A&P Body Tissues
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
78 Terms
Simple Squamous Epithelium: Appearance
Flat and sheet-like, single layer

Simple Squamous Epithelium: Location
Air Sacs of lungs, the lining of the heart, blood vessels, and lymphatic vessels
Simple Squamous Epithelium: Function
Allows materials to pass through by diffusion and filtration, and secretes lubricating substance
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: Appearance
Cube-like, single layer
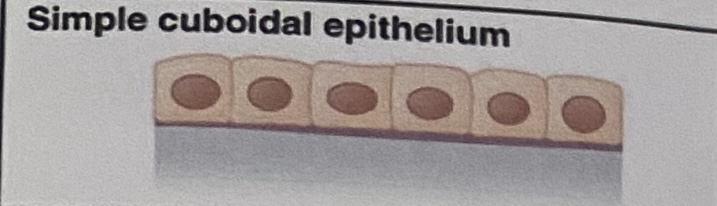
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: Location
In ducts and secretory portions of small glands, and in kidney tubules
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium: Function
Secretes and absorbs
Simple Columnar Epithelium: Appearance
Tall narrow pillars, single layer, usually has cilia or microvilli
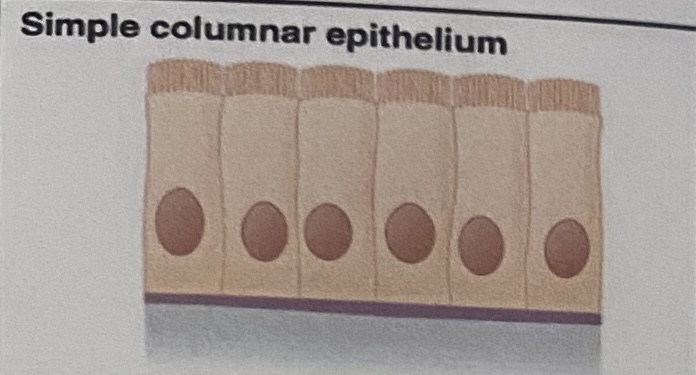
Cilia
Tiny hair-like structures on tissue used to move substances in the body
Microvilli
AKA Brush Border, tiny protrusions which increase surface area
Simple Columnar Epithelium: Location
Ciliated tissues are in bronchi, uterine tubes, and uterus. The non-ciliated (smooth) tissue are in the digestive tract and bladder
Simple Columnar Epithelium: Function
Absorbs; Also secretes mucus and enzymes
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: Appearance
“Goblet cells”, varying heights of cells, **single layer but looks like multiple
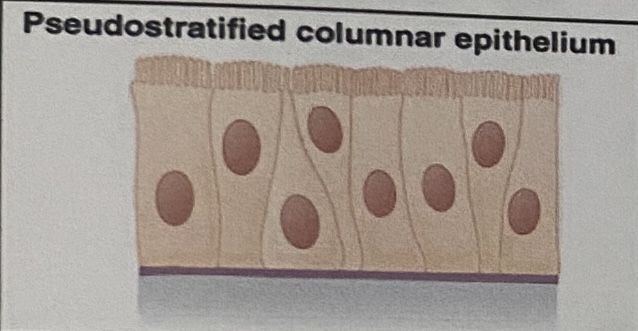
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: Location
Ciliated tissue lines the trachea and a lot of the upper respiratory tract
Pseudostratified Columnar Epithelium: Function
Secretes mucus; ciliated tissue moves mucus
Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Appearance
Multiple layers of stacked flat cells

Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Location
Skin, and lines the esophagus, mouth, and vagina
Stratified Squamous Epithelium: Function
Protections against abrasion (friction)
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Appearance
Multiple layers of cube-like cells packed together
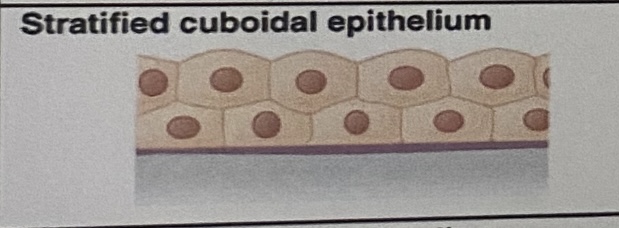
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Location
Sweat glands, salivary glands, and the mammary glands
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium: Function
Protective tissue
Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Appearance
Multiple layers of column-like cells
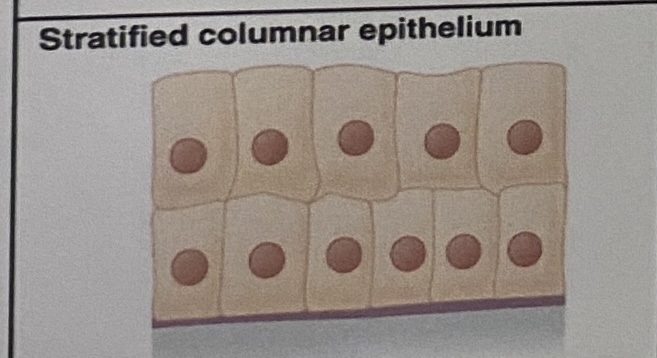
Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Location
The male urethra and the ducts of some glands
Stratified Columnar Epithelium: Function
Secretes and protects
Transitional Epithelium: Appearance
Cuboidal when relaxed, squamous when stretched, varying shapes packed together in multiple layers
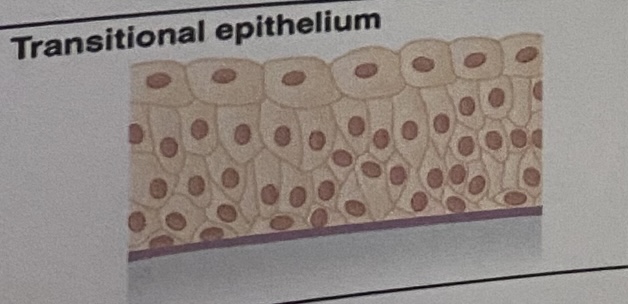
Transitional Epithelium: Location
Lines the bladder, urethra, and the ureters
Transitional Epithelium: Function
Allows the urinary organs to expand and stretch
Histologist
Someone who studies tissues, prepares tissue
Tissue
Groups of cells with similar structure and function
Connective Tissues: Areolar Appearance
Cobwebs, most widely distributed tissue
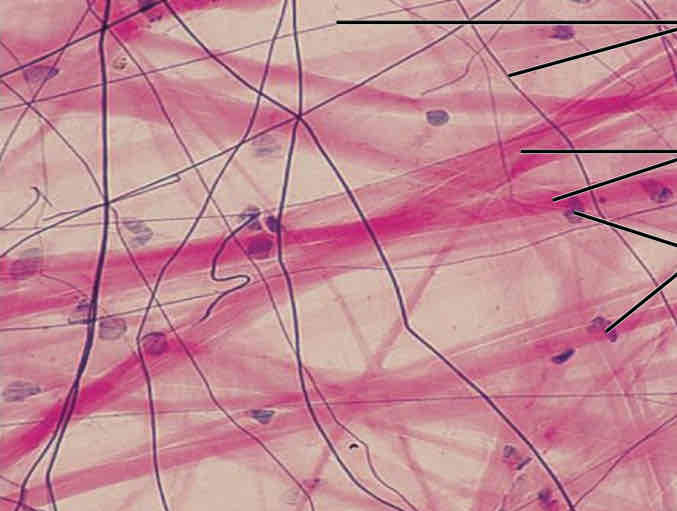
Connective Tissues: Areolar Function
Packing tissue, contains all fiber types and soaks up excess fluid
Connective Tissues: Areolar Location
under epithelial tissue and around organs
Connective Tissues: Adipose Appearance
Fat cells, circular cells “adiPOSE” “PotaTOES”
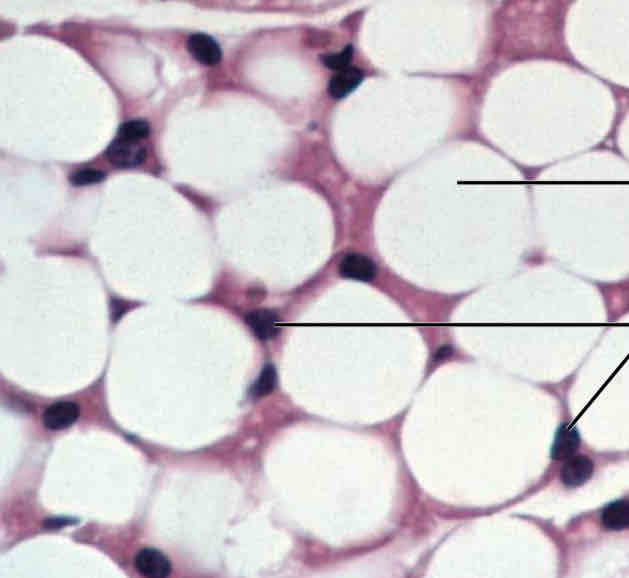
Connective Tissues: Adipose Function
Insulates the body, protects some organs (cushioning), serves as a site of fuel storage
Connective Tissues: Adipose Location
Under the skin, around the kidneys and heart
Connective Tissues: Reticular Appearance
“Cherry blossom trees”, look like tree branches and are a network of interwoven fibers
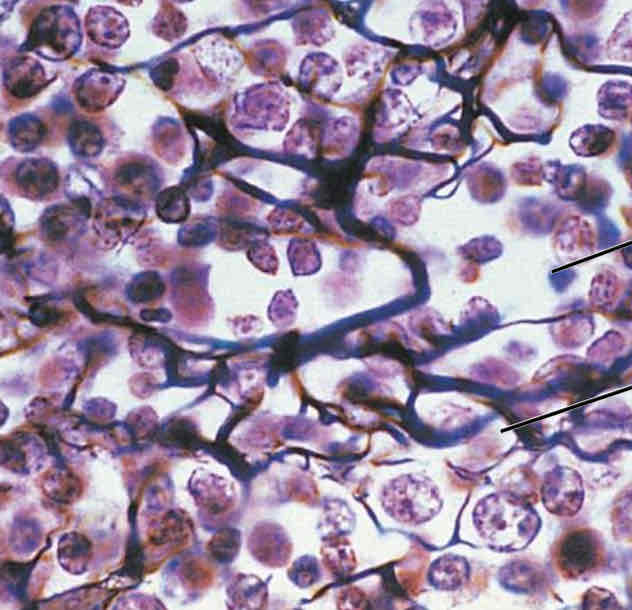
Connective Tissues: Reticular Function
Provides structure and support for organs below (creates soft skeleton)
Connective Tissues: Reticular Location
Lymph nodes, spleen, and bone marrow
Connective Tissues: Dense Regular Appearance
Wavy fibers running in the same direction
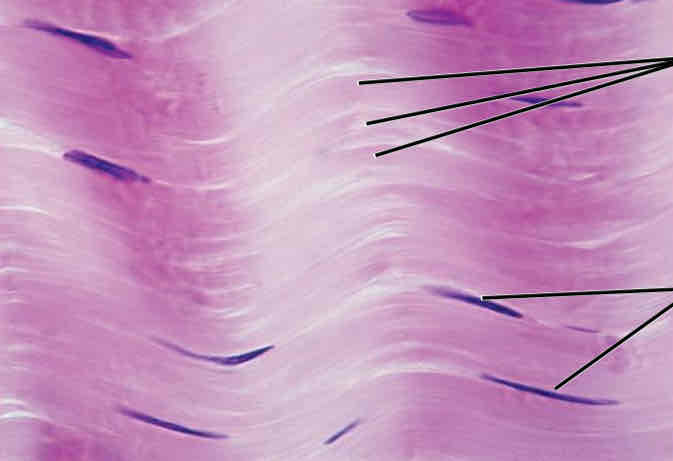
Connective Tissues: Dense Regular Function
Supports, protects, and holds organs in place
Connective Tissues: Dense Regular Location
Within the tendons and ligaments
Connective Tissues: Dense Irregular Appearance
“Marbled” fibers running in all sorts of directions
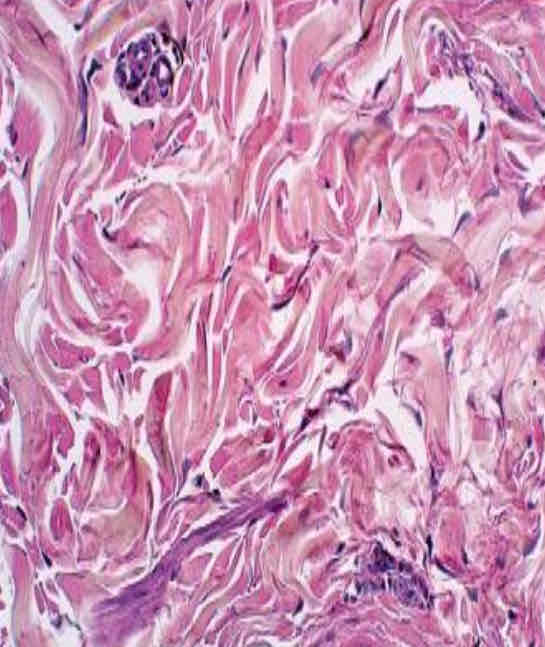
Connective Tissues: Dense Irregular Function
Provides strength by making the skin resistant to tearing
Connective Tissues: Dense Irregular Location
In the dermis, in fibrous coverings that surround organs and joints
Connective Tissues: Elastic Dense Appearance
Looks marbled as well, but not as disorganized as Dense Irregular
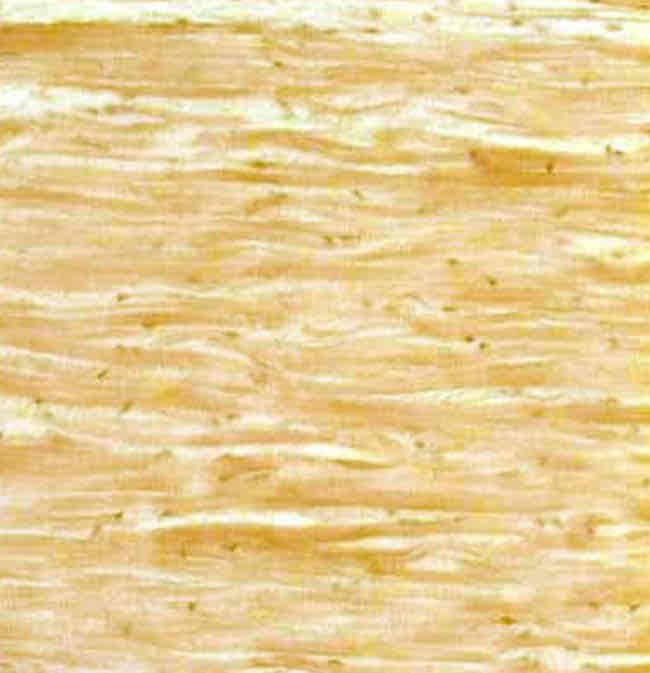

Connective Tissues: Elastic Dense Function
Enables organs and parts of organs to stretch and contract (bounce back after stretching)
Connective Tissues: Elastic Dense Location
Walls of arteries, ligaments connecting vertebrae, lungs
Connective Tissues: Bone Appearance
Like the rings on a tree trunk when cut, circular
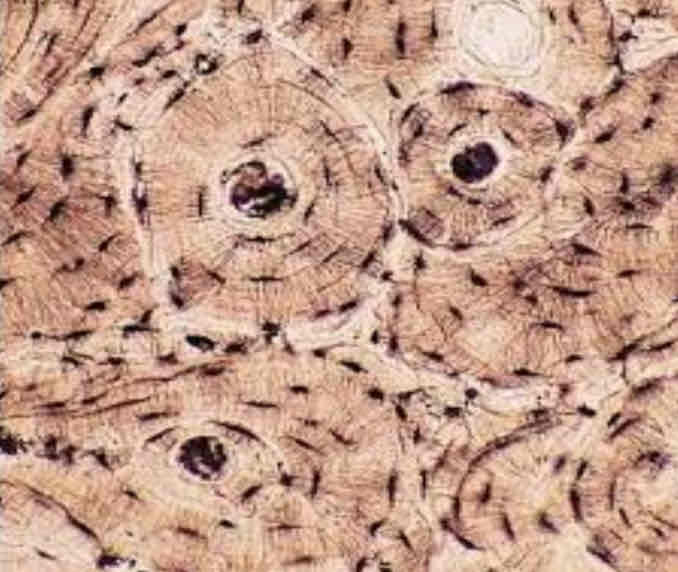
Connective Tissues: Bone Function
To protect and support the body
Connective Tissues: Bone Location
Compact and spongy bone
Connective Tissues: Blood Appearance
Spread out, bunch of circular shapes with larger circles mixed in (white blood cells)
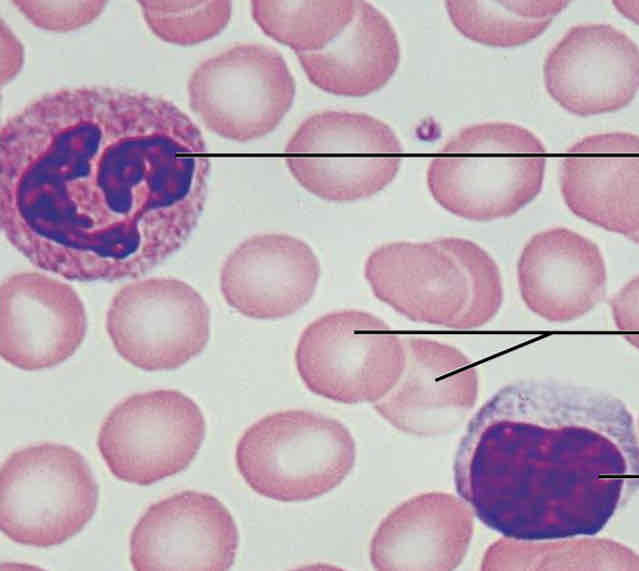
Connective Tissues: Blood Function
To transport materials throughout the body
Connective Tissues: Blood Location
Within blood vessels
Connective Tissues: Elastic Cartilage Appearance
All cartilage has chondrocytes (“cells within cells”), almost looks like many miniature eyes
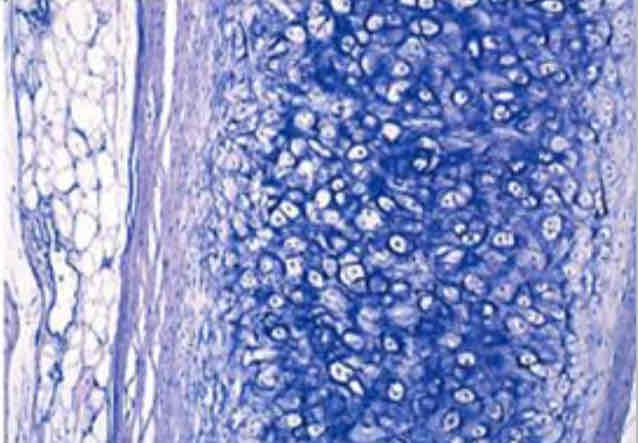
Connective Tissues: Elastic Cartilage Function
To provide elasticity
Connective Tissues: Elastic Cartilage Location
External ear, epiglottis
Connective Tissues: Hyaline Cartilage Appearance
Most common type of cartilage, many spread out circles (not as spread out as blood)
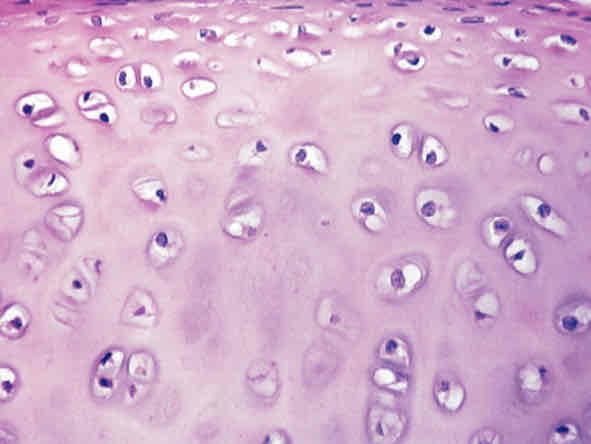
Connective Tissues: Hyaline Cartilage Function
Helps your bones move smoothly past each other in your joints
Connective Tissues: Hyaline Cartilage Location
Articulate cartilage at the ends of bones, tip of nose, costal cartilage, trachea
Connective Tissues: Fibrocartilage Cartilage Appearance
Like a Van Gogh painting, thin wavy lines, almost blurry
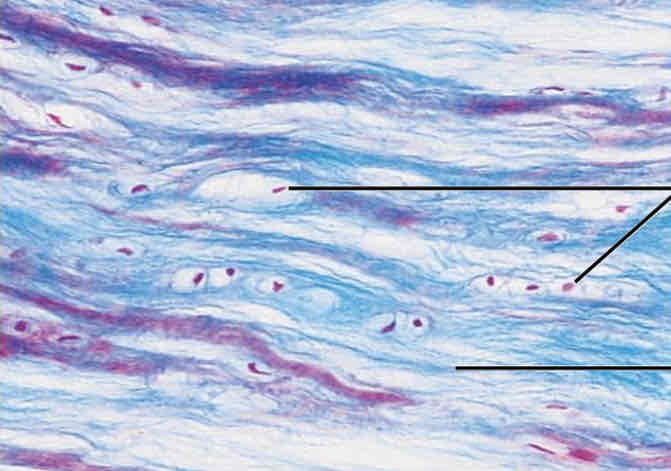
Connective Tissues: Fibrocartilage Cartilage Function
To resist compression and tension
Connective Tissues: Fibrocartilage Cartilage Location
Intervertebral disks, cartilage of the knee
Types of Fibers: Collagen
The strongest fiber, flexible cable-like structure
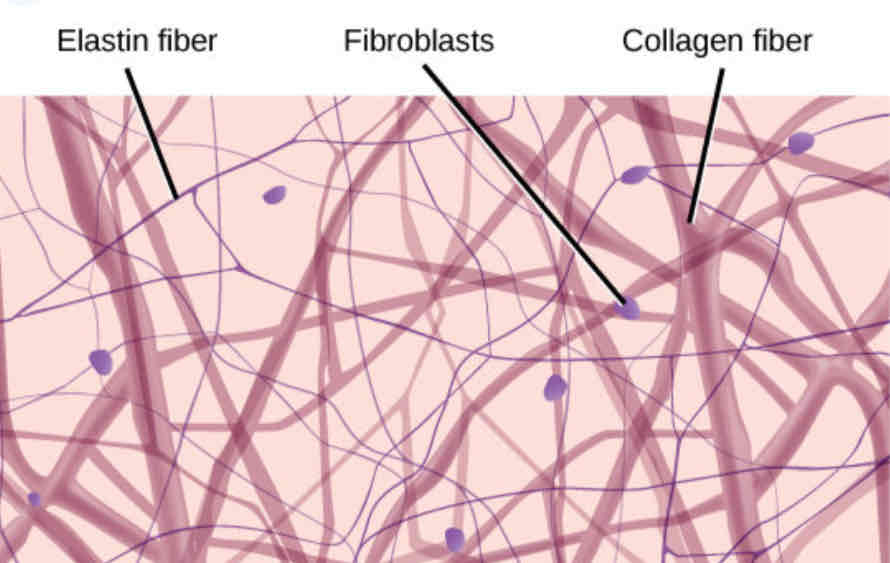
Types of Fibers: Reticular
Thin web-like fibers
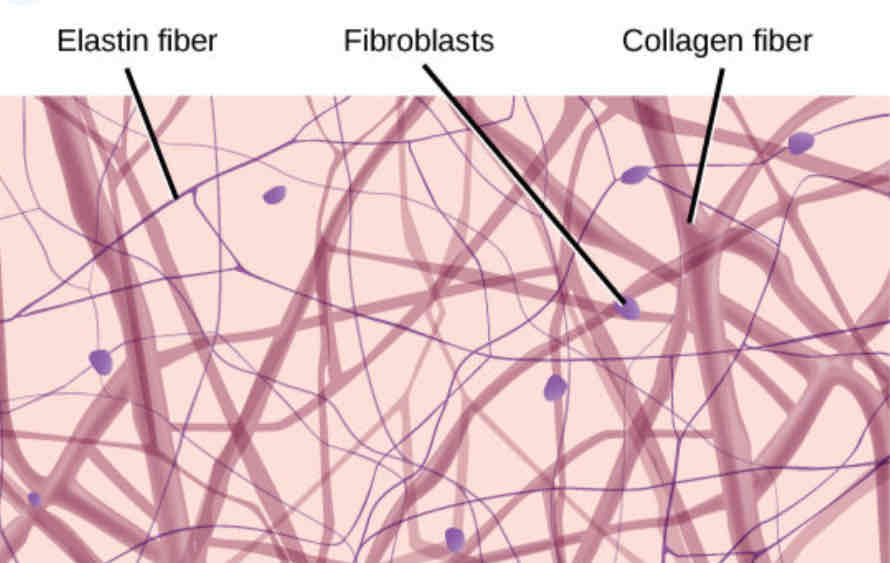
Types of Fibers: Elastic
Stretchy fibers, tree branch appearance
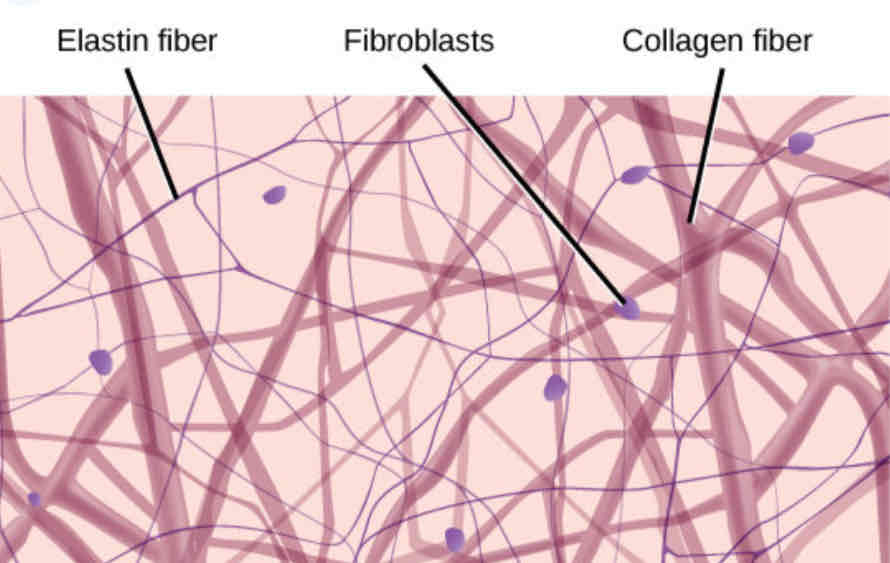
Ground Substance
An amorphous gelatinous material that fills the space between fibers and cells
Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Appearance
Striated cells, more than one nucleus, can be controlled voluntarily
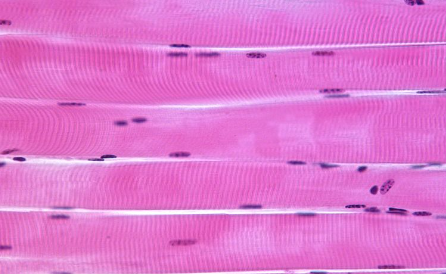
Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Function
To contract and produce movement
Muscle Tissue: Skeletal Location
Throughout the body, attached to bones via tendons
Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Appearance
Striated cells, one nucleus per cell, “branching”
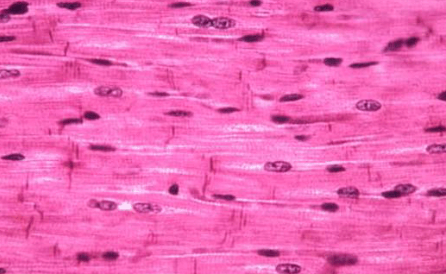
Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Function
Pump blood (involuntarily)
Muscle Tissue: Cardiac Location
Found ONLY in the heart
Muscle Tissue: Smooth Appearance
No visible striations, one nucleus per cell, “spindles”
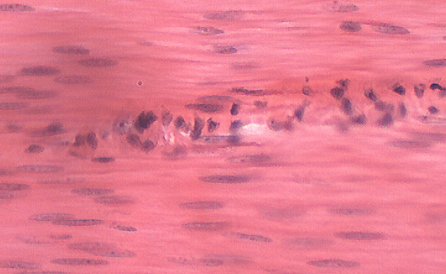
Muscle Tissue: Smooth Function
To maintain blood pressure and flow, controls wall movement and diameter of hollow organs
Muscle Tissue: Smooth Location
Inside/outside hollow organs, attached to other smooth muscle cells
Nervous Tissue: Appearance
Composed of neurons and nerve support cells
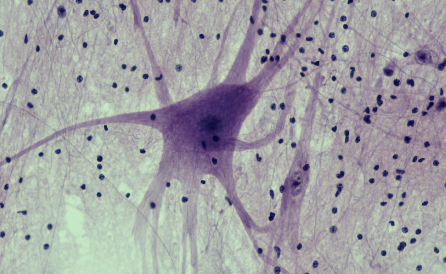
Nervous Tissue: Function
To send impulses to other areas of the body
Irritability - Ability of neurons to detect and respond to stimuli
Conductivity - Ability of neurons to transmit electrical impulses
Nervous Tissue: Location
Brain and spinal cord
Nervous Tissue: Support cells and what they do
Schwann cells, made of myelin sheets, insulate, support, and protect neurons