Density - The Science
1/20
Earn XP
Description and Tags
MEE1004: Mechanics of Materials - Lecture 4
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
21 Terms
What determines density
Atomic weight, atom size, atomic packing.
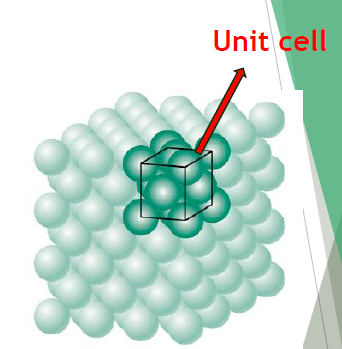
Crystalline Materials
Have a regularly repeating pattern of structural units called unit cells.
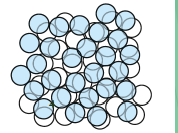
Amorphous / non-crystalline materials
Materials that lack an ordered internal structure.
Unit cell
Characterising unit of a crystal structure.
Atomic packing factor
The fraction of volume in a crystal structure that is occupied by the atoms.
Atomic packing factor equations

Types of structures
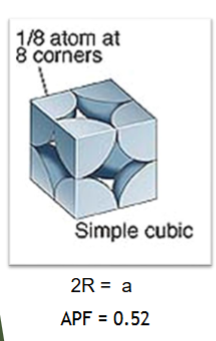
Simple cubic
Body-centred cubic (BCC)
Face-centred cubic (FCC)
Close packing hexagonal (CPH)
Simple cubic
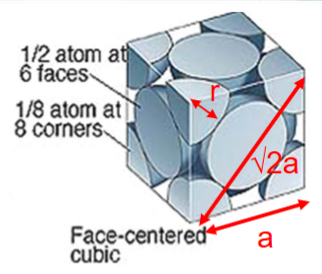
Face centred cubic (FCC) structure
An atom at all 8 corner positions and at the centre of all six faces.
4R = √2a
APF = 0.74
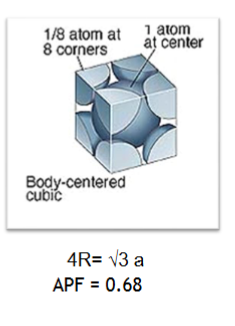
Body centred cubic (BCC)
Close packed hexagonal (CPH)
Each atom is surrounded by six nearest neighbours arranged in a hexagonal ring, and twelve next nearest neighbours arranged in a slightly distorted octahedral shape.
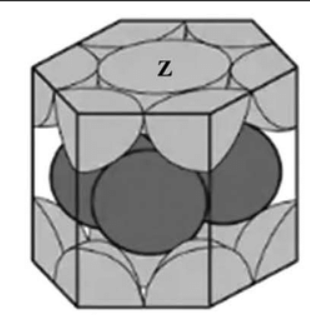
Close packed atomic structures
Packing fraction for CPH and FCC is 0.74 - meaning spheres occupy 74% of all available space.
Non close packed atomic structures
BCC APF = 0.68
Simple cubic APF = 0.52
Amorphous material: APF less than and equal to 0.64
Atomic packing in Ceramics
Generally compounds made of two or more elements (A and B).
A pair of atoms (A + B) is associated with each lattice point in the structure.
Atomic packing in Glasses
Made of natural materials such as sand.
Amorphous silica (SiO2) forms the basis of almost all glasses.
APF for amorphous material
≤0.64
Technique used for producing amorphous structured materials
Quenching (rapid cooling).
Thermoplastics
Any plastic polymer material that becomes pliable or mouldable at a certain elevated temperature and solidifies upon cooling,
Thermoplastic properties
Weak hydrogen bonds between molecule chains easily broken / rearrange
Melt easily
Easily shaped / mould / recycled
Thermoset
A polymer that is obtained by irreversibly hardening (“curing”) a soft solid or viscous liquid prepolymer (resin). T
Thermoset properties
Stiffer and stronger inter-molecular bonding
Crosslinks cannot be broken easily
Cannot be shaped / mould / recycled