BFC2140
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
What is valuation principle?
The benefits and cost of a decision should be evaluated
the decision will increase market value when benefits exceeds costs
What is Franking credit?
The credit used by individual shareholder to reduce his/her own taxation liability
Define Agency problem
When managers, despite being hired as the agents of shareholders, put their own self-interest ahead.
What is limited partners?
Have limited liability
no management authority and cannot legally be involved in the management of the business
Define imputation system
Overcome the double taxation of corporate profits
allowing company to transfer a tax credit to the shareholder for the amount of the tax the company has paid
What is Arbitrage?
The practice of buying and selling equivalent goods in different markets to take advantage of a price difference
Law of one price
Market tries to push towards equilibrium where cashflow must have the same price.
Define Perpetuity
A stream of equal cash flows that occur at regular interval that lasts forever
Arrives at the end of the first period (payment in arrears)
Define Annuity and the type of annuity
A stream of equal cash flows that ends after some fixed number of payments.
Ordinary Annuity:
Pays at the end of the period
Annuity due:
Pay at the start of the period
What is a bond?
A tradeable debt security, usually issued by a government or semi government body to raise money
Received a fixed rate over a period of time
Repaid with interest on predetermined maturity date
What is a share trading when Coupon rate = discount rate?
the bond trade at par
What is a share trading when Coupon rate < discount rate? How does this affect the price and value?
price < par value the bond trade at discount
price is less than par value
which is not valuable to investors
What is a share trading when Coupon rate > discount rate? How does this affect the price and value?
par value The bond trade at a premium
Price is more than par value
What are the factors that would impact the bond price?
1. Interest rate changes
Market interest rate increase =the YTM also increases
Higher YTM = investors demand for a higher return for the bond
Leads to higher discount rate =reducing present value and the bond's price
Time affect
Zigzag pattern
Price slowly rising as coupon payment nears
Drop after payment has been made
Interest rate risk
Unexpected changes in interest rate --> risk that arises for bond owners
Greater time to maturity = greater interest rate risk
Lower coupon rate = greater interest rate risk
What is share equity?
Corporate create and issue shares to raise equity capital, and incur a cost of equity
More difficult to value due to uncertainty of promised cash flow and have no maturity
Part ownership in a company
What are the types of shares?
ordinary shares
preference shares
partly paid shares
Define ordinary shares
Carry no special or preferred rights
The right to vote and participate in any dividends or an distribution of assets
Define preference shares
Priority or preference over ordinary shareholders to payments of dividends
Voting rights are restricted
Many different types of preference shares
Define partly paid shares
Issued without the company requiring payment of the full issue price
The company is entitled to call for all or part of the outstanding issue price
Shareholder is legally obliged to pay for the call
Similar rights as ordinary shareholder
What is the difference between a public and private corporation?
Public corporation is listed on the ASX and their shares are traded on an exchange, while shares of private corporation are not traded on a public exchange.
What is the difference between primary and secondary market?
A primary market is where the company sells shares of itself to investors. The secondary market is where investors can buy and/or sell the company's shares with other investors.
What is a corporation’s key objective?
The corporation key objective is to generate a profit and maximise the wealth of its shareholders, as well as generating a long term value.
What are the key tasks a corporation financial manager should undertake?
Investment decision-Includes weighing the benefits and cost of a potential investment to be qualified as good use of money
Financing decisions-Whether to raise more capital or obtain a bond during difficult financial situation
Management of cash flow from operating activities-ensure the business has enough cash on hand to meet day-to-day activities
What is a bond issuer?
View the bond as a liability
Received the money from the bond
Obligated to pay the periodic interest payments
Obligated to pay the principal amount and the final coupon payment
What is a bond holder?
a lender (investor) --> seek a steady stream of income
View the bond as an asset
Highlight the difference between yield and coupon rate.
Coupon rate is the interest rate on the bond issued by the issuer, and is determined by the issuer
Yield rate is the required rate of return demanded by the bond investor, and is determined by the investors
Define NPV
The difference between the net present value of the benefit and net present value of cost
A range of discount rate
How to evaluate projects with different lives?
Using Matching cycle or replacement chain approach or EAA
What are the advantage and disadvantage of NPV?
Advantage:
Uses cash flows
Discount cash flow properly
consider the time value
Direct application of value principle
Disadvantage:
Relies on accurate estimate of discount rate
can be time consuming to compute
Define IRR
Sets NPV of cash flows equal to zero = average return of investment
Summarises the merit of a project
The higher the IRR = the better it is
When IRR<k = generates insufficient return
IRR > k = project's rate of return is greater than cost
The required rate of return is the minimum return that a project must earn in order to be acceptable
Define EAA
Intention of comparing projects with different lives
Takes NPVs and spread across the lives
Computing the annuity = PMT
Define conventional CF projects
A negative cash flow is followed by a series of positive cash flows
Define non-conventional CF projects
Two or more changes of signs - different cash flows
What is payback period?
Number of years required to cover a project's cost
Only accept if the payback period is within the specified want
What are the pitfalls of IRR?
Mutually exclusive projects = where k<crossover rate creates a conflict between IRR and NPV, but k>crossover rate there is no conflict
IRR is not feasible
Multiple rates of returns, such as non-conventional cfs
Lending project and borrowing project can have the same IRR
Define profitability index
For project ranking and capital restrictions
When have capital rationing issue
Investment return measurement
Finds the ratio
Higher PI = better
What to leave out in an incremental cash flow?
sunk cost
research cost
accounting income
allocated overhead
financing cost
What is a free cash flow?
the left over cash after counted for investments in working capital and long term assets
amount that is generated for a project
What is NWC?
Short term in nature
To be settled in cash within a year
Managing working capital is critical to a firm because the working capital usually ties up funds that could be deployed elsewhere in the firm to earn returns or distribute to shareholders
Minimising NWC to maximise FCF/ the firm value
If depreciation expense is not a cash flow, why do we have to subtract it and add it back? Why not just ignore it?
It is important to include depreciation because it provides a tax saving or tax shield, where it affects the cash flow positively by reducing the taxable income.
Define break even analysis
A financial tool used to determine the point at which a business or project generates enough revenue to cover its total costs
The minimum level of sales or output to break even
The level of a parameter = NPV is zero
Define sensitivity analysis
A capital budgeting tool that determines how the NPV varies as a single underlying assumption is changed
How responsive is the output to changes in variables
Assessing the sensitivity of NPV calculation to the uncertainty about the cost of capital used as the discount rate
Define scenario analysis
Determines how the NPV varies as the number of the underlying assumptions are changed simultaneously
Analysis situations involving major economic shocks
Define Decision tree analysis
Evaluate risky investments that involve sequential decisions
Enable decision maker to study the various decision points in relation to subsequent chance, events and choose from alternatives
Shows magnitude, profitability and inter-relationship of all possible outcomes
Relationship between present decision and future events
Taking account of the probability of various events occurring and the effect of those decisions on the NPV of the project
How do you calculate average daily COGS or sales?
COGS/365 or sales/365
What does negative cash conversion mean?
The firm generally receives cash before it pays its supplier.
What is a trade credit?
An agreement between customer and supplier
Customer can purchase goods without paying cash upfront but at later scheduled date
The difference between receivables and payables that is the net amount of a firm's capital consumed as a result of those credit transactions
For buyer can calculate the cost of giving up the discount of EAR = (1+r)^n-1, where n is 365/days (full term days- days pay before discount) and r is dollar of discount/amount left to paid
Trade credit : Pros and Cons for buyers
Pros for buyers:
Improve cash flow because payment is not due till later
Simple and easy access to financing at no extra cost
Improves the customer's business profile as well as the relationship with the suppliers
Cons for buyers:
High cost if payment are not made on time due to penalty charges or negative impact on the business profile
Trade credit : Pros and Cons for sellers
Pros for sellers:
Strong relationship with its clients and encourage customer loyalty
Higher sales volumes as buyers are more likely to purchase more when there are no additional cost
Cons for sellers:
Delayed revenue = may impact operating cost
Risk of buyers not paying
What should the firm do when the effective annual cost of buyer is more than interest rate?
A high EAR is the cost the buyer will bare if they choose not to take the discount
If bank charge less interest compared to the EAR then the buyer should take the discount because when they borrow money the cost is less than not choosing to take the discount and they can use the money to pay for the supply to get that benefit.
What are the type of accounts receivable managements
Accounts receivable days:
The average number of days that it takes a firm to collect on its sales
Aging schedule:
Categorises accounts by number of days they have been on the firm's books
Can be prepared using either the number of accounts or the dollar amount of the accounts outstanding
Payment patterns:
Provide information on the percentage of monthly sales that the firm collects in each month after the sales
Explain what is stretching payable account and the consequences.
When a firm pays its account payable after the term days.
Cheaper cost of borrowing
However, could impose cash on delivery or discontinue any business with the firm altogether.
Inventory management
Holding appropriate level to help prevent stock outs
Holding too much inventory can be costly = acquisition cost +carrying cost
Just in time (JIT) inventory management = when a firm acquires inventory precisely when needed so that inventory balance is always zero or very close to it
What is the importance of cash management?
Cash earns zero to no interest
The cash can be used for day to day operation needs, precautionary balance (unexpected losses) and compensating balance (bank requirements)
Cash can also be used for alternative investments, such as short term investments that can be turned into cash easily
Define measuring return
Measure of profit on an investment
Can be measured over any interval of time
Higher risk requires higher return = expected return
Risk is uncertainty associated with future possible outcome
doesn’t provide good indication even with decade long of historical data = share are volatile
Define variance
average value of squared deviations from mean. A measure of volatility
Define standard deviation
square root of variance and a common proxy for risk
Holding period return (HPR)
Total return received by an investor from holding an asset or a portfolio of asset over a period of time
Useful to compare returns on investment purchased at different periods of time
Considers not only the appreciation of the asset but also the income payments
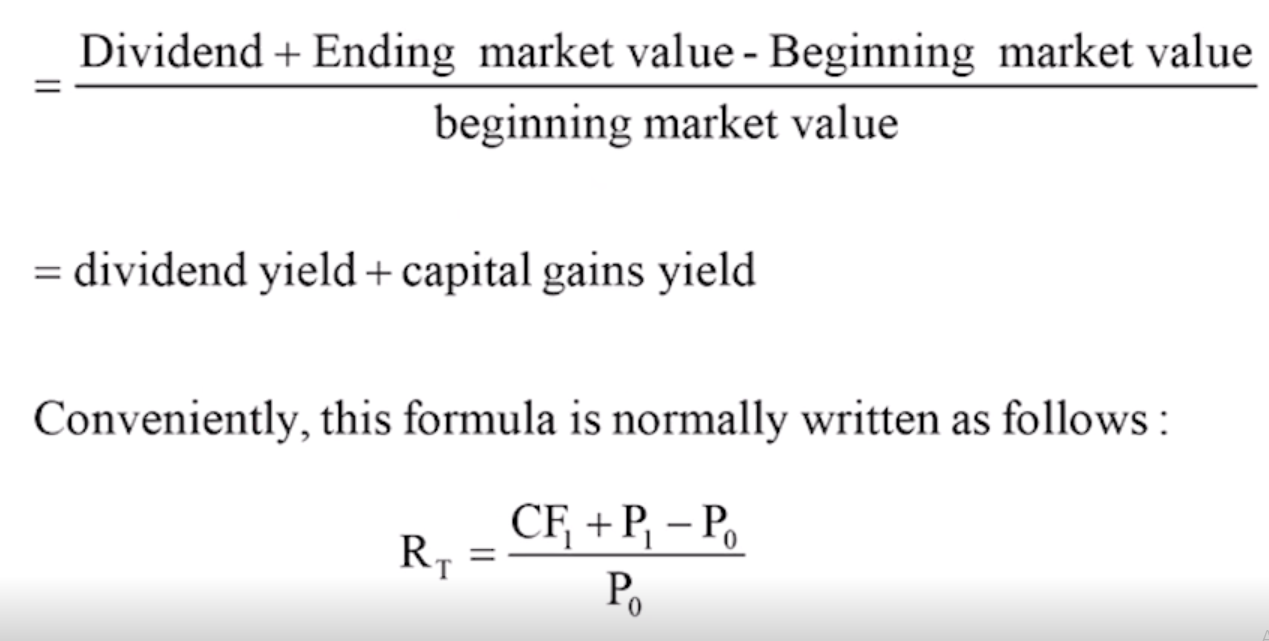
What are the methods to calculate expected return?
Using a probability distribution (Individual security)
Using a time series approach
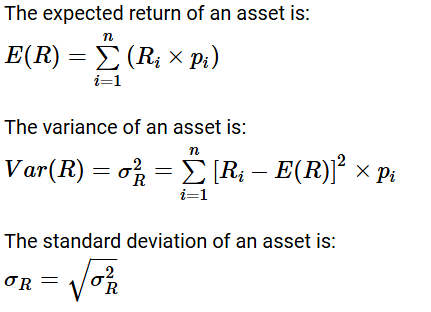
probability distribution (Individual security) method
There is uncertainty associated with returns from shares
Assuming that we can assign probabilities to the returns expected
The sum of return of the product of return* probability
Risk is measured in terms of how much a particular return deviates from an expected return
Time series method
Use historical stock market data
Assume that the distribution of the past returns can be useful in some way to estimate the possible future returns for the investors
N is minus 1 because it is a sample historical data
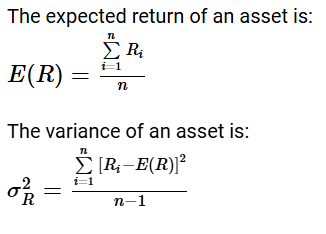
Define coefficient of variation
Statistical measure that compares the risk-to-return relationship among different assets/securities
How much risk faced by an investor on a security per unit of return
The lower the cv the better
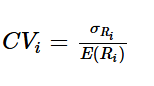
Define a portfolio
A collection or combination of many assets that are of different asset classes such as stocks, bonds, cash, real estate and more
To balance risk and return based on the investor's risk tolerance, time horizon and investment goals = diversification = risk minimization
Weighted average of the return of all the assets in a portfolio
Portfolio risk is not a weighted average
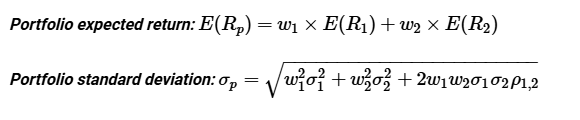
Define correlation
Combining the two assets in the same portfolio may reduce the portfolio risk = if they are not perfectly or positively correlated with another asset
Measure of the extent to which two securities' returns tend to move together
Closer to 1 = the assets are highly correlated so when one asset decrease the other also decreases
Closer to -1 = the assets are less correlated so when one asset decrease the other may increase
Range from -1 to +1
Degree of co-movement

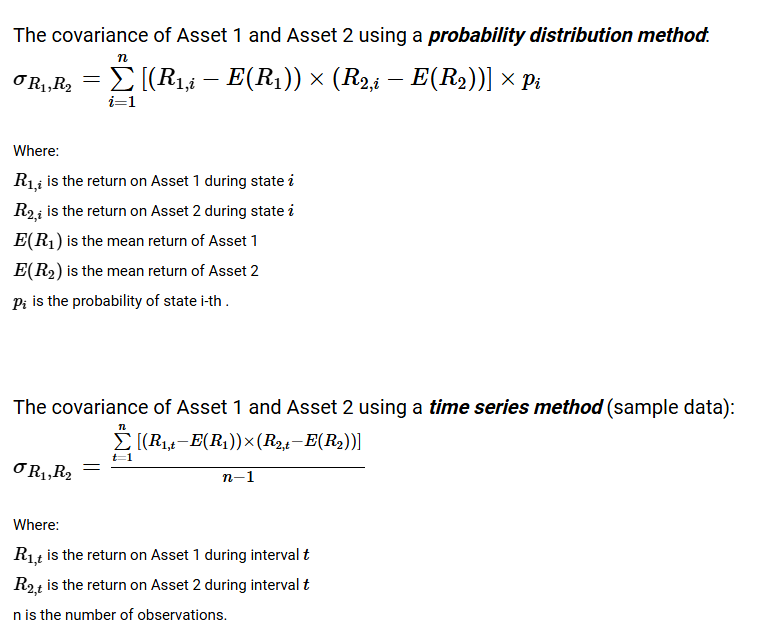
Define Covariance
Covariance = a measure of correlation = (-infinity, infinity)
Unsystematic risk
Risk factors affecting only that firm
Also called diversifiable risk
Can be removed by holding a well diversified portfolio
systematic risk
Economy-wide sources of risk that affect the overall stock market
Depend on its sensitivity to the effects of these market-wide factor
Risk premium of a security is determined by its systematic risk and does not depend on its diversifiable risk
No relationship between volatility and average returns for individual securities
Define beta
Best measure of the risk of a security in a large portfolio
Measure the responsiveness of a security to movements in the market portfolio
If:
Beta =1, stock is as risky as the market
Beta >1, stock is riskier than the market
Beta <1 stock is less risky than the market
Beta = 0, the security has no relationship with the market
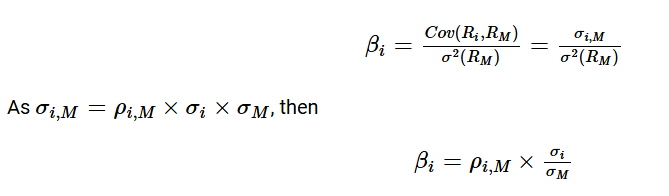
Define CAPM
Expected return= risk-free rate +risk premium for systematic risk
Expected return = risk-free rate + (beta*market risk premium)
Only high systematic risk will result in higher expected return
Used to determine the expected return on investment based on its systematic risk
Calculate required rate of return considering risk-free rate of return, expect market return and the systematic risk of that investment
allows to infer beta based on historical data = more accurate estimates of returns for shares than historical average return
Security market line
The linear relationship between expected returns for individual securities and systematic risk, measured by beta
The line can move because of inflation = expecting a higher compensation
Above the SML = underpriced because it is generating a higher expected return than the systematic risk provided
Below the SML = overpriced because it is generating a lower expected return than the systematic risk provided
Define cost of capital
The rate of return the firm must earn to maintain its market value and attract investors
Project > COC = profitable and adds to the firm's value
Project < COC = will harm the firm's value
Types of cost of capital
Also known as WACC
Combination of cost of debt and cost of equity
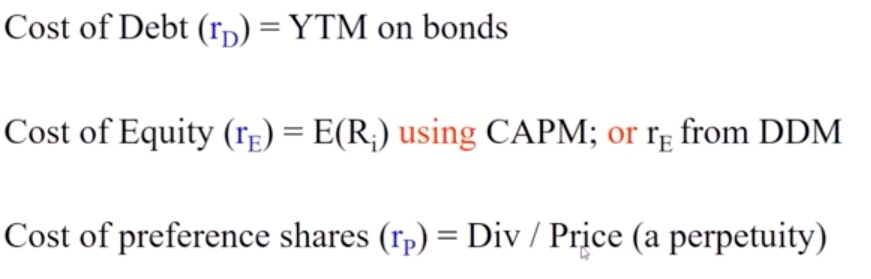
Cost of debt
The required rate of return on the company’s debt
It is the YTM to an existing debt and not the coupon rate
Interest paid on debt is tax deductible
Kd*(1-T) = because interest expense reduces tax liability
Cost of preference share
Pay a constant dividend every period = perpetuity
R= d/p
Cost of equity
Return required by investors given the risk of the cash flow from the firm
dividends are not tax deductible so there is no impact on the cost of equity
WACC
it is the average required return on the asset based on market’s perception of those risk
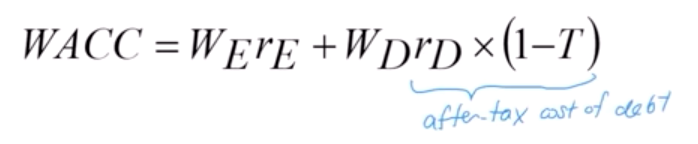
WACC with preference shares
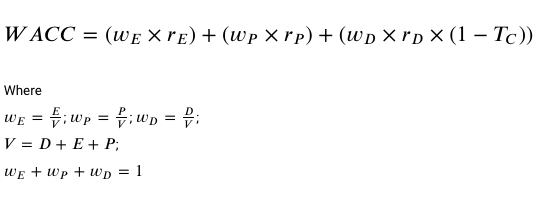
Why is cost of capital important?
Provides an indication of how the market views the risk of the companies assets
Can help determine the required return for capital budgeting
What are the assumptions to value a project using WACC?
Average risk:
assume that the market risk of a project is equal to the average market risk of the firm’s investment
Constant debt-equity ratio:
assume that the firm adjusts its leverage continuously to maintain a constant ratio of the market value of debt to the market value of equity
Limited leverage effects:
assume that the main effect of valuation follows from interest tax deduction
What are the limitation of WACC?
WACC is only appropriate to evaluate projects with systematic risks that are exactly the same as those for the company as a whole
only used to evaluate projects varying levels of risk = discount rate may be too low or too high in some cases
When should WACC be used to evaluate individual security?
the level of systematic risk for that project is the same as the overall portfolio of projects that currently comprised in the company
the project uses the same financing mixed
What is a perfect capital markets?
Securities are fairly priced. = same set of securities are traded at competitive market prices equal to the present value of their future cash flows
No tax consequences or transactions costs or other cost associating with financing decisions or security trading
Investment cash flows are independent of financing choices. = are not based on financing decisions but by return on investment
Define leverage
Levered equity is where the firm has outstanding debt
leverage will increase the risk of the firm’s equity and raise its equity cost of capital
What is Modigliani and Miller theory in a perfect market?
in an unlevered firm, cash flows to equity equal the free cash flows from the firm’s asset
in a levered firm, the cash flows are divided between debt and equity holders
The total to all investors equals the free cash flows generated by the firm’s asset
What is MM proposition 1 ?
In a perfect capital market, the total value of a firm is equal to the market value of the free cash flows generated by its assets and not affected by its choice of capital structure
VL= E+D = Vu
What is home made leverage?
investors use leverage in their own portfolios to adjust firm’s leverage
it is a perfect substitute for firm leverage in perfect capital markets
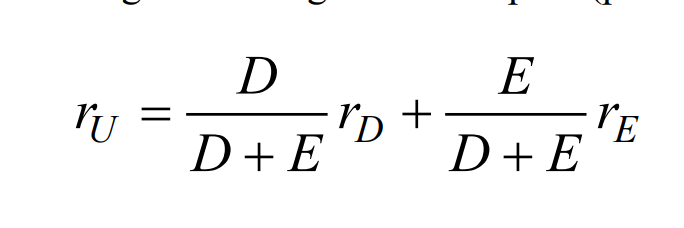
What is MM proposition 2 ?
The cost of equity increases in a manner to offset exactly the use of cheaper debt funds, to compensate the associated risk
the cost of levered equity equals to the cost of unlevered equity, plus a premium proportional to the debt-equity ratio
the more debt used, the more return equity investors are expected to compensate for the increased risk
What is interest tax shield?
When a firm uses debt = provides a corporate tax benefit each year
The value of the tax saved due to deductibility of interest expense
Increases amount paid to investors
Interest tax shield = corporate tax rate * Interest payments
If increasing debt also increases the firm value, why not shift to 100% debt?
With more debt, there is greater chance that the firm will default on its debt obligations
a firm that has trouble meeting its debt obligation is in financial distress
What is trade off theory?
the total value of a levered firm is equal to the value of the firm without leverage plus the present value of the tax savings from debt, less the present value of financing distress cost
suggests that an optimal level of debt exists = when marginal cost and benefits are equaled = levered firm is maximised
cost of financial distress decreases the value of the firm = increases with probability of default = increase level of debt
Agency costs can reduce the firm’s value = if there is excessive risk taking or under investment problem

What are the qualitative factors used to determine the pv of financial distress cost?
the probability of financial distress
the magnitude of the direct and indirect costs related to financial distress that the firm will incur
What does trade off theory resolve about leverage?
the presence of financial distress cost can explain why firms choose debt levels that are too low to fully exploit the interest tax shield
Differences in magnitude of financial distress costs and the volatility of cash flows can explain the differences in the use of leverage across industries
What is asymmetric information?
When managers’ information about the firm and its future cash flows is likely to be superior to that of outside investors
managers use leverage to convince investors that the firm will grow
What is market timing?
Market timing is an asymmetric information
the proposition that managers sell new shares when they believe the share is overvalued, and rely on debt
retained earnings if they believe the share is undervalued
What is Pecking order Hypothesis?
managers have a preference to fund investment using retained earnings, followed by debt, and will only choose to issue equity as last resort
different from trade off theory
does not suggest an optimal capital structure, but rather addresses the impact of information asymmetries between company managers and outsiders
How should a financial manager determine the right capital structure for the firm?
The firm should increase its leverage to a point at which the tax savings resulted from increasing leverage are just offset by the increased probability of incurring the costs of financial distress.
What is Efficient Market Hypothesis? (EMH)
The price of the security accurately reflect the information available
If the market processes new information efficiently, the reaction of the market prices to new information will be instantaneous and unbiased
Investors cannot earn abnormal returns by using information that is already available
Define Overreaction
Initial price movement can be expected to be reversed
Define Underreaction
Initial price movement can be expected to continue
Define weak form efficiency
the information contained in the past sequence of prices of a security is fully reflected in the current market price of that security