CHAPTER 11 - efferent division, autonomic and somatic motor control
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
what are the 2 divisions of the nervous system
autonomic
somatic
what is autonomic division
processes occuring automatically
what is somatic division
processes with conscious control
what are the 2 divisions of the autonomic division
sympathetic
parasympathetic
what are antagonistic branches
opposing actions to cause homeostasis
i.e: parasympathetic and sympathetic
what is parasympathetic
rest and digest
restore body functions
inhibitory
what is sympathetic
fight or flight
energetic rection
excitatory
how does behavioural coordination work
autonomic (parasympathetic or sympathetic)
endocrine (hormone released)
behaviour (action)
what are the things controlled by autonomic centers in the brain
water balance
temperature
hunger
respiration
cardiac
vomiting
swallowing
where do sympathetic pathways originate
thoracic and lumbar section of the spinal cord
length of pre and post ganglion in sympathetic pathways
pre ganglion - short
post ganglion - long (to reach target)
where do parasympathetic pathways originate
brain stem, sacral region of spinal cord
length of pre and post ganglion in parasympathetic pathways
pre ganglion - long
post ganglion - short
what neurotransmitter do sympathetic pre ganglion neurons release
acetylcholine
what neurotransmitter do parasympathetic pre ganglion neurons release
acetylcholine
what neurotransmitter do sympathetic post ganglion neurons release
norepinephrine “fight or flight”
what neurotransmitter do parasympathetic post ganglion neurons release
acetylcholine “rest and digest”
what do receptor does pre ganglion acetylcholine bind to
(both parasympathetic and sympathetic)
nicotinic receptors
what receptor does norepinephrine bind to in sympathetic post ganglion
adrenergic receptors
what receptor does acetylcholine bind to in parasympathetic post ganglion
muscarinic receptors
what division is responsible for fight or flight
sympathetic
what division is responsible for rest and digest
parasympathetic
what is a ganglion
cluster of nerve cell bodies outside of the CNS
what is a neuroeffector junction
a synapse between post ganglion and its target
what are varicosities
swollen regions along axon terminals of autonomic neurons
contain vesicles filled with neurotransmitters
what are the autonomic target cells
smooth muscle
cardiac muscle
exocrine glands
endocrine glands
lymphoid tissue
adipose tissue
where does neurotransmitter synthesis occur
in varicosities
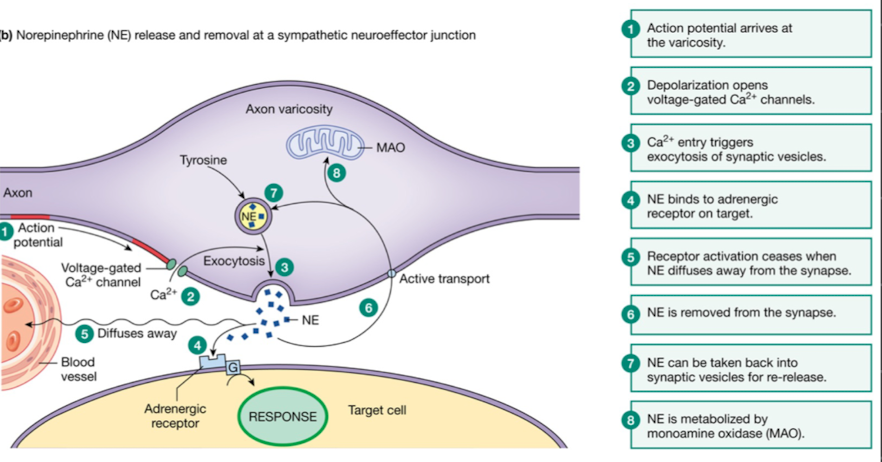
Eight steps of norepinephrine release at a varicosity of a sympathetic neuron
action potential arrives at varicosity
depolarization opens voltage-gated Ca2+ channels
Ca2+ triggers exocytosis of synaptic vesicles (norepinephrine)
Norepinephrine binds to adrenergic receptors on target
receptor activation ceases when norepinephrine diffuses away from the synapse
norepinephrine is removed form the synapse
norepinephrine can be recycled into synaptic vesicles
norepinephrine is metabolized by monoamine oxidase
2 key parts of adrenal glands
adrenal cortex - true endocrine gland
adrenal medulla - modified synaptic ganglion
primary hormone of adrenal glands
norepinephrine
how do adrenal glands secrete neurotransmitters
long preganglionic sympathetic neuron transmit a signal from spinal cord to adrenal medulla
sympathetic nerves release ACh onto adrenal medulla cells
Acetylcholine binds to receptors on adrenal cells, causing them to become excited.
excitement opens channels that let calcium ions into the cells
The calcium triggers the adrenal cells to release adrenaline (epinephrine) and noradrenaline (norepinephrine) into the bloodstream.
CNS origin of sympathetic neurons
1st - 2nd thoracic lumbar segments
CNS origin of parasympathetic neurons
midbrain, medulla, 2nd- 4th sacral segments
location of peripheral ganglia (sympathetic)
vertebrae (3 of them are located on aorta)
location of peripheral ganglia (parasympathetic)
on/near target cells
what releases nerurotransmitters for sympathetic and parasympathetic
varicsosities
what neurotransmitter is released at sympathetic target cells
norepinephrine (adrenergic neurons
what neurotransmitter is released at parasympathetic target cells
acetylcholine ( cholinergic neurons)
what happens after inactivation of neurotransmitters in sympathetic pathway
recycle back into varicosities or diffusion
what happens after inactivation of neurotransmitters in parasympathetic pathway
enzyme breakdown or diffusion
receptor on both sympathetic and parasympathetic target cells
adrenergic
pre ganglion synapse on both parasympathetic and sympathetic pathways
ACh on nicotinic receptors
post ganglion synapse on sympathetic pathways
norepinephrone on alpha or beta adrenergic receptors
post ganglion synapse on parasympathetic pathways
ACh on muscarinic receptor
what is a neuromuscular junction
connection between a neuron and a muscle where signals from neuron tell the muscle to contract
4 components of a neuromuscular junction
motor neuron: neuron carries signal from spinal cord to muscle
synaptic cleft: tiny gap between neuron and muscle fiber
motor end plate: part of muscle fibers that contain the receptors
acetylcholine: neurotransmitter that triggers action
6 steps in somatic neurotransmitter release
action potential arrives: neuron signal reaches the presynaptic membrane
calcium channels open: voltage-gated calcium channels allow Ca2+ to enter neuron ending
release of ACh: Ca2+ trigger ACh release
ACh binds to receptor: ACh travels across synaptic cleft, binds to nicotinic receptors on motor end plate
muscle contraction: binding causes ion channels in muscle to open ending in muscle contraction
ACh breakdown: acetylcholine breaks down ACh into acetyl and choline, allows muscle to relax
number of neurons in efferent path (somatic)
1 long neuron
number of neurons in efferent path (autonomic)
2 (preganglion and post ganglion)
neurotransmitter/receptor at neuron target synapse (somatic)
ACh/ nicotinic
neurotransmitter/receptor at neuron target synapse (autonomic)
ACh/ muscarinic OR norepinephrine/ alpha or beta adrenergenic
target tissue of somatic motor pathway
skeletal muscle
target tissue of autonomic pathway
smooth, cardiac muscle; some endocrine, exocrine glands; some adipose tissue
neurotransmitters are released from (somatic)
axon terminals
neurotransmitters are released from (autonomic)
varicosities and axon terminals
effects on target tissue (somatic)
excitatory (muscle contraction)
effects on target tissue (autonomic)
excitatory (sympathetic) or inhibitory (parasympathetic)
function of somatic systems
posture and movement
function of autonomic systems
visceral function, movement of internal organs, secretion, controls metabolism