TEST 2- Orientalizing to Late Archaic Period
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
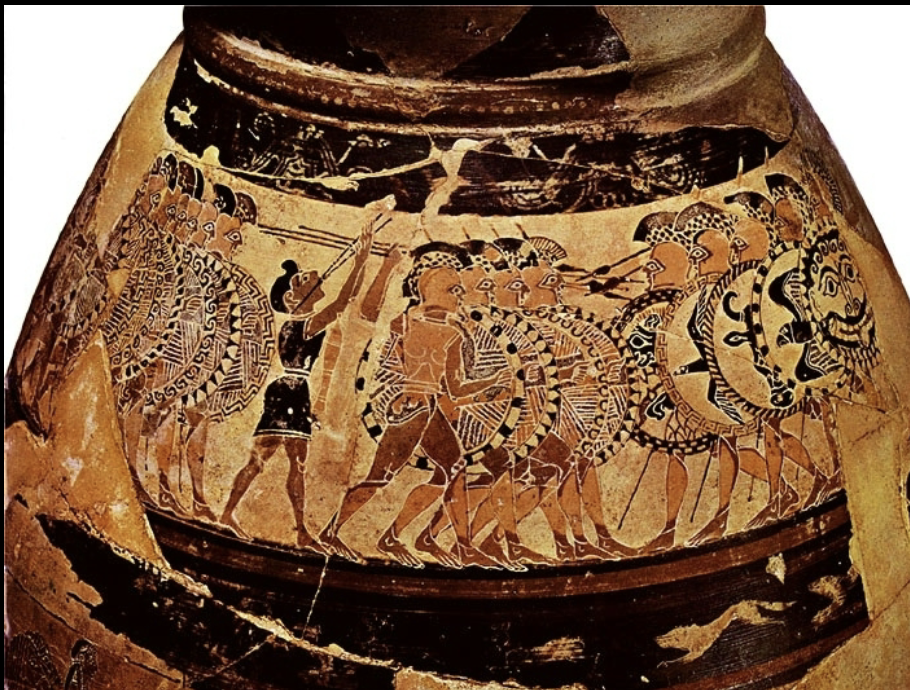
Hoplite
A heavily armed foot soldier of ancient Greece, known for their distinctive round shield and long spear. Hoplites typically fought in a phalanx formation, emphasizing discipline and teamwork in battle. Example: Chigi Vase

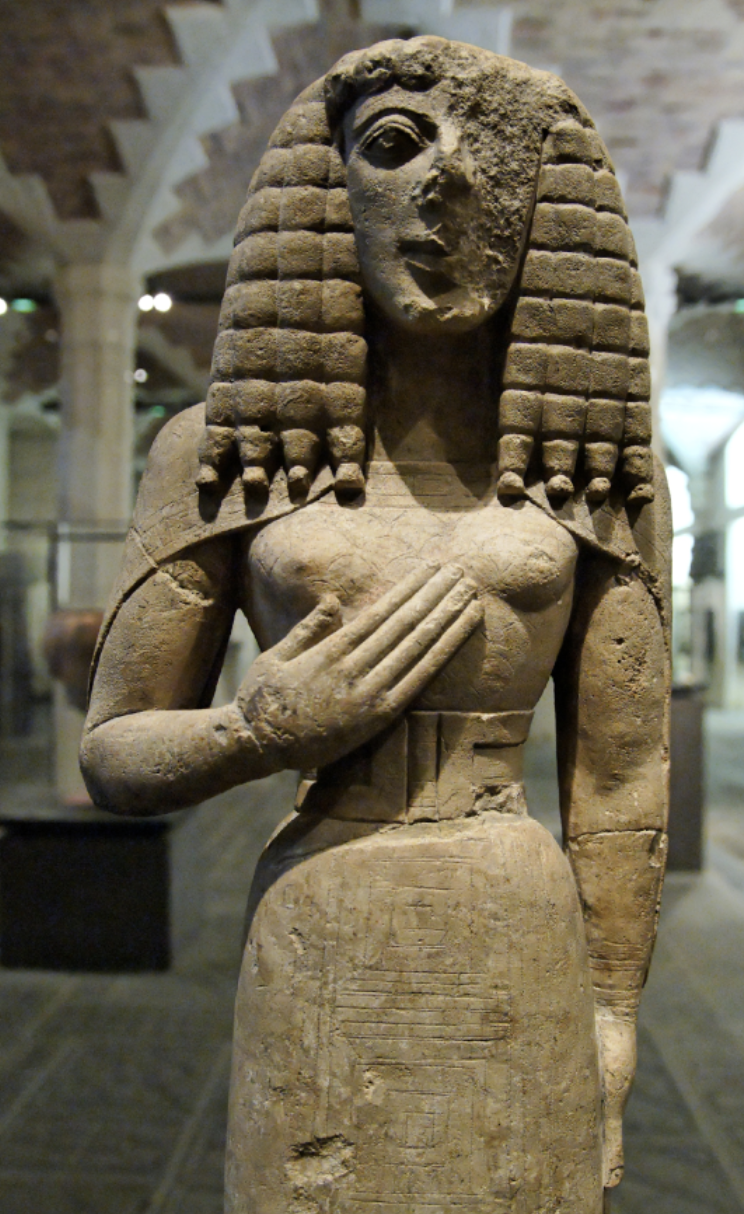
Daedalic
style of Greek art characterized by a stiff, frontal pose and stylized features, prevalent during the early Archaic period. Example: Lady of Auxerre

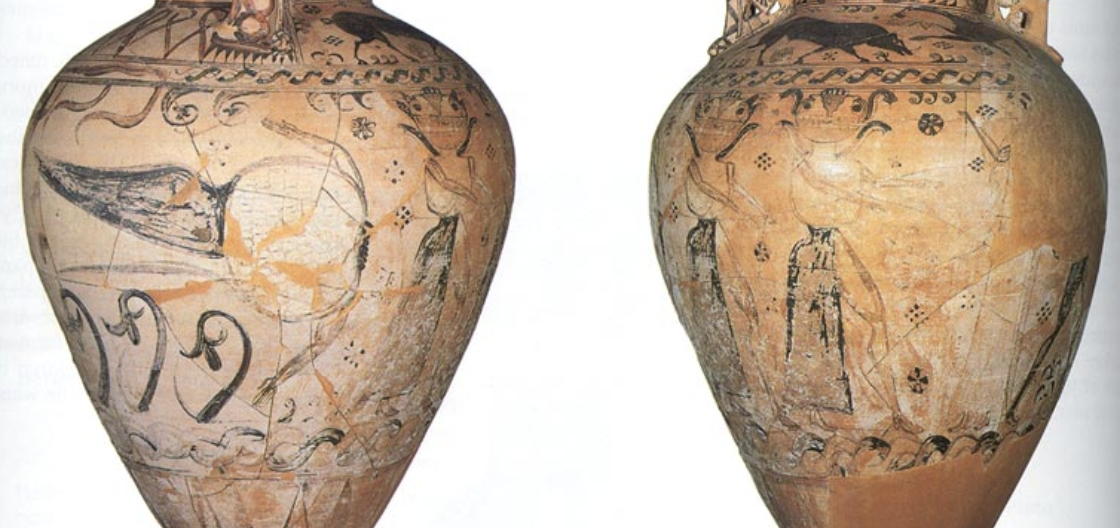
Iconography
the visual imagery and symbols used in a work of art, often conveying specific meanings or themes in the context of culture and history. Example: Eleusis Amphora

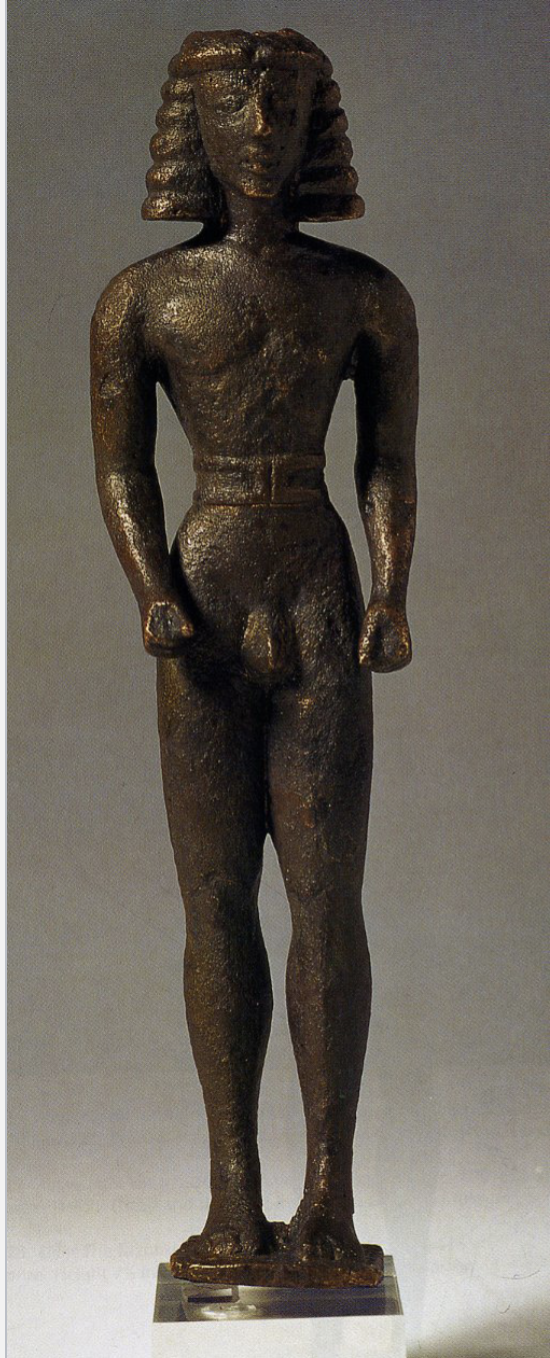
Kouros (male)
an idealized young male figure from ancient Greece, often depicted in a standing position and serving as a grave marker or representation of athleticism and beauty. Example: Kouros of Delphi

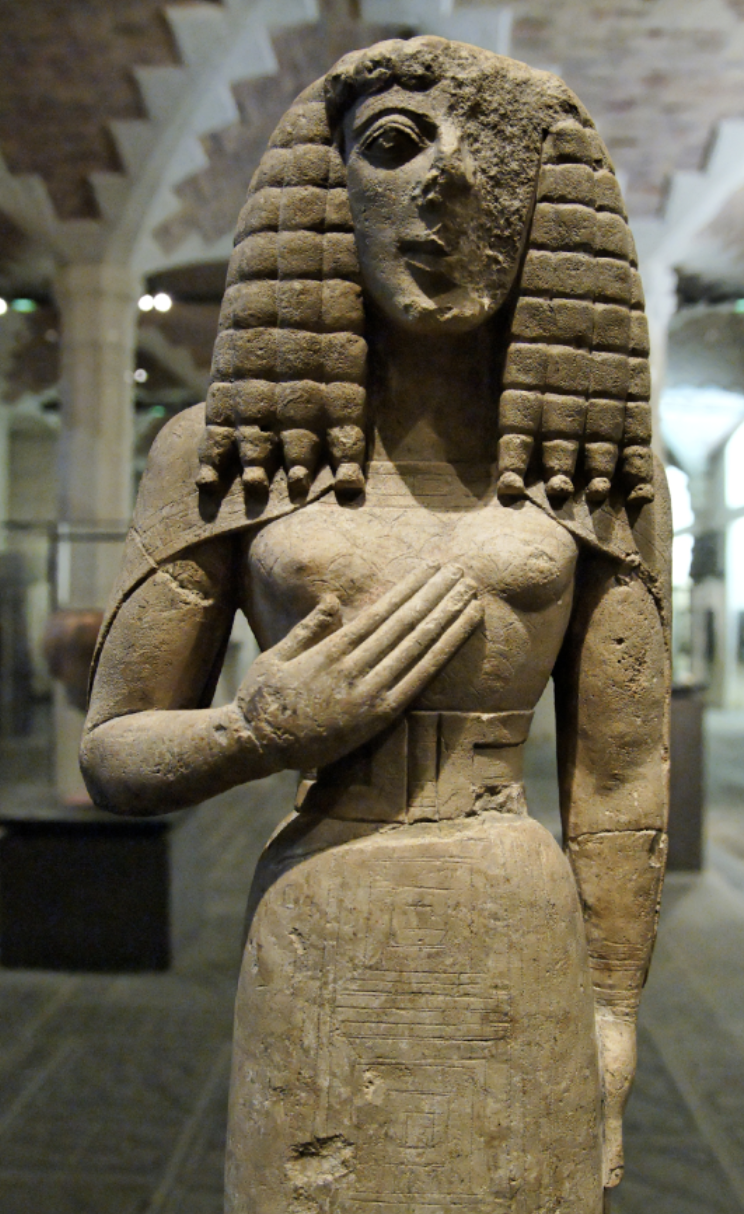
Kore (female)
an idealized young female figure from ancient Greece, typically depicted in a standing pose, often associated with religious functions or as a grave marker. Example: Lady of Auxerre

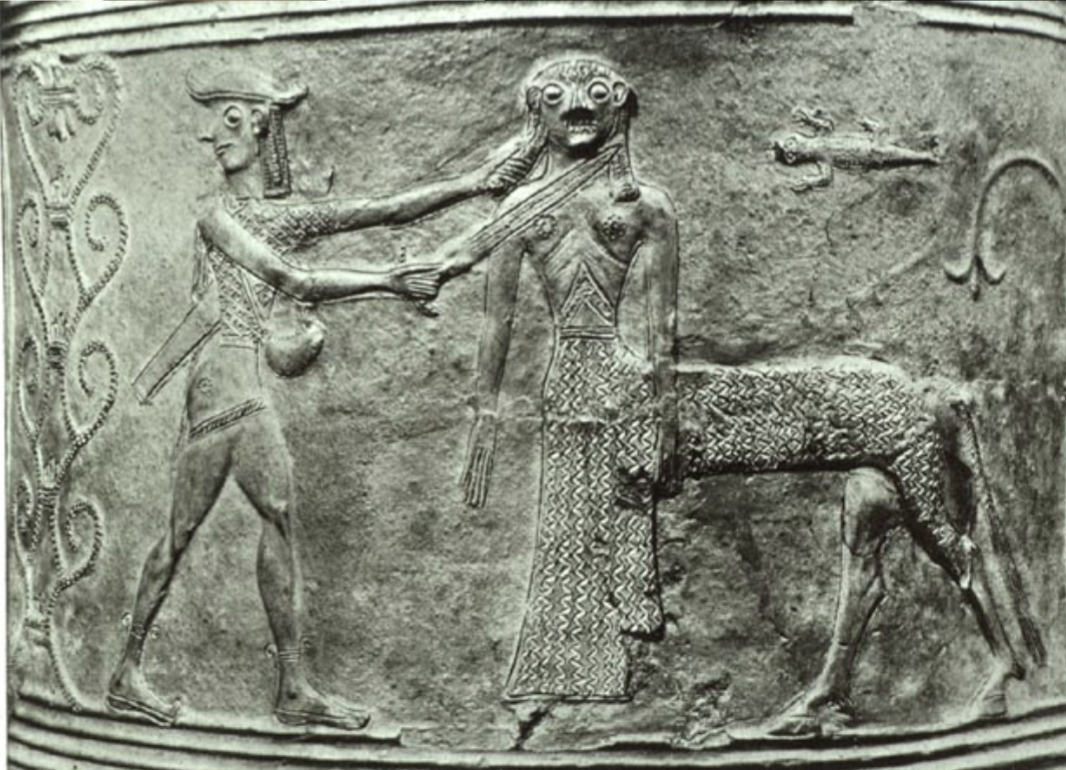
Centaur
a mythical creature from Greek mythology, featuring the upper body of a human and the lower body of a horse, often representing duality and the struggle between civilization and barbarism. Example: Storage Jar from Tinos

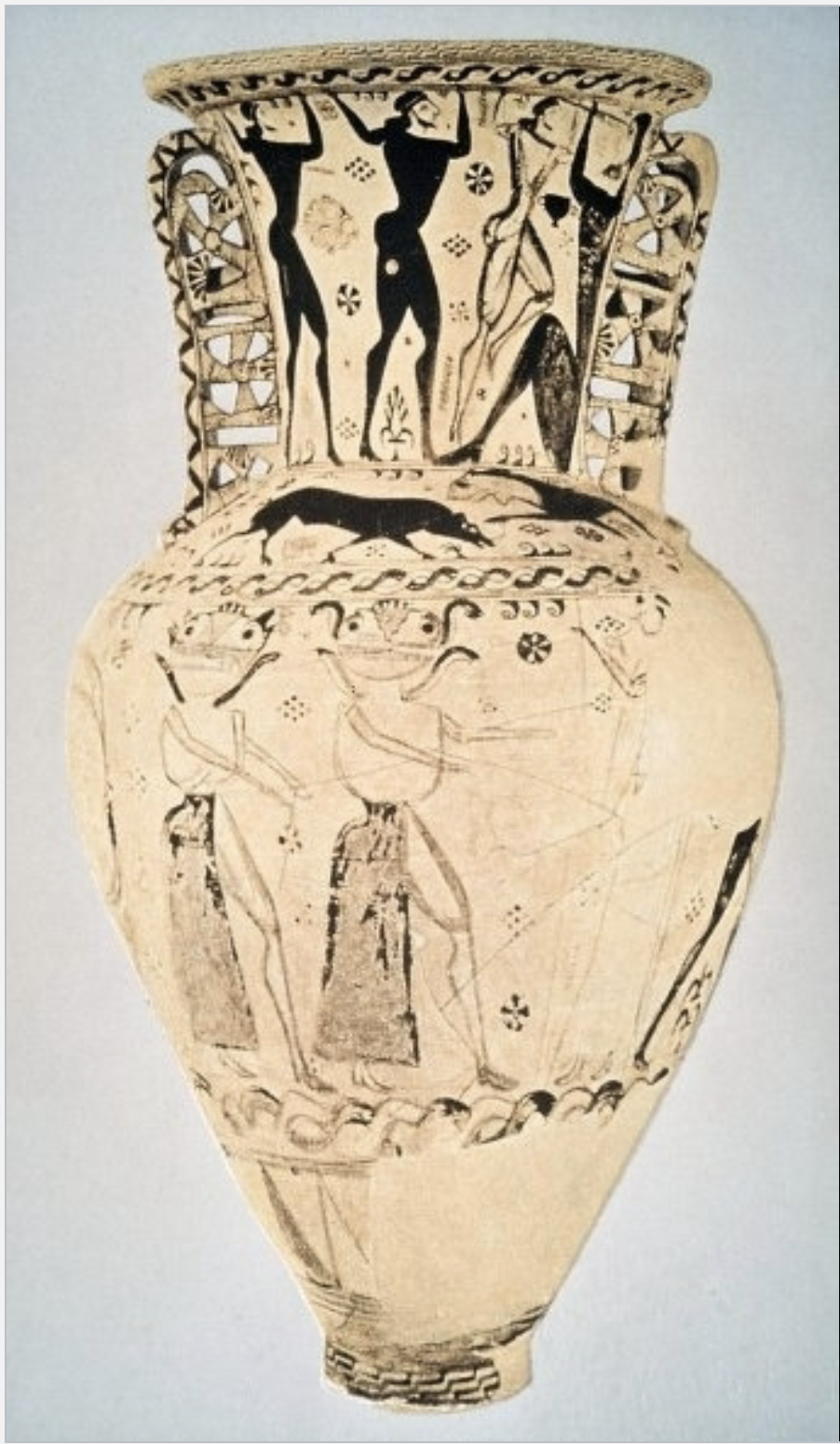
Medusa
a Gorgon from Greek mythology, often depicted as a winged female creature with snakes for hair, whose gaze could turn people to stone. Example: Eleusis Amphora

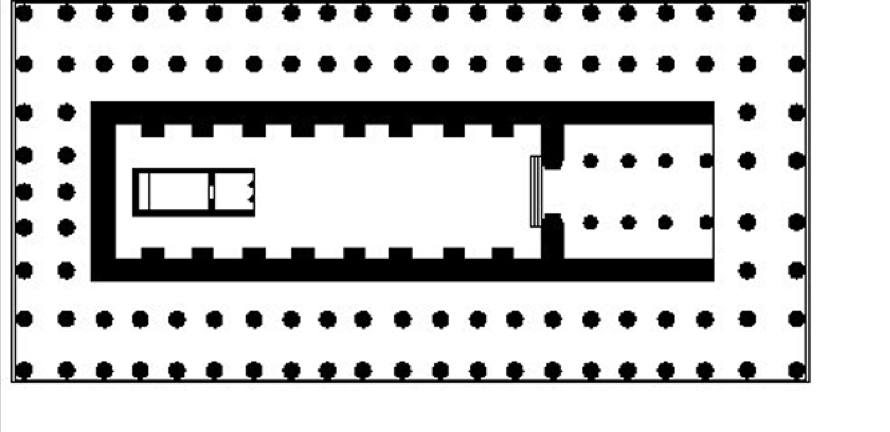
Naos
the inner chamber of a Greek temple, typically housing the cult statue and considered the most sacred part of the structure. Example: Temple of Poseidon
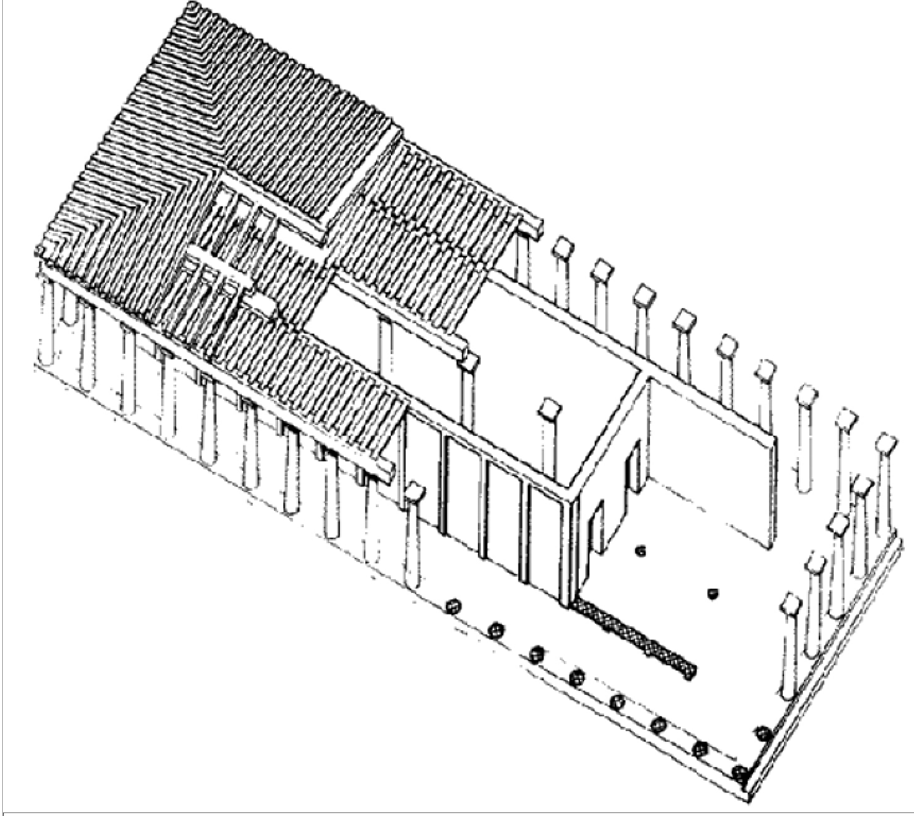
Peristyle
the row of columns surrounding or forming a part of a building, particularly in classical architecture, often used to create a walkway or support an open space. Example: Temple of Apollo, Didyma
Stylobate
The continuous top step of a classical temple’s platform on which the columns rest. Temple of Apollo, Didyma
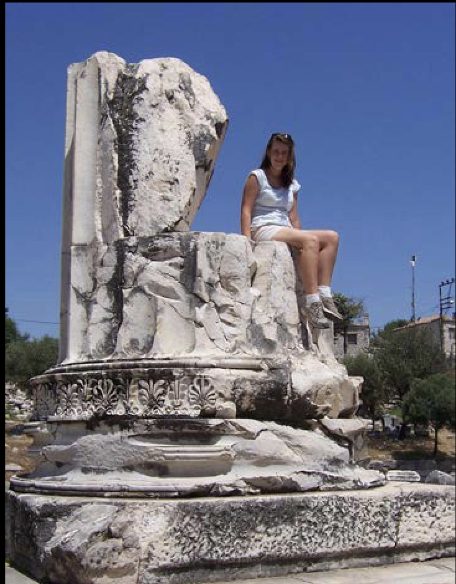

Base
The bottom part of a column that supports the shaft and spreads its weight onto the stylobate. Example: Croesus Temple
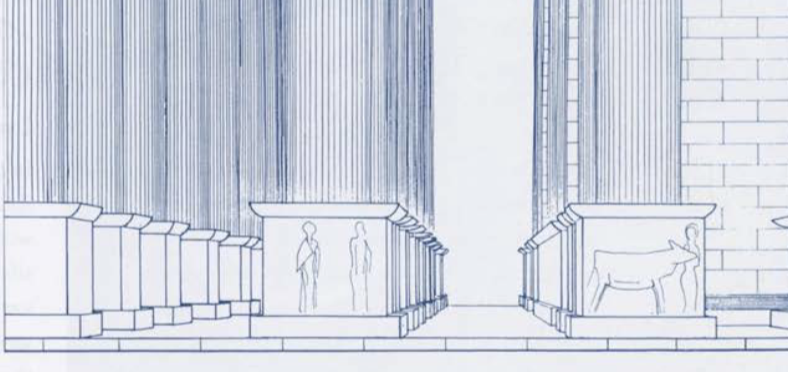
Column
A vertical architectural support made up of a base, shaft, and capital that holds up a structure or entablature. Example: Temple of Apollo at Syracuse

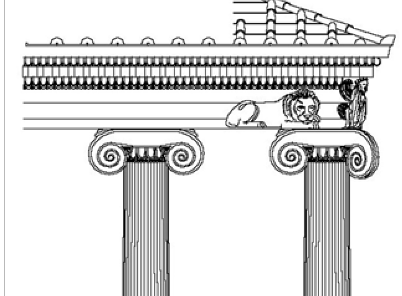
Capital (greek temple)
the top part of a column that spreads the weight of the entablature and often features decorative design. Shows the most obvious difference between Doric and Ionic temples. Example: Temple of Apollo, Didyma

Entablature
The horizontal structure supported by columns, consisting of the architrave, frieze, and pediment. Example: Temple at Selinous

Architrave
The lowest section of the entablature, resting directly on the columns above the capital. Example: Temple to Apollo at Didyma
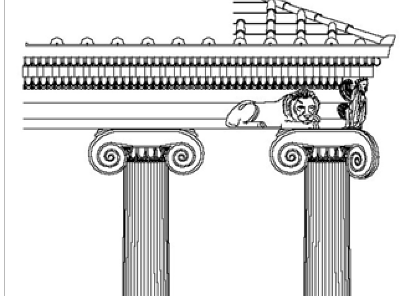
Freize
the middle band of the entablature, often decorated with relief sculpture or inscriptions and in the Doric order, comprised of triglyphs and metopes. Example: Selinous Temple

Pediment
The triangular upper part of a building’s façade, above the entablature, is often filled with sculpture. Example: Corfu Temple

Volute
A spiral, scroll-like ornament, commonly found on Ionic column capitals. Example: Temple of Apollo, Didyma