Biology Key Terms Unit 2: Cell Biology
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
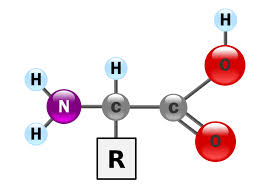
amino acid
Building blocks of proteins, amino acids are organic compounds that combine to form proteins and play key roles in various biological processes.
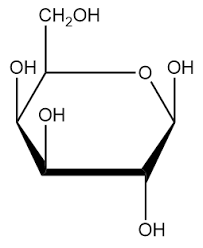
carbohydrate
Organic molecules made of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen, carbohydrates serve as a primary energy source for living organisms and are also involved in structural functions.
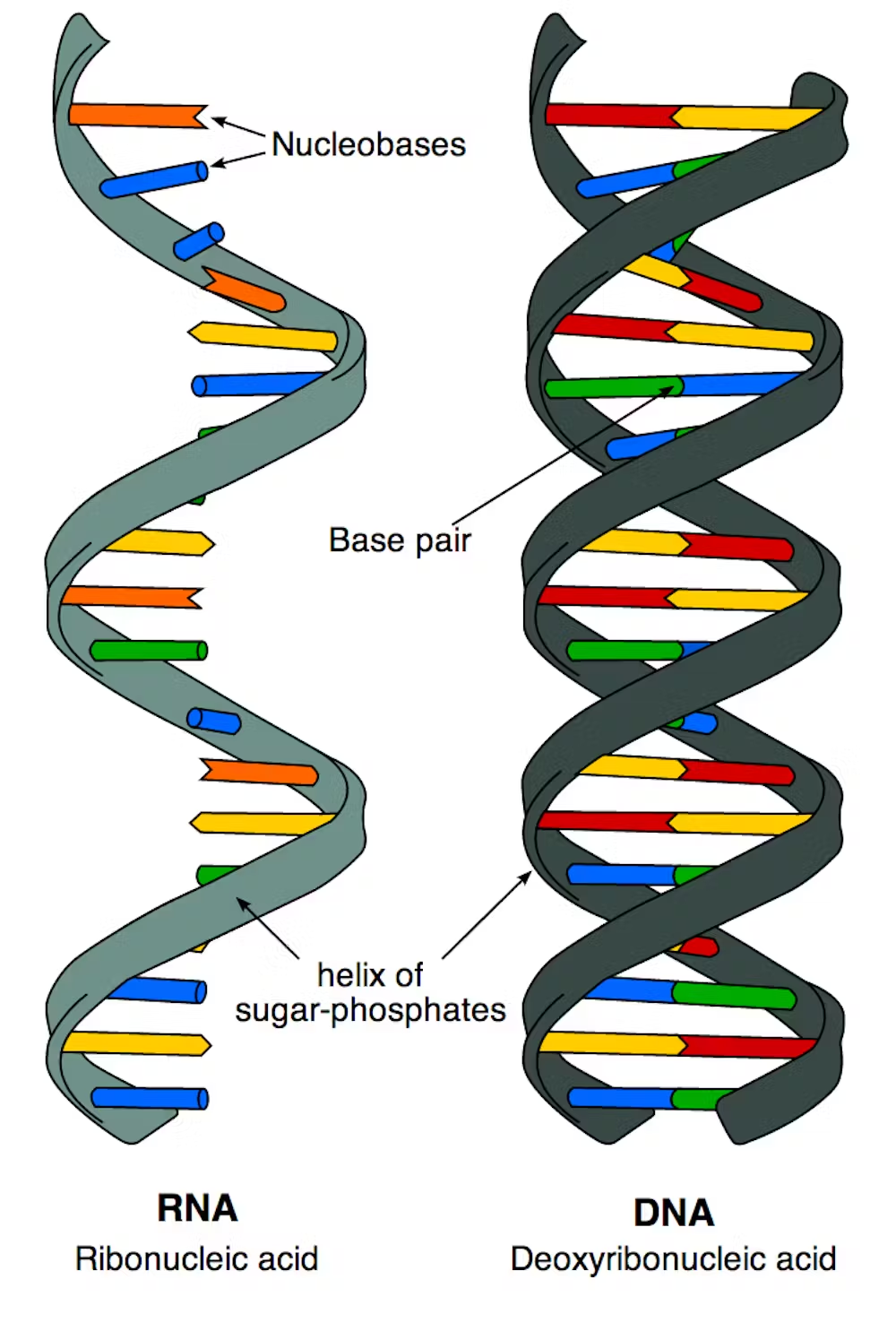
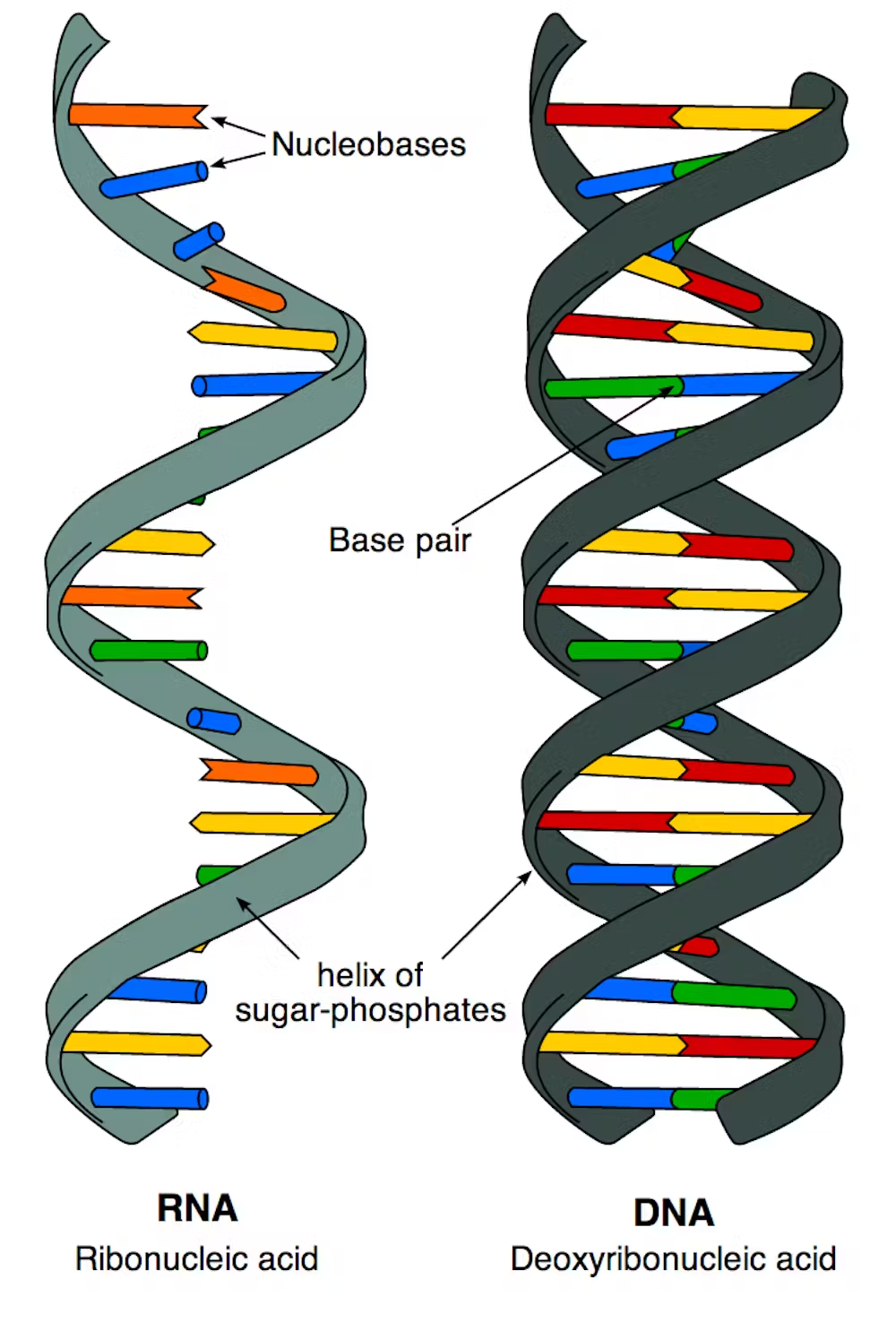
deoxyribonucleic acid
(DNA) is the molecule that carries the genetic instructions for life in all known living organisms.
fat
A substance composed of triglycerides, fat serves as an important energy reserve and is integral to cell structure and function.
lipids
are a diverse group of hydrophobic molecules including fats, oils, and hormones, important for energy storage and cellular structure.
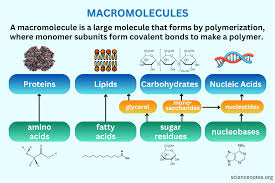
macromolecule
is a large molecule made up of smaller subunits, including proteins, nucleic acids, carbohydrates, and lipids, which are essential for various biological functions.
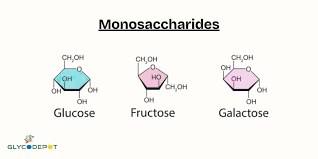
monosaccharide
any of the class of sugars (e.g., glucose) that cannot be hydrolyzed to give a simpler sugar.
Nucleic Acid
a complex organic substance present in living cells, especially DNA or RNA, whose molecules consist of many nucleotides linked in a long chain.
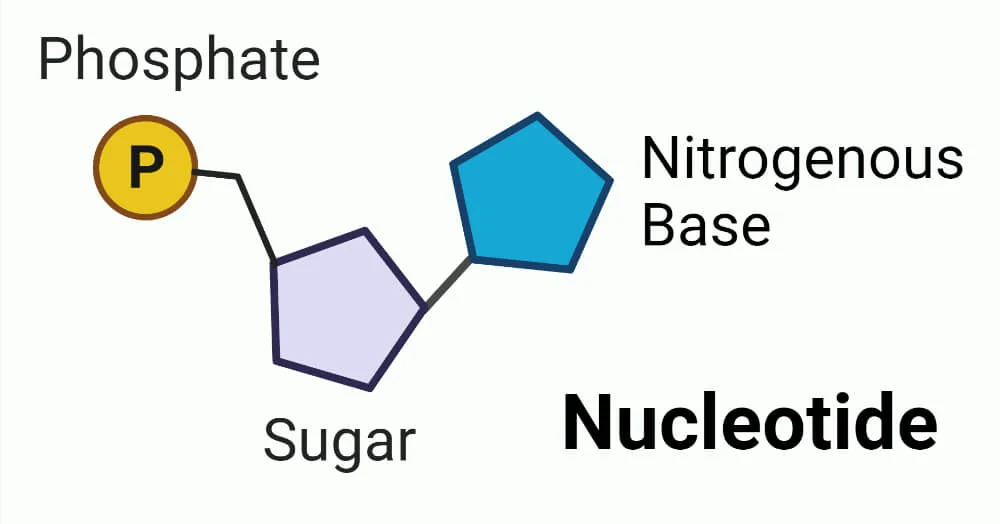
nucleotide
a compound consisting of a nucleoside linked to a phosphate group. Nucleotides form the basic structural unit of nucleic acids such as DNA.
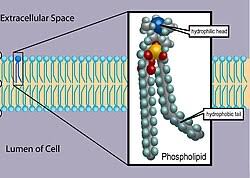
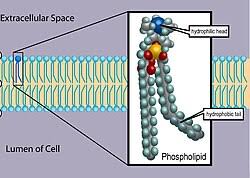
phospholipid
a lipid containing a phosphate group in its molecule, e.g., lecithin.
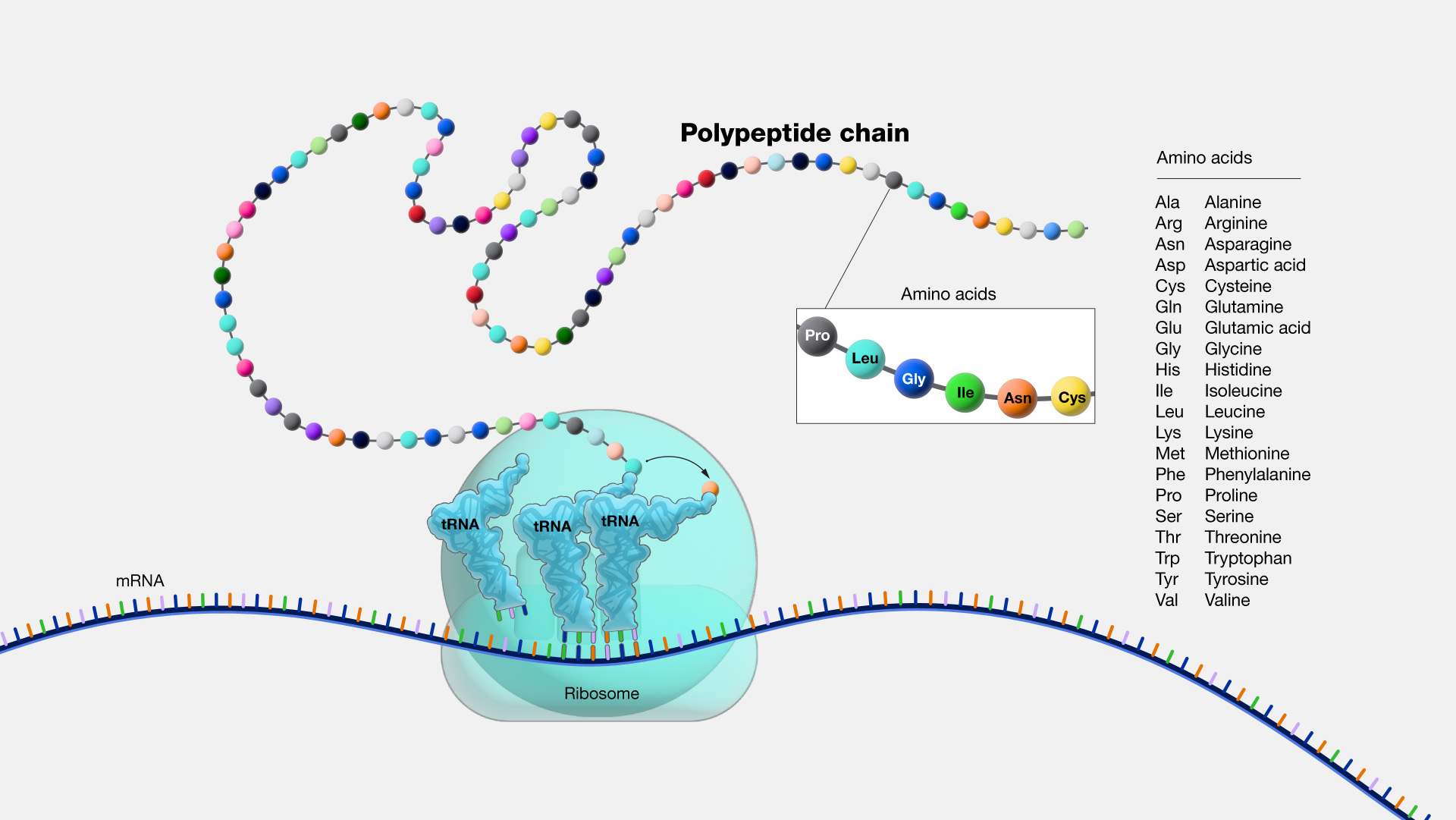
polypeptide
a linear organic polymer consisting of a large number of amino-acid residues bonded together in a chain, forming part of (or the whole of) a protein molecule.
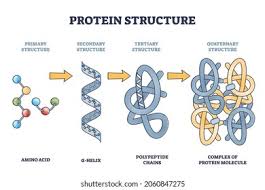
protein
1.
any of a class of nitrogenous organic compounds that have large molecules composed of one or more long chains of amino acids and are an essential part of all living organisms, especially as structural components of body tissues such as muscle, hair, etc., and as enzymes and antibodies.
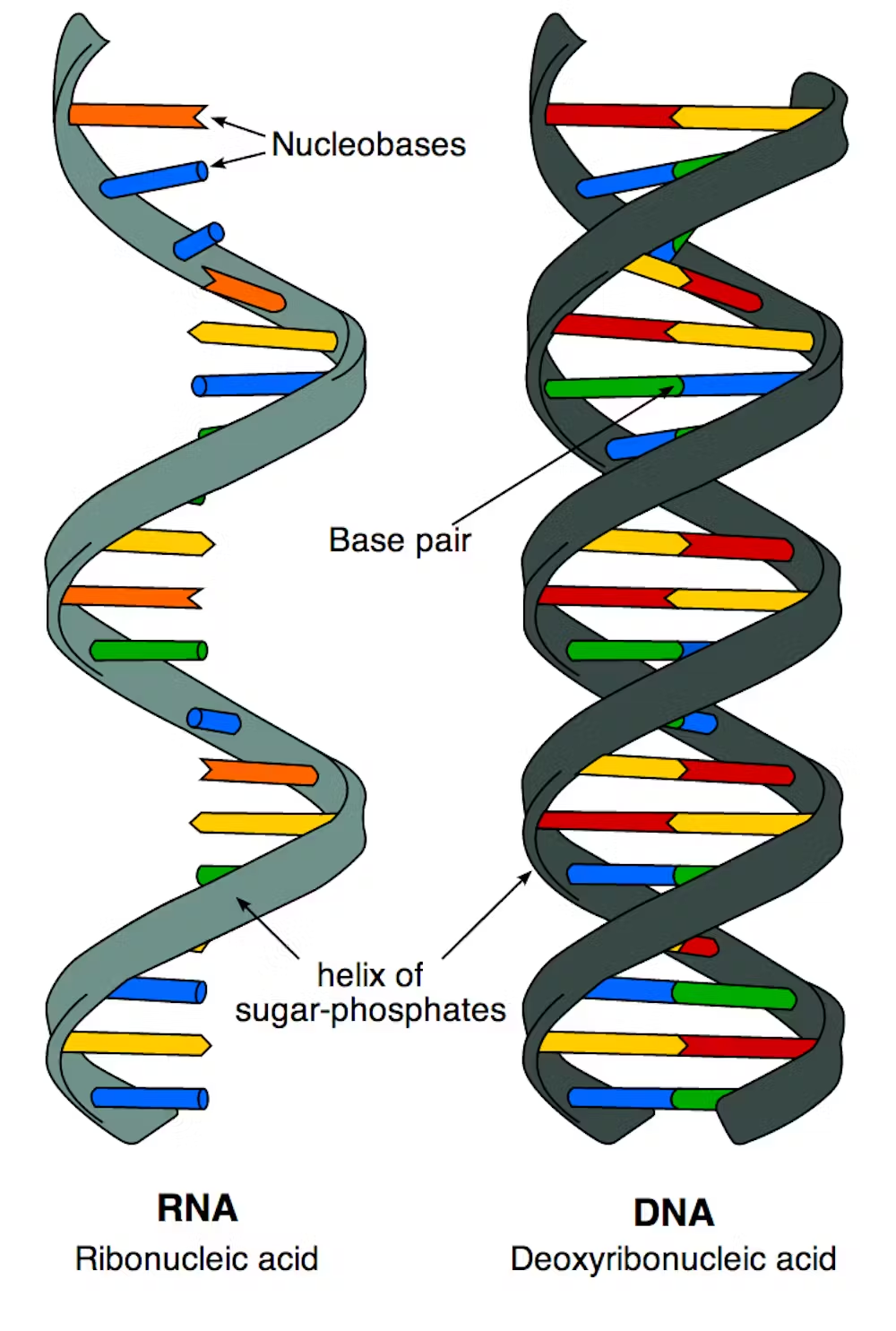
ribonucleic acid (RNA)
a nucleic acid present in all living cells. Its principal role is to act as a messenger carrying instructions from DNA for controlling the synthesis of proteins, although in some viruses RNA rather than DNA carries the genetic information.
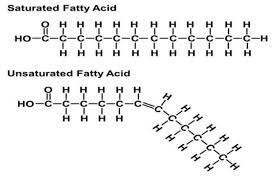
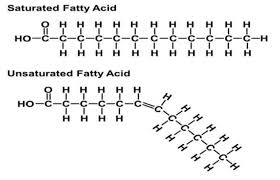
saturated fatty acid
a glyceride in which the fatty acid chains have all single bonds between the carbon atoms. Glyceride fats with single bonds are called saturated because they are "saturated with" hydrogen atoms, having no double bonds available to react with more hydrogen.
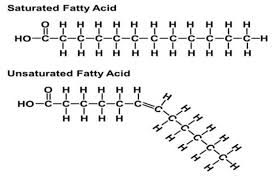
unsaturated fatty acid
An unsaturated fat is a fat or fatty acid in which there is at least one double bond within the fatty acid chain. A fatty acid chain is monounsaturated if it contains one double bond, and polyunsaturated if it contains more than one double bond.