INTELLIGENCE, EMOTION, AND MOTIVATION
1/110
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
111 Terms
motivation
the process by which activities are started, directed, and continued so that physical or psychological needs or wants are met.

extrinsic motivation
type of motivation in which a person performs an action because it leads to an outcome that is separate from or external to the person.

intrinsic motivation
type of motivation in which a person performs an action because the act itself is rewarding or satisfying in some internal manner.
instincts
the biologically determined and innate patterns of behavior that exist in both people and animals.

instinct approach
approach to motivation that assumes people are governed by insticts similar to those of animals.

need
a requirement of some material (such as food or water) that is essential for survival of the organism

drive
a psychological tension and physical arousal arising when there is a need that motivates the organism to act in order to fulfill the need and reduce the tension

drive-reduction theory
approach to motivation that assumes behavior arises from physiological needs that cause internal drives to push the organism to satisfy the need and reduce tension and arousal

primary drives
those drives that involve needs of the body such as hunger and thirst
acquired (secondary) drives
those drives that are learned through experience or conditioning, such as the need for money or social approval

homeostasis
the tendency of the body to maintain a steady state
stimulus motive
a motive that appears to be unlearned but causes an increase in stimulation, such as curiosity

arousal theory
theory of motivation in which people are said to have an optimal (best or ideal) level of tension that they seek to maintain by increasing or decreasing stimulation

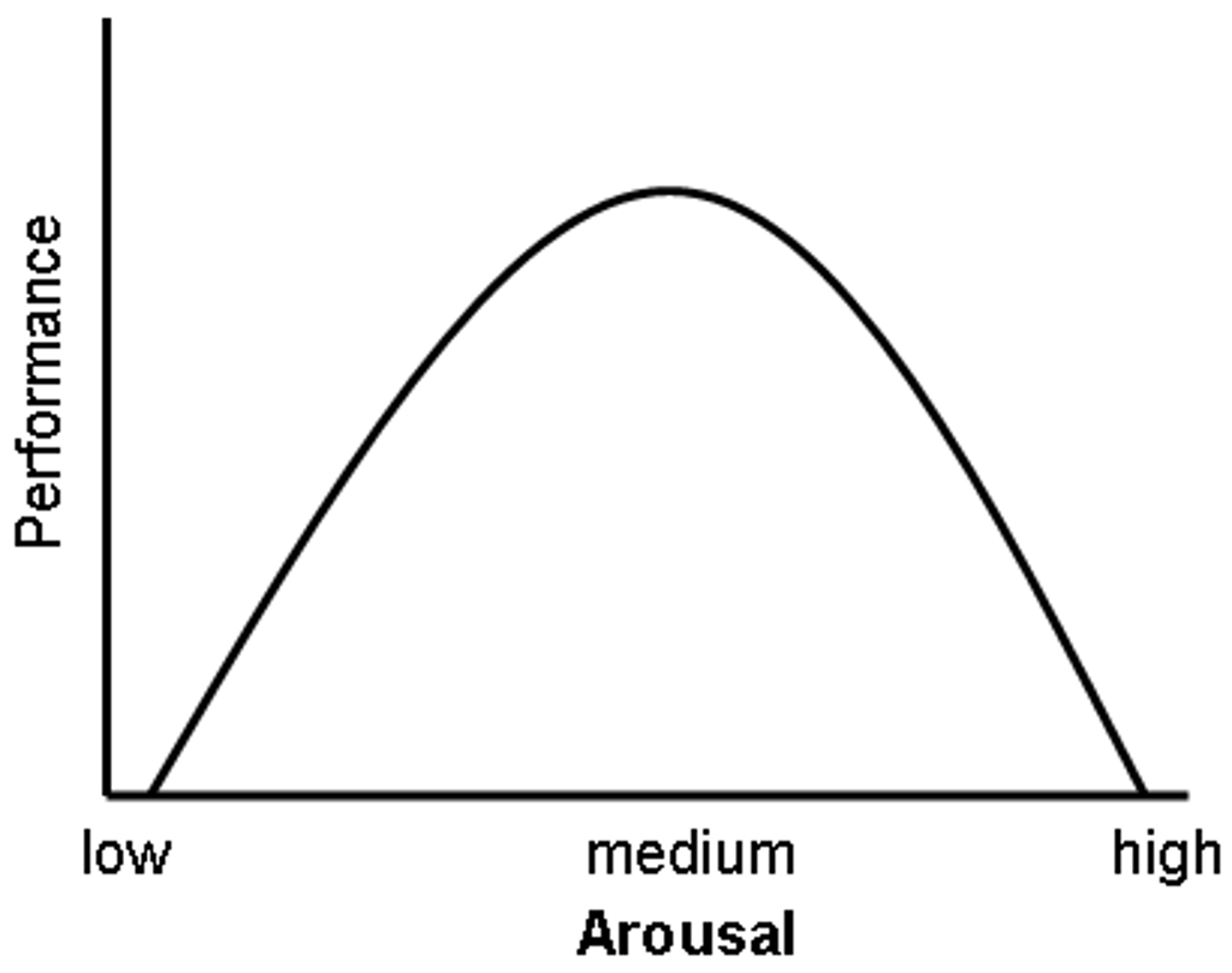
Yerkes-Dodson law
law stating performance is related to arousal; moderate levels or arousal lead to better performance than do levels of arousal that are too low or too high. This effect varies with the difficulty of the task: Easy tasks require a high-moderate level whereas more difficult tasks require a low-moderate level
incentives
things that attract or lure people into action

incentive approaches
theories of motivation in which behavior is explained as a response to the external stimulus and its rewarding properties
self-actualization
according to Maslow, the point that is seldom reached at which people have sufficiently satisfied the lower needs and achieved their full human potential
weight set point
the particular level of weight the body tries to maintain

basal metabolic rate (BMR)
the rate at which the body burns energy when the organism is resting

leptin
a hormone that, when released into the bloodstream, signals the hypothalamus that the body has had enough food and reduces the appetite while increasing the feeling of being full
anorexia nervosa
a condition in which a person reduces eating to the point that a weight loss of 15 percent below the ideal body weight or more occurs
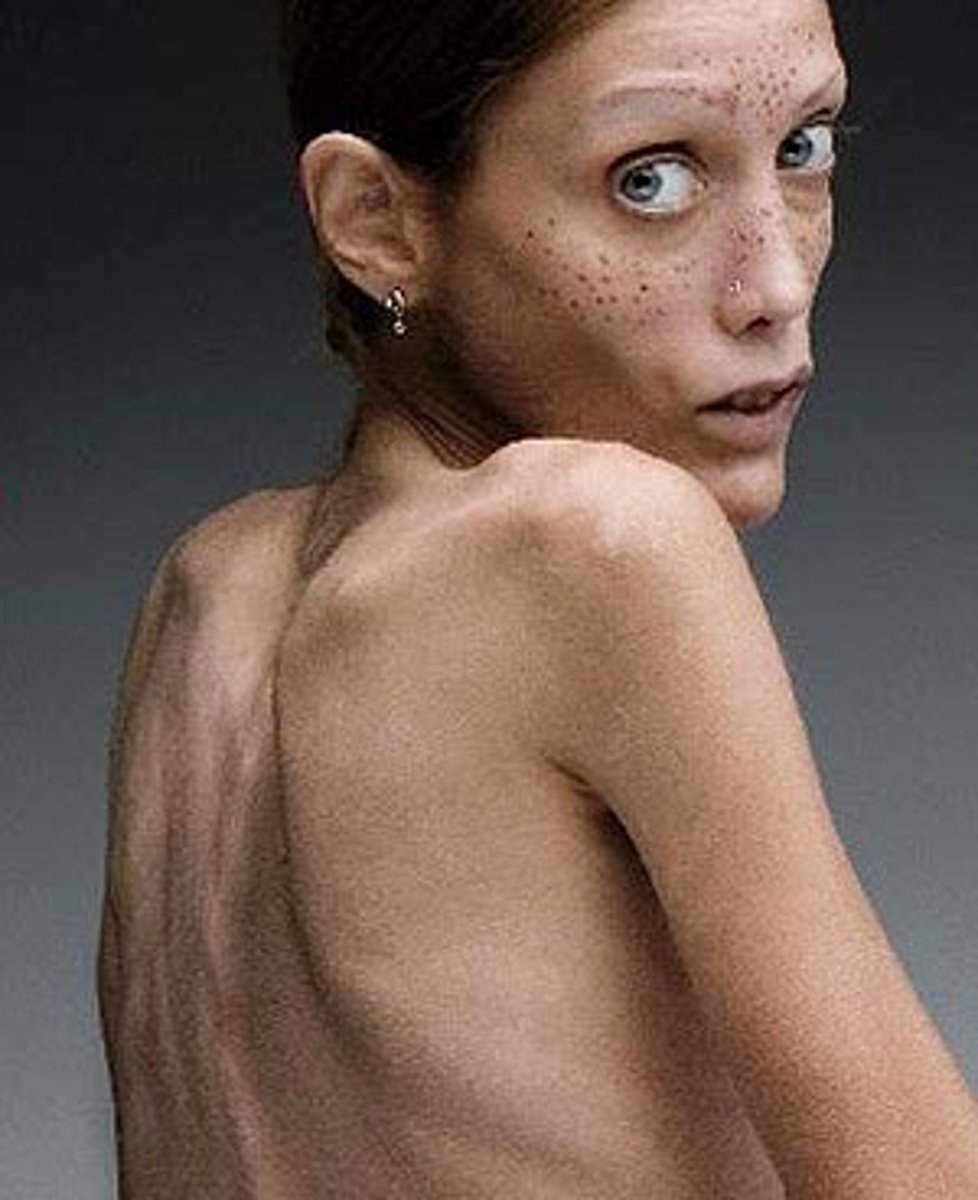
bulimia nervosa
a condition in which a person develops a cycle of "binging," or overeating enormous amounts of food at one sitting, and then using unhealthy methods to avoid weight gain

emotion
the "feeling" aspect of consciousness, characterized by a certain physical arousal, a certain behavior that reveals the emotion to the outside world, and an inner awareness of feelings

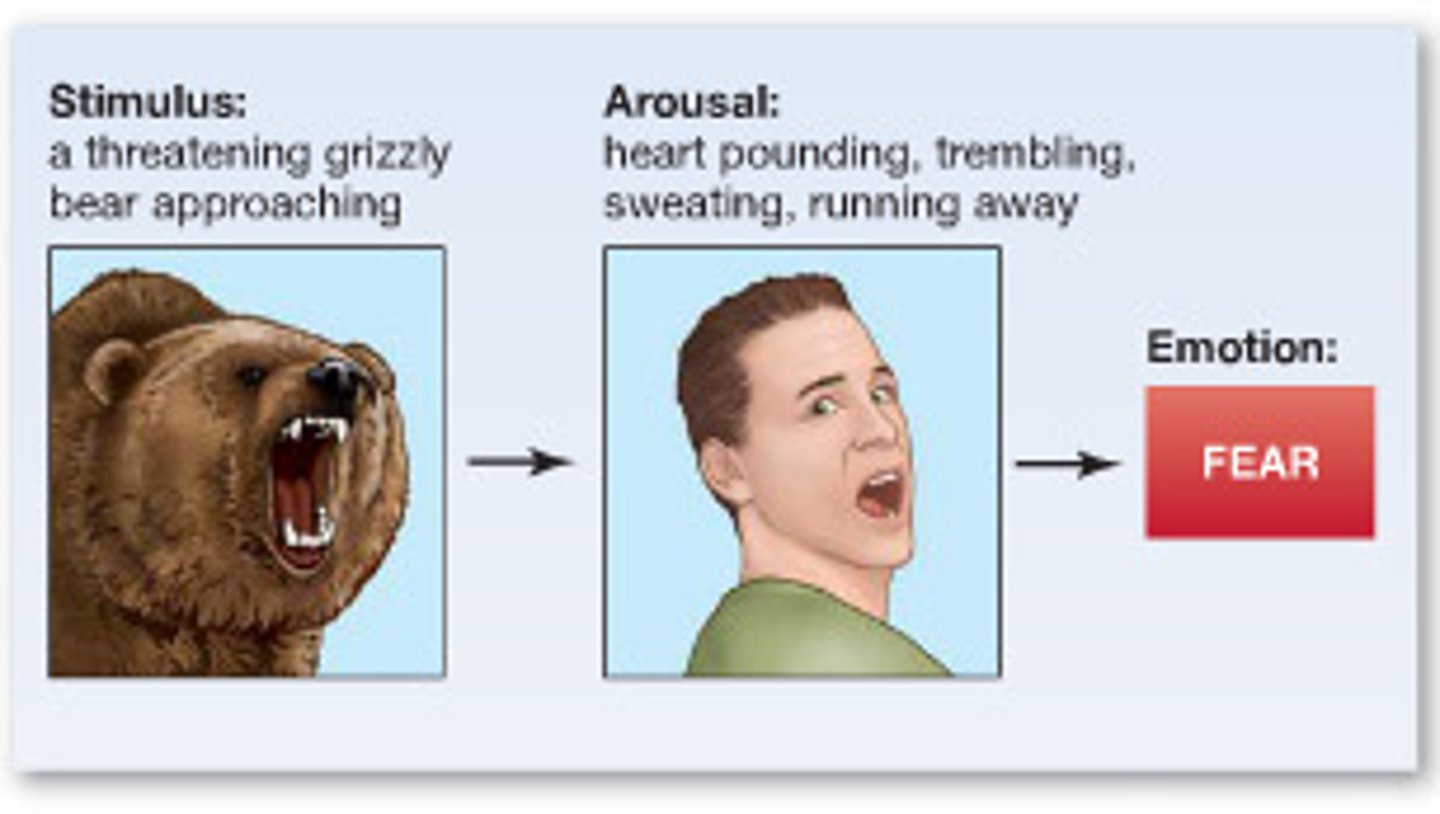
James-Lange theory of emotion
theory in which a physiological reaction leads to the labeling of an emotion. I am afraid because I am shaking
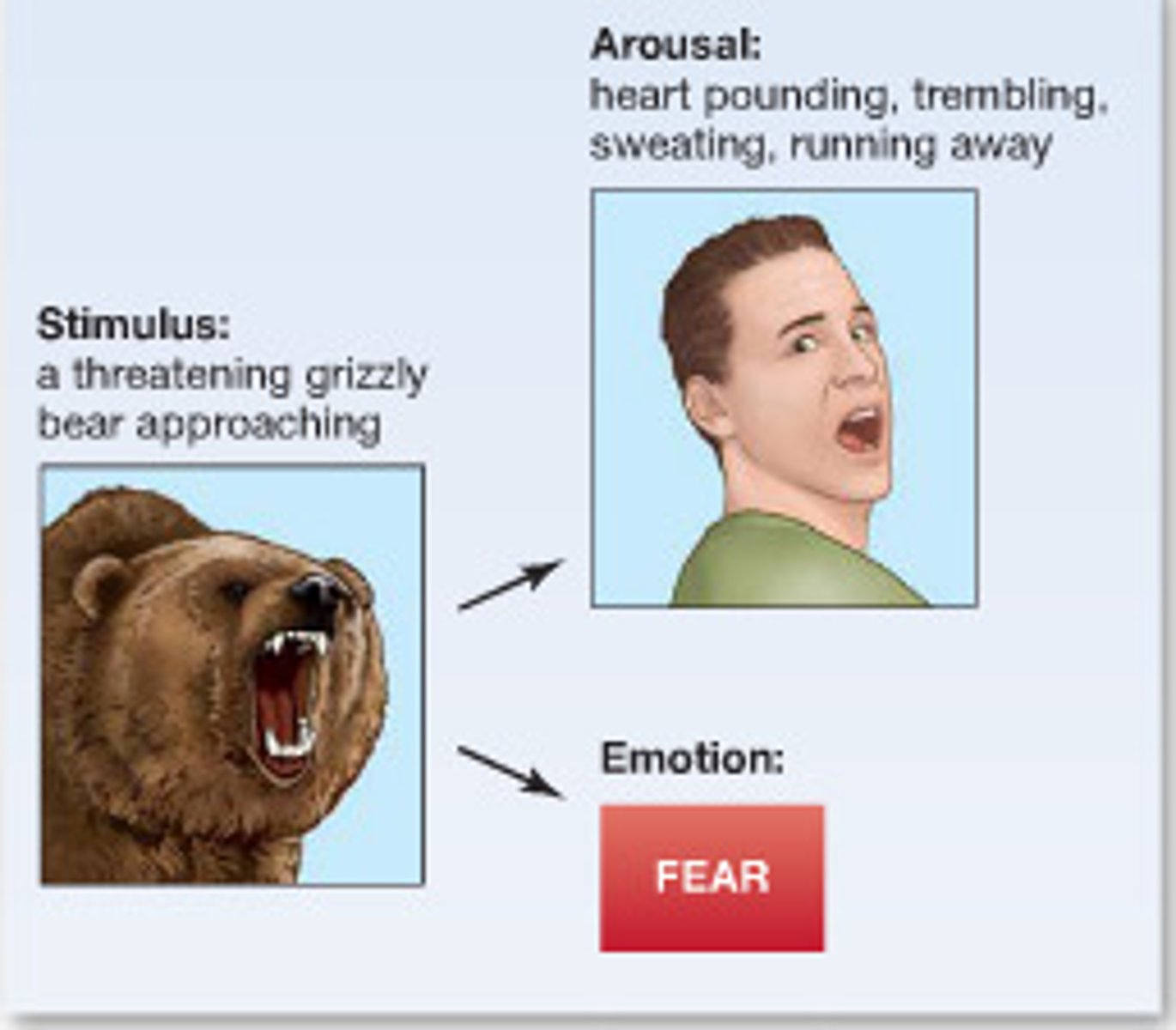
Cannon-Bard theory of emotion
theory in which the physiological reaction and the emotion are assumed to occur at the same time. I am shaking and afraid at the same time
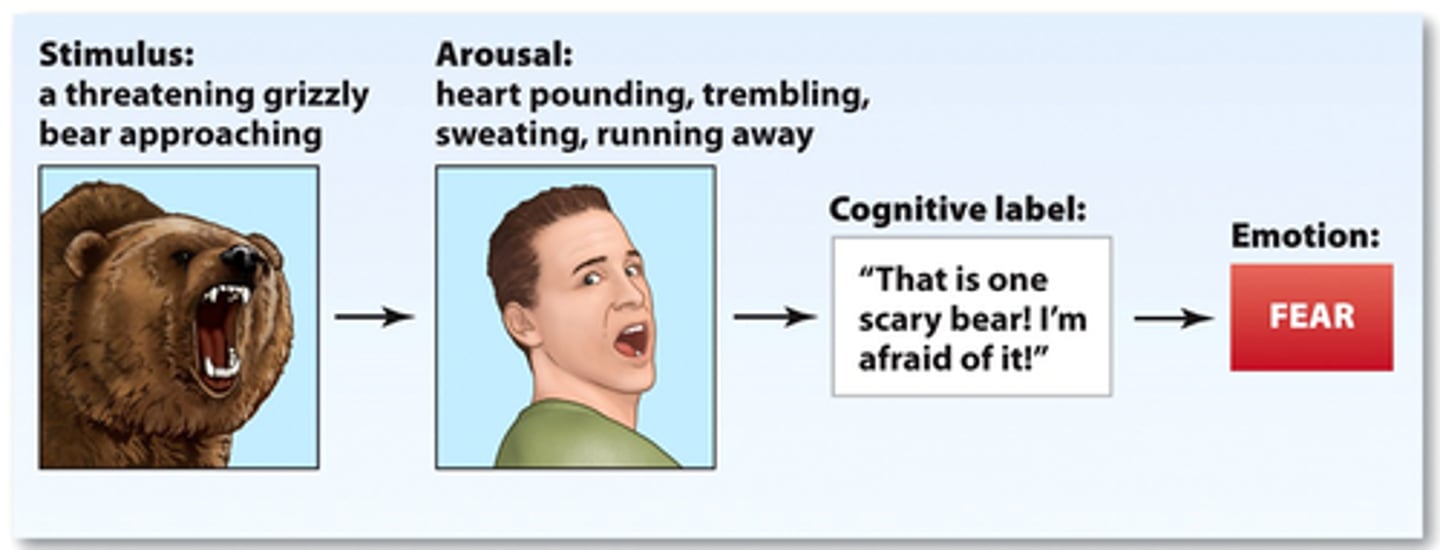
Schachter's cognitive arousal theory/
Singer and Schachter's Two Factor
theory of emotion in which both the physical arousal and the labeling of that arousal based on cues from the environment must occur before the emotion is experienced. That huge bear is dangerous and that makes me feel afraid
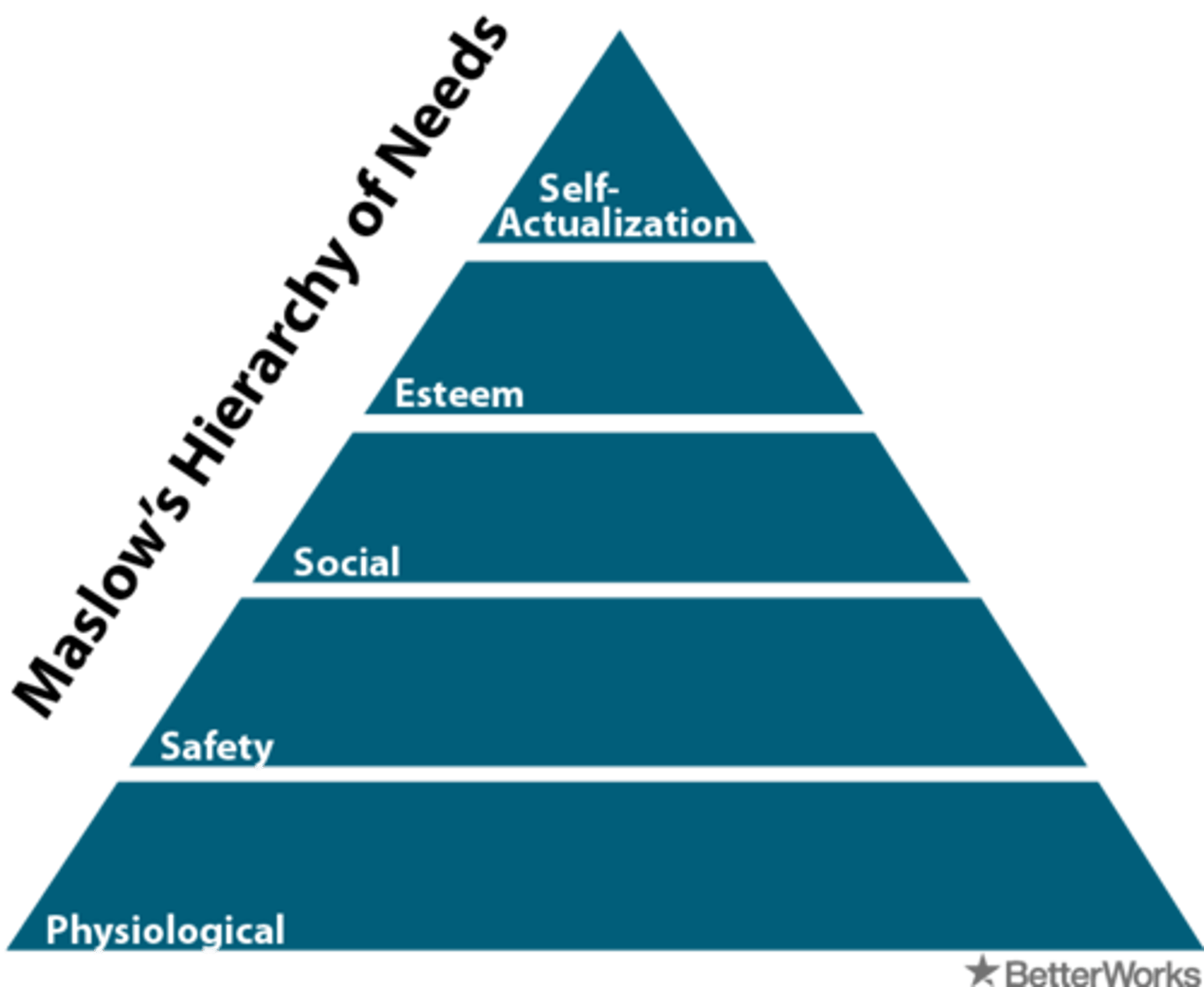
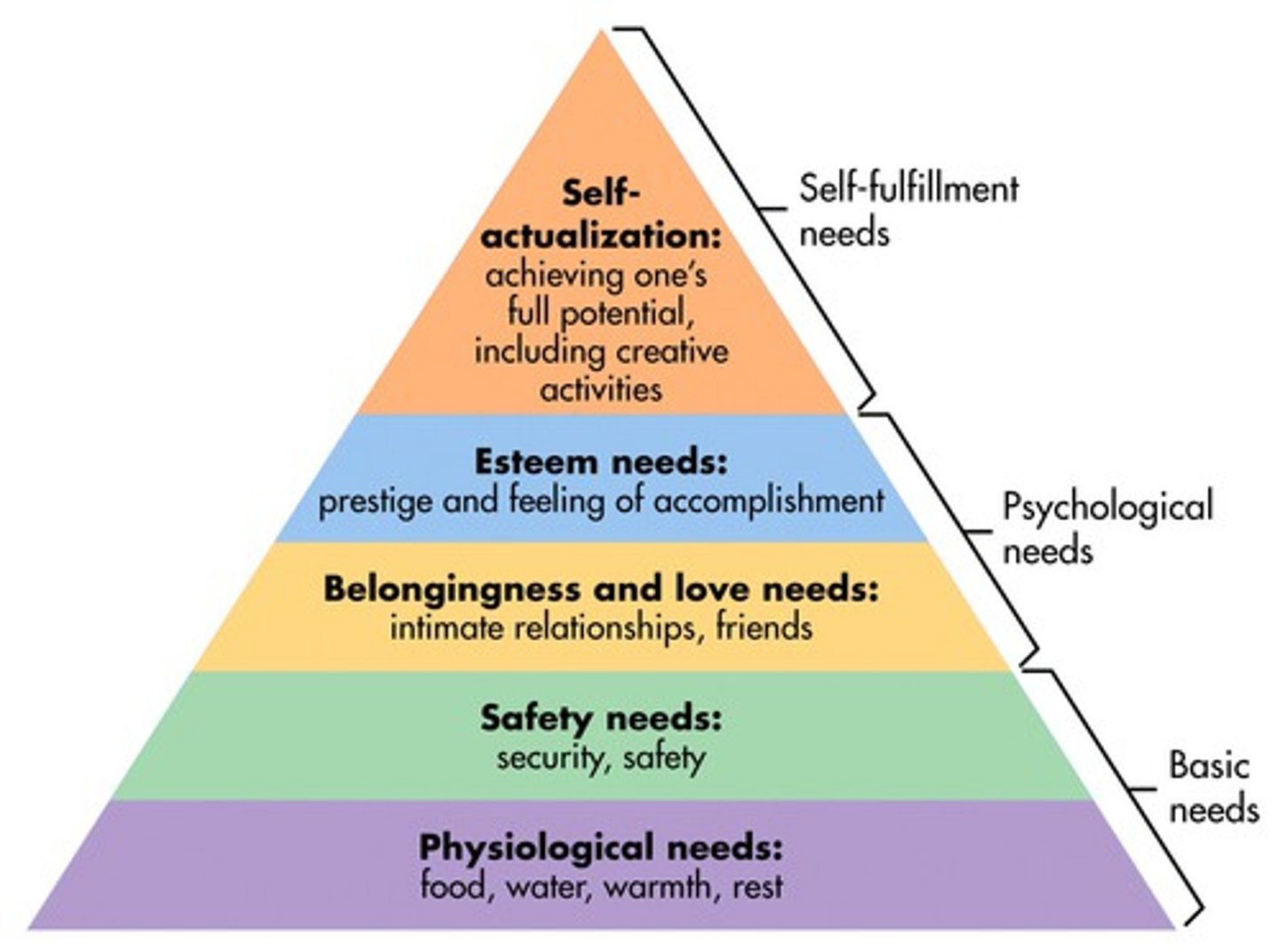
Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Humanist theory of motivation that says we must first fulfill lower level needs before achieving personal fulfillment and self actualization
Physiological-Safety-Belongingness and Love-Esteem-Cognitive-Self Actualization
ventromedial hypothalamus
stops the eating response; lets us know we are full
if damaged, we would continue to eat

lateral hypothamalus
initiates the eating response; lets us know we are hungry
if damaged, we would starve

Achievement motivation
a desire for significant accomplishment: for mastery of things, people, or ideas; for attaining a high standard
Adaptation-Level Phenomenon
our tendency to form judgments (of sounds, of lights, of income) relative to a neutral level defined by our prior experience
Aerobic exercise
Rhythmic, nonstop, moderate to vigorous activity that requires large amounts of oxygen
Behavioral medicine
an interdisciplinary field that integrates behavioral and medical knowledge and applies that knowledge to health and disease
Binge-eating disorder
significant binge-eating episodes, followed by distress, disgust, or guilt, but without the compensatory purging, fasting, or excessive exercise that marks bulimia nervosa
Biofeedback
a system for electronically recording, amplifying, and feeding back information regarding a subtle physiological state, such as blood pressure or muscle tension
Catharsis
Emotional release
Coping
alleviating stress using emotional, cognitive, or behavioral methods
Coronary heart disease
the clogging of the vessels that nourish the heart muscle; the leading cause of death in North America
Emotion-focused coping
attempting to alleviate stress by avoiding or ignoring a stressor and attending to emotional needs related to one's stress reaction
Estrogen
Female sex hormone
Feel-good, do-good phenomenon
The tendency to be helpful when in a good mood
Flow
a completely involved, focused state of consciousness, with diminished awareness of self and time, resulting from optimal engagement of one's skills
General adaptation syndrome (GAS)
A model of the body's response to chronic stress; the three phases are alarm (fight-or-flight response), resistance, and exhaustion.
Glucose
A simple sugar that is an important source of energy.
Health psychology
a subfield of psychology that provides psychology's contribution to behavioral medicine
Industrial-organization (I/O) psychology
the application of psychological concepts and methods to optimizing human behavior in workplaces
Organizational psychology
a subfield of I/O psychology that examines organizational influences on worker satisfaction and productivity and facilitates organizational change
Personnel psychology
a subfield of I/O psychology that focuses on employee recruitment, selection, placement, training, appraisal, and development
Polygraph
a machine, commonly used in attempts to detect lies, that measures several of the physiological responses accompanying emotion
Problem-focused coping
Attempting to alleviate stress directly by changing the stressor or the way we interact with that stressor.
Psychoneuroimmunology (PNI)
the study of how psychological, neural, and endocrine processes together affect the immune system and resulting health
Psychophysiological illness
literally, "mind-body" illness; any stress-related physical illness, such as hypertension and some headaches
Refractory period
a resting period after orgasm, during which a man cannot achieve another orgasm
Relative deprivation
the perception that one is worse off relative to those with whom one compares oneself
Sexual disorder
a problem that consistently impairs sexual arousal or functioning
Sexual orientation
an enduring sexual attraction toward members of either one's own sex (homosexual orientation) or the other sex (heterosexual orientation)
Sexual response cycle
the four stages of sexual responding described by Masters and Johnson - excitement, plateau, orgasm, and resolution
Social leadership
group-oriented leadership that builds teamwork, mediates conflict, and offers support
Stress
A nonspecific, emotional response to real or imagined challenges or threats; a result of a cognitive appraisal by the individual
Structured interviews
interview process that asks the same job-relevant questions of all applicants, each of whom is rated on established scales
Subjective well-being
self-perceived happiness or satisfaction with life. Used along with measures of objective well-being (for example, physical and economic indicators) to evaluate people's quality of life.
Task leadership
goal-oriented leadership that sets standards, organizes work, and focuses attention on goals
Testosterone
Male sex hormone
Type A
competitive, hard-driving, impatient, verbally aggressive, and anger-prone people
Type B
easygoing, relaxed people
PYY
secreted by small intestine after meal, suppresses appetite
Ghrelin
A hunger-arousing hormone secreted by an empty stomach
Orexin
hunger-triggering hormone secreted by hypothalamus
Obstatin
Secreted by stomach; sends out "I'm full" signals to the brain.
parental investment theory
a theory that stresses the evolutionary basis of many aspects of parental behavior, including the extensive devotion parents have in their offspring
unit bias
when the portion size is larger, people will eat more
Garcia effect
taste aversion, when nausea and a food are paired, the food will be averted in the future
neophobia
dislike of things unfamiliar
Theory X managers
assume that employees are basically lazy and extrinsically motivated.
Theory Y managers
Managers who assume that engaging in effortful behavior is natural to human beings; they recognize that people seek out responsibility and that motivation can come from allowing employees to suggest creative and meaningful solutions.
approach-approach conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two attractive alternatives
approach-avoidance conflict
conflict occurring when a person must choose or not choose a goal that has both positive and negative aspects
avoidance-avoidance conflict
Conflict that results from having to choose between two distasteful alternatives
Opponent Process Theory of Emotion
following a strong emotion, an opposing emotion counters the first emotion, lessening the experience of that emotion; on repeated occasions, the opposing emotion becomes stronger
cogntive appraisal theory
In the absence of physiological arousal, we decide what to feel after interpreting or explaining what has just happened. Two things are important in this: whether we interpret the event as good or bad for us, and what we believe is the cause of the event.
facial feedback hypothesis
emotional expressions can cause the emotional experiences they signify
Microexpressions
small, brief facial movements that signal emotional experiences, even in people who have been trained to hide their emotions
intelligence
mental quality consisting of the ability to learn from experience, solve problems, and use knowledge to adapt to new situations
factor analysis
a statistical procedure that identifies clusters of related items (called factors) on a test; used to identify different dimensions of performance that underlie one's total score
general intelligence (g)
a general intelligence factor that according to Spearman and others underlies specific mental abilities and is therefore measured by every task on an intelligence test
savant syndrome
a condition in which a person otherwise limited in mental ability has an exceptional specific skill, such as in computation or drawing
analytical (academic problem-solving) intelligence
according to Sternberg, a type of intelligence that is assessed by intelligence tests, which present well-defined problems having a single right answer
creative intelligence
according to Sternberg, a type of intelligence that is demonstrated in reacting adaptively to novel situations and generating novel ideas
practical intelligence
according to Sternberg, a type of intelligence that is often required for everyday tasks, which are frequently ill-defined, with multiple solutions
Spearman's general intelligence (g)
intelligence theory that a basic intelligence predicts our abilities in varied academic subjects
Thurstone's primary mental abilities
intelligence theory that our intelligence may be broken down into 7 factors: word fluency, verbal comprehension, spatial ability, perceptual speed, numerical ability, inductive reasoning, and memory
Gardner's multiple intelligences
intelligence theory that our abilities are best classified into 8 independent intelligences, which include a broad range of skills beyond traditional school smarts
Sternberg's triarchic
intelligence theory that our intelligence is best classified into 3 areas that predict our real-world success: analytical, creative, and practical
emotional intelligence
the ability to perceive, understand, manage, and use emotions
intelligence test
a method of assessing an individual's mental aptitudes and comparing them with those of others, using numerical scores
mental age
a measure of intelligence test performance devised by Binet; the chronological age that most typically corresponds to a given level of performance
Stanford-Binet
the widely used American revision of Binet's original intelligence test
intelligence quotient (IQ)
defined originally as the ratio of mental age (ma) to chronological age (ca) multiplied by 100; on contemporary intelligence tests, the average performance for a given age is assigned a score of 100
aptitude test
a test designed to predict a person's future performance
achievement test
a test designed to assess what a person has learned