Su: Virus Background
1/57
Earn XP
Description and Tags
lecture 1 anti-hiv agents, just the intro material
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
58 Terms
are viruses made of cells?
hell no
viruses depend on the host for…
multiplication and survival
drugs are not commonly used to treat viruses due to…
simplicity of their structure
limited targets for drugs
delay required for infection to establish
immune response
T/F: viruses contain both RNA and DNA
FALSE BITCH
what is the purpose of the genome in a virus
to code for the replication proteins, and produce the new viral particles in the host
virus genome structure
made of either an RNA or DNA core, this core is encapsulated in an envelope of protective proteins (aka the capsid)
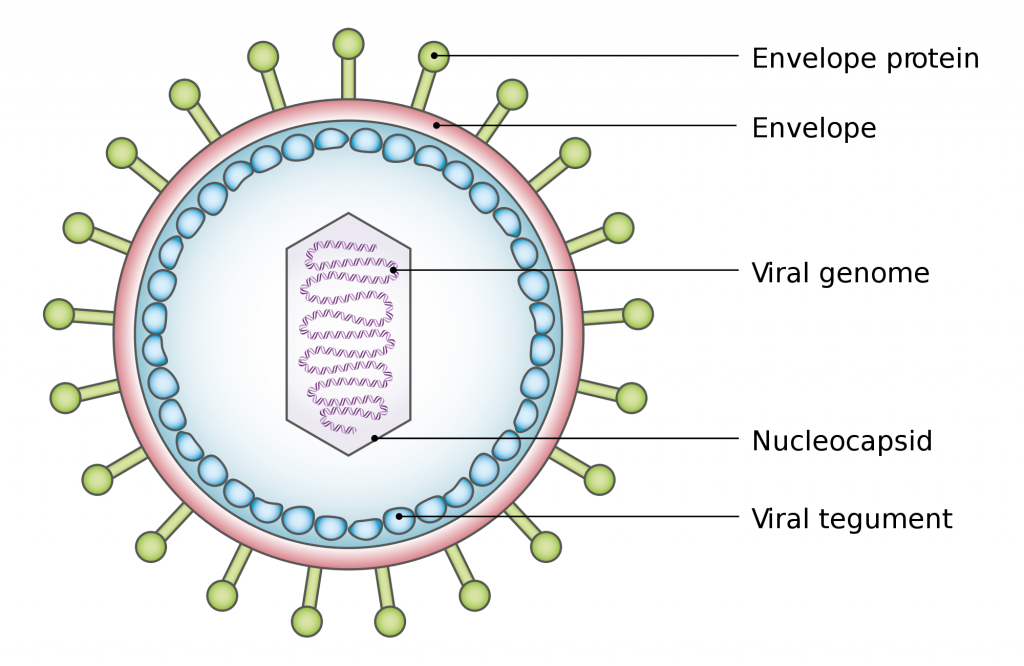
virus capsid function and structure
protective envelope that covers the genome, made of lipids and proteins
genome replication of a virus depends on…
energy and protein machinery in the host
first step of multiplication of viral genetic material in a host
separation of the genome from the capsid
viral proteins are either ___ or ___
structural or non structural
structural viral proteins
become incorporated into the virus and become a part of the viron
non structural viral protein example
nucleic acid polymerases
viron
the virus containing particle, infectious form of the virus
bacteriophages infect…
bacteria
plant viruses are usually made of ____
RNA
example of plant virus made of RNA
tobacco mosaic virus
example of plant virus made of DNA
Gemini virus and maize
what are the three types of animal viruses
DNA
RNA
retrovirus
examples of DNA animal viruses
HSV1 and HSV2
HSV1 is associated with which illnesses
oral herpes and cold sores
HSV2 is associated with which infections
genital herpes
examples of RNA animal viruses
rhinovirus
paramyxovirus
orthomyxovirus
rhinovirus causes which illness
common cold
paramyxovirus causes which illness
measles and mumps
orthomyxovirus causes which illness
influenza
retroviruses causes
HIV1 and HIV2
viroids
plant pathogens, naked strands or circles of RNA with no protein coat
unconventional viruses are also called
prions
prions are ____ that are made from ____
infectious protein particles;
mutated genes
general virus replication:
step 1: virus chemically recognizes and attaches to the host cell at specific binding sites via…
spikes or polypeptides
general virus replication:
step 2: penetration, the whole virus/genetic material enters the ___ of the host
cytoplasm
general virus replication:
step 2: penetration, particles can be transported along ___ to specific sites and start replication there
microtubules
general virus replication:
step 2: penetration; what is uncoating?
nucleic acids of the virus leave the capsid and enter the host
general virus replication:
step 2: what does uncoating lead to
sensitization of the virus to nucleases
general virus replication:
step 3: viral DNA will tell the host cell to…
replicate the viral nucleic acids, make new viral enzymes, make new capsid proteins
general virus replication:
step 3: after the host cell makes the viral nucleic acids, new viral enzymes, and capsid proteins, they are all incorporated into ____
the hosts plasma membrane
general virus replication:
step 4: viral material is assembled into new particles with their ____
RNA or DNA polymerase
general virus replication:
step 5: ____ are released
new viral particles
RNA virus replication:
step 1:
virus enters the host
RNA virus replication:
step 2: RNA template is used to make DNA via _____
(tell me process and the enzyme responsible)
reverse transcription; reverse transcriptase
RNA virus replication:
step 2: reverse transcription of RNA to DNA yields _____
double helix RNA/DNA
RNA virus replication:
step 3: viral RNA is removed via ____
RNase H
RNA virus replication:
step 4: _____ replicates with the help of host enzymes
ssDNA
RNA virus replication:
step 5: duplex viral DNA integrates into the host DNA via which enzyme
integrase
RNA virus replication:
step 5: once the viral DNA is integrated into the host DNA it is then called _____
provirus
RNA virus replication:
step 6: the provirus makes ___ with help of the host enzymes
mRNA
RNA virus replication:
step 7: mRNA makes viral proteins that will ____ and can be ___
alter the host cells functions, cancerous
RNA virus replication:
step 8: virus is released via _____
budding
RNA virus replication:
step 8: budding might kill the ____
host cell
what are the human immune system defenders
T and B cells
survival of the host depends on…
severity of infection and immune response of the host
developing drugs to treat HIV is hard bc…
viruses can mutate and develop resistance
pts with HIV have chances getting _____ from other pathogens
opportunistic infections
what is the main target when choosing a drug to treat HIV
reverse transcriptase
Anti-HIV drugs that work by inhibiting reverse transcriptase will interfere with the ____ of HIV and stop the ____ of the viral particle
replication, synthesisw
what are the two kinds of anti-HIV drugs that inhibit reverse transcriptase
nucleoside inhibitors
non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
anti-HIV drugs can also inhibit ___ which will prevent the cleavage of viral proteins, maturation of the virus, and blocks the release of the virus
protease
anti-HIV drugs can also inhibit protease which will lead to
prevent the cleavage of viral proteins, maturation of the virus, and blocks the release of the virus