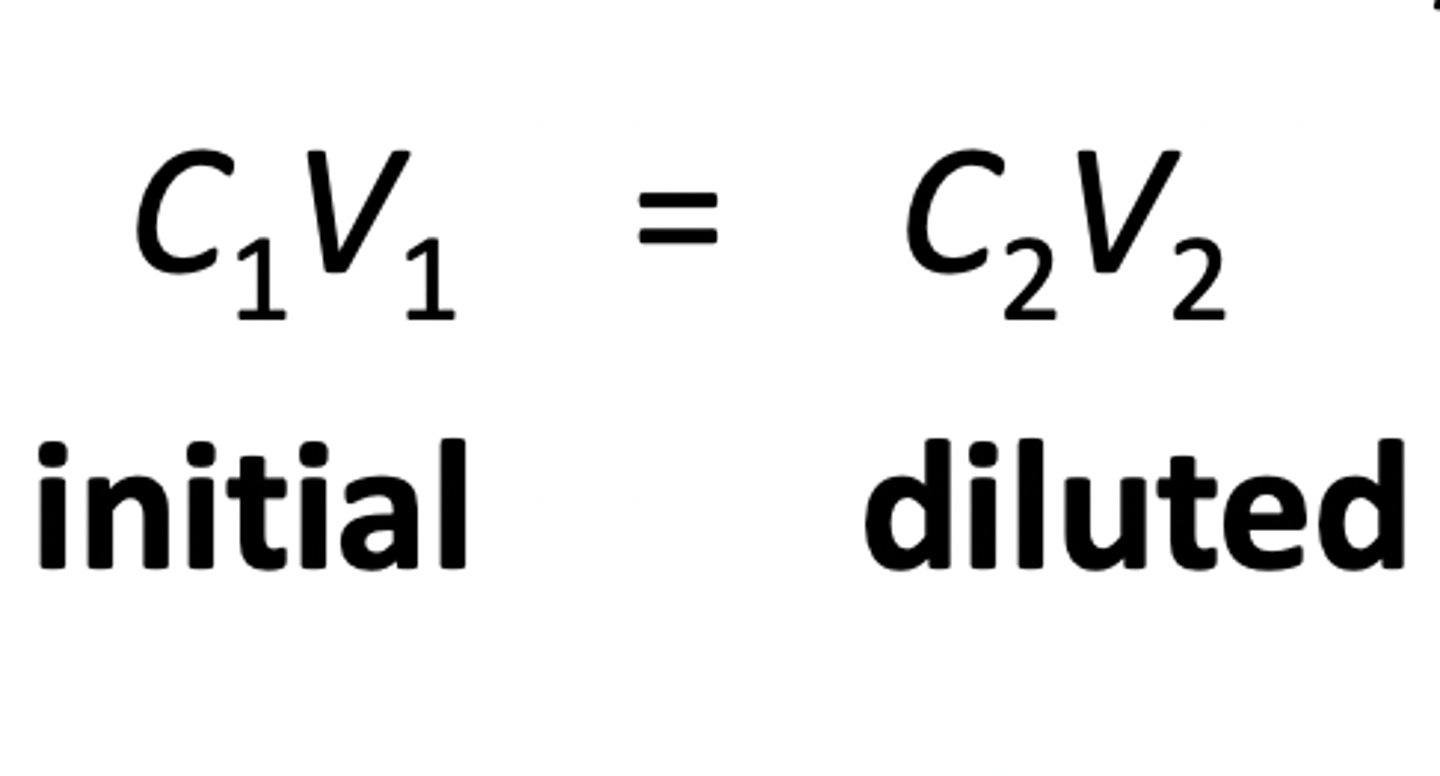CHEM 107 C Lecture #5 - The Mole and Chemical Quantities
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
6.02 x 10^23 anythings
1 mole of anything = _______ anythings
The Mole
the amount of a substance containing the same number of discrete entities (atoms, molecules, ions, etc.) as the number of atoms in a sample of pure carbon-12 weighing exactly 12 g
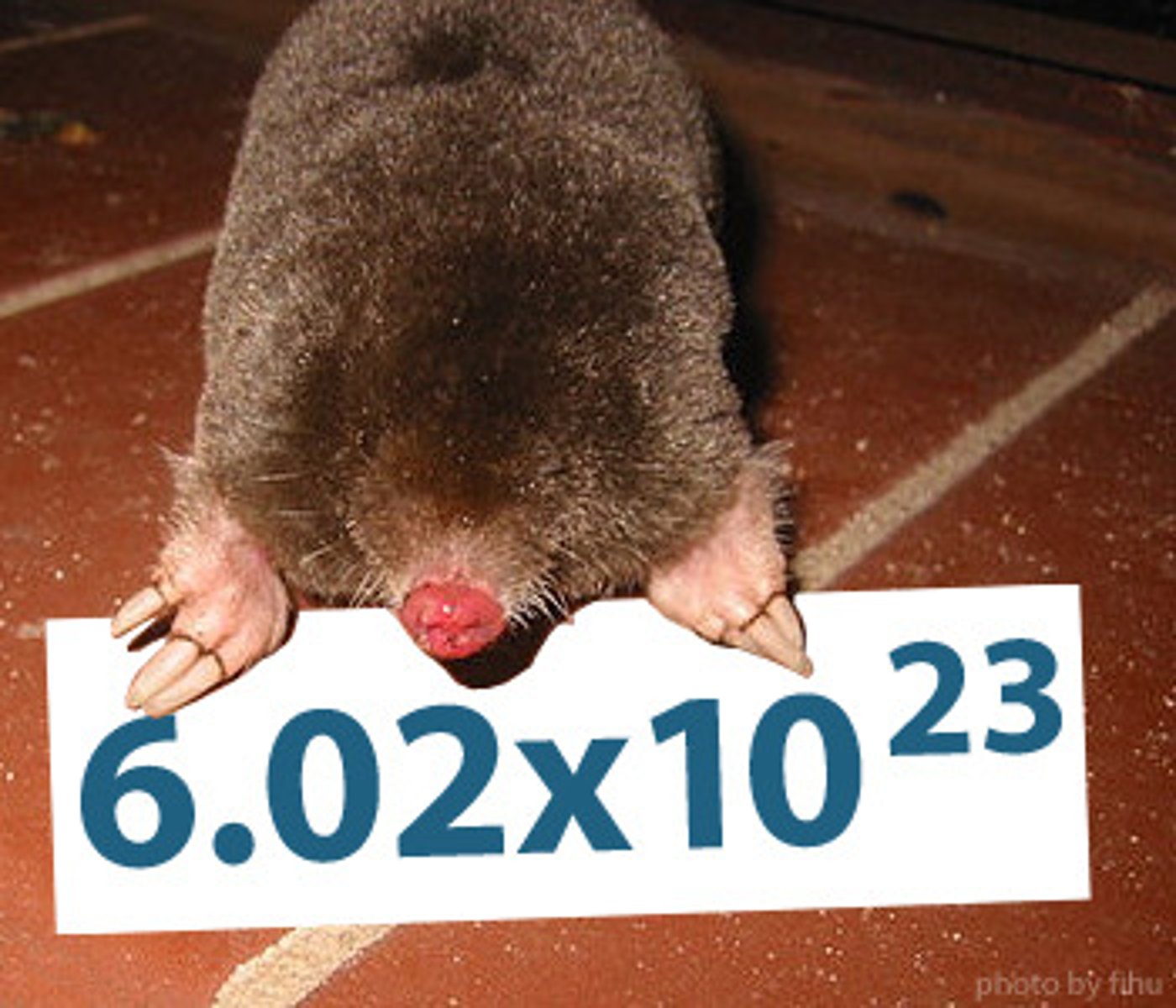

Avogadro's Number
6.02214179 x 10^23
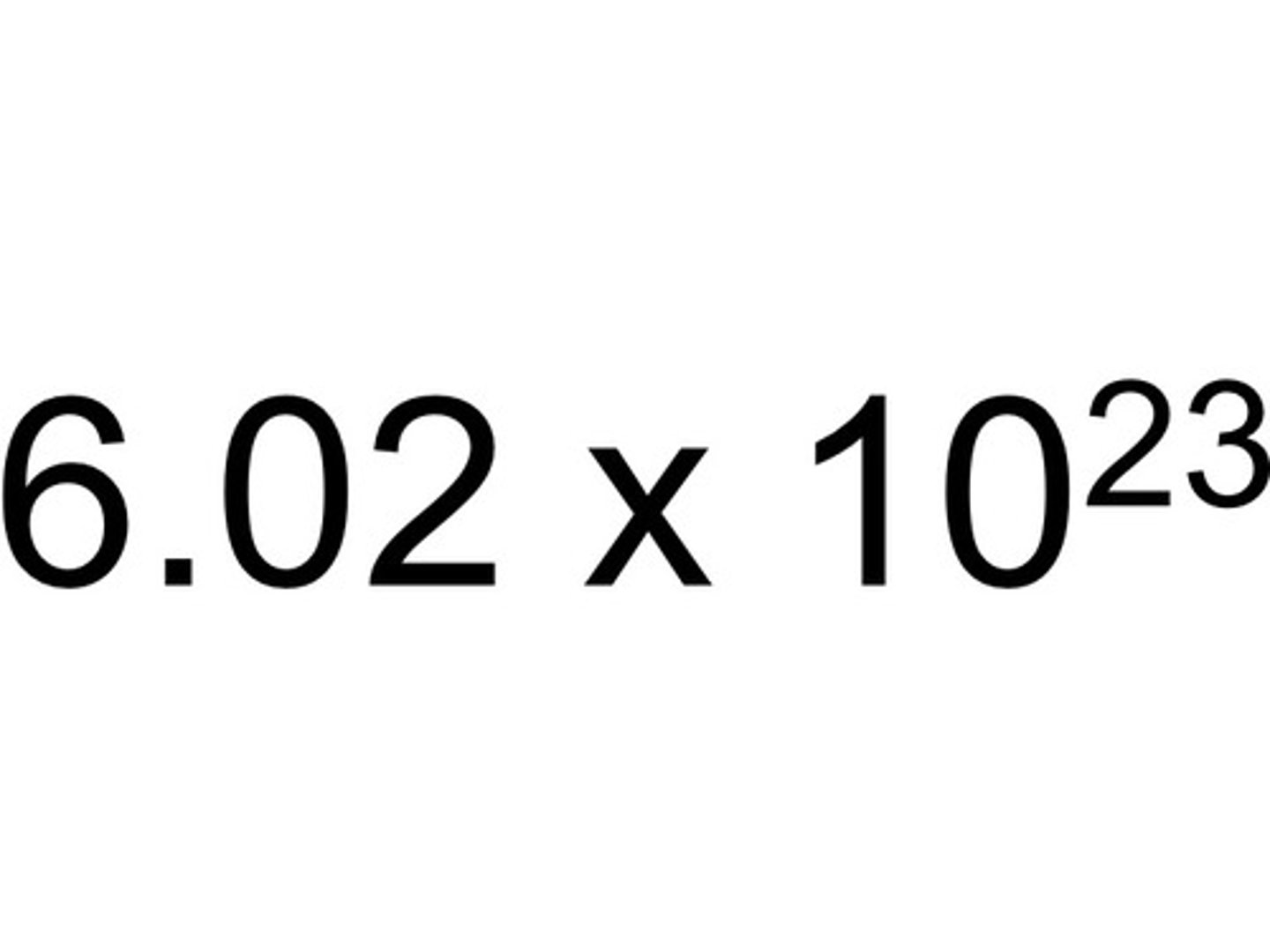
(6.02 x 10^23) particles / 1 mole
mole as a conversion factor

Molar Mass
the mass in grams of 1 mole of that substance, a property expressed in units of grams/mol
- equal to an element's atomic mass in amu

mass to moles to particles
converting from mass to particles

particles to moles to mass
converting from particles to mass

Percent Composition
% E = (mass of E / mass of whole sample) * 100%
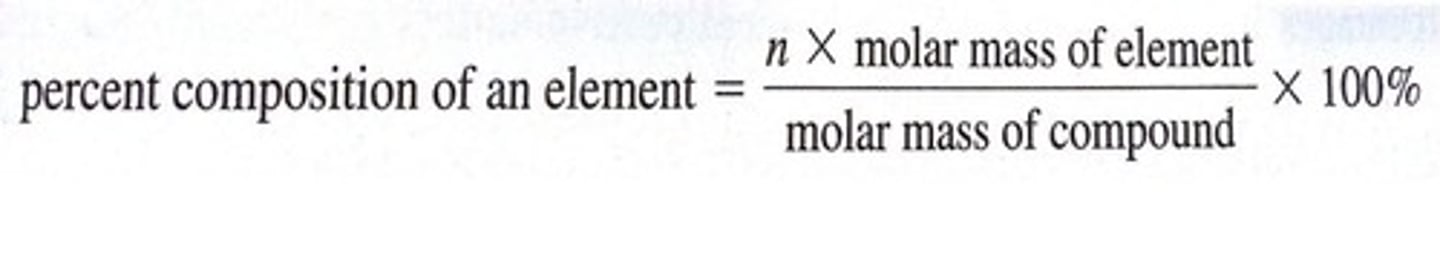
Empirical formula
Formula showing the simplest whole-number ratio of the number of atoms/ions in the compound
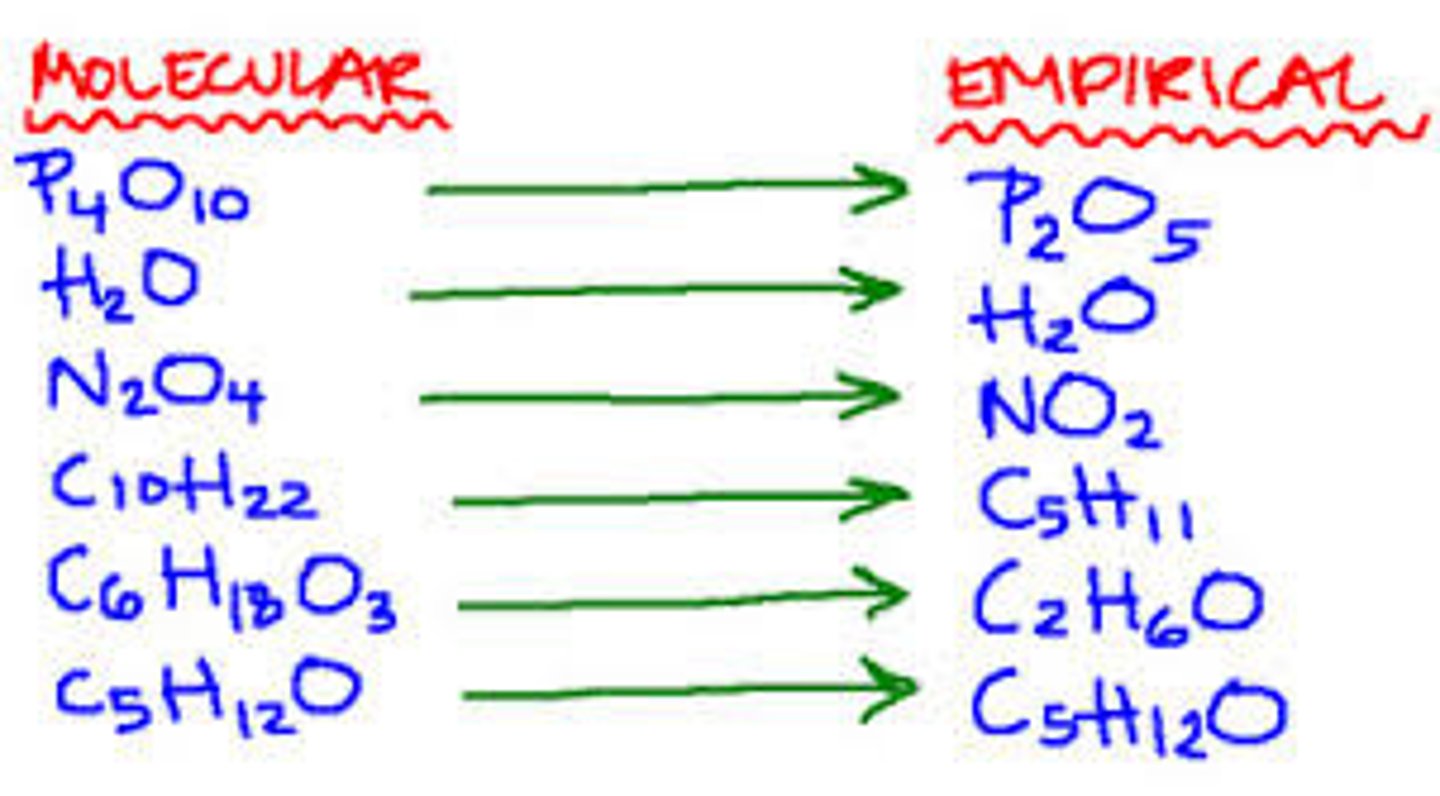
Molecular formula
Formula showing the actual number of atoms of each element in a molecule of the compound

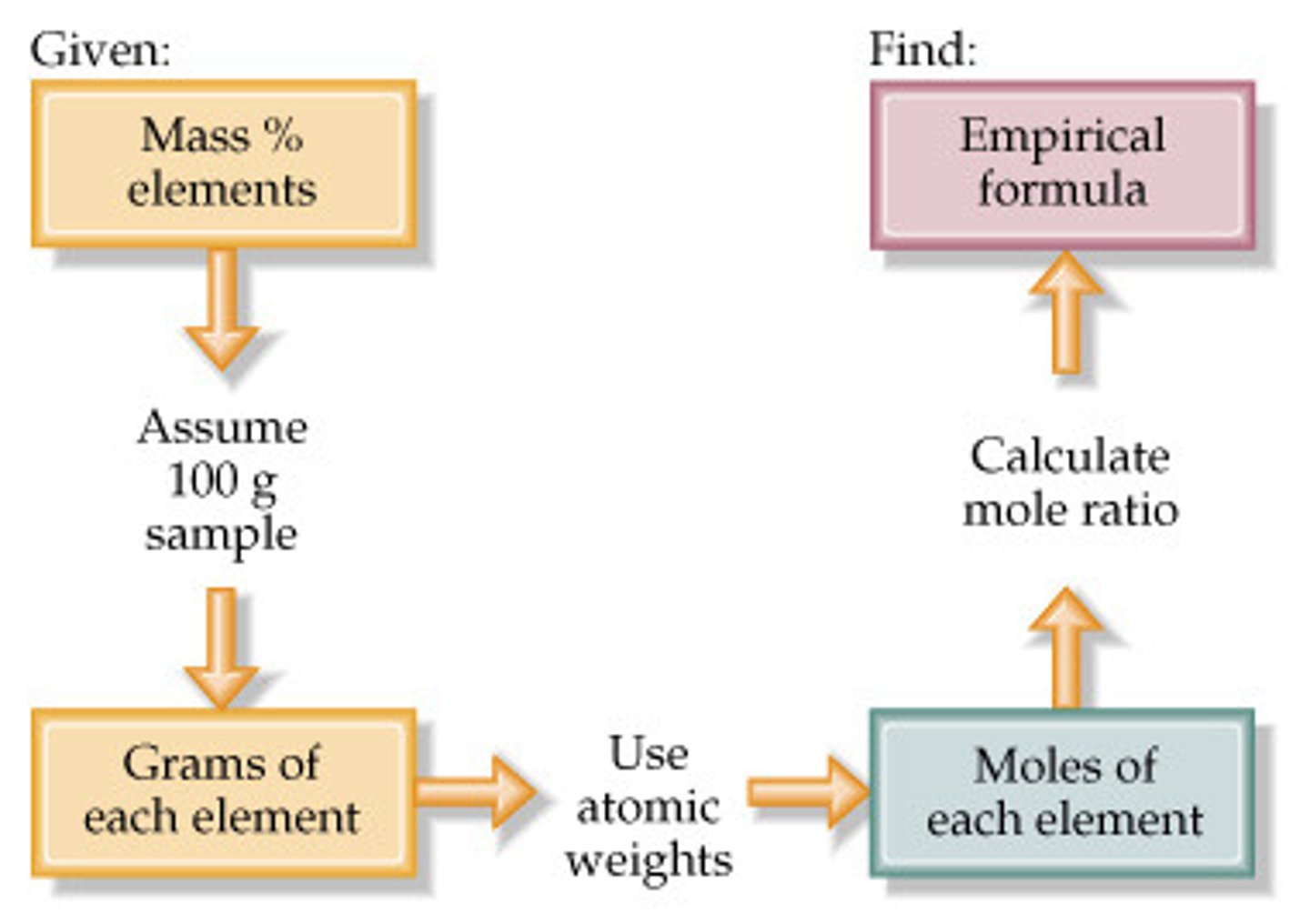
Steps for % Composition to Empirical Formula
1. Convert from % composition to mass (x100g)
2. Convert form mass to moles using molar mass of the element
3. Divide the moles of each element by the smallest # of moles
4. Apply the results as the subscripts to the empirical formula
5. If subscripts are not integers, multiply all numbers by a multiplier to make them into integral whole numbers
Steps for Empirical Formula to Molecular Formula
1. Find the empirical formula first
2. Determine the molar mass of the empirical formula (empirical mass)
3. Find the factor (X) using: X = Molecular Mass / Empirical Mass
4. Multiply each subscript of the Empirical Formula by the factor X

Solution
A homogenous mixture with particles the size of a typical ion or small molecule
Solute
the substance that is dissolved, present in smaller amounts

Solvent
the substance in which the solute dissolves, present in the larger amount

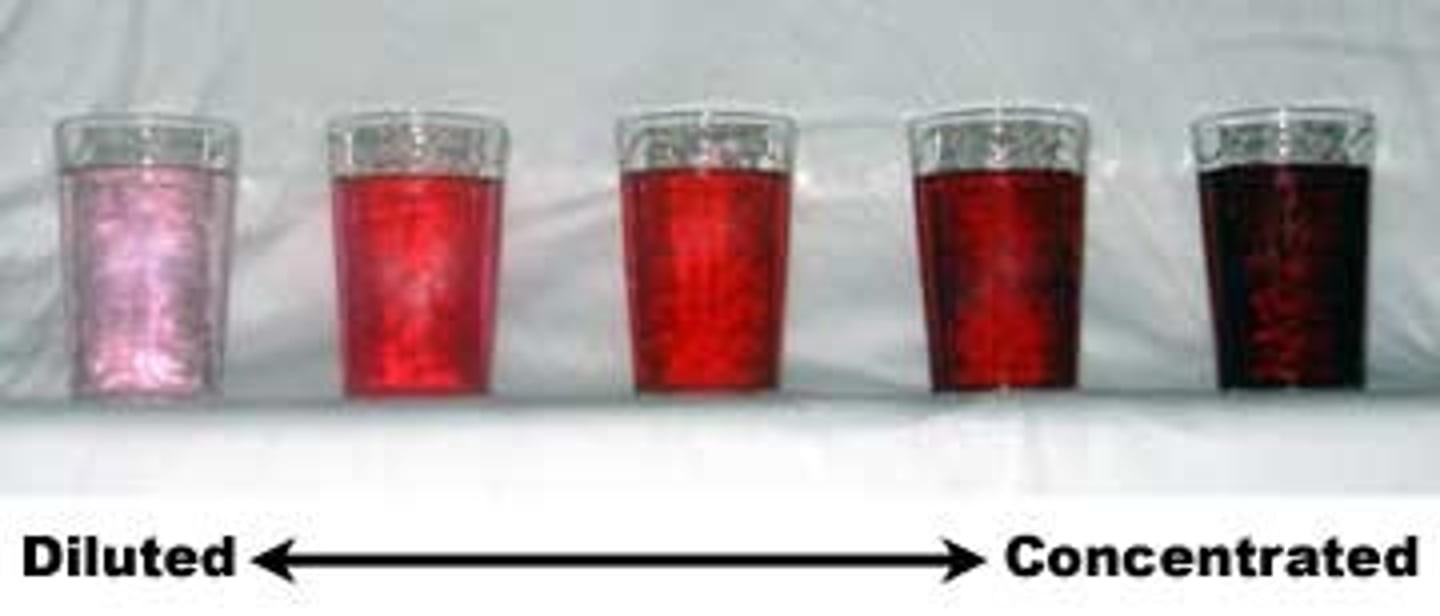
Concentration
A measurement of how much solute exists within a certain volume of solvent
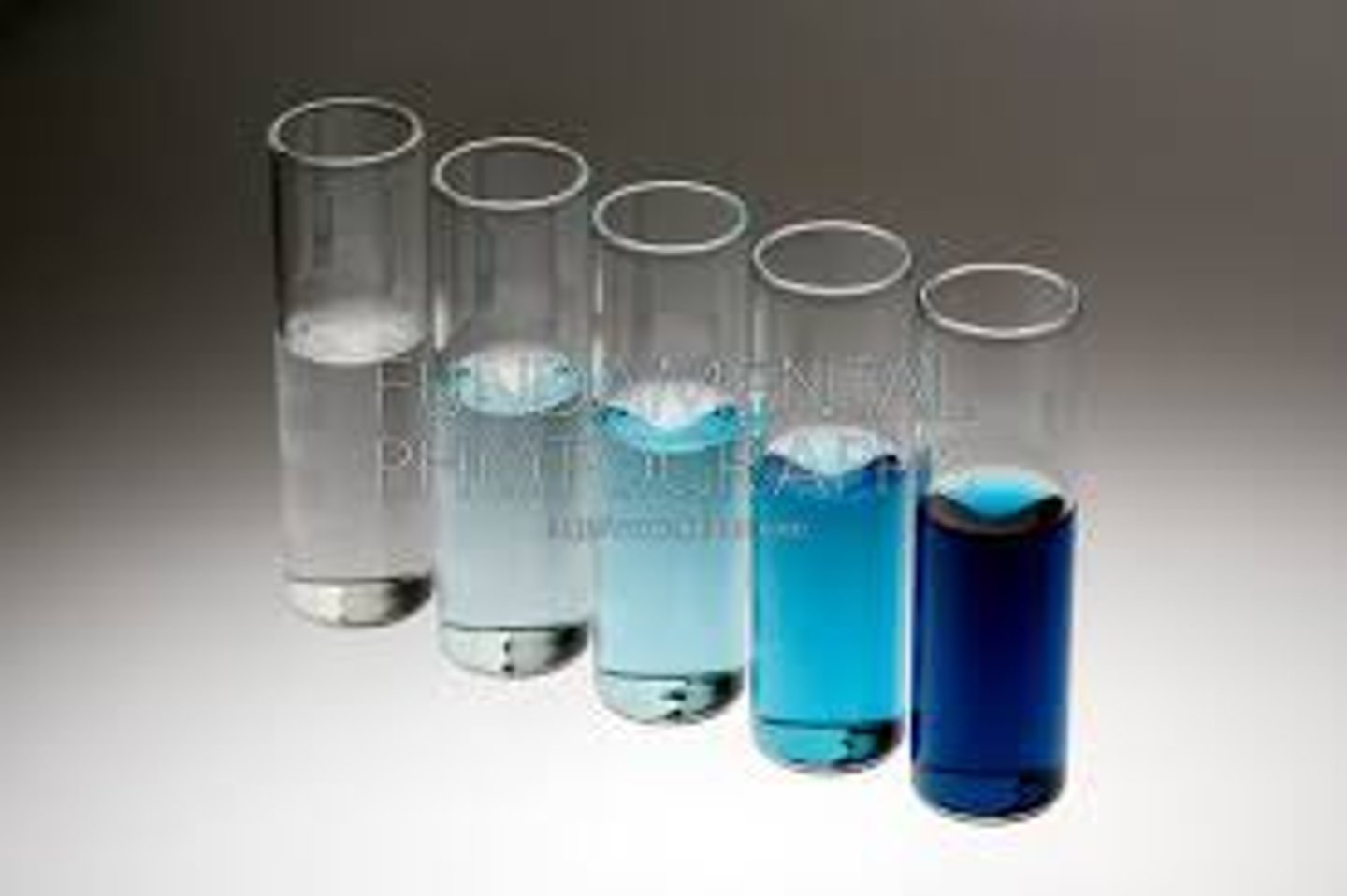

Mass/Volume Percent
%(m/v) = mass of solute (g) /mass of solution (mL) x 100%
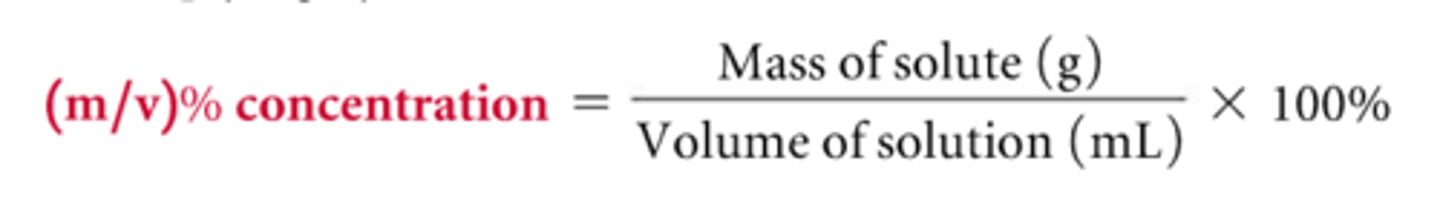
Mass/Mass Percent
% (m/m) = g of solute / g of solution x 100%
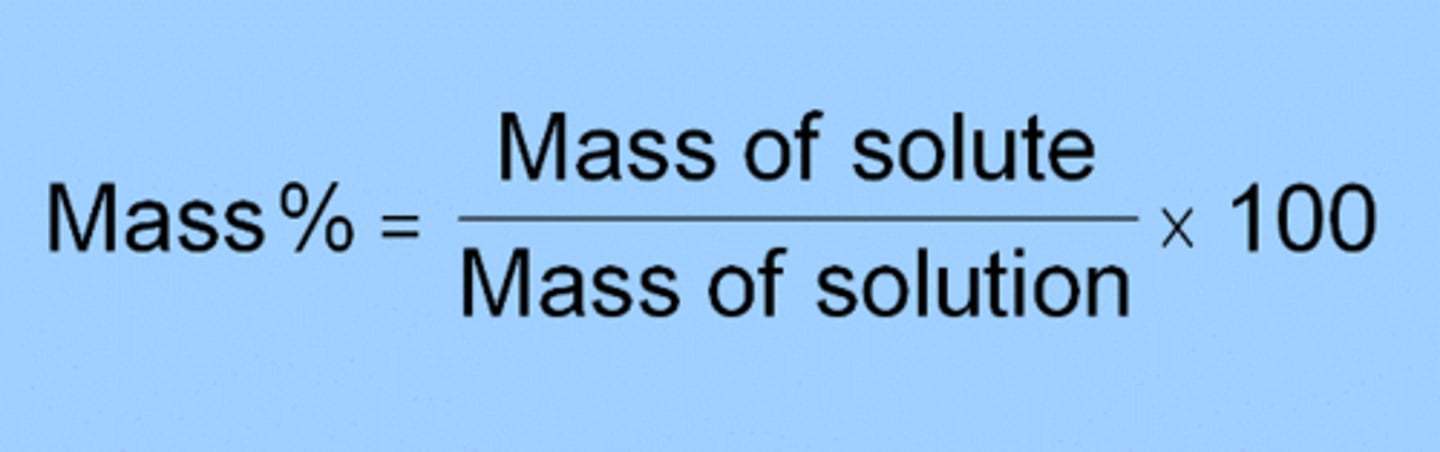
Volume/Volume Percent
% (v/v) = volume of solute / volume of solution x 100%
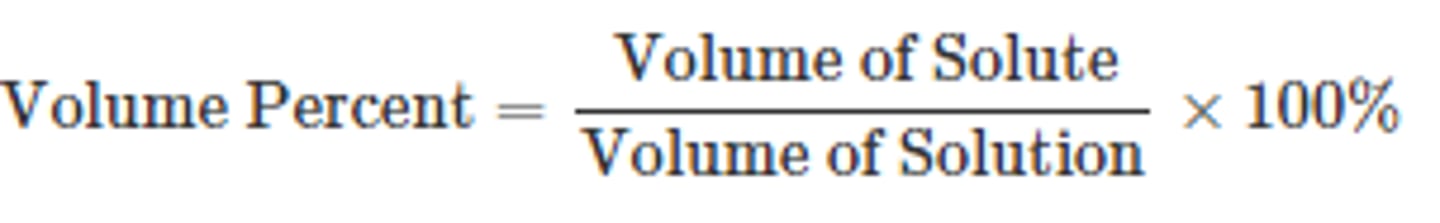
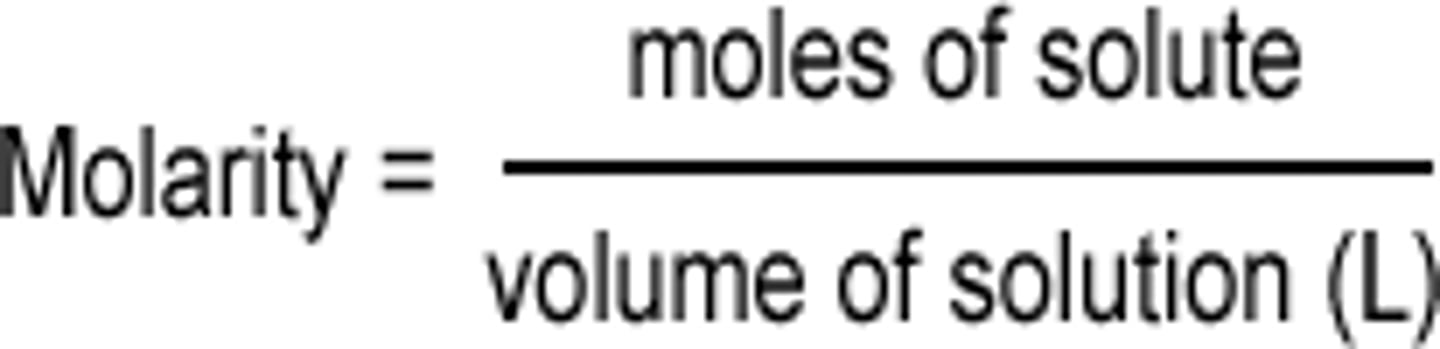
Molarity (M)
M = Moles of solute / liters of solution
Dilution
preparing a less concentrated solution from a more concentrated solution
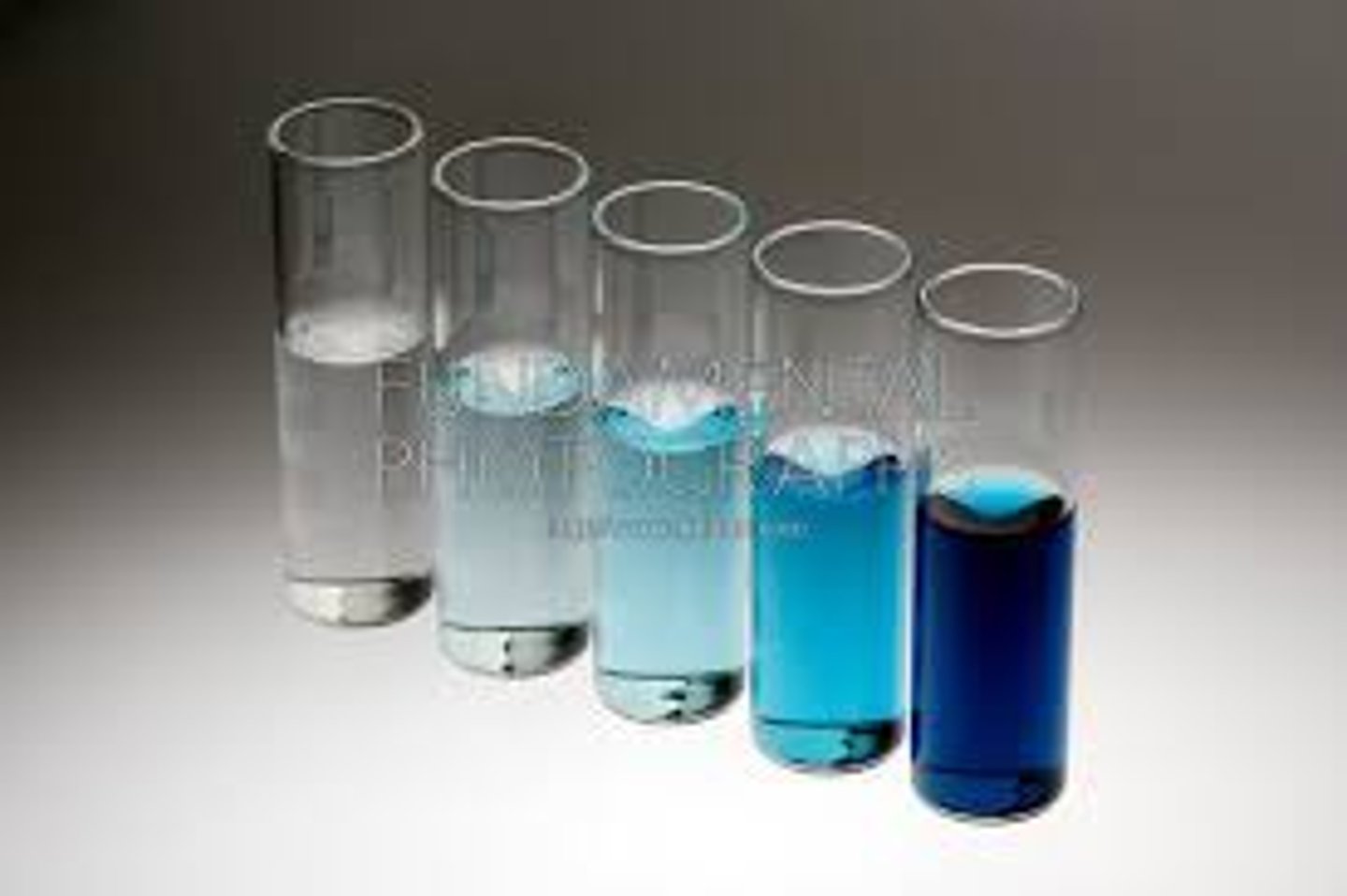

Initial/Diluted Solutions Ratios
C1V1 = C2V2
OR
M1V1 = M2V2