Gene Therapy
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
Gene Therapy
Aims to treat or cure genetic abnormalities by replacing faulty genes with healthy ones. Single-gene disorders have the potential to be fixed by correcting the underlying cause of the disease.
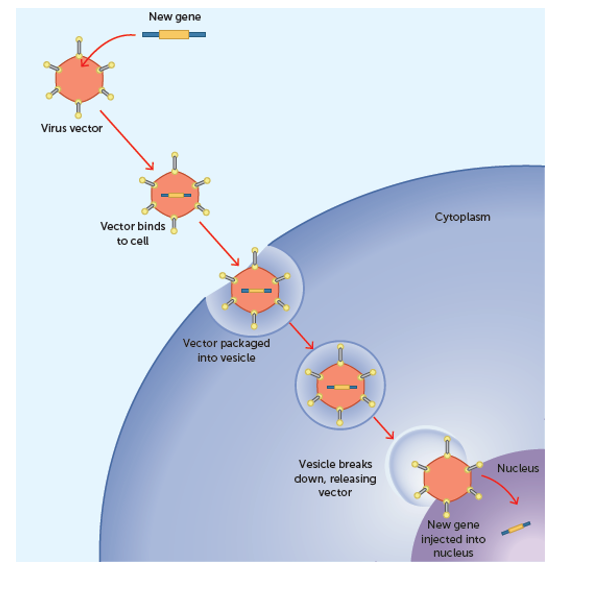
Vectors in gene therapy
Agents which deliver genes to cells. Often plasmids: circular pieces of DNA from bacteria or viruses. Used as they are:
-extra chromosomal making it easier to introduce foreign DNA into a cell than integrating DNA into chromosome.
-self-replicating
The DNA from the vector can be incorporated into the cell’s nucleus and undergo transcription and translation to produce the desired protein
Relation to diabetes mellitus
Gene therapy could make it possible to treat type 1 Diabetes by delivering healthy insulin-producing genes to cells in the pancreas.
1) The gene of interest is isolated - a gene that produces insulin
2) The gene is introduced into a vector
3) The vector is injected into the beta cells of islets of Langerhans in the pancreas
4) The DNA in the nucleus takes up the functioning gene and uses the information to make insulin.
Cell Replacement Therapy
Any disorder involving the loss or injury to normal cells is a potential candidate for this. Involves replacing damaged cells with healthy cells produced from stem cells (undifferentiated cells)
Alzheimer’s Disease
Most common form of dementia caused by changes in the brain, degeneration and a decrease in neurotransmitters.
Treatment of Alzheimers
1) stem cells are obtained
2) stem cells are induced to become specific cells (neurons)
3) differentiated stem cells are transplanted into the patient’s brain
4) used to replaces lost or injured neurons.
Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Occurs when nerve cells in the basal ganglia which produce the neurotransmitter dopamine, become impaired and/or die.Symptoms include uncontrollable movements, such as shaking, and difficulty with balance and coordination.
Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease (PD)
Can be treated with cell replacement therapy
1) Stem cells obtained and induced to become neurons
2) differentiated stem cells are transplanted into the patient’s brain
3) new nerve cells produce dopamine