A&P II: Exam 4
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Choose the answer choice described in the following statement. Wavelike smooth muscle contractions that move foodstuffs through the alimentary tube.
Peristalsis
The chemical and mechanical processes of food breakdown are called ________.
digestion
The absorptive effectiveness of the small intestine is enhanced by increasing the surface area of the mucosal lining. Which of the following accomplish this task?
villi, and microvilli
Choose the answer choice described in the following statement. Process by which simpler chemical units pass through the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract into the blood or lymph.
Absorption
Which of the following is least involved in the mechanical breakdown of food, digestion, or absorption?
the esophagus
The function of the hepatic portal circulation is to ________.
collect absorbed nutrients for metabolic processing in the liver
You have just eaten a meal high in complex carbohydrates. Which of the following enzymes will help to digest the meal?
amylase
Outline the flow of food through the digestive tract from the mouth to the anus.
Mouth -> Pharynx -> Esophagus -> Stomach -> Small Intestine -> Duodenum -> Jejunum -> ileum -> Large Intestine -> Cecum -> Ascending Colon -> Transverse Colon -> Descending Colon -> Sigmoid Colon -> Rectum -> Anus
Describe the nerve supply to the digestive tract.
The digestive tract is supplied by both intrinsic and extrinsic nerves. The intrinsic nerve supply, also known as the enteric nervous system, includes the submucosal and myenteric plexuses, which regulate local activities such as secretion and muscle contraction. The extrinsic nerve supply comes from the autonomic nervous system: parasympathetic nerves, which is primarily the vagus nerve, enhance digestive activity, while sympathetic nerves inhibit it.
Describe the role of the pancrease, liver and gallbladder in digestion.
The pancreas secretes digestive enzymes l(amylase, lipase, and proteases) into the small intestine to break down carbohydrates, fats, and proteins. It also releases bicarbonate to neutralize stomach acid. The liver produces bile, which emulsifies fats to aid in their digestion and absorption. The gallbladder stores and concentrates bile, releasing it into the small intestine when fats are present.
Proximal convoluted tubule is_______.
Site at which most of the tubular reabsorption occurs
Glomerulus is ______.
Site of filtrate formation
Peritubular capillaries are________.
Blood supply that directly receives substances from the tubular cells
Collecting duct is___________.
Site that drains the distal convoluted tubule
The path urine takes after it is formed until it leaves the body is the urethra, urinary bladder, and finally the ureter.
false
The entire responsibility for urine formation lies with the nephron.
true
The collecting duct is impermeable to water in the presence of ADH.
false
State the 4 organs of the urinary system and their functions.
The 4 organs of the urinary system and their functions:
1. Kidneys – Filter blood to remove waste products and form urine. They also regulate electrolyte balance, blood pressure, and pH.
2. Ureters – Transport urine from the kidneys to the urinary bladder through peristaltic movements.
3. Urinary Bladder – Temporarily stores urine until it is ready to be excreted.
4. Urethra – Conducts urine from the bladder to the outside of the body during urination.
State the vessel that feeds blood into and the vessel that sends blood out of the glomerulus.
The afferent arteriole feeds blood into the glomerulus.
The efferent arteriole carries blood out of the glomerulus.
State the structures (in order) that urine flows through as it goes from the renal pyramid to the ureter.
1. Renal pyramid
2. Minor calyx
3. Major calyx
4. Renal pelvis
5. Ureter
Role of Liver?
Produces and secretes bile into the small intestine and gallbladder
Role of Gallbladder?
Stores bile produced by the liver, concentrates bile and releases it into the small intestine
Role of Pancreas?
Secretes pancreatic juice which contains enzymes that breakdown carbohydrates, lipids, proteins and nucleic acids.
Explain the role of amylases in digestion.
Break down carbohydrates
Explain the role of proteases in digestion.
Break down proteins
Explain the role of lipases in digestion.
Break down fats
What are the 4 macromolecules and their respective building blocks?
Carbs → Monosaccharides
Proteins → Amino acids
Lipids → Fatty acids
Nucleic acids → Nucleotides
Of the alimentary canal organs, which two play the biggest role in digestion?
Small intestine and stomach
Of the alimentary canal organs, which plays the biggest role in absorption?
Small intestine
What is the function of the digestive system? (3)
Break down food
Release nutrients from food
Absorb nutrients
Proximal convoluted tubule is_______.
Site at which most of the tubular reabsorption occurs
Glomerulus is ______.
Site of filtrate formation
Peritubular capillaries are________.
Blood supply that directly receives substances from the tubular cells
Collecting duct is___________.
Site that drains the distal convoluted tubule
True or False
The path urine takes after it is formed until it leaves the body is the urethra, urinary bladder,
and finally the ureter.
False
True or False
The entire responsibility for urine formation lies with the nephron.
True
True or False
The collecting duct is impermeable to water in the presence of ADH.
False
State the 4 organs of the urinary system and their functions.
Ureters-transport urine from kidneys to bladder
Urinary bladder-temporary storage reservoir for urine
Urethra-transports urine out of the body
Kidney-maintains body’s internal environment and forms urine
Whats the function of the Ureters?
Transport urine from kidneys to bladder
Whats the function of the Urinary Bladder?
Temporary storage reservoir for urine
Whats the function of the Urethra?
Transports urine out of the body
Whats the function of the Kidneys?
Maintains body’s internal environment and forms urine
State the vessel that feeds blood into and the vessel that sends blood out of the glomerulus.
Into-afferent arteriole
Out of-efferent arteriole
What vessel feeds blood into the Glomerulus?
Afferent Arteriole
What vessel sends blood out of the Glomerulus?
Efferent Arteriole
State the structures (in order) that urine flows through as it goes from the renal pyramid to the
ureter.
Renal pyramid→ Minor Calyx→ Major Calyx→ Renal Pelvis → Ureter
Which region of the nephron plays the biggest role in reabsorption?
Proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
Which region of the nephron plays the biggest role in secretion?
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT)
Describe how the anatomy of the renal corpuscle structures allows for blood filtration.
Renal corpuscle = Glomerulus + Bowman’s capsule
If glucose is found in the urine, would this be concerning?
Yes, it’s an indicator of diabetes
If a large amount of proteins is found in the urine, would this be concerning?
Yes, it’s an indicator of glomerulus damage
State the 4 organs of the urinary system and their functions.,
Ureters → transport urine from kidneys to bladder;
Urinary bladder → temporary urine storage;
Urethra → transports urine out;
Kidneys → filter blood, produce urine
What are the 3 regions of the internal kidney?
Renal cortex, renal medulla, renal pelvis
State the vessel that feeds blood into and the vessel that sends blood out of the glomerulus
Into → afferent arteriole; Out of → efferent arteriole
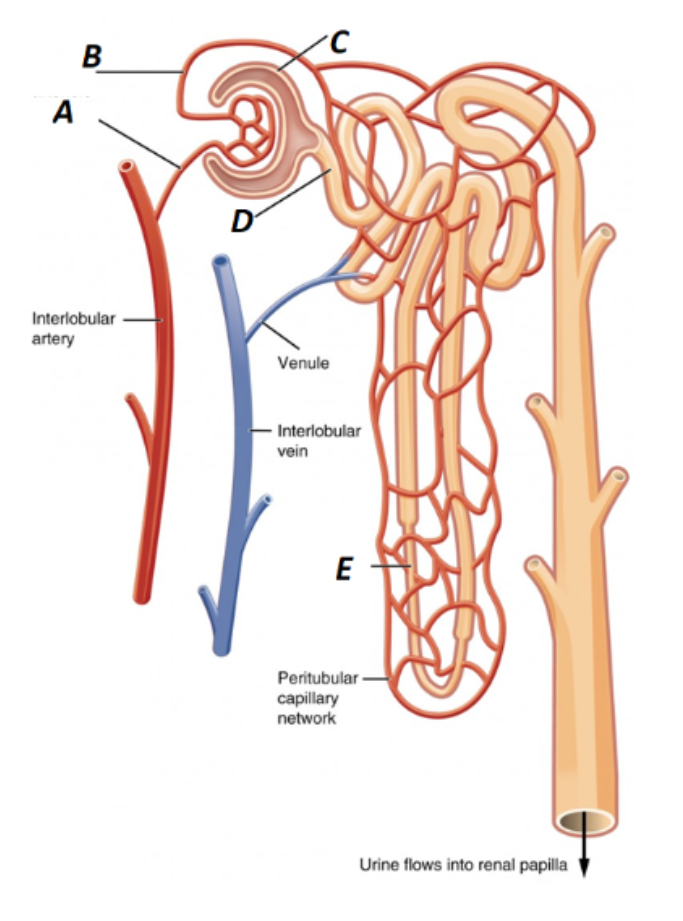
Label A in the kidney image
Afferent Arteriole
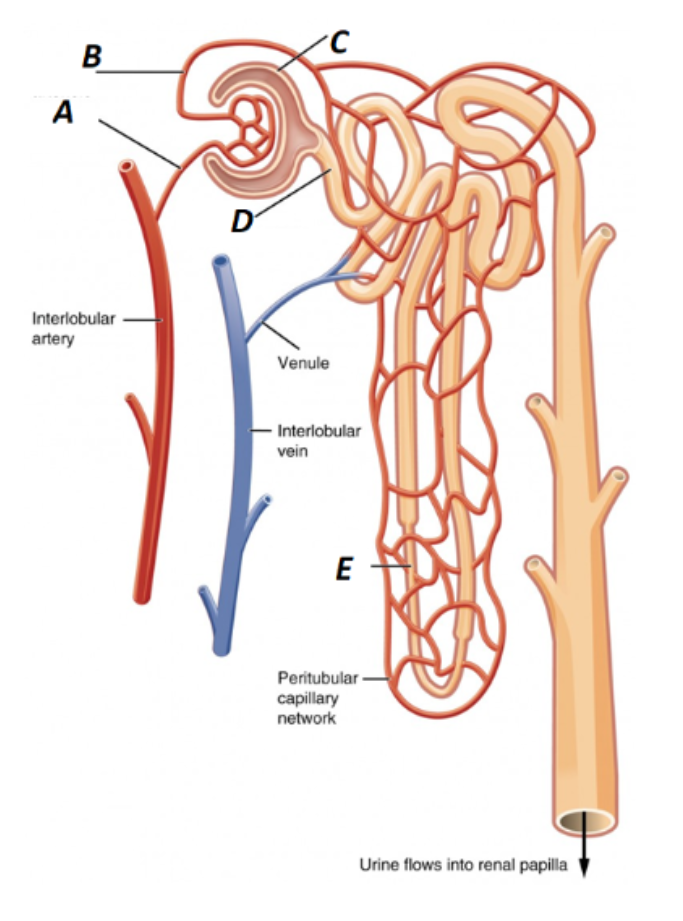
What is B labeled as in the kidney?
Efferent Arteriole
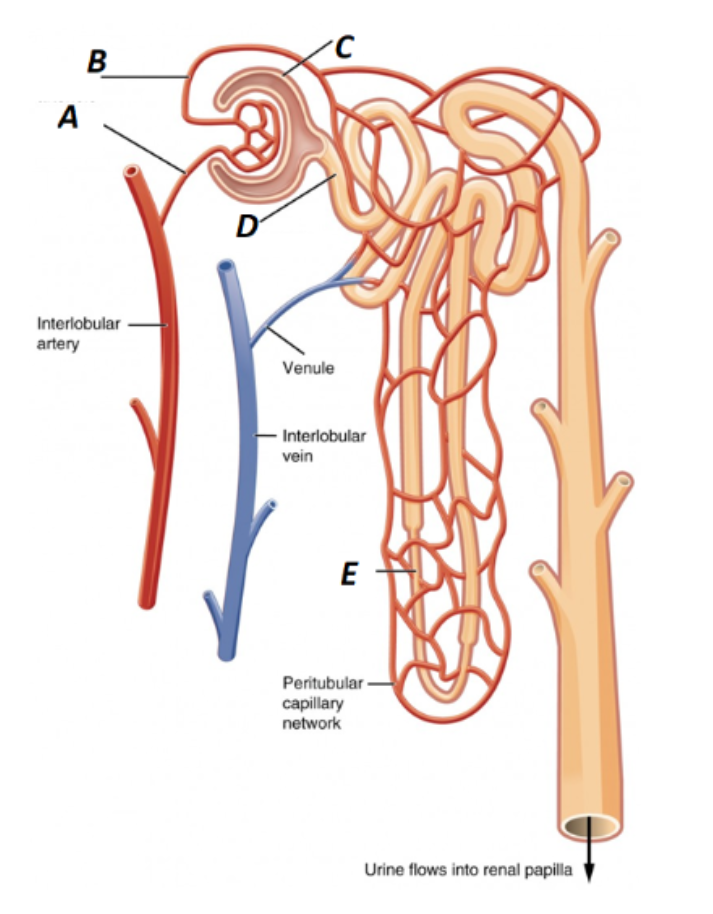
What is C labeled as in the kidney?
Bowman’s Capsule
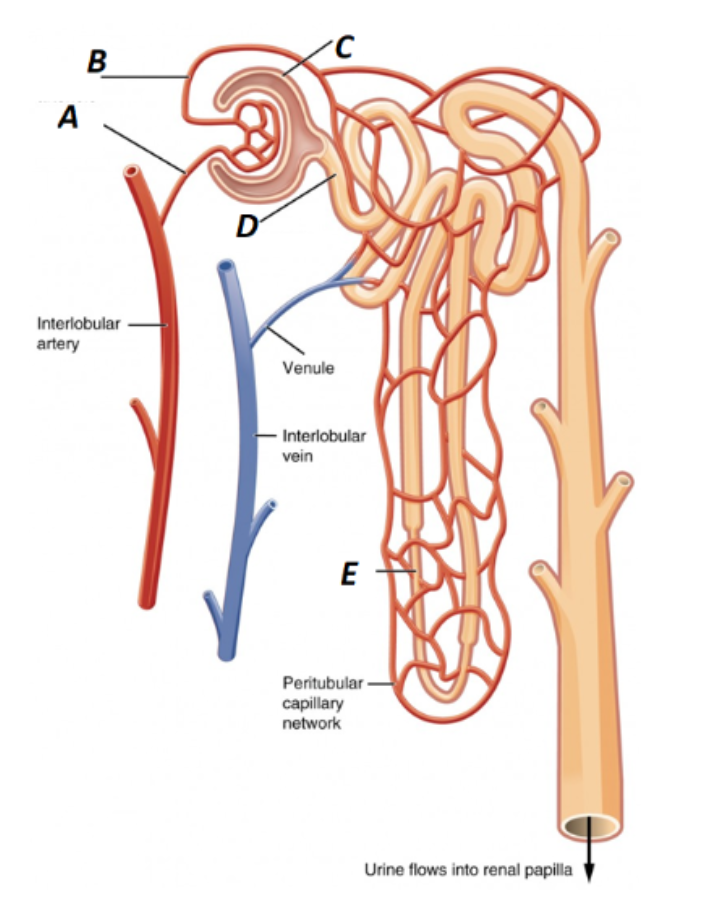
What is D labeled as in the kidney?
Proximal Convoluted Tubule
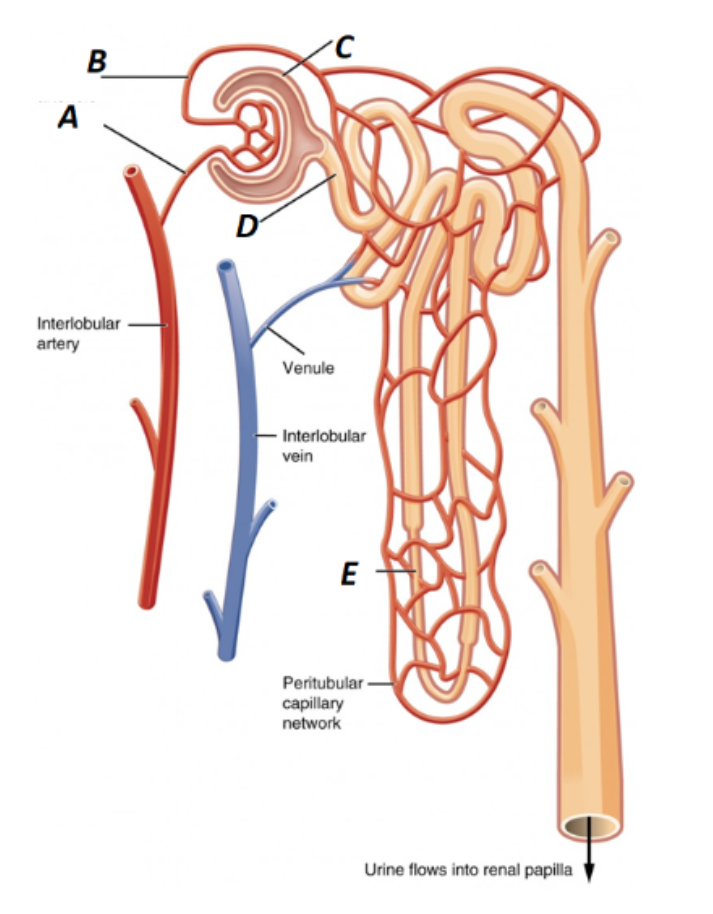
What is E labeled as in the kidney?
Loop of Henle (nephron loop)
What is the glomerulus composed of and what is its function?
Capillaries with fenestrated epithelium (leaky) → allows glomerular filtration
Where does the filtrate go after leaving the glomerulus?
Bowman’s capsule → proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)
What is the function of the proximal convoluted tubule (PCT)?
Tubular reabsorption and secretion of solutes (Na+, Cl-, glucose)
What parts of the nephron reabsorb water?
PCT, loop of Henle, DCT, collecting ducts
What parts of the nephron are under hormonal control for reabsorption?
Distal convoluted tubule (DCT), collecting duct
State the hormones involved in absorption regulation and their roles
ADH → inserts aquaporins, ↑water reabsorption; Aldosterone → ↑Na+ & water reabsorption, K+ loss; ANP → ↓blood Na+; PTH → ↑Ca2+ reabsorption in DCT
True or False
The amount of testosterone and sperm produced by the testes is dependent on the influence of FSH alone.
False
True or False
Ovarian follicles contain mature eggs.
False
True or False
The corpus luteum secretes progesterone.
True
Which of the following hormones controls the release of anterior pituitary gonadotropins?
GnRH
If gametes were diploid like somatic cells, how many chromosomes would the zygote contain?
Twice the diploid number, and with every succeeding generation, the chromosome number would continue to double and normal development could not occur.
Which of the following is true of testosterone?
Testosterone is produced by the Leydig cells
During the secretory phase of the menstrual cycle, ________ reaches its highest levels.
Progesterone
Folliculogenesis and Oogenesis are interrelated processes that are both part of the ovarian cycle. Explain one way that the 2 processes are connected.
Folliculogenesis and oogenesis are connected because the developing follicle supports and nurtures the maturing oocyte (egg) inside it. As the follicle grows and develops during folliculogenesis, it provides the necessary environment and hormonal signals for the oocyte to resume meiosis and continue its development. Without folliculogenesis, oogenesis could not successfully occur.
Describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Spermatogenesis is the process by which sperm are produced in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. It begins with spermatogonia, which are stem cells that divide by mitosis. Some spermatogonia differentiate into primary spermatocytes. These primary spermatocytes undergo meiosis I to form two secondary spermatocytes. Each secondary spermatocyte undergoes meiosis II to produce two spermatids. Finally, spermatids mature into spermatozoa (sperm cells) through a process called spermiogenesis.
What structure of the male reproductive system undergoes surgery during a vasectomy and how does this lead to surgical sterilization?
During a vasectomy, the vas deferens is cut and sealed. The vas deferens is the tube that carries sperm from the epididymis to the urethra. By cutting the vas deferens, sperm can no longer be transported out of the body during ejaculation, leading to sterilization because sperm are absent from the semen.
Compare and contrast mitosis and meiosis in terms of number of cells produced, ploidy, and cell identity.
Mitosis → 2 cells, diploid, identical
Meiosis → 4 cells, haploid, non-identical
How may cells does Mitosis create, whats their ploidy, and cell identity?
2 cells, diploid, identical
How many cells does Meiosis produce, whats their ploidy, and cell identity?
4 cells, haploid, non-identical
Describe the process of spermatogenesis.
Spermatogenesis occurs in the testes (seminiferous tubules).
Begins with spermatogonia (diploid stem cells) dividing by mitosis.
Primary spermatocytes (diploid) undergo meiosis I → two secondary spermatocytes (haploid).
Secondary spermatocytes undergo meiosis II → four spermatids (haploid).
Spermatids mature into sperm (spermatozoa) through spermiogenesis.
How does cutting and sealing the vas deferens (vasectomy) result in surgical sterilization?
Blocks the path sperm takes to exit the male reproductive system.
Explain the roles of the hypothalamus, anterior pituitary, Sertoli cells, Leydig cells, GnRH, FSH, LH, testosterone, ABP, and inhibin in testosterone regulation.
Hypothalamus → releases GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone)
↓Anterior pituitary → releases FSH and LH
↓LH → stimulates Leydig cells → produce testosterone
↓FSH → stimulates Sertoli cells → produce ABP (androgen-binding protein) → helps concentrate testosterone in seminiferous tubules
↓Sertoli cells → release inhibin → negative feedback to anterior pituitary to decrease FSH
↓Testosterone → negative feedback to hypothalamus and anterior pituitary → lowers GnRH and LH release
What are the male gonads and their function?
Testes → Produce sperm
What are the female gonads and their function?
ovaries → produce oocytes
What are the male and female gonads and their functions?
Male: testes → produce sperm; Female: ovaries → produce oocytes
Trace the path sperm travels after production in seminiferous tubules
Straight tubule → rete testis → efferent ductules → epididymis → vas deferens → penis
Describe the process of spermatogenesis
Spermatogonial stem cell → mitosis → primary spermatocyte → meiosis I → secondary spermatocytes → meiosis II → spermatids → spermiogenesis → spermatozoa (sperm)
Where is semen made and what does it consist of?
Seminal vesicles, prostate, bulbourethral glands → sperm + seminal vesicle secretions + prostate fluid + bulbourethral fluid
Explain the endocrine regulation of testosterone
Hypothalamus → GnRH → anterior pituitary → LH & FSH → LH → Leydig cells → testosterone; FSH → Sertoli cells → ABP → binds testosterone; Negative feedback: testosterone → ↓GnRH, LH, FSH; inhibin → ↓FSH
What are the three layers of the uterus wall?
Perimetrium, myometrium, endometrium
Describe the process of oogenesis
Ovarian stem cells → mitosis → primary oocytes (before birth) → puberty → meiosis I → secondary oocyte + polar body → if fertilized → meiosis II → haploid ovum → zygote
What are the six stages of folliculogenesis?
1. Primordial follicle;
2. Primary follicle (granulosa cells);
3. Secondary follicle (theca + granulosa cells);
4. Tertiary follicle (antrum forms);
5. Ovulating follicle (oocyte released);
6. Corpus luteum
Describe the hormonal regulation of ovulation.
"Hypothalamus → GnRH → anterior pituitary → LH, FSH → LH, FSH → follicle maturation → estrogen → estrogen → ↑GnRH, LH, FSH → LH surge → ovulation"
What are the three phases of the menstrual cycle and hormone changes?,
1. Menses → low estrogen & progesterone;
2. Proliferative → ↑estrogen;
3. Secretory → ↑progesterone