Module 2 Overall Flashcards
1/85
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
86 Terms
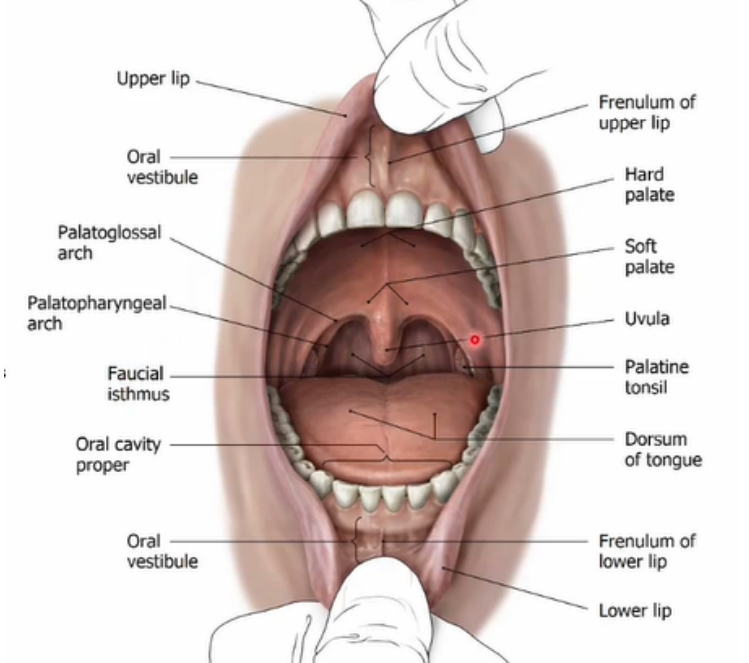
Parts of the nasal/oral cavity
Nose
Nasopharynx
Mouth
Vestibule
Oral cavity proper
Oropharynx
Laryngopharynx
Larynx
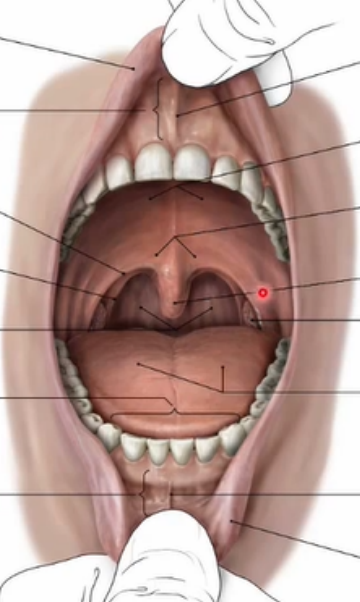
Label the diagram of the vestibule and oral cavity proper
Functions of the tongue
Digestion
Speech
Breathing
Taste
sweet
sour
salty
bitter
umami
What are the main surfaces of the tongue
Dorsal
Ventral
Describe the dorsal part of the tongue
Contains oral part [also called palatal part] (anterior 2/3) and pharyngeal part (posterior 1/3)
Oral/pharyngeal parts divided by:
Palatoglossal fold - contains palatoglossal muscle
Sulcus terminalis - V shaped groove separating the parts
Foramen caecum - remnant of embryonic duct associated with the thyroid gland
Describe the ventral part of the tongue
Contains:
Body
Apex
Root
What does the tongue develop from
2 lateral swellings and 1 medial swelling from the 1st pharyngeal arch
What are the lingual papillae found on the palatal tongue
Fungiform - white spots
Filiform - spongy looking papilla
Vallate papilla - (7-12 of them), look like mushrooms, line the sulcus terminalis
Foliate papilla - on side of tongue, look like ridges
Note** All papilla have tastebuds EXCEPT filiform
V-FLuffy Fungus Feeds Taste (Vallate, Filiform, Fungiform, Foliate)
(FLuffy = no flavor)
Describe the structure of the pharyngeal tongue
from the sulcus terminalis to the epiglottis
lingual tonsils between these structures - lymph nodes
pharyngeal fold, palatine tonsil, palatopharyngeal fold
median and lateral glossoepiglottic folds (MGF/LGF)
attachments between posterior tongue and epiglottis
Valleculae = indentations between MGF and LGF that are sites of food lodgement
Describe the structures on the ventral surface of the tongue
Lingual frenulum
deep lingual veins (lateral to frenulum)
fimbriated folds (further lateral from frenulum)
sublingual folds
on floor of oral cavity in alveolar-lingual sulcus
sits above sublingual glans and secretes saliva
sublingual papilla - on either side of lingual frenulum
for opening of submandibular duct of submandibular gland
What is the alveolar lingual sulcus
a horseshoe cavity that wraps around the attachment of the tongue to the floor of the mouth
contains submandibular duct and submandibular gland
What are the extrinsic muscles of the tongue and their innervations
Genioglossus (innervated CN XII): protrusion and deviation of the tongue
Hyoglossus (CN XII): depression and retraction of the tongue for sucking
Styloglossus (CN XII): lifts tongue up and back
Palatoglossus (CN X): elevates posterior tongue for swallowing
Geniuses Hide Silly Palates
What are the attachment sites of the extrinsic tongue muscles
Genioglossus
upper genial tubercle/mental spine to the hyoid bone and base of tongue
Hyoglossus
Hyoid bone to the side of the tongue
Styloglossus
styloid process to the side of the tongue
Palatoglossus
palatal aponeurosis to the side of the tongue
Hard Palate
formed by palatine process of maxilla and horizontal plate of the palatine bone
Landmarks of the hard palate
incisive foramen
greater palatine foramen
lesser palatine foramen
posterior nasal spine
Soft tissue landmarks:
incisive papilla (posterior to the maxillary papilla)
rugae
median raphe
Soft palate
oral mucosa on oral side
respiratory mucosa on nasal side
within palate
muscles and palatal aponeurosis
fat and glands
Palatine Aponeurosis
thin, firm, fibrous sheet formed by an extension of the tendon of the tensor palati muscles
provides support for other muscles to attach to
Muscles of the palate and their innervations
Levator palati (CN IX and CN X): lifts palate up and back
Tensor palati (CN V3): tightens the soft palate ad pulls the auditory tube open
Palatoglossus (CN X): elevates tongue
Palatopharyngeus (CN X): depress the soft palate and narrows/shortens the isthmus and pharynx
Uvular (CN X): assists in palatopharyngeal closure
Tense Living People Prefer Ubers
Attachment sites of palatal muscles
Lavator palati
attaches from petrous temporal bone → the palatal aponeurosis
Tensor palati
attaches from the scaphoid fossa → the hamulus → palatal aponeurosis
Palatoglossus
attaches from soft palate → tongue
Palatopharyngeus
attaches from soft palate → pharynx
Uvula
attaches from posterior nasal spine and palatine aponeurosis → uvula mucosa
What percentage of the body’s blood does the brain receive
30%
How much does the brain weigh
1.4 kg
What are the meninges layers of the brain
Dura mater (outer layer)
arachnoid mater
pi mater (inner)
What fills the space between the meninges layers
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)
Anatomical directions of the brainstem
Rostral = up
Caudal = down
Ventral = front
Dorsal = back
Anatomical directions of the cerebrum
Rostral = front
Caudal = back
Ventral = down
Dorsal = up
Grey matter
Makes up 40% of the brain
makes up surface of brain
consists of cell bodies, dendrites, nerve terminals, and synapses
where info is processed and integrated
White matter
comprises 60% of the brain
makes up deep part of brain
comprised of nerve axons
where info is transmitted between grey matter regions
Brainstem
most caudal part of brain
attaches to spinal cord
comprised of
medulla oblongata
pons
midbrain
regulates BP, HR, respiratory function
Diencephalon
located rostral to brainstem
consists of
thalamus
hypothalamus
involved in homeostasis
Cerebellum
attached to dorsal side of brainstem
contains 50% of brain’s neurons
responsible for motor control and planning of movements that require multiple segments
Cerebrum (telencephalon)
makes up 80% of brain volume
consists of
cortex
gyri (thick folds)
sulci (shallow grooves)
hemispheres separated by longitudinal fissure
Lobes of the cerebrum and their functions
Parietal
somatosensory processing (touch, vibration, proprioception)
Occipital
visual processing
Temporal
hearing, comprehension, cognition, emotion
Frontal
motor control, speech, emotion, cognition, personality
Insular
sensation for internal parts of the body, pain, nociception, emotion
Duration of pregnancy
30-48 weeks
Oocyte
female egg
carries x chromosome
~100 microns in size
rich in cholesterol
surrounded by zona pellucida
Sperm
male germ cell
y chromosome
~50 microns in size
Week 1 of embryological stage
Fertilization and implantation
Zygote → blastomere (2 cell size) → morula (16 cell size) →blastocyst
Zygote remains incased in zona pellucida the whole time
Blastocyst
Contains blastocyst cavity (blastocoel) and inner cell mass
Inner cell mass:
Trophoblast - becomes placenta
Embryoblast - becomes future embryo
Week 2 of embryological stage
Implantation and bilaminar formation
Differentiation of trophoblast into:
syncytiotrophoblast
cytotrophoblast
Differentiation of embryoblast into:
epiblast (embryo)
hypoblast (yolk sac)
New tissues form bilaminar disk
ZP hatches and uses L-selectins to adhere to uterine wall
Week 3a of embryological stage
Gastrulation and Organogenesis
Oral pharyngeal membrane develops (future oral cavity)
head of embryo develops
primitive streak develops (tail)
differentiates into:
Endoderm
Mesoderm
Ectoderm
What does endoderm give rise to
digestive tract
respiratory tract
endocrine glands
What does mesoderm give rise to
muscle
bone
circulatory system
What does ectoderm give rise to
Neural tissue
Skin
Glands
Teeth
Week 3b embryological stage
Heart formation
mesoderm differentiates into:
somatic (dorsal) mesoderm layer: bones, ligaments, blood vessels, connective tissue of limbs
splanchnic (ventral) mesoderm layer: heart tube
Week 4 Embryological stage (Neurulation)
Ectoderm differentiates into:
Central - neural ectoderm, forms neural tube and groove →brain and spinal cord
Lateral - dermal ectoderm
Week 4 Embryological stage (Neural crest cell formation)
NCC develop from neural ectoderm into:
dentine
pulp
periodontal tissue
TMJ condylar cartilage
melanocytes
neural cells and glia
sensory organs
When does the body cavity formation occur
Weeks 3-4
Week 4 Embryological stage (Stomodeum formation)
Stomodeum = groove between head and the heart - leads to formation of oral cavity
also begins to form frontonasal prominence and cardiac bulge
Week 5 embryological stage (pharyngeal arches)
Formation of Pharyngeal Arches
Arches develop from all 3 germ layers:
Ectoderm = dermal coverage and sensory placodes
Mesoderm = muscle, bone/cartilage, vascular progenitors
Endoderm = inner linings
What are the pharyngeal arches
5 pairs of pharyngeal arches:
1
2
3
4
6
Note** pharyngeal arch 5 is not visible
What are the parts of the pharyngeal apparatus
Arches:
main portion containing mesenchymal tissue, muscle, bone, nerves
Clefts:
external surface of each pharyngeal arch
Pharyngeal pouches
located internally and opposite to clefts
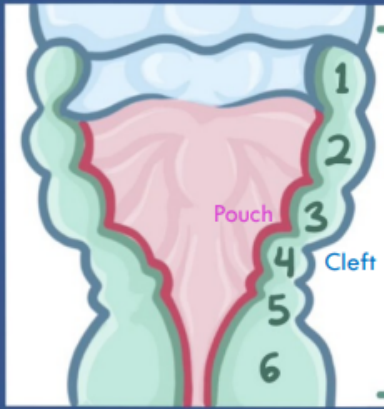
1st pharyngeal arches
contributes to all things related to chewing
When formed, divides into maxillary and mandibular processes
become the maxilla and mandible
forms trigeminal ganglion
becomes trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Muscles developed from the 1st pharyngeal arch
temporalis
masseter
medial pterygoid
lateral pterygoid
mylohyoid
anterior belly of digastric
tensor tympani
tensor veli palatini
Other derivatives of the 1st pharyngeal arch
malleus
maxilla
zygomatic bone
hard palate
vomer
mandible
temporal bone (squamous)
anterior ligament of malleus
sphenomandibular ligament
maxillary artery
2nd pharyngeal arches
contribute to everything swallowing and smiling
gives rise to facial nerve (CN VII) and vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
Muscles developed by 2nd pharyngeal arch
all muscles of facial expression
posterior belly of digastric belly
stylohyoid
stapedius
Other derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal arches
hyoid bone
part of temporal bone
tapes
long limb of incus
styloid process
lesser horn of hyoid
upper part of hyoid
stylohyoid ligament
temporal bone
stapedial artery
caroticotympanic arteries (arteries of the nose and throat)
1st/2nd pharyngeal pouches and clefts
Pouches and Clefts located between the 1st and 2nd arches
1st pouch: forms internal acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane, eustachian tube
1st cleft: forms external acoustic meatus, tympanic membrane
1st/2nd pouches and clefts form the ear
3rd Pharyngeal arch
forms glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
forms common carotid and internal carotid arteries
4th pharyngeal arches
forms vagus nerve (CN X)
forms superior parathyroid epiglottic cartilages
5th pharyngeal arches
become incorporated into 4th arch, therefore not visible
6th pharyngeal arches
forms vagus nerve (CN X)
forms intrinsic muscles of larynx, cricoid cartilage
Mnemonic for Arches the Cranial Nerves they Form
Tense Face Gives Voice
Trigeminal → 1st arch
Facial → 2nd arch
Glossopharyngeal → 3rd arch
Vagus → 4th / 6th arch
Pharyngeal arch contributions to the tongue
1st arch: innervates anterior 2/3rds of tongue via CN V (trigeminal)
3rd and 4th arches: innervates posterior 2/3rd of tongue via CN IX (glossopharyngeal) and CN X (vagus)
3rd pharyngeal pouch
forms thyroid and parathyroid glands
4th pharyngeal pouch
forms parathyroid gland
What happens to the other clefts
they disintegrate
if they remain, they can become branchial cleft cysts
Week 5 of embryological stage (facial development)
Frontal prominence
divides into medial and lateral nasal process
contains olfactory pits → future nostrils
Maxillary and mandibular processes
become more prominent in week 5
Oral pharyngeal membrane
disintegrates, allows connection of resp. and digestive tracts.
Week 6 of embryological stage (upper lip formation)
Formed by fusions of medial/lateral nasal processes and maxillary processes
Medial nasal process forms bridge of nose and philtrum of upper lip
Lateral nasal process forms lateral nostrils
Cleft lip
Upper lip cleft: Failure of fusion of the medial nasal process with the maxillary process
Midline cleft: failure of fusion between two medial nasal processes (can be unilateral or bilateral)
Occurs 1:700 births, males > females
Week 6 of embryological stage (maxilla formation)
1st pharyngeal arch gives rise to maxillary process
maxillary process, palatine process are ossified to form hard palate - via periosteal osteoblasts
maxillary sinus forms during 3rd month of pregnancy
maxilla continues to grow down and forward until 14-15 years old
Week 7 of embryonic stage (palate formation)
fusion of medial nasal processes form primary palate and maxillary anterior teeth
fusion of maxillary processes forms secondary palate
Cleft palate
1:700 births, females > males
failure of fusion of medial nasal process and maxillary process
Week 7 of embryonic stage (lower face formation)
mandibular processes fuse to for lower lip and mandible
mandible forms in 2 parts:
main body - formed around meckel’s cartilage
ramus/condyle - fuses with main body at 4 months
Meckel Makes the Mandible, Condyle Keeps it Growing
Features of skeletal muscle
peripheral, multi-nucleated
striated
non-branching cells
Skeletal muscle organization
Skeletal muscle > Muscle fascicle > muscle fiber > myofibril > myofilaments (sarcomeres)
Features of cardiac muscle
single, central nucleus
striated
branching via intercalating disks
Features of smooth muscle
non-striated, tapered shaped (fusiform)
single, central nucleus
non-branching
Primary muscles of mastication
temporalis
masseter
lateral pterygoid
medial pterygoid
Accessory muscles of mastication
digastric
buccinator
supra-hyoid muscle
infra-hyoid muscle
Articulating surfaces of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ)
head of condyle of mandible
mandibular/glenoid fossa
articular tubercle on the temporal bone
articular disc between superior and inferior synovial cavities
Stabilizing structures of the TMJ
joint capsule and lateral ligament
postglenoid tubercle
stylomandibular ligament
sphenomandibular ligament
Ginglymoarthrodial joint
involved in hinging and sliding motion
ginglymus = hinging
arthrodial = sliding
Functions:
depression (open mouth)
elevation (closing mouth)
protrusion (forward movement)
retrusion (backward movement)
lateral movements
Temporalis
Origin:
temporal fossa, along inferior temporal line
Insertion:
coronoid process and anterior border of the ramus
Actions:
elevation, retrusion
Innervation:
anterior and posterior deep temporal branches of anterior division of mandibular branch of the trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Masseter
Superficial Head
Origin:
inferior border of the anterior 2/3rds of the zygomatic arch and the maxillary process of the zygomatic bone
Insertion:
angle of the mandible, inferior and lateral ramus
Deep Head
Origin:
medial border of zygomatic arch, inferior border of posterior 1/3rd of zygomatic arch
Insertion:
superior and lateral ramus, coronoid process
Actions (both):
elevation
protrusion
Innervations (both):
masseteric branch of anterior division of mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Lateral Pterygoid
Upper Head:
Origin:
infratemporal surface of sphenoid
Insertion:
capsule of TMJ, anterior and medial portion of articular disc, neck of mandible
Lower Head:
Origin:
lateral surface of lateral pterygoid plate
Insertion:
neck of condyle of mandible
Actions:
depression, protrusion, lateral movements
Innervations:
lateral pterygoid branch of anterior division of mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve (CN V3)
Medial Pterygoid
Superficial Head
Origin:
pyramidal process of palatine bone and maxillary tuberosity
Insertion:
medial ramus and angle of mandible
Deep Head
Origin:
medial surface of lateral pterygoid plate
Insertion:
medial ramus and angle of mandible
Actions (both):
elevation
protrusion
lateral movements
Innervations (both):
medial pterygoid branch of mandibular branch of trigeminal nerve