Rivers - AQA GCSE Geography
1/45
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
46 Terms
Hydraulic action
The force of the water hitting the river bed and banks. This is most effective when the water is moving fast and when there is a lot of it.
Abrasion
When the load carried by the river repeatedly hits the bed or banks dislodging particles into the flow of the river.
Attrition
When stones carried by the river knock against each other, gradually making the stones smaller and more rounded.
Solution
When the river flows over limestone or chalk, the rock is slowly dissolved. This is because it is soluble in mildly acidic river water.
Mouth
The place where the river ends, usually where the river joins the sea.

Source
The place where a river starts, usually in an area of highland.

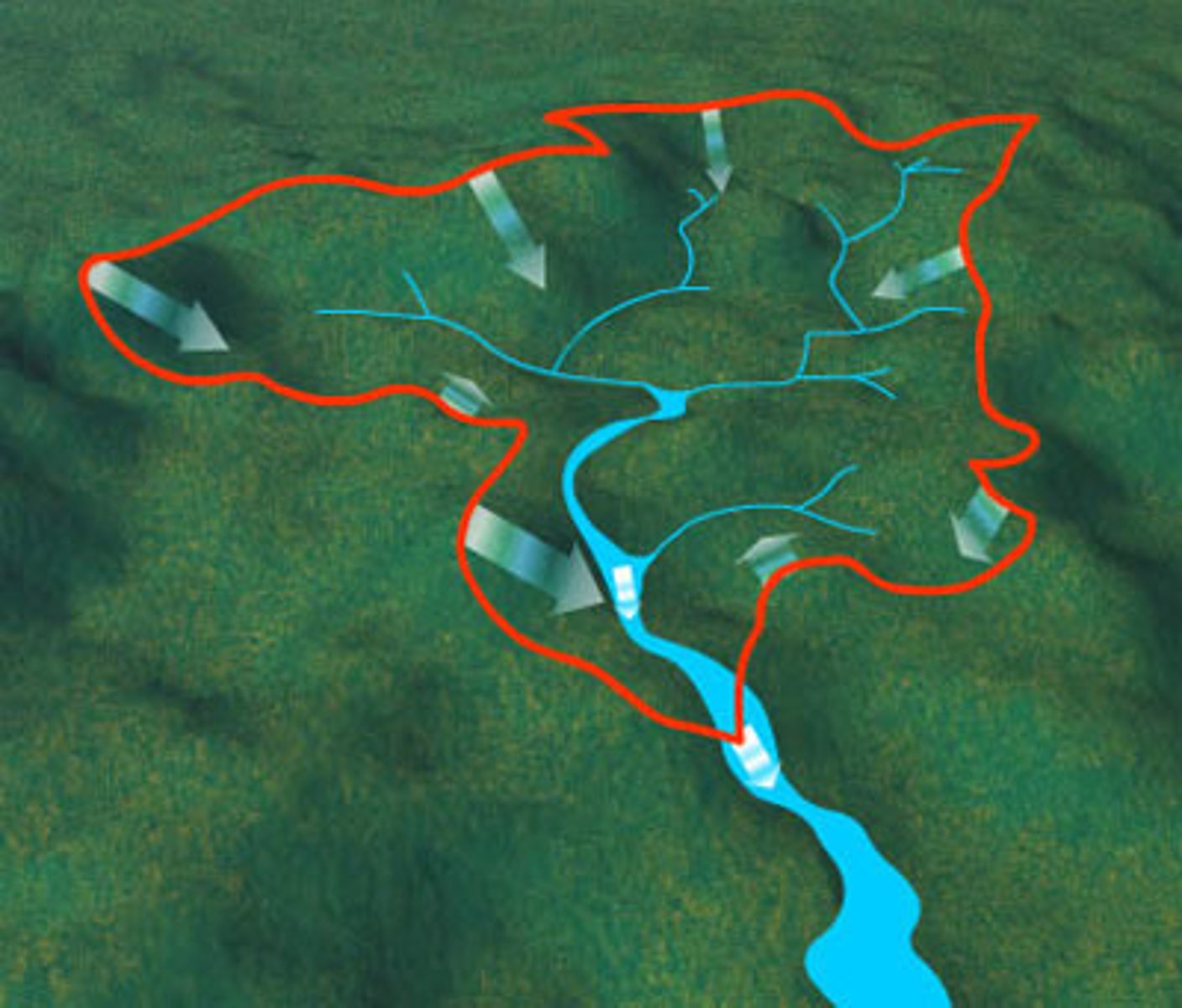
Watershed
The edge of a river basin.

Tributary
A small stream which joins a larger river.

Confluence
The point at which 2 rivers meet/ where a tributary joins a larger river.

Catchment
The area where water drains into a drainage basin.

Drainage basin
the area of land drained by a river and its tributaries
Condensation
When a gas cools and turns into a liquid. This forms clouds at high altitudes.

Transpiration
When plants release water vapour from their bodies.

Precipitation
The fancy word for rain, sleet, snow, hail etc

Evaporation
When a liquid turns to a gas and rises.

The Hydrological (Water) Cycle
This cycle shows how water moves between the land, seas and atmosphere via precipitation, evaporation etc

Upper course
This is the name given to the start of a river's journey, here it is small, youthful and full of energy.
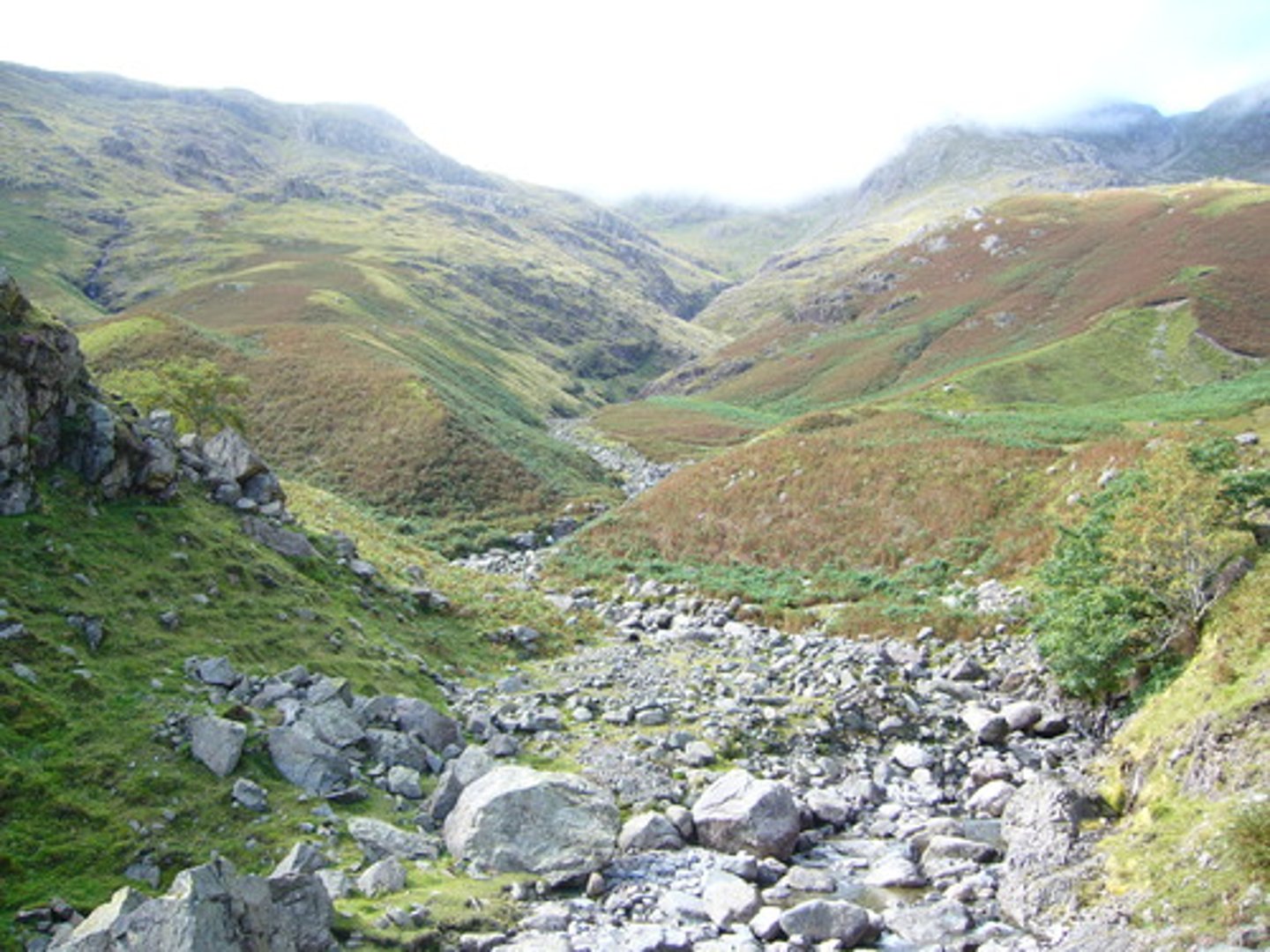

V-Shaped valleys
These are formed in the upper course of a river due to vertical erosion.
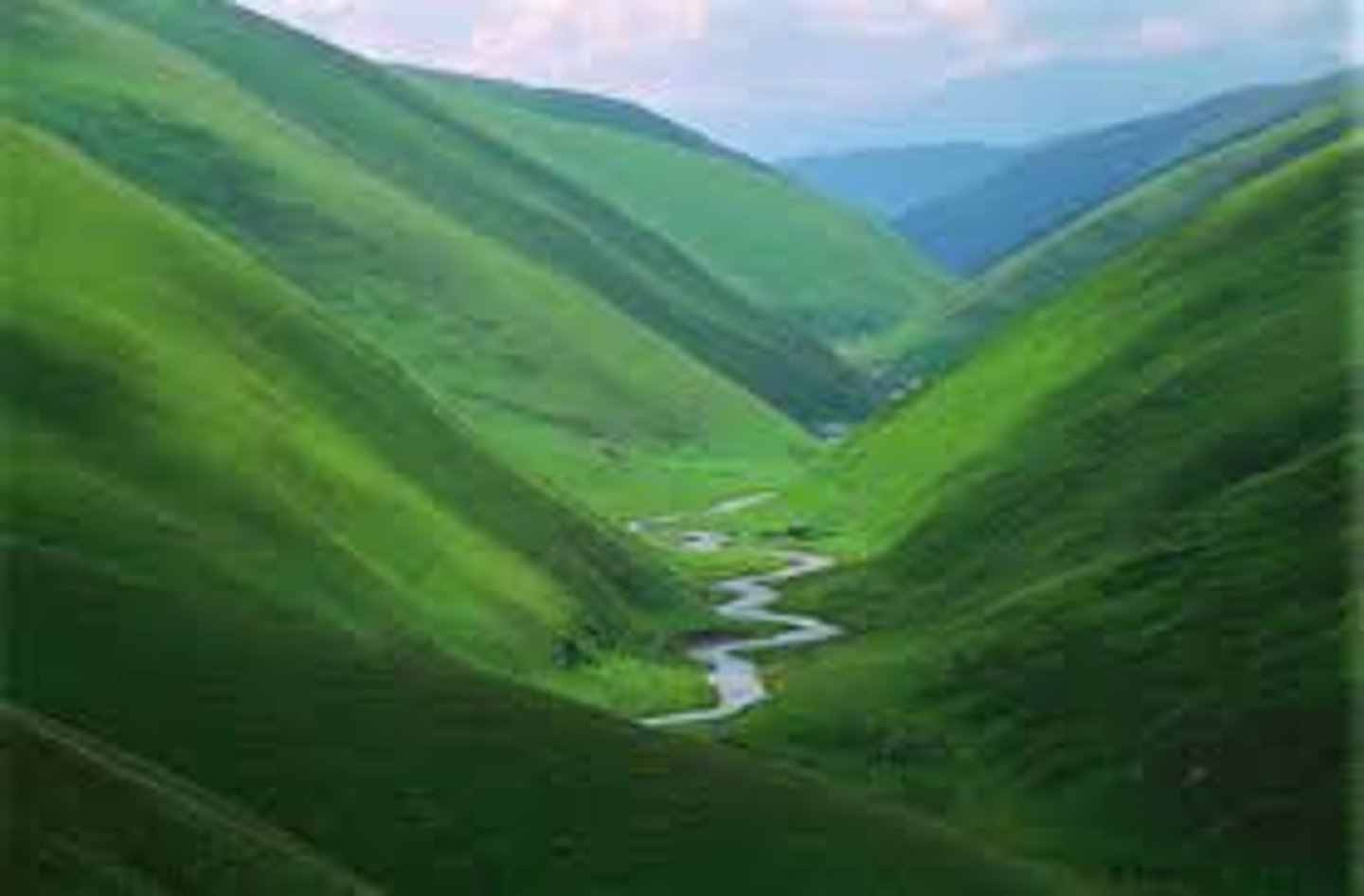

Interlocking spurs
These are formed in the upper course of the river as it flows downhill and winds its way between harder and softer rock.

Waterfalls
These are formed in the upper course of a river when it flows over hard and soft rock. The soft rock is cut back more quickly than the hard rock and a plunge pool is formed. This creates overhangs which collapse due to gravity.
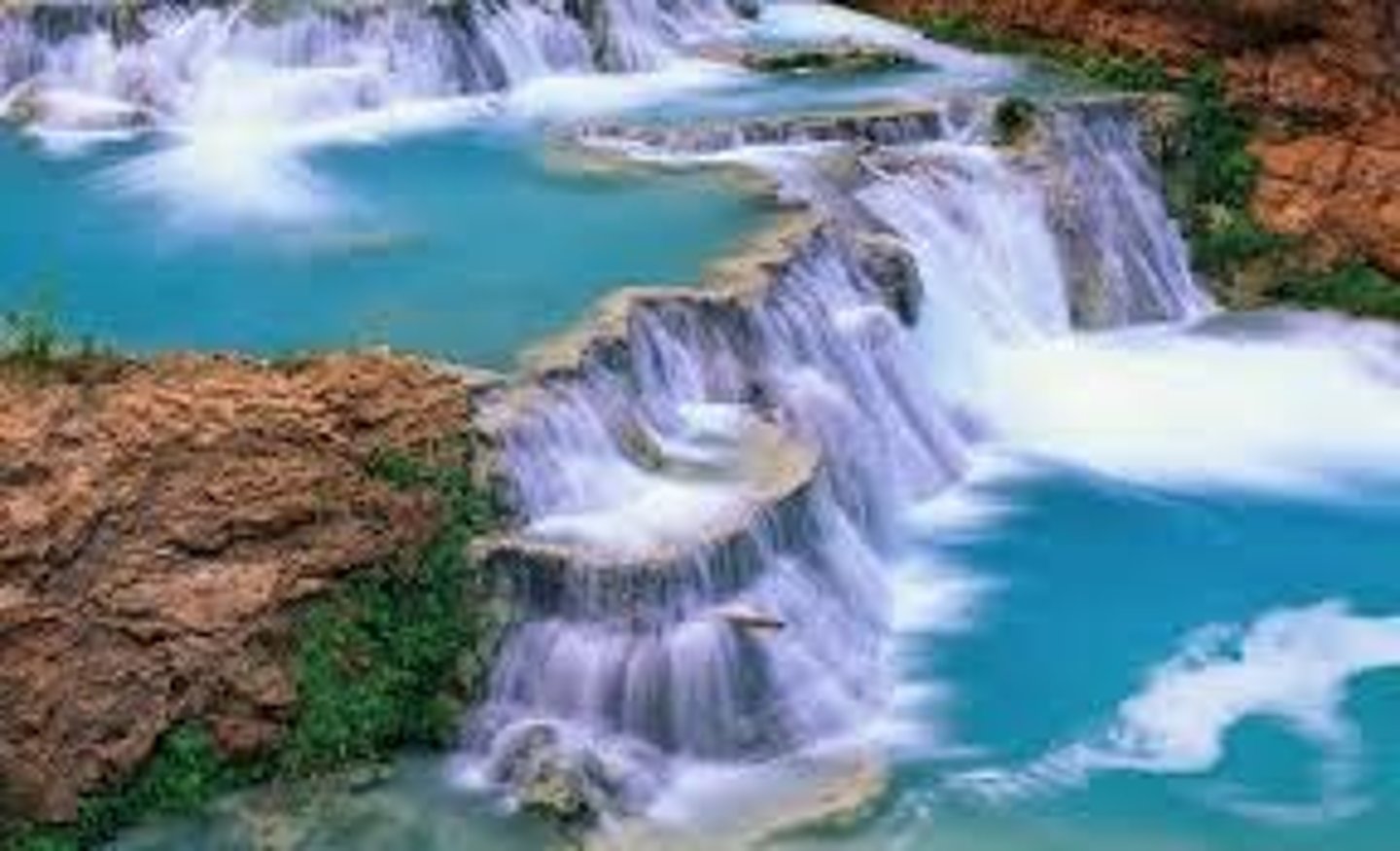

Plunge pool
This is a feature formed at the bottom of a waterfall, it is created by the force of the water hitting the riverbed. It is deepened by corrasion between the boulders.
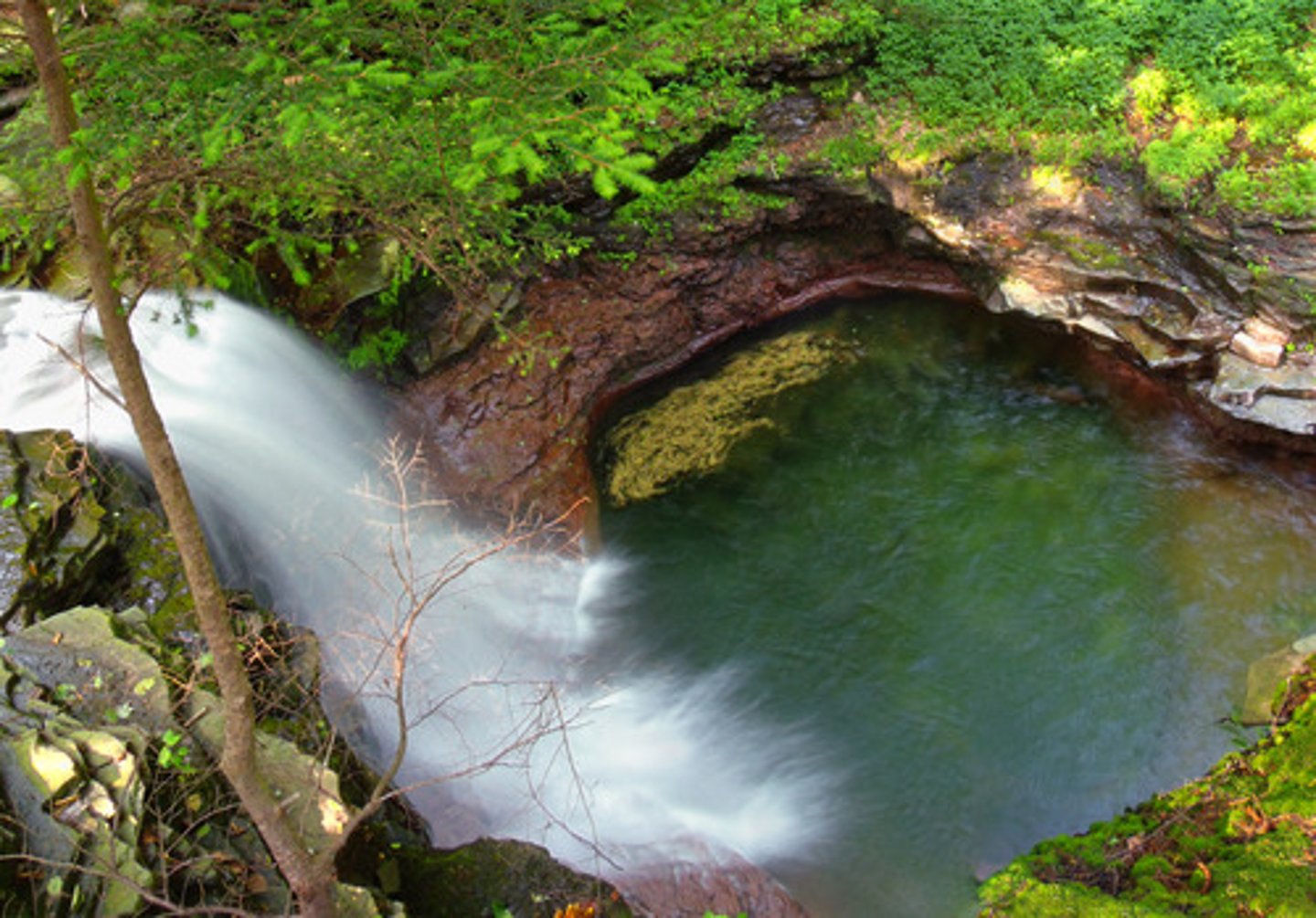

Steep-sided gorge
This is a feature left behind when a waterfall retreats upstream.
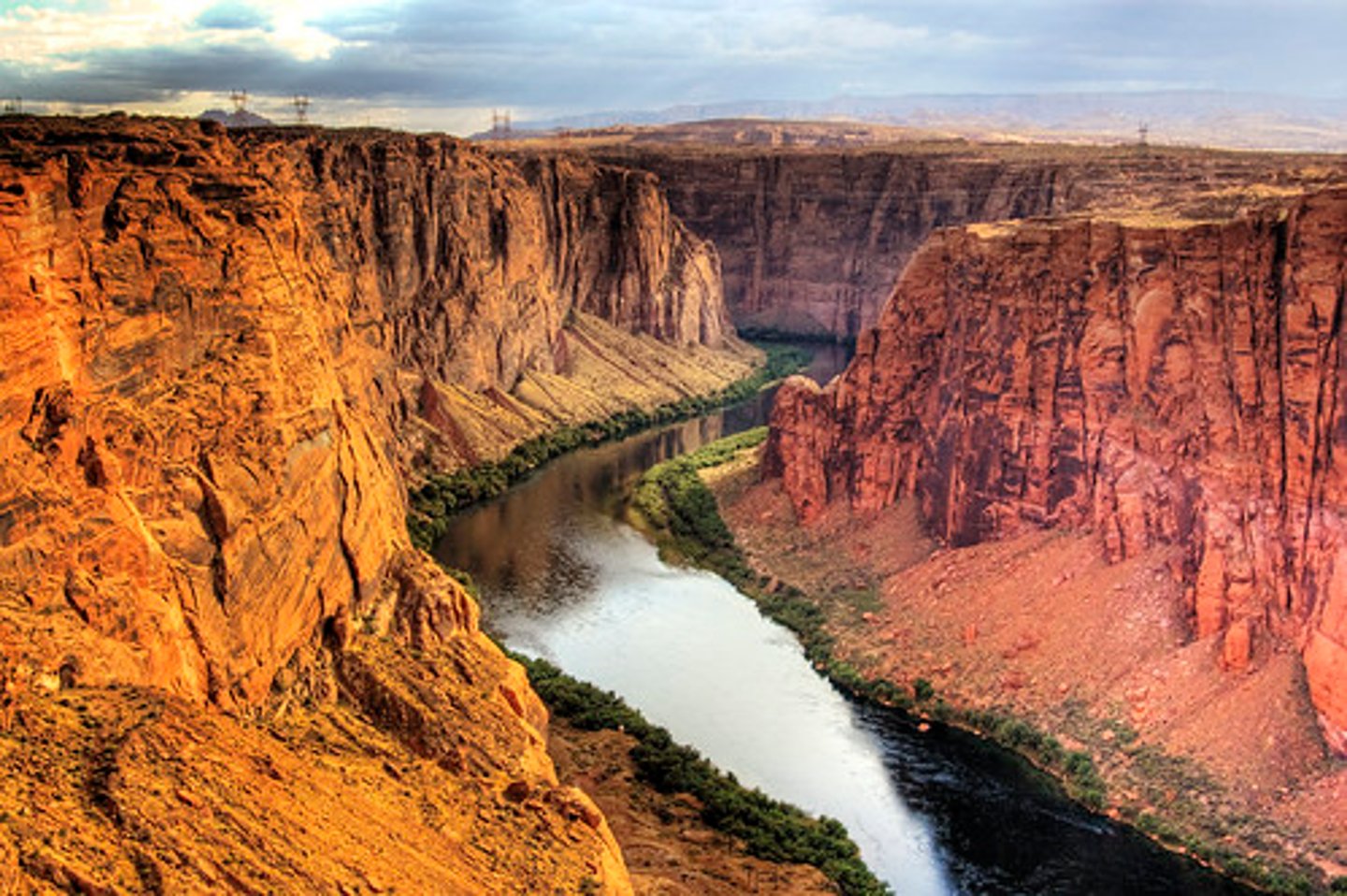

Vertical erosion
This is the type of erosion that occurs mostly in the upper course of a river, after it has used most of its energy to overcome the force of friction.

Lateral erosion
This is the type of erosion that occurs mainly in the lower course of a river, it is erosion in a sideways direction.

Middle course
This is the middle section of the river's journey.
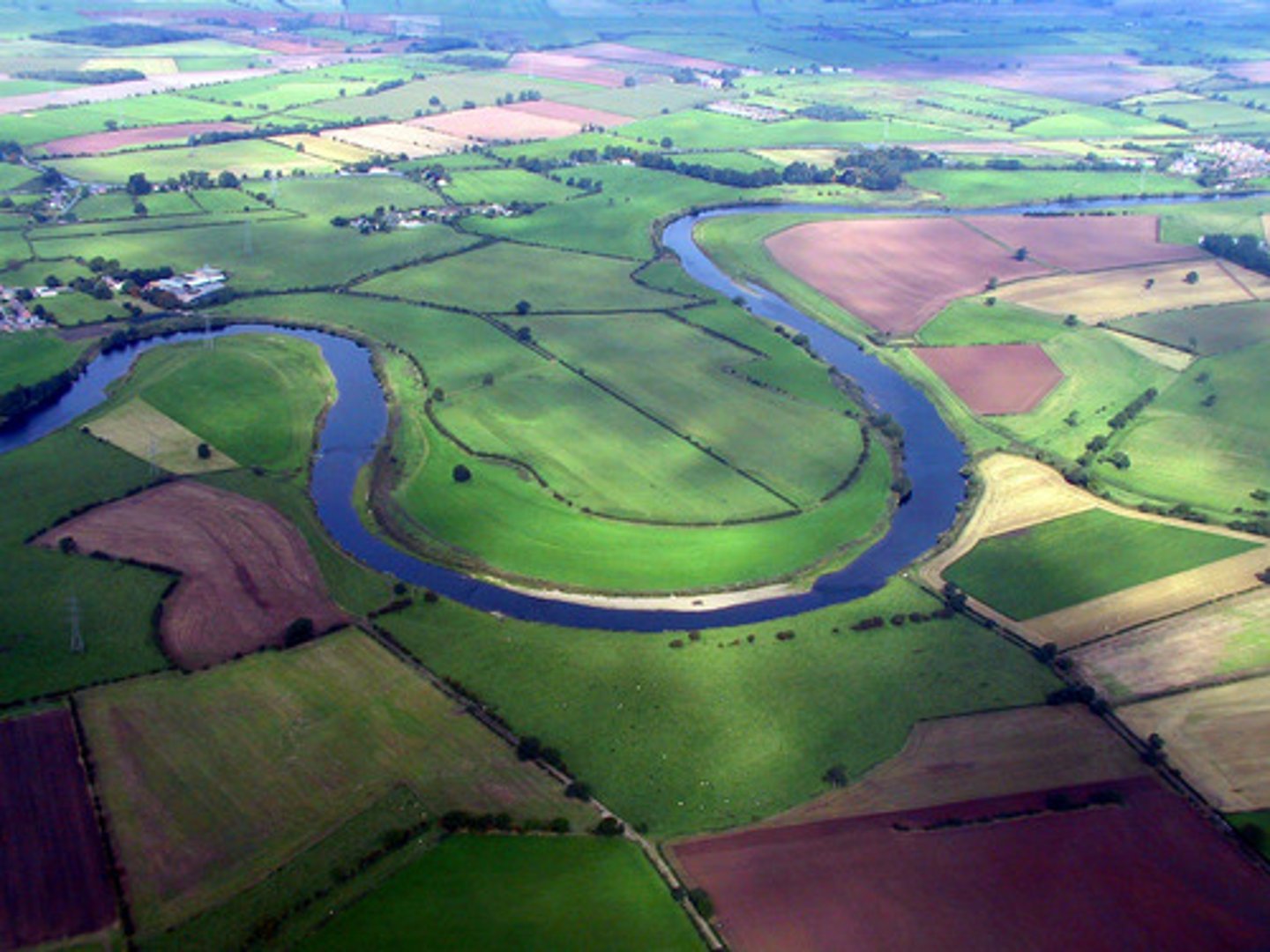

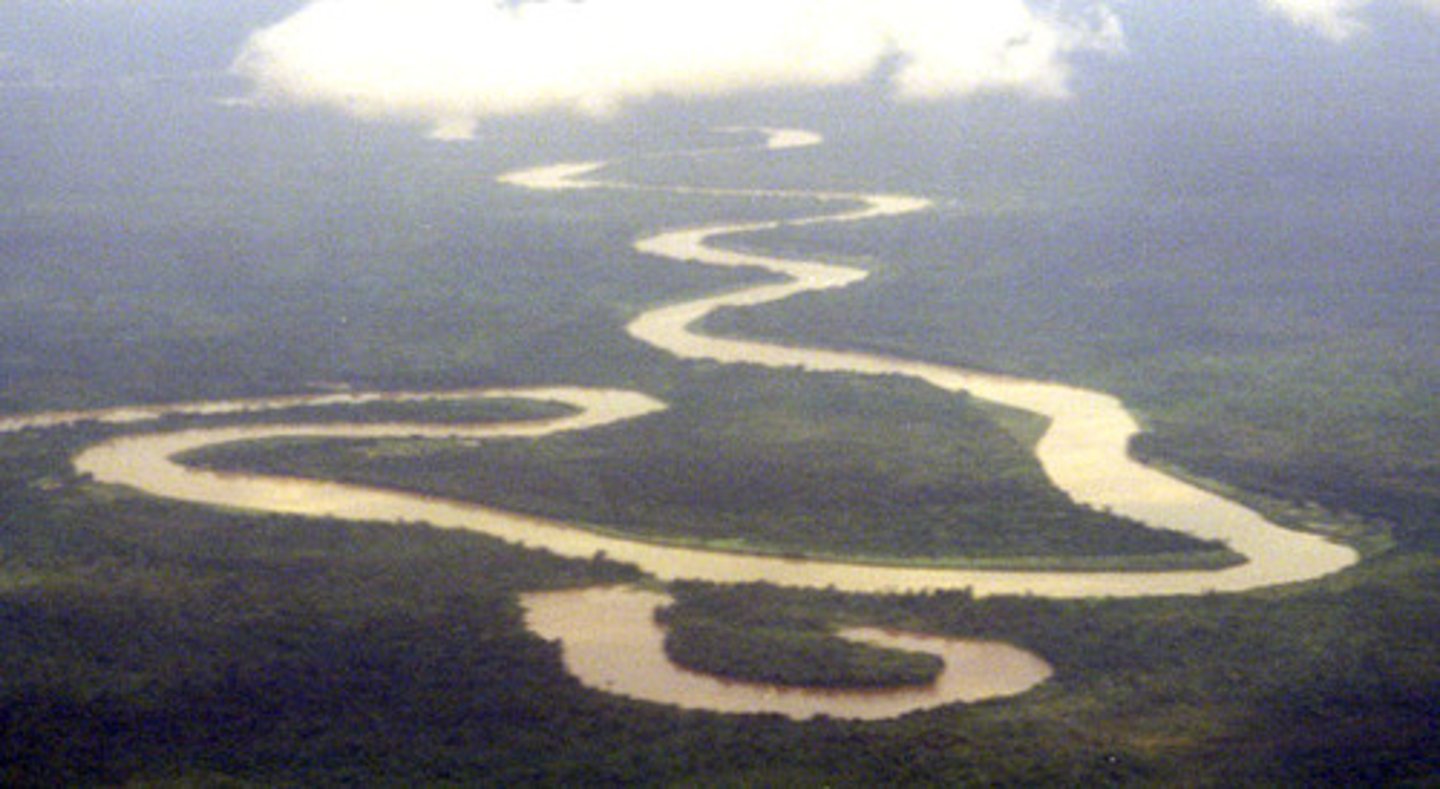
Meanders
Bends in the river that occur in the middle course.
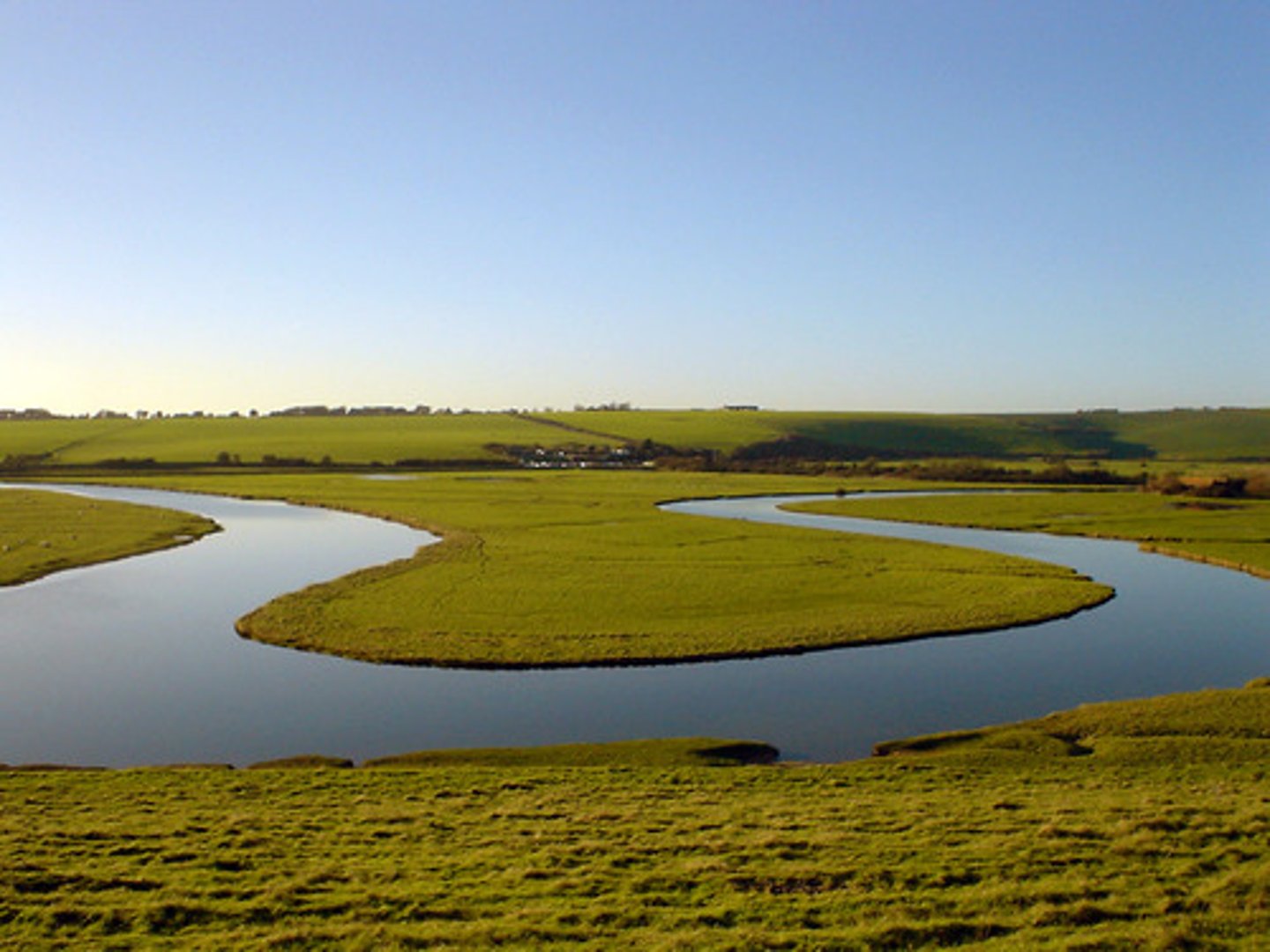

River beach/slip-off slope
This is a feature formed on the inside bend of a meander due to deposition (due to low velocity and high friction).
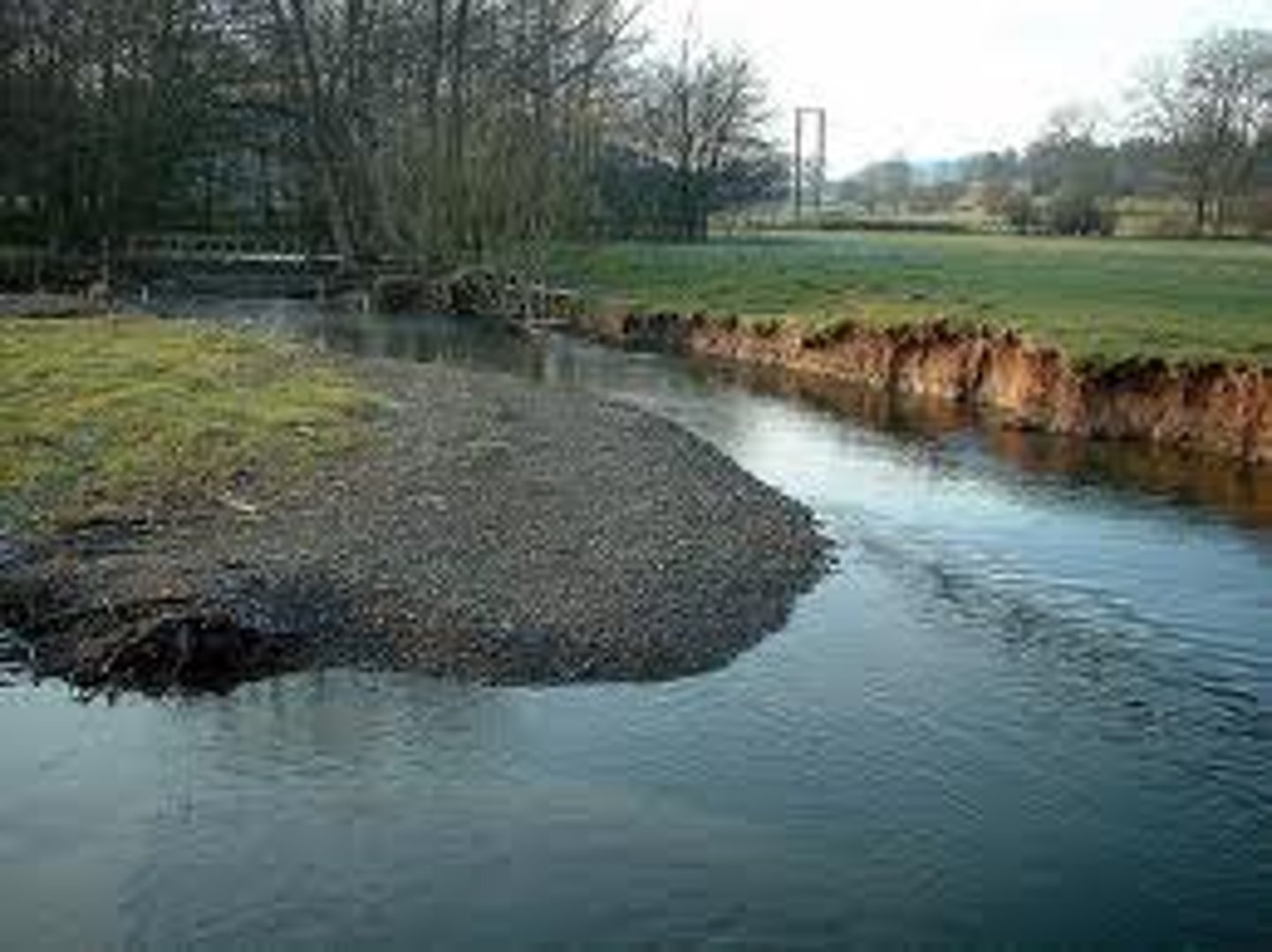

River cliff
This is a feature formed on the outside of a meander where the river erodes the banks through hydraulic action and corrasion.
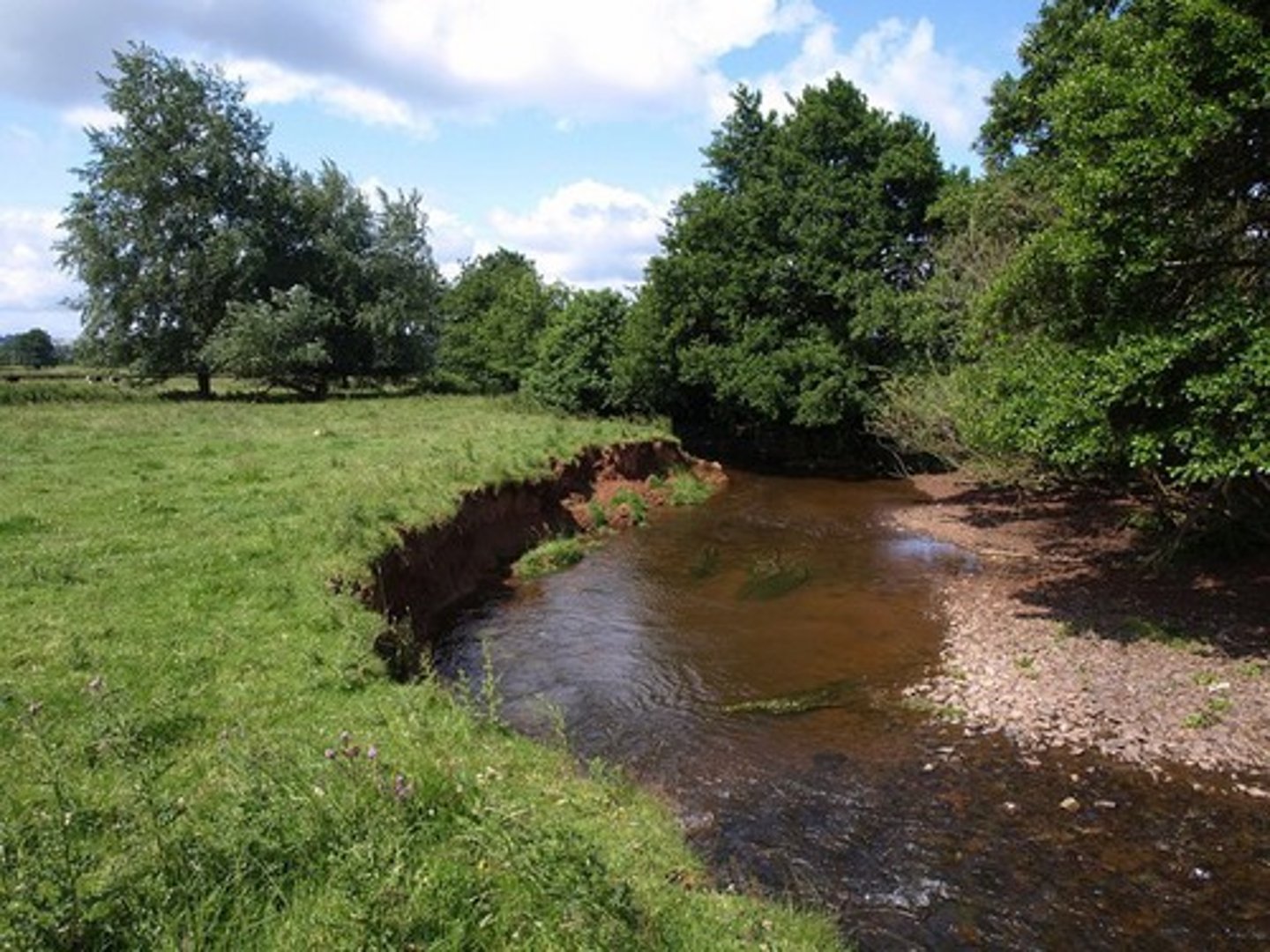

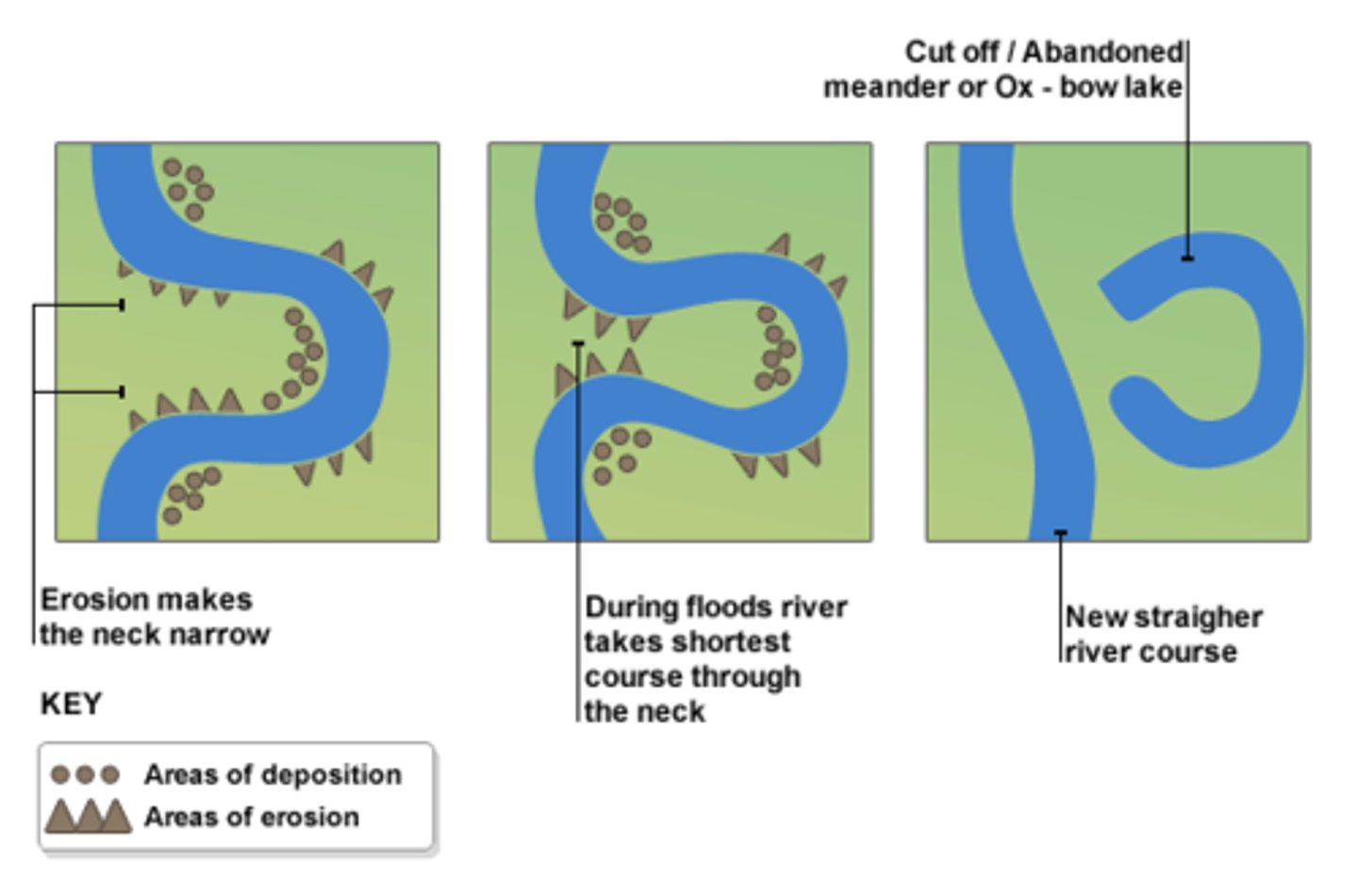
Meander migration
This is the name of the process in which a meander moves and becomes more curvy due to constant erosion and deposition.
Erosion
This is the destructive action of the water in the river which wears away land.

Ox bow lakes
This is a feature formed when the neck of a meander narrows so much that the river simply cuts through.

Lower course
This is the last section of a river's journey, here it is large and fast flowing.

Levees
These are natural barriers formed by the continuous flooding onto the flood plain. The river deposits heavier materials at the front and lighter materials further away.

Floodplain
This is a feature formed when the river floods and deposits sediment. These are usually very fertile.

Solution
When smaller particles of bedload are transported by dissolving it in the water.
Traction
When big boulders are transported by rolling along the bed of the river.
Saltation
When small rocks are transported by bouncing on the bed of the river.
Suspension
When very small bits of rocks are transported by it being suspended and carried along with the water flow.
River Management
Plans and processes implemented on rivers to control water flow and discharge or for a profit.
River discharge
How much water is flowing in to the river at a given location and time.
Peak discharge
The greatest volume of water that flows in the river at a given time.
Flood hydrograph
Graph of stream discharge over a time period for a specific place, lag time, peak, rising limb, falling limb, base flow
Permeable rock
The ability of a rock or sediment to let fluids pass through its open spaces, or pores.
Impermeable rock
Rock that does not allow liquid or gas to flow through it.
Groundwater
Water that fills the cracks and spaces in underground soil and rock layers.
Estuary
the area where a freshwater stream or river merges with the ocean