Electronic Principles, DC Current and AC Current (2a)
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
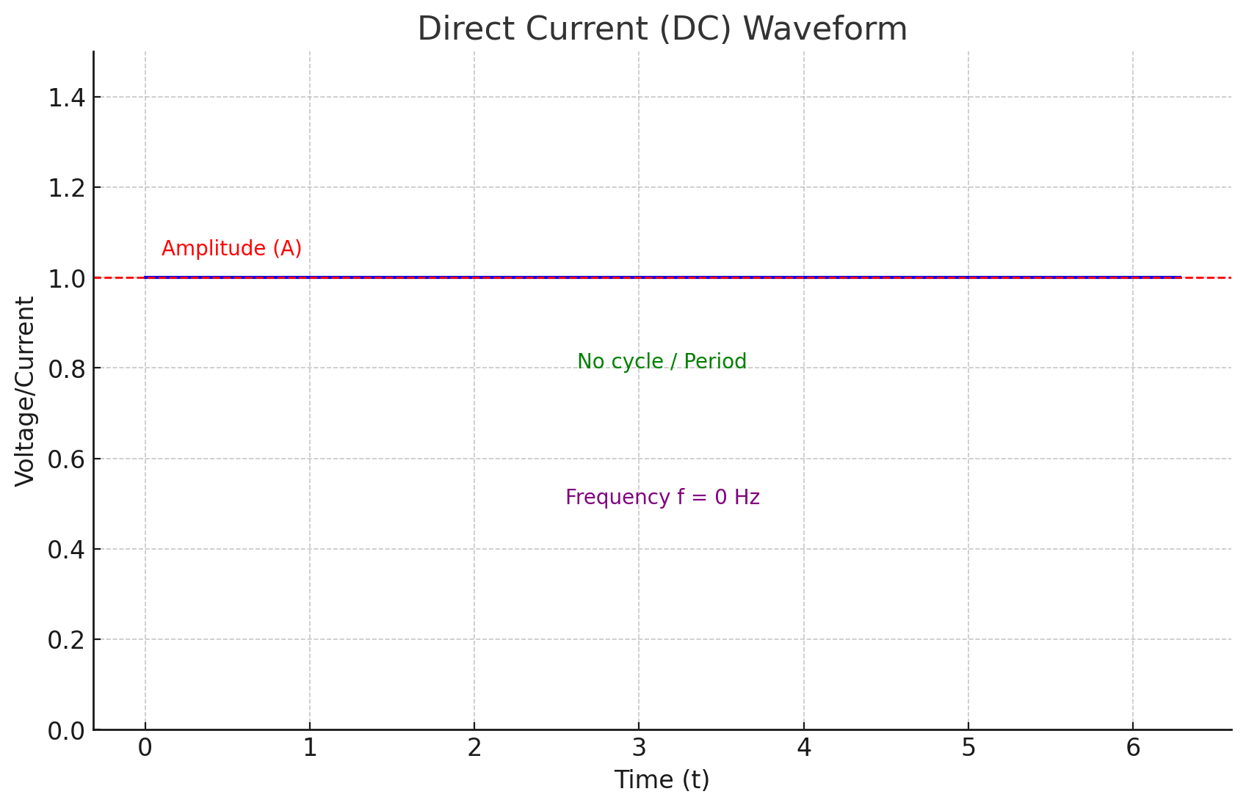
Direct Current
is a current that travels in one direction only. It is the unidirectional flow of charge.
•The electrons move steadily in one direction.
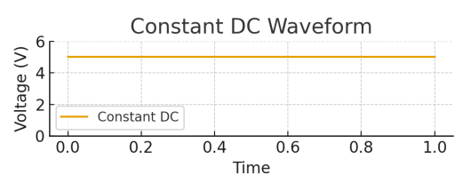
what is Pure or Constant DC
•Voltage remains constant over time.
•Represented by a flat horizontal line on a time-voltage graph
•Example – Ideal battery output.
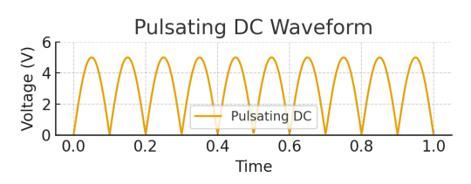
Pulsating DC
•Still flows in one direction but fluctuates in magnitude.
•Fluctuating.
Example – output of a rectifier before filtering
Alternating Current
fluctuates back and forth, periodically.
has electron flow in both directions, alternating between forward and backward. It also has changes in polarity.
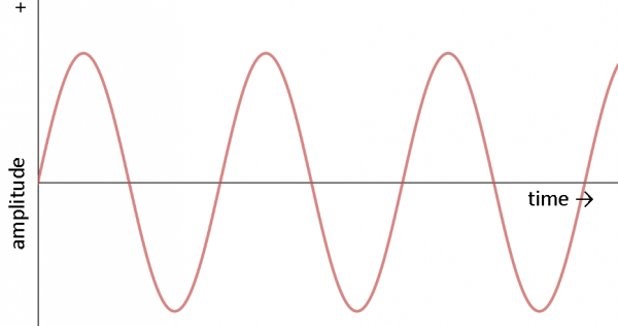
Waveforms
A steady DC produces a constant voltage between two points without any additional resistance.
Amplitude
is the measurement of the distance of any point of the wave that is above or below the centre of the mean line.
The peak amplitude
is the point if the wave that is farthest from the mean line ; it can be positive (above the mean line) or negative (below the mean line).
The cycle
of a wave is one complete evolution of its shape.
The period
is the amount of time it takes to complete one cycle . The symbol for period is T and its measurement is done in seconds (s) or milliseconds (ms).
The frequency is the number of…
complete cycles in a given amount of time. The symbol for frequency is f. Frequency is measured in Hertz (Hz); it is named after the German physicist Heinrich Hertz.
Sine Wave
(also called a sinusoidal wave) is the shape that results from plotting the mathematical equation y = sin(x).
is the shape that occurs most often in ocean waves, sound waves, and light waves.
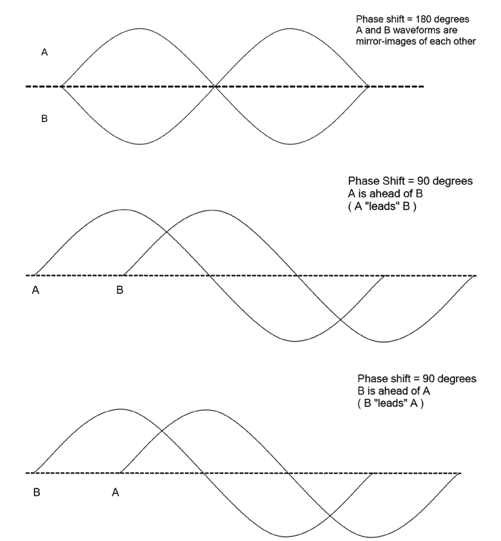
Phase
the relationship between two waves. Two overlapping waveforms
AC is constantly fluctuating, so how do we determine the voltage?
•One measure is the peak positive voltage when the positive charged voltage is at its highest point above the mean line.
•Another measure is the peak negative voltage, when the voltage is at the lowest point below the mean line.
•This is an important measure because you will want to ensure that any circuits you design can tolerate the peak voltages.
What does peak voltage (VP or VPK) represent in AC circuits?
Peak voltage is the maximum voltage reached at the top or bottom of an AC wave. It is shown with subscripts P or PK (e.g., 200VP or 200VPK). Circuits needing a steady flow use a different measurement than peak voltage.
What happens when two waveforms are out of phase, and how are they described?
When two waveforms are out of phase, the phase difference at any point can be measured. The first wave is the leading wave, and the second is the lagging wave. The phase shift is measured along the time axis.
What happens when two waveforms of the same frequency and voltage have a 180° phase shift?
They cancel each other out because their voltages are opposite at every point in the waveform, except at the center (mean) line where they meet. This is called destructive interference.
How do you find the average voltage of an AC waveform?
you average all points along the wave, the result is always zero, because there are an equal number of points above and below the mean line.
How can you find the average voltage of just half a sine wave cycle?
You can use calculus, or for a sine wave, multiply the peak voltage (VP) by 0.636. This gives the average value: VP × 0.636.
What gives a more workable measurement of AC voltage?
The root-mean-square (RMS) voltage, also called effective voltage, represents a usable measure of AC voltage for practical applications
How do you calculate the RMS voltage for a sine wave?
Multiply the peak voltage (VP) by 0.707: VRMS = VP × 0.707. This gives the DC equivalent of the AC voltage.