OCR GCSE CS Paper 2
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Abstraction
Simplifying a problem by ignoring unnecessary information
What is decomposition
Breaking a problem down into smaller tasks so that it is easier to solve
What is alogithmic thinking
Following logical steps to solve a problem

What does this do in a flowchart
Start/stop terminator

What does this do in a flowchart
Process
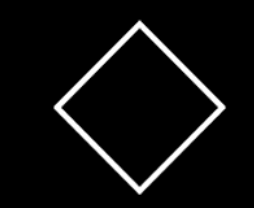
What does this do in a flowchart
Decision (if statement)

What does this do in a flowchart
Input/Output
What does this do in a flowchart
Subroutine

What is an algorithm
A set of instructions in a logical sequence used to solve a problem
How does binary search work
Selects the midpoint of the list, compares to the value, removes part of the list depending on whether the data was higher or lower
How does merge sort work
‘Divide and conquer’, divides a list in half over and over until everything is separate, then everything is merged together again in order
How does bubble sort work
Repeated passes through the data set, swapping items if they are not in the correct order.
Stops when a pass occurs with no changes made
How does insertion sort work
Starting from the first value, compare a value to everything before it and move it into the correct position
Advantages of local variables
Saves memory, easier to debug, subroutines using them can be reused
Advantages of global variables
Variables can be used anywhere, can be used for constants
What does // do
Integer division - shows the ‘whole number of times’ a number goes into another
15 // 6 = 2
What does % do
Modulo division - shows remainder
15 % 6 = 3
What is the word for datatype conversion
Casting
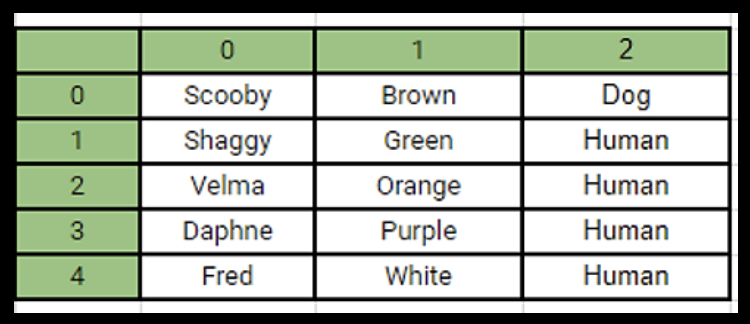
In a 2D array table, what is the order to read it?
Row then column
What is the basic SQL structure
SELECT FROM WHERE
What is an example of a wildcard in SQL
*
What are the things to consider to ensure a program is secure and robust
Anticipating misuse
Input sanitisation
Validation
Verification
Authentication
Maintainable code
What are the types of input validation
Range check
Type check
Format check
Presence check
Lookup table to limit inputs
Length check
What makes programs maintainable
Subroutines
Indentation
Naming conventions
Comments
Constants
Types of testing
Iterative testing
Final testing
Four types of test data
Normal data
Boundary data
Invalid data
Erroneous data
Why do programmers use high level languages
Easier readability as closer to human language
Faster development
Portability across different platforms
What are low level languages for
Speed or direct interaction with hardware e.g. drivers
Two types of low-level language
Machine code, Assembly language
What is machine code
0111001001010101010010101010010010100101001
What does a translator do
Changes a program to another language, usually machine code
Interpreter
Converts high level language one line at a time and executes it
Compiler
Converts high level language at once for execution at a later date
Interpreter vs compiler complexity
Interpreters are smaller, simpler programs
Interpreter vs compiler execution speed
Interpreters must translate every time, compilers create more efficient code making the programs run faster
Interpreter vs compiler error reporting
Compiler analyses the entire program and records location of errors in an error file
Interpreter stops the program from running when it reaches an error
Interpreter vs compiler repetition
Compilers must recompile whenever a change is made, however does not have to recompile whenever the program is run
Interpreters have to translate every time they are run even without changes
IDE features
Editor
Translators
Break point
Variable watch
Trace
Error diagnostics and debugger
Editor purpose
Editing cos
Low level language definition
A language close to the computer’s instruction set