American Imperialism and the Spanish-American War
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Imperialism
Policy of stronger nations dominating weaker ones.
Old Imperialism
Colonization by European powers since the 16th century.
Berlin Conference
1884 meeting to divide Africa among European powers.

New Imperialism
Late 19th-century American expansionist policies.
Alfred Thayer Mahan
Naval captain advocating for a strong U.S. navy.
Social Darwinism
Belief in Anglo-Saxon superiority justifying imperialism.
U.S. Foreign Policy
Strategy to expand influence through imperialism.
Expansionism
Policy to spread influence via colonial possessions.
Raw Materials
Natural resources extracted from colonies.
Overseas Markets
Foreign markets for American goods.
Naval Bases
Strategic locations for military ships.
Treaty of Kanagawa
1854 agreement opening Japan to U.S. trade.
Seward's Folly
Criticism of Alaska purchase, later proven valuable.
Alaska Purchase
1867 acquisition of Alaska for $7.2 million.
Midway Islands
Pacific islands purchased by the U.S. under Seward.
Samoa
Island with shared U.S., German, and UK control.
Hawaii
Autonomous kingdom that became a U.S. state.
Queen Liliuokalani
Hawaiian queen overthrown by American interests.
Annexation of Hawaii
Hawaii became a U.S. territory in 1898.
Sanford B. Dole
Advocate for Hawaii's annexation and governance.
Sphere of Influence
Area with special trading privileges for a nation.
Open Door Policy
1899 U.S. policy for equal trading rights in China.
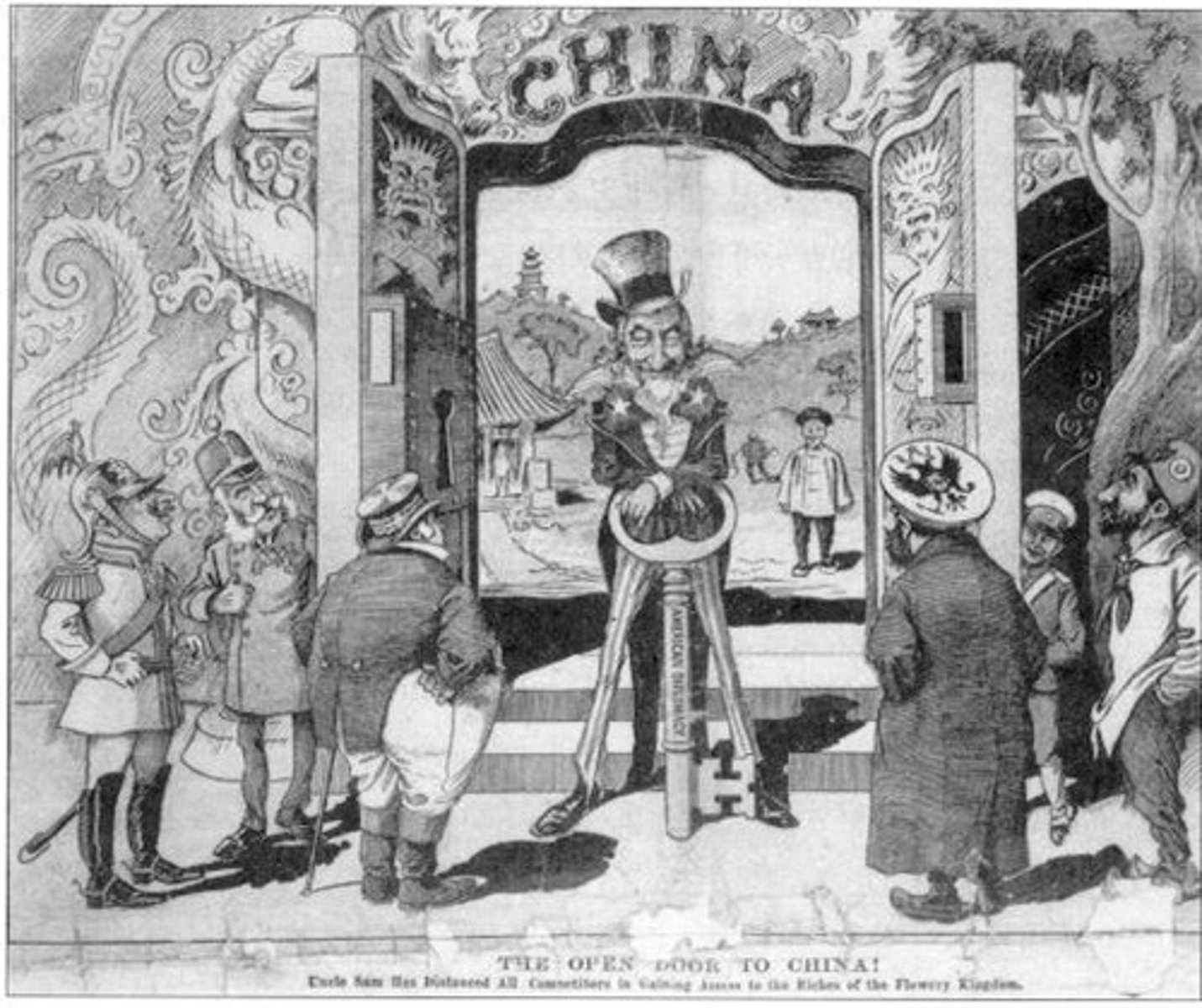

Equal Trading Rights
All nations should trade equally, regardless of influence.
Boxer Rebellion
Chinese nationalists opposed foreign involvement in China.
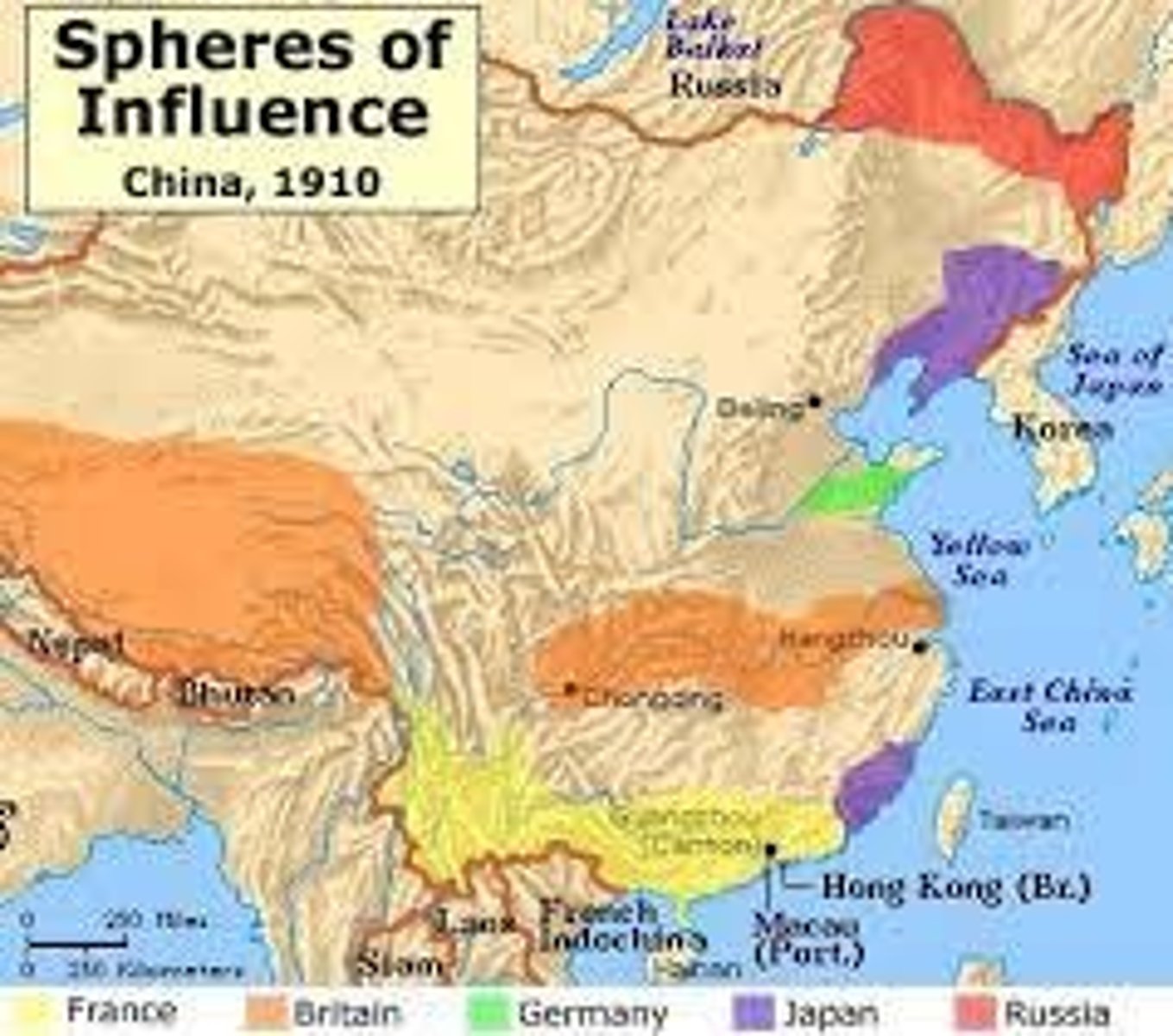
Spanish-American War
Conflict in 1898 between U.S. and Spain.
Cuban Rebellion
Cuba fought for independence from Spanish rule.
Jose Marti
Leader of the Cuban rebellion against Spain.
Reconcentration Camps
Spanish forced Cubans into camps to control rebellion.
Remember the Maine
Slogan after battleship Maine sank in Havana.
De Lome Letter
Spanish ambassador criticized McKinley, increasing tensions.
Yellow Journalism
Sensationalized news reporting to influence public opinion.
Joseph Pulitzer
Publisher known for sensational journalism in New York.
William Randolph Hearst
Publisher who promoted yellow journalism techniques.
Cuban Independence
U.S. recognized Cuba's independence from Spain.
Maine Explosion
Battleship Maine exploded, killing 260 crew members.
Cuban Sugar Plantations
Cuba's wealth stemmed from sugar production.
American Investments
U.S. interests in Cuba prompted intervention concerns.
Grover Cleveland
Opposed U.S. intervention in the Cuban conflict.
William McKinley
President during the Spanish-American War declaration.
Cuban Casualties
95,000 Cubans died from disease and starvation.
Spanish Brutality
Newspapers depicted Spain as violent against Cubans.
Political Power of Press
Media significantly influenced public and political opinion.
American Neutrality
Initial U.S. stance before entering the Spanish-American War.
Cuban Riots
Riots in Havana escalated tensions leading to war.
Spanish American War
Conflict between the U.S. and Spain in 1898.
Philippines
First military action occurred in this Spanish colony.
Theodore Roosevelt
Navy Secretary who ordered Dewey's attack.
George Dewey
Commodore who led the Manila Bay attack.
Manila Bay
Site of Dewey's surprise attack on Spanish fleet.
Emilio Aguinaldo
Leader of Filipino rebels seeking independence.
Luzon
Island where American forces seized the capital.
Cuban Campaign
Military operations conducted in Cuba during the war.
Santiago Harbor
Location where Spanish fleet was trapped.
Rough Riders
1st Regiment of U.S. Cavalry Volunteers led by Roosevelt.
Battle of San Juan Hill
Key battle where Americans captured the hill.
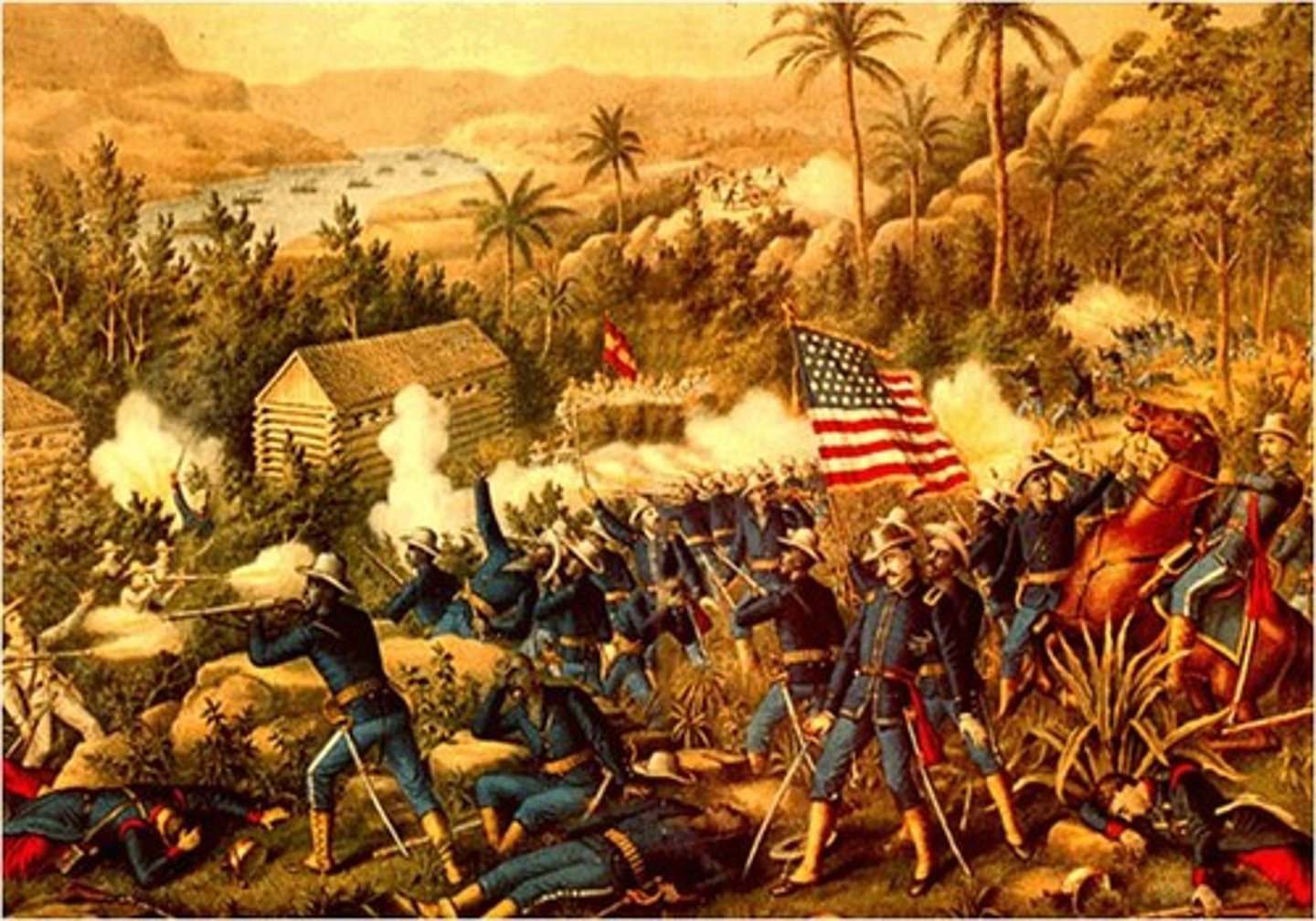

African American soldiers
One quarter of American forces in Cuba.
U.S. Navy blockade
Naval strategy to trap Spanish fleet in Santiago.
Spanish fleet destruction
Ended the Spanish-American War after four-hour battle.
McKinley's Call to Service
Led to nearly 1,000,000 enlistments in the army.
Cuban rebels
Local forces that allied with American troops.
American troops arrival
U.S. forces arrived in the Philippines in July.
Spanish resistance
Opposition faced by American and Cuban forces.
Blockade of Santiago
American naval blockade preventing Spanish escape.
Independence declaration
Filipino rebels declared independence from Spain.
Spanish-American War
Conflict resulting in U.S. territorial acquisitions.
Treaty of Paris (1898)
Ended Spanish-American War; U.S. gained territories.
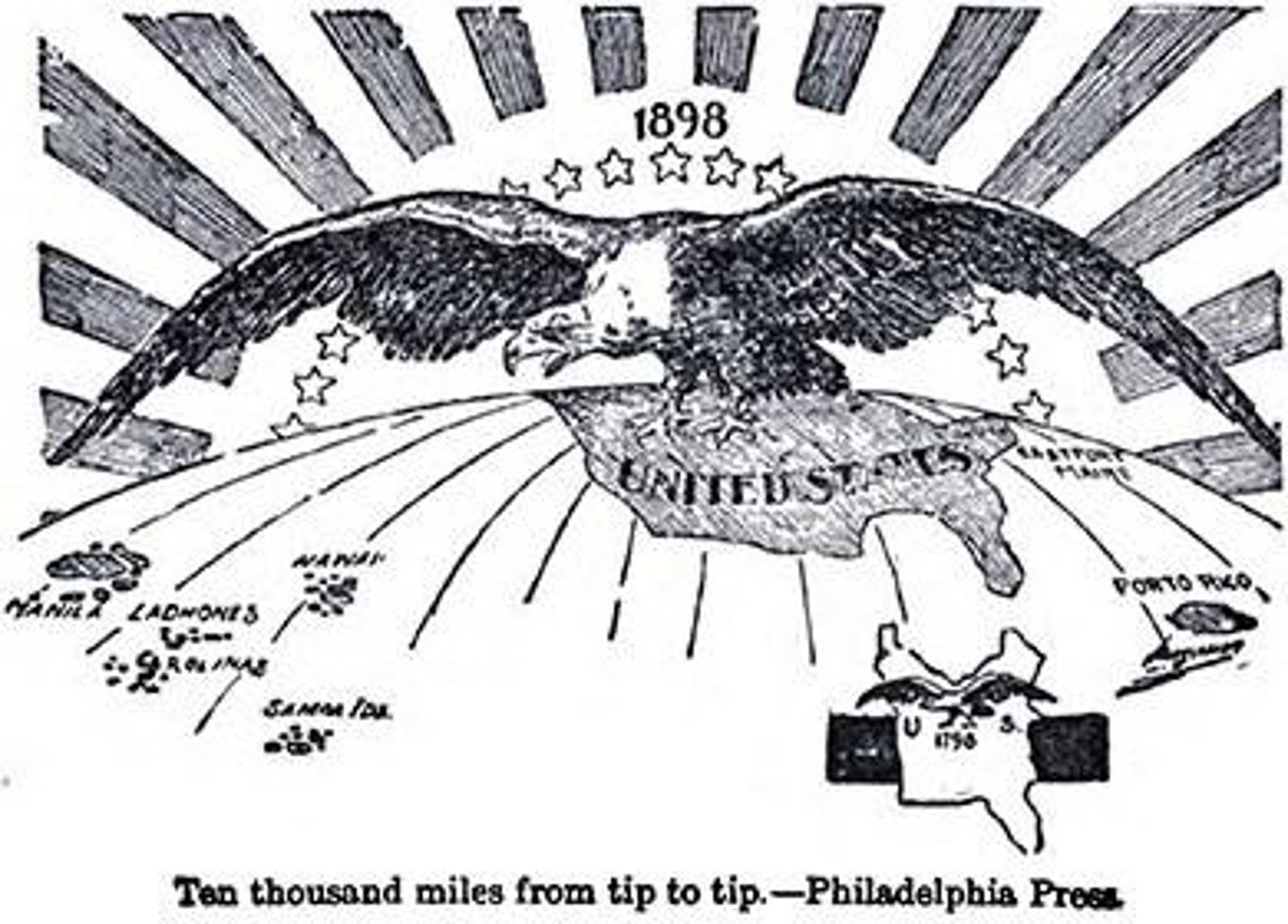
Cuba's Independence
Cuba became independent from Spain post-war.
Puerto Rico Acquisition
U.S. annexed Puerto Rico after the war.
Guam Acquisition
U.S. acquired Guam from Spain in 1898.
Philippines Acquisition
U.S. paid $20 million for Philippines islands.
Foraker Act (1900)
Granted U.S. citizenship to Puerto Ricans.
Popular Vote for Governors
Puerto Rico elected governors since 1948.
Commonwealth Status (1952)
Puerto Rico adopted commonwealth status in 1952.
Platt Amendment (1901)
Allowed U.S. intervention in Cuban affairs.
'A Splendid Little War'
Term coined by John Hay for the war.
War Duration
Spanish-American War lasted four months.
American Casualties
Only 400 American casualties during the war.
Tropical Disease Deaths
5,500 died from diseases like yellow fever.
Anti-Imperialism Debate
Opposition to U.S. imperialism in the Philippines.
Pro-Imperialist Argument
Filipinos needed American guidance for governance.
Emilio Aguinaldo
Leader of the Philippine Republic against U.S.
Philippine-American War
Conflict between U.S. and Filipino forces (1899-1902).
American Atrocities
U.S. soldiers committed atrocities in the Philippines.
American Anti-Imperialist League
Formed in 1899 to oppose imperialism.
Theodore Roosevelt
26th U.S. President known for Big Stick Diplomacy.
Panama Canal
Built to connect Atlantic and Pacific Oceans.
French Canal Failure
French abandoned canal due to diseases.
Panama Canal Lease Cost
U.S. purchased lease from French for $40 million.
Big Stick Diplomacy
TR's approach using military threat for foreign policy.
Panama Canal
51 miles long, built in 10 years, vital trade route.
Roosevelt Corollary
U.S. may intervene in Latin America for debt collection.
Drago Doctrine
Prohibited foreign armed intervention for debt collection.
Monroe Doctrine
U.S. policy opposing European colonialism in Americas.
Great White Fleet
Roosevelt's naval fleet showcasing U.S. naval power.
Dollar Diplomacy
Taft's policy using financial leverage in foreign affairs.
USS Maine
First armored battleship of the U.S. Navy.
Captain Alfred Thayer Mahan
Naval strategist advocating for a strong U.S. Navy.
Steel-hulled ships
Modern ships built for strength and durability.
Nicaragua Loan Incident
U.S. intervention due to Nicaragua's loan repayment issues.
Secretary Hays
Negotiated Panama Canal treaty for U.S. interests.