Prescribing in Pregnancy
1/41
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
42 Terms
What questions should we ask when considering drug use in pregnancy?
- Is the drug safe?
- Necessary?
- Are there alternatives that are as effective/safer?
- Effect of pregnancy on drugs and drugs on pregnancy.
- Assess need for extra monitoring of mum and baby
Which source should we not use to check drug safety in pregnancy?
BNF - as not tested by manufacturers
What counts as 1st trimester?
1-13 weeks

What counts as second trimester?
13-28 weeks

What counts as 3rd trimester?
After 28 weeks

What happens in 1st trimester than means alterations in medications may be required?
Increase in blood vol but reduced protein binding due to pregnancy steroids.
Why might repeat doses be required in pregnancy?
- Risk of vomiting.
- Transit time reduces.
- Increased absorption.
In which trimester is there the highest risk of teratogenic drugs having an effect?
1st trimester
List some drugs that are contraindicated in pregnancy: MR WILLS
- Methotrexate.
- Radioactive iodine.
- Lithium.
- Isotretinoin.
- Sodium valproate.
- Warfarin.

Where are 3x places to find drug information in pregnancy and breastfeeding?
UKTIS - UK teratology information service.
E-lactancia.
LactMed.
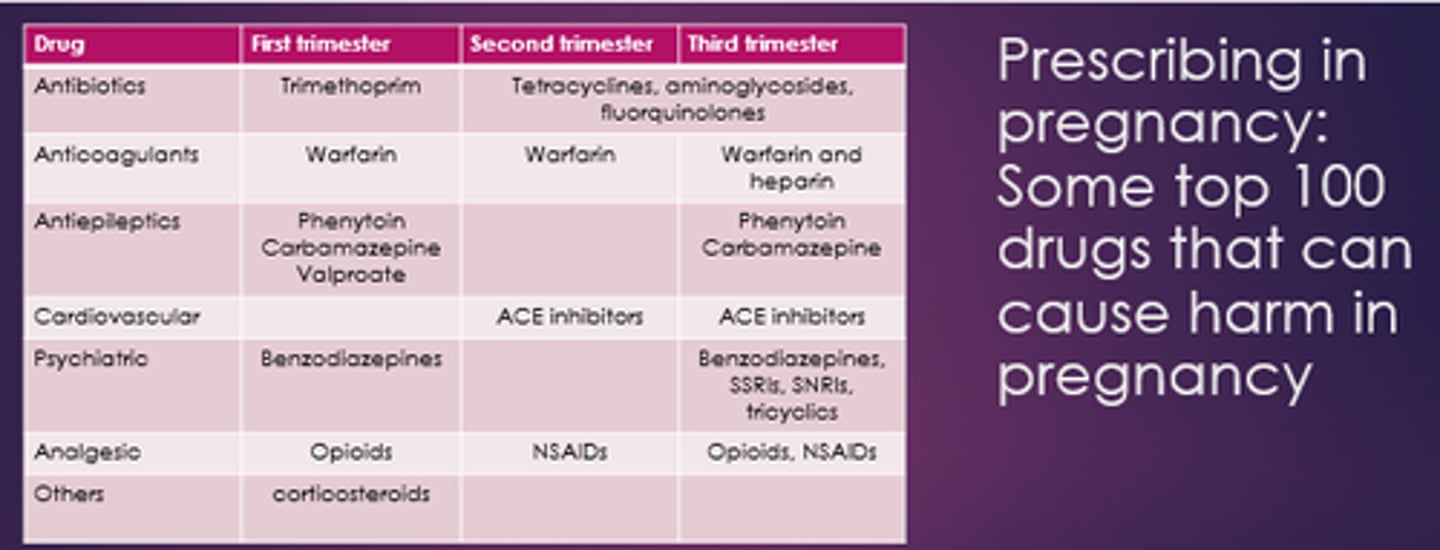
Name some drugs that can cause harm in 1st trimester.
- Trimethoprim.
- Warfarin.
- Phenytoin.
- Carbamazepine.
- Valproate.
- Opioids.
- Corticosteroids
Why can opioids be problematic in pregnancy?
Babies can go through withdrawal
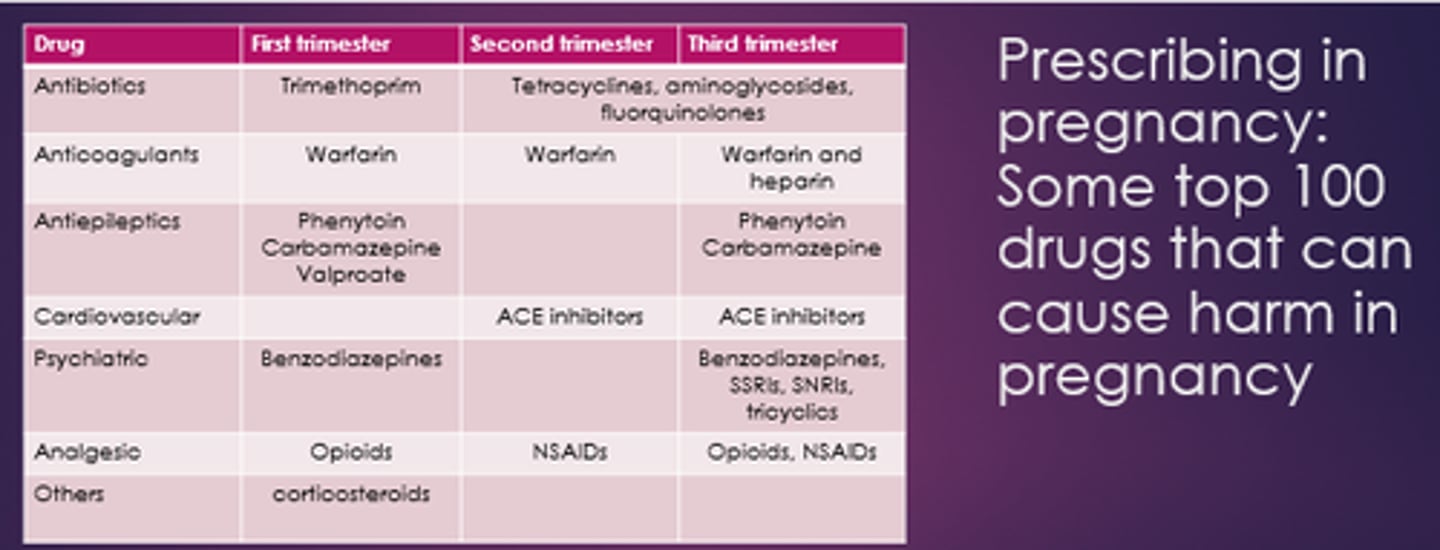
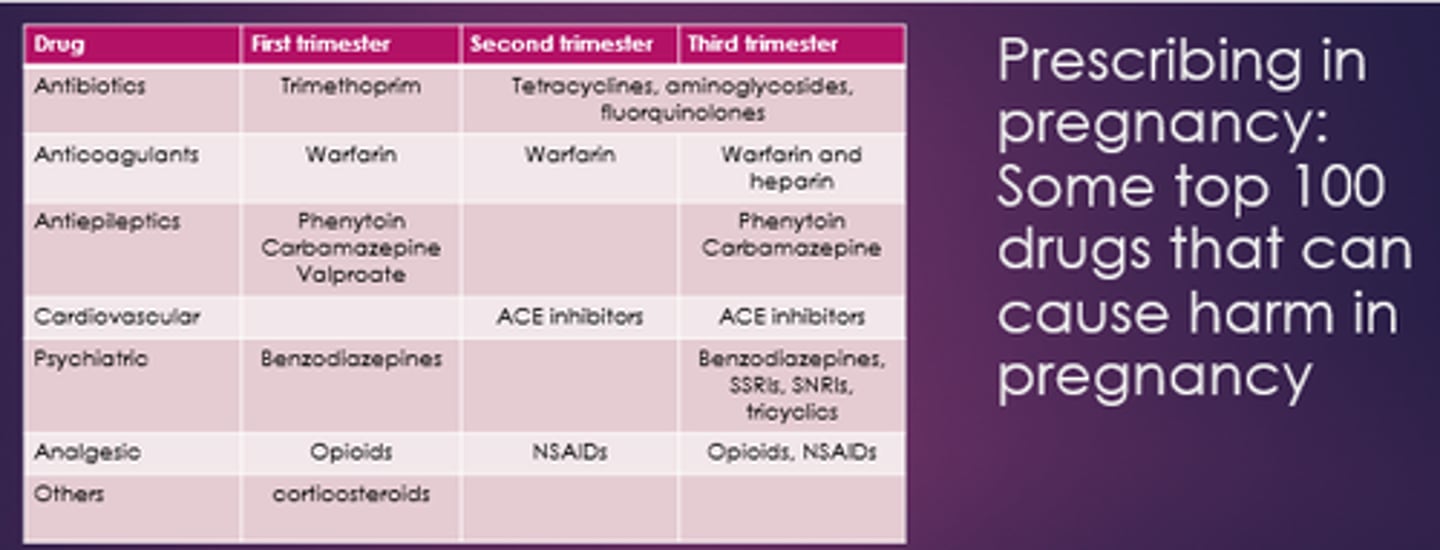
Name some drugs problematic in 2nd and 3rd trimester.
- Tetracyclines.
- Aminoglycosides.
- Fluoroquinolones.
- Warfarin.
- Phenytoin.
- Carbamazepine.
- ACEis.
- Opioids, NSAIDs.
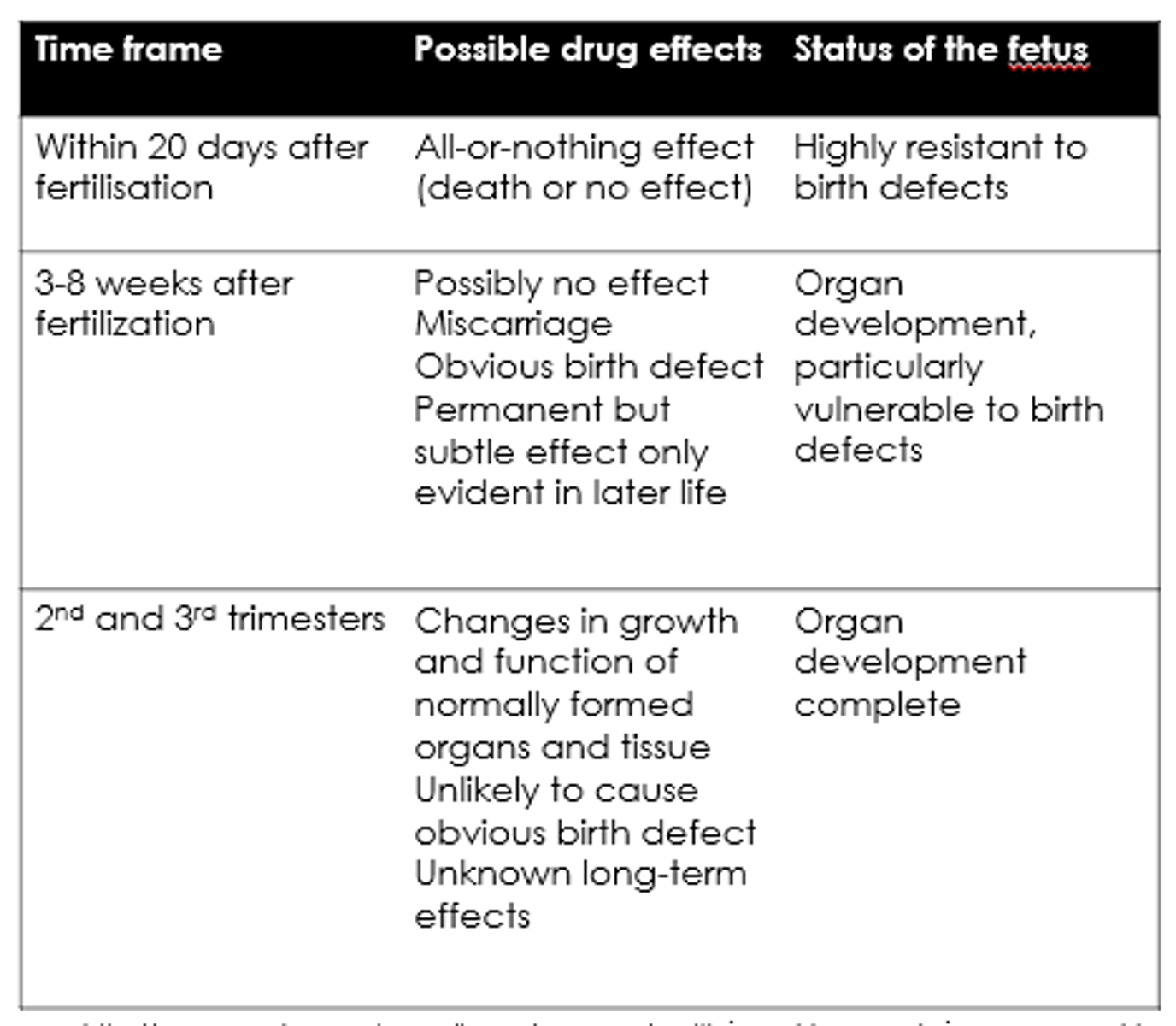
What are the possible drug effects within 20 days of fertilisation?
All-or-nothing - death or no effect.
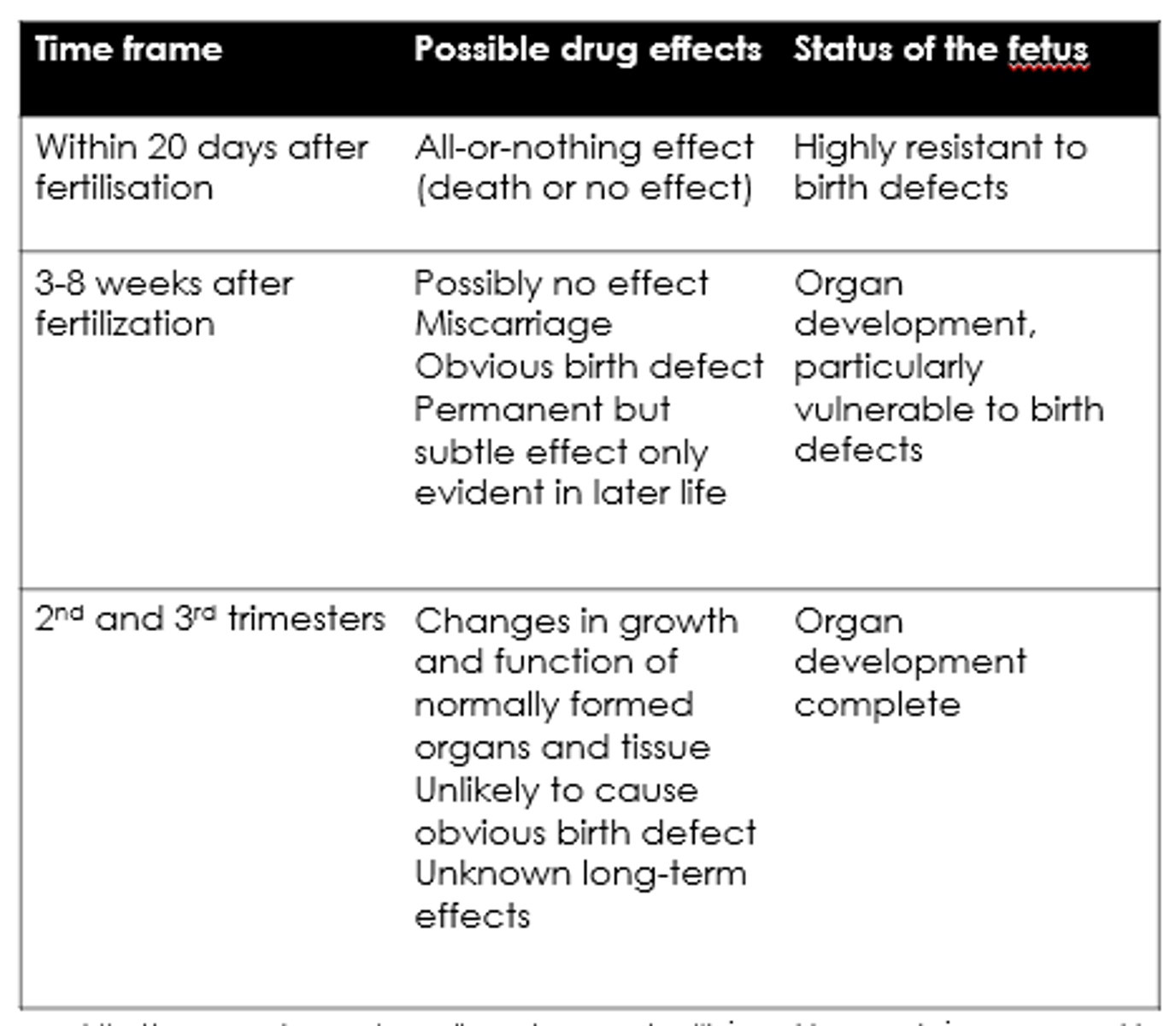
What are the possible drug effects 3-8 weeks after fertilisation?
- Possibly no effect.
- Miscarriage.
- Birth defects.
- Permanent but subtle effects.
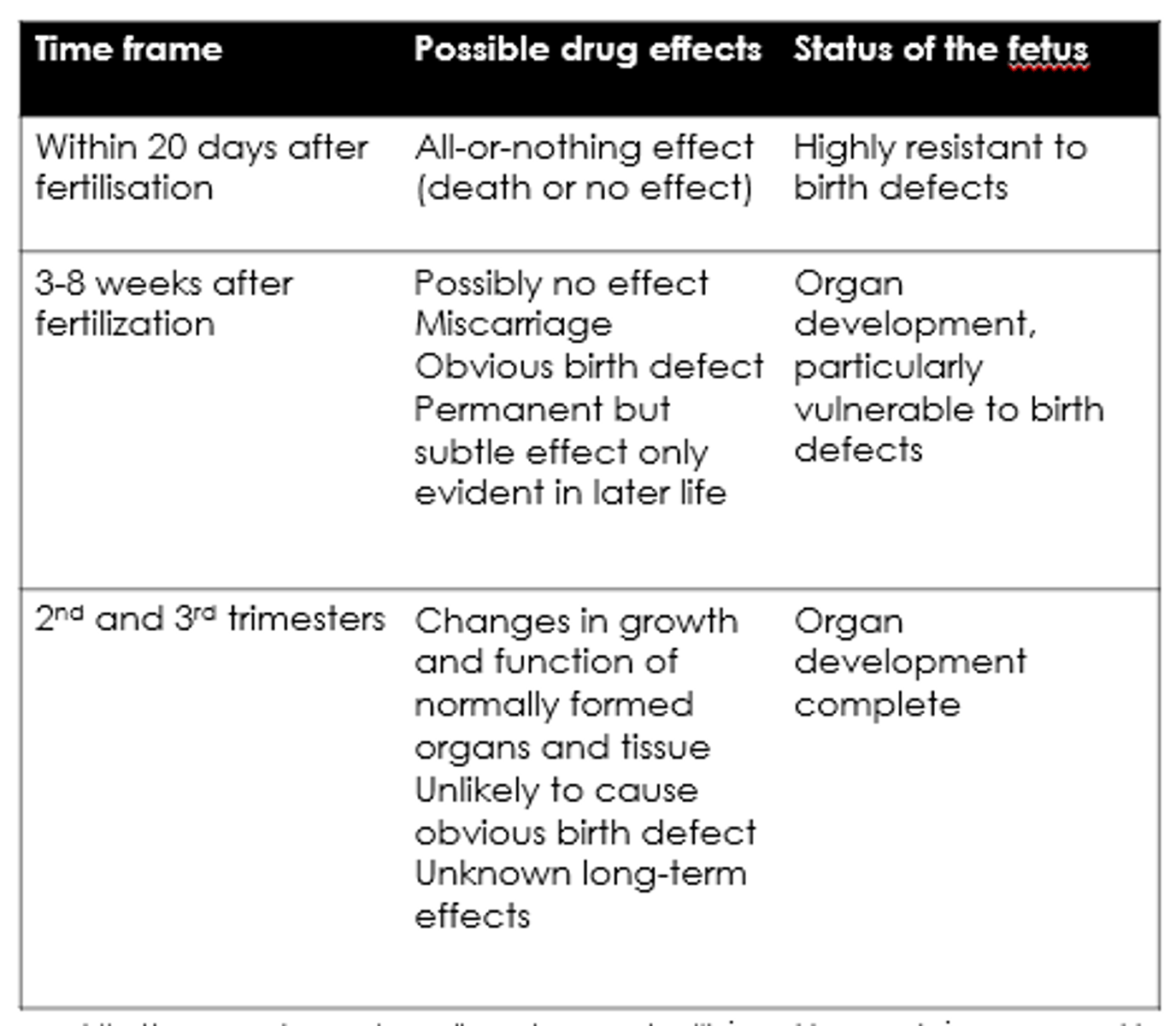
What are the possible drug effects in 2nd + 3rd trimesters?
- Changes in growth and function.
- Unknown long term effects.
What should be considered in pre-pregnancy?
- Folic acid supplementation.
- Safer alternatives?
- Should they delay pregnancy to optimise condition?
- Only switch drugs if meds unsafe, and there's a suitable alternative.

What happens in early pregnancy?
Plasma levels change, reduced absorption, dilution, excretion.
- Can increase drug concs.
- Teratogenesis.
- Side fx of hormones of pregnancy.
What drugs may be used to treat hyperemesis in pregnancy?
- Cyclizine.
- Metoclopramide.
- Prochlorperazine.
- Ondansetron.
- Steroids.

What can happen if a teratogenic agent is taken during embryogenesis (up to 8 weeks)?
Anatomical malformation

How should we manage epilepsy with pregnancy?
- Delay pregnancy til fully under control?
- High dose folic acid - 5mg od in women w/epilepsy.
Why do women with epilepsy take high dose folic acid in epilepsy?
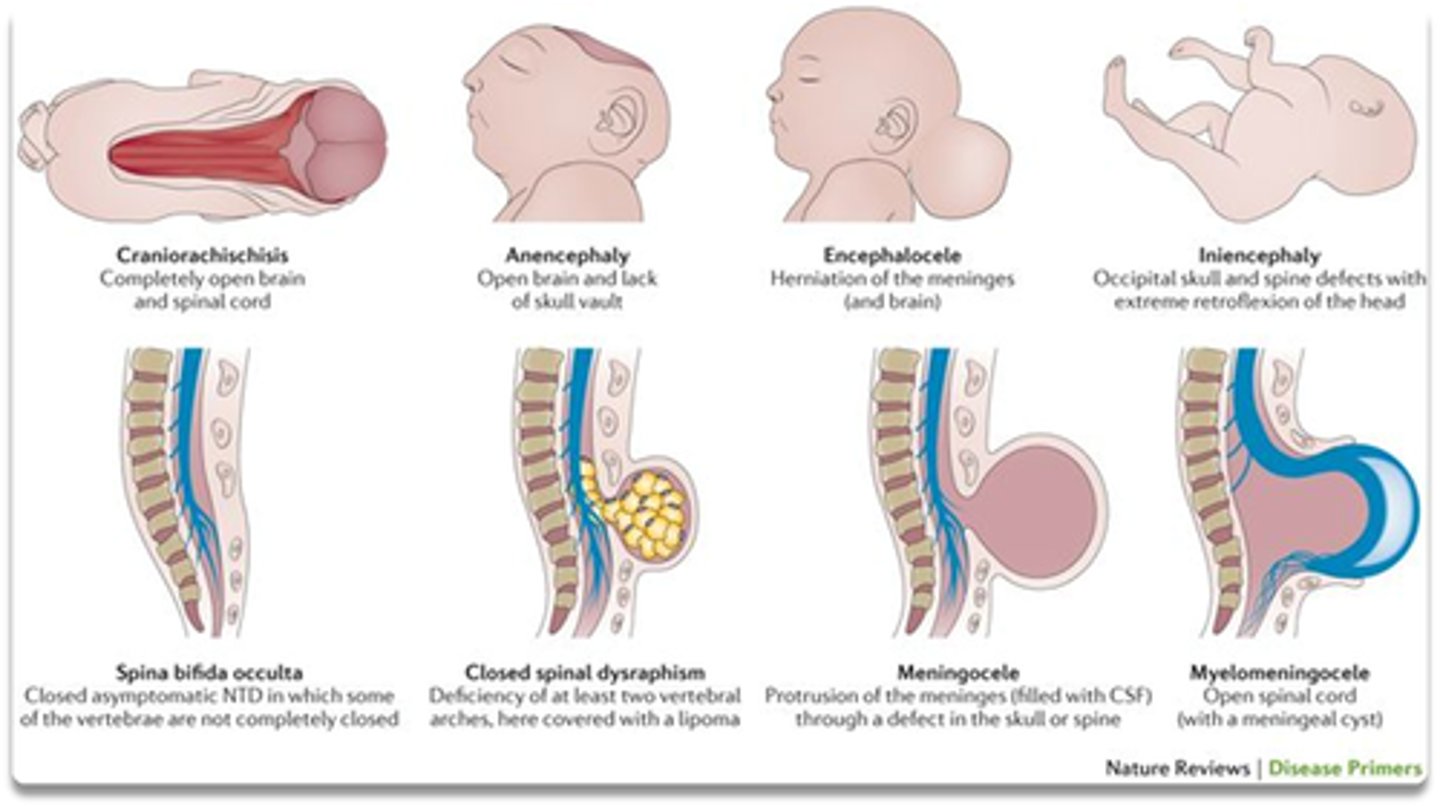
Bc most anti-epileptics reduce folate, and want to prevent neural tube defects.
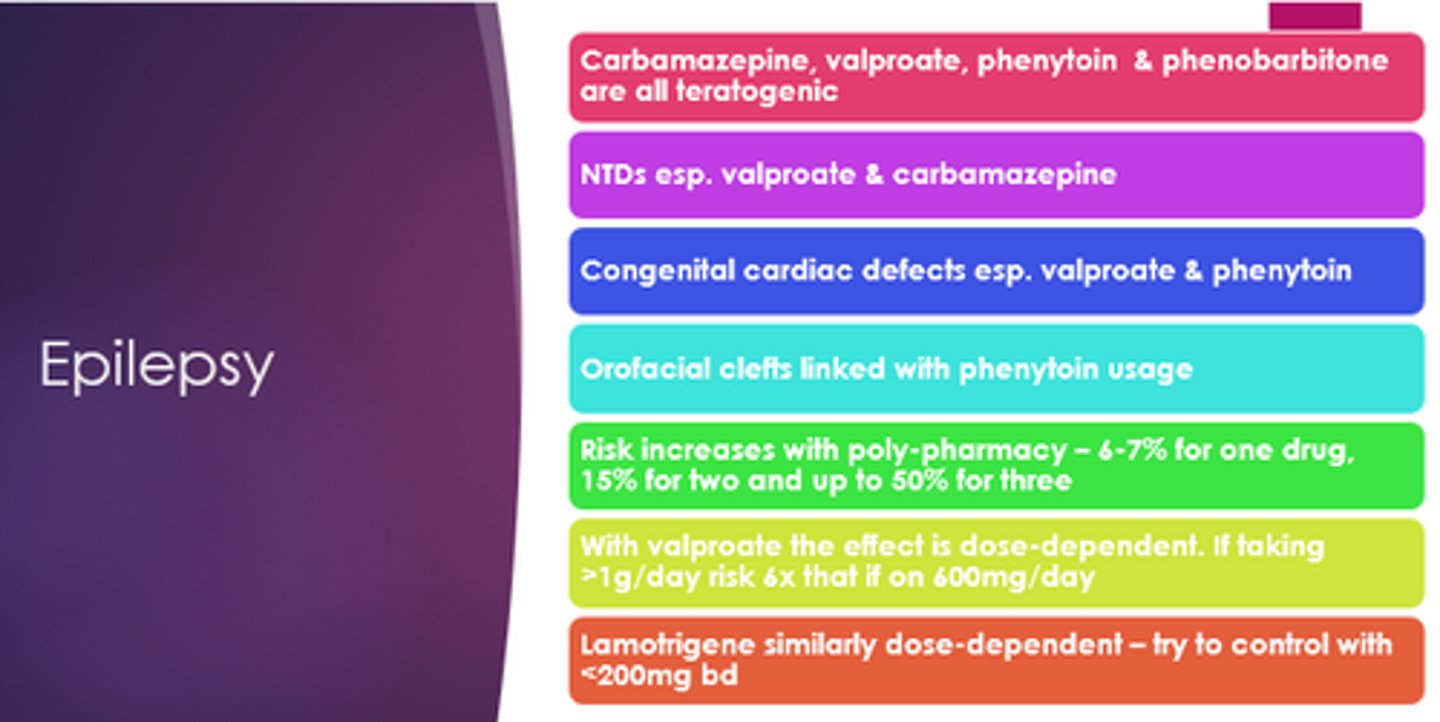
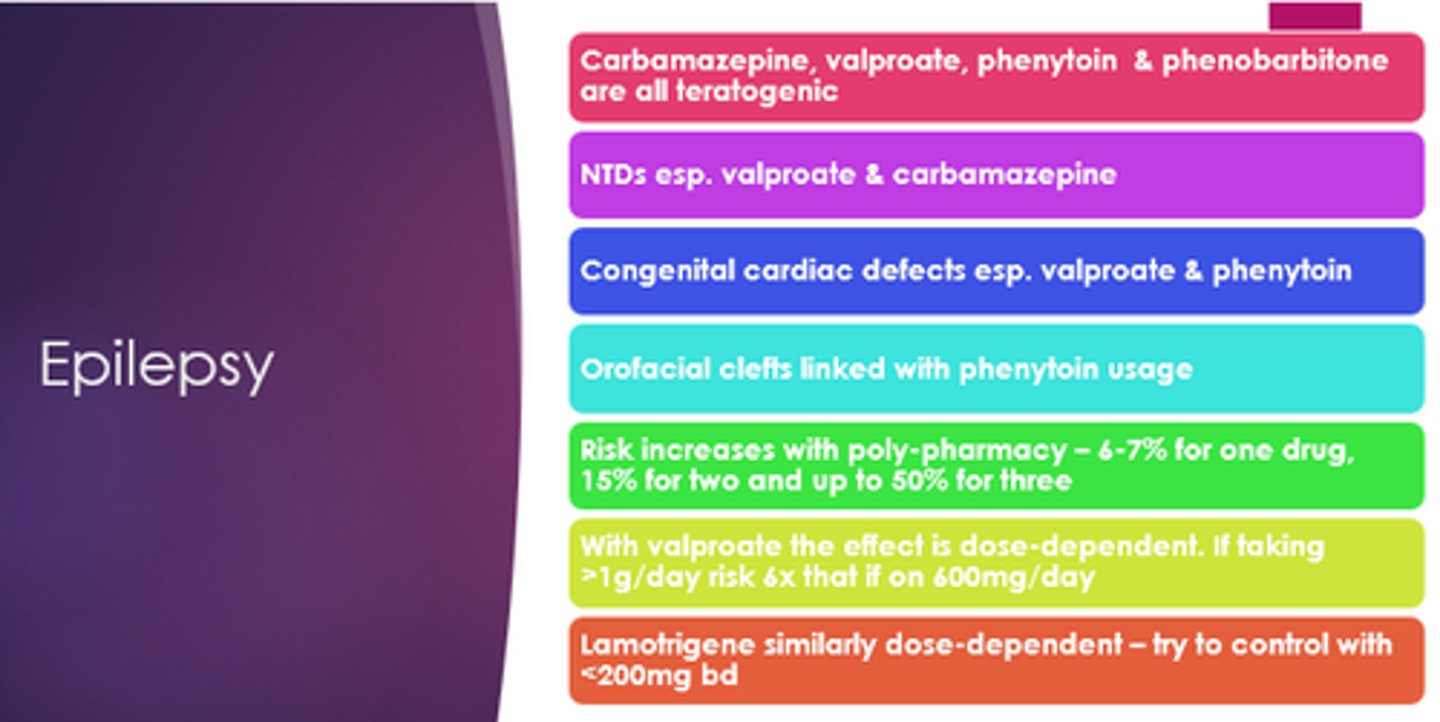
Which epilepsy medicines are teratogenic?
Carbamazepine, valproate, phenytoin, phenobarbitone.
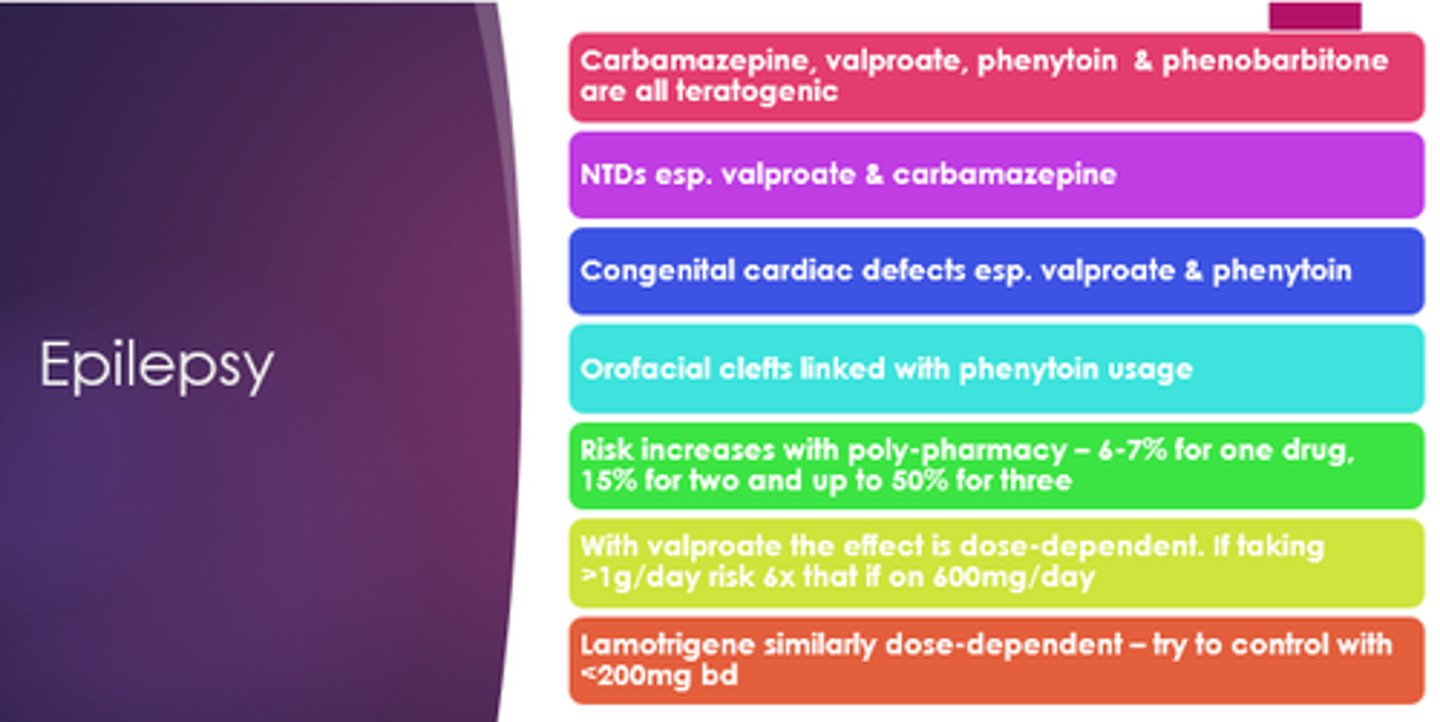
Which epilepsy medications especially can cause neural tube defects?
Valproate and carbamazepine
Which epilepsy medicines especially can cause congenital cardiac defects?
Valproate and phenytoin
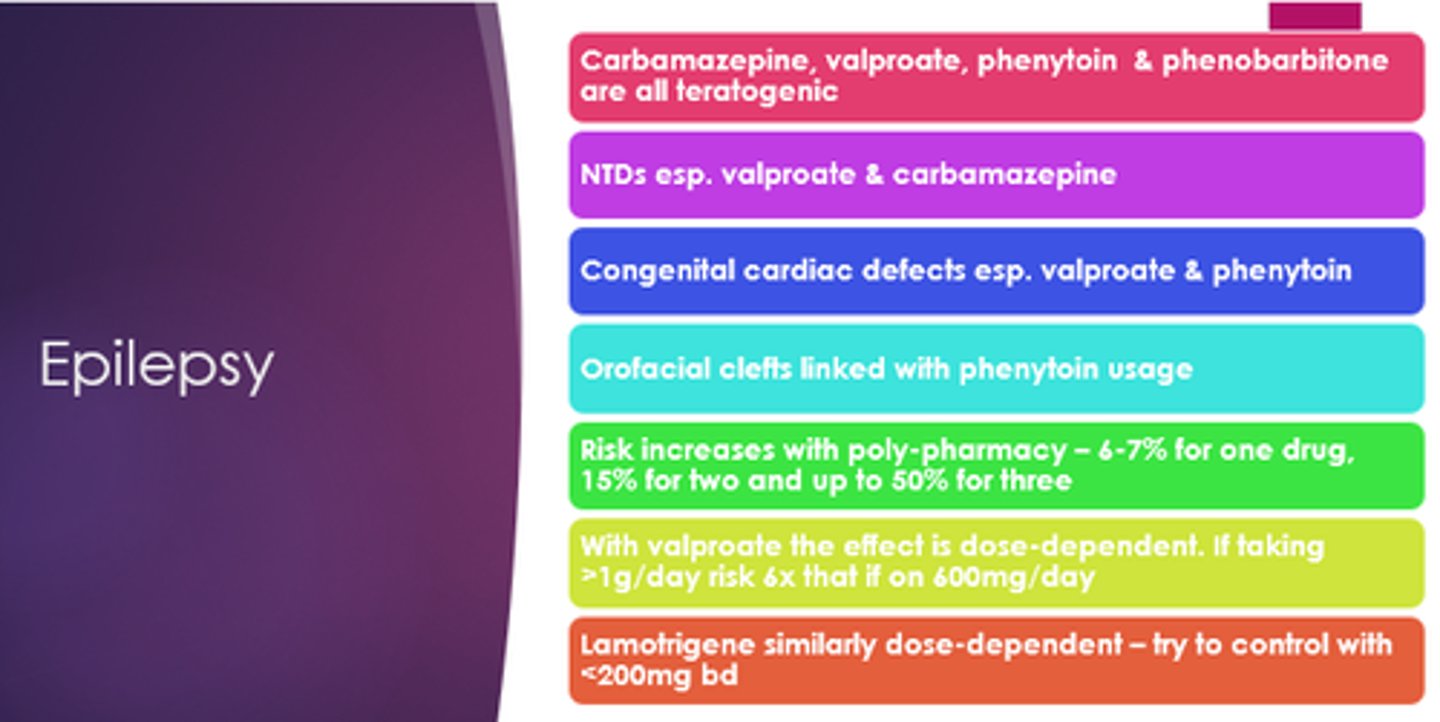
Which epilepsy drug are orofacial clefts linked with?
Phenytoin
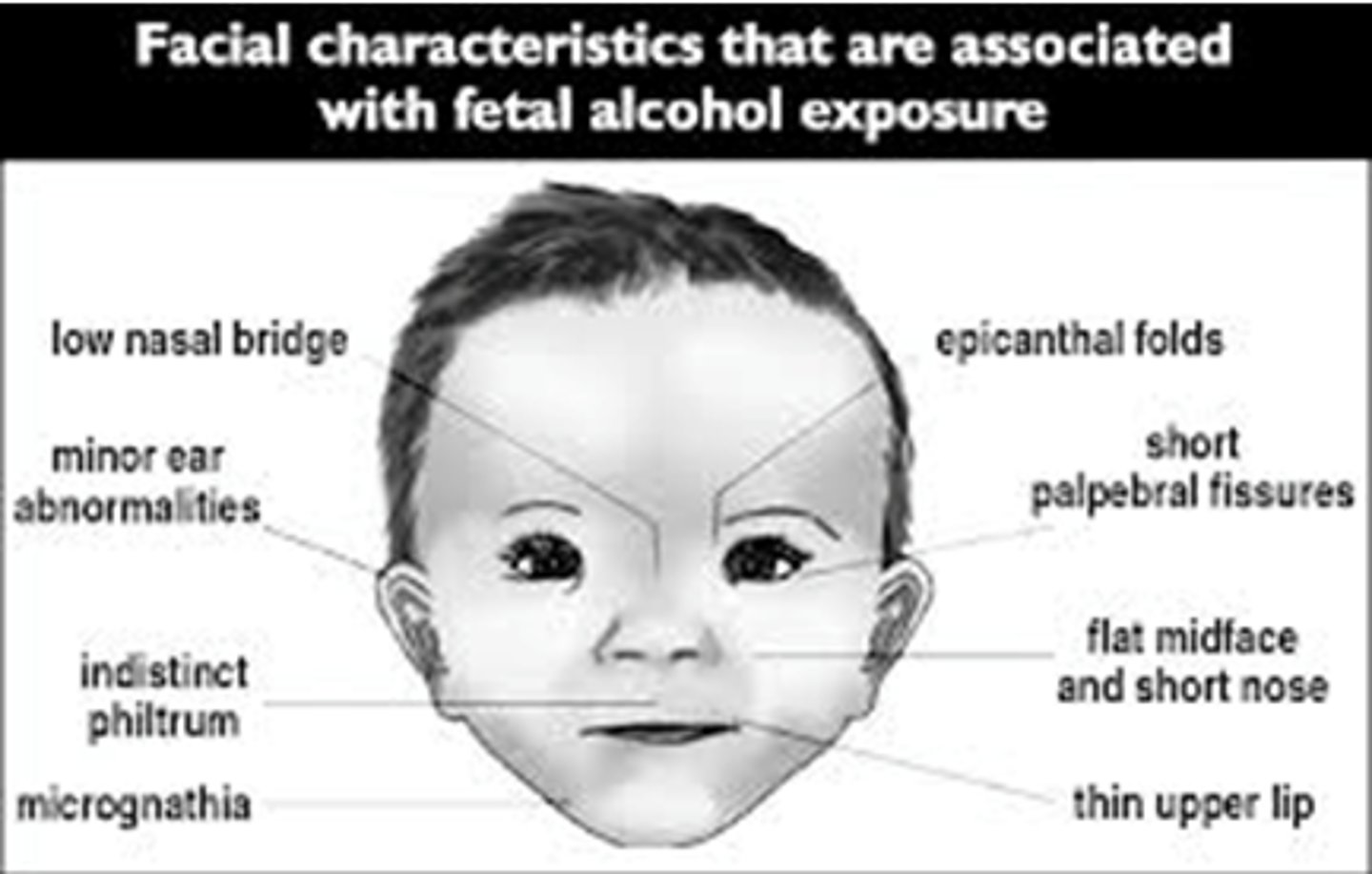
What are some mino malformations associated with use of anticonvulsants in pregnancy?
- Low-set ears.
- Broad nasal bridge.
- Irregular teeth.
- Hypoplastic nails and digits.
BUT epilepsy itself is associated w/increased risk of congenital abnormalities.
What is the British Thoracic Society Advice surrounding asthma treatment in pregnancy?
Treat as normal!
Including systemic coirticosteroids and high flow O2 to prevent maternal and foetal hypoxia

What are some complications of asthma in pregnancy?
- Foetal growth restriction.
- Preterm birth.
- Increased perinatal mortality.
- Neonatal hypoxia.
- Hyperemesis.
- Hypertension.
- Pre-eclampsia.
- Complicated labour

What specific guidance does SIGN give for managing asthma in pregnancy?
- Asthma review in early pregnancy.
- Use inhalers as normal (SABA + LABA, ICS, oral theophylline).
- Offer OCS for exacerbations.
- If leukotriene receptor antagonists or LAMAs needed, they should not be stopped.
Better to control!
What is the number one treatment for type 1, 2 and uncontrolled gestational diabetes?
Insulin!
Why might there be a raise in baseline blood glucose levels in pregnancy?
Human placenta produces lactogen, cortisol and glucagon.
All are anti-insulin.
What are the risks to the neonate if gestational diabetes diagnosed in 2nd/3rd trimester?
- Macrosomia 4.5kg (larger than avg).
- Shoulder dystocia (stuck in pelvis).
- Neonatal admission.
- Neonatal hypoglycaemia.
What is euglycaemia?
Well controlled blood glucose.
What anti-hypertensives are commonly used in pregnancy?
- Nifedipine.
- Labetalol.
- Methyldopa.
- Hydralazine.

Which anti-hypertensives are contraindicated in pregnancy?
ACEis/ARBs and diuretics.

What is seen in pre-eclampsia?
Increased proteinurea shows signs of kidney damage and hypertension.
Increased LFTs, headache, N+V, oedema.
Eclampsia is a medical emerg.
What is eclampsia?
Seizures that occur in pregnant women with pre-eclampsia.
What is recommended surrounding mental health in pregnancy?
- SSRI benefits outweigh risks.
- Placental transfer can occur.
- Risk of neonatal withdrawal.
- Monitor for 48hours after birth.
- Breastfeeding benefits outweigh risks.
- No evidence switching between SSRIs is any benefit.

What's the safest analgesic to use in pregnancy?
Paracetamol.

What are the risks with using NSAIDs after 20 weeks?
Can decrease amniotic fluid vol.
Avoid throughout, esp. in 3rd trim.

What is the risk of using opioids in pregnancy?
Neonatal withdrawal if taken for a long period of time, esp. in month leading up to birth.
