Market failure and socially undesirable outcomes 3 : Market power (HL only)
1/32
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
33 Terms
revenues definition
payments that firms receive when they sell the goods and services that they produce.
total revenue vs average revenue
total revenue = PxQ → amount of money a firm gets when they sell a g/s
average revenue = TR/Q = P → revenue per unit output sold
marginal revenue
formula = change in TR/ change in quantity
additional revenue from producing one more unit of output
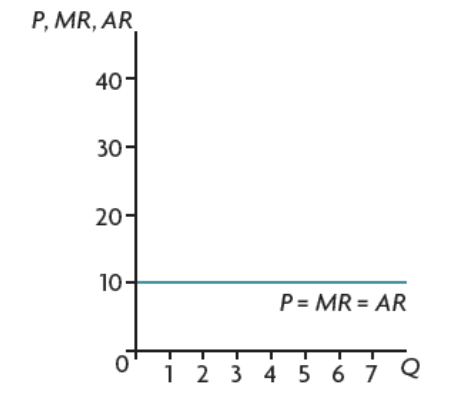
average + marginal revenue for price taker firms
AR=MR=P
straight horizontal line → price is constant
price taker vs price maker
price taker → cannot control the price → exists with perfect competition (price does not change with output)
price maker → can set their own price → monopoly, oligopoly, monopolistic competition (price changes with output)
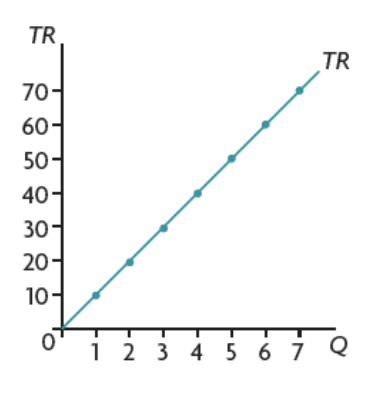
total revenue for price taker firms
increases by the same amount
examples of firms that are price takers
agricultural farmers
commodity producers
individual stock investors
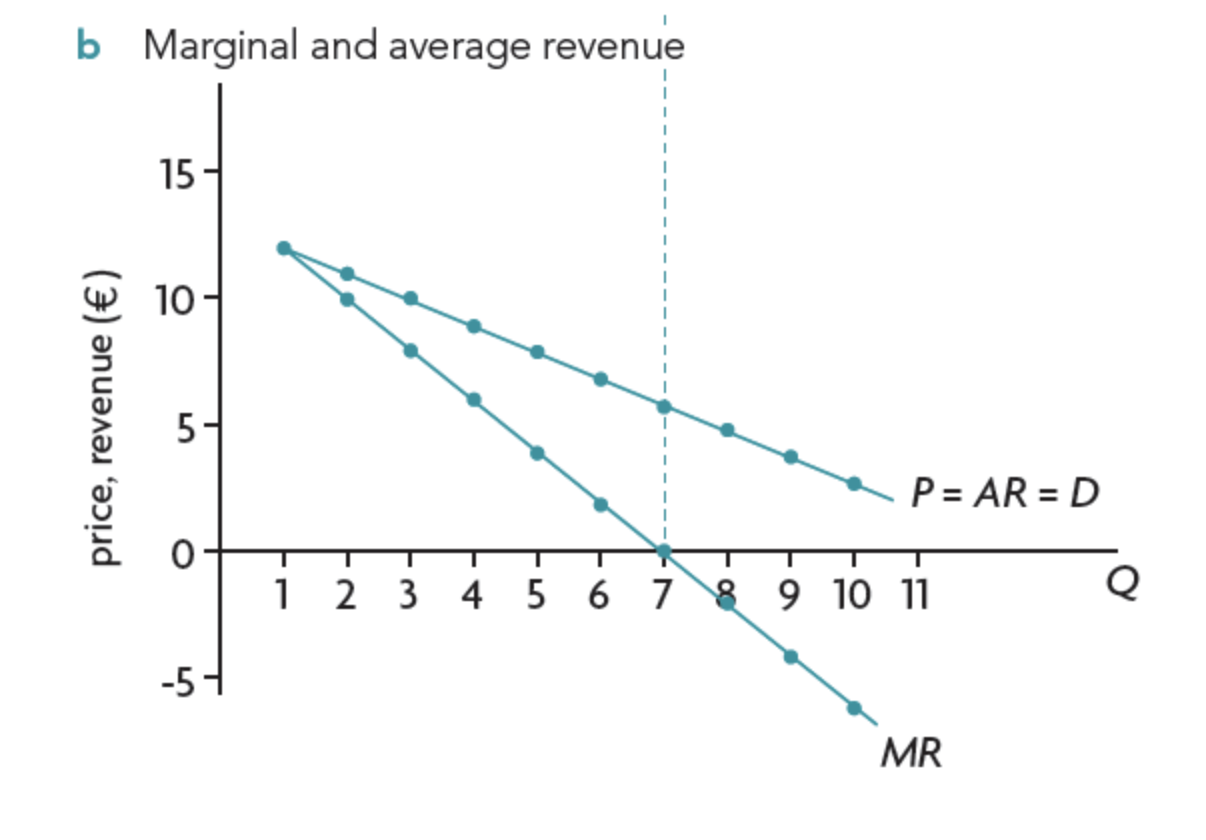
Average revenue + marginal revenue for price taker firms
MR is twice as steep as AR
MR is negative → firm is loosing revenue with each extra unit of output
when MR = 0 TR is at maximum
Total revenue for price taker firms
revenue is maximized at the local maximum (where MR=0)

PED and TR
PED is rel. elastic → price increases → TR increases
PED is rel. inelastic → price increases → TR decreases
costs of production definition
payments by firms to obtain and use factors of production in their production process
fixed vs variable costs definition
fixed - costs that don’t change with output (short run)
variable - costs that change with output
Total costs
total amount of money spent on producing a certain quantity
= fixed + variable costs
Average costs
costs per unit output produced
average fixed costs + average variable costs
Marginal cost
additional costs to produce an extra unit of output
= change in total costs / change in quantity
the relationship between average costs + marginal costs in the short run
MC<AC → average cost is falling
MC>AC → average cost is rising
MC intersect AC at AC’s minimum

what is meant by short run vs long run
short run - at least one factor of production is fixed
long run - all factors of production are variable
total product vs marginal product
total - the total quantity of output produced by a firm
marginal - the additional output that results from one additional variable input
relationship between marginal and total product
when MP=0, TP is maximized
when MP is rising TP rises faster
when MP is falling TP falls slower
relationship between marginal and average product
MP>AP → AP increases
MP<AP → AP decrease
law of diminishing marginal returns
states that as more and more units of a variable input are added to one or more fixed inputs the marginal product of the variable input at first increases, but then it reaches a point after which the marginal product of the variable input starts to decrease
relation of marginal costs to diminishing marginal returns
marginal product increases → marginal cost decreases
when marginal product is at maximum → marginal costs is at minimum
when marginal product falls → marginal costs increase
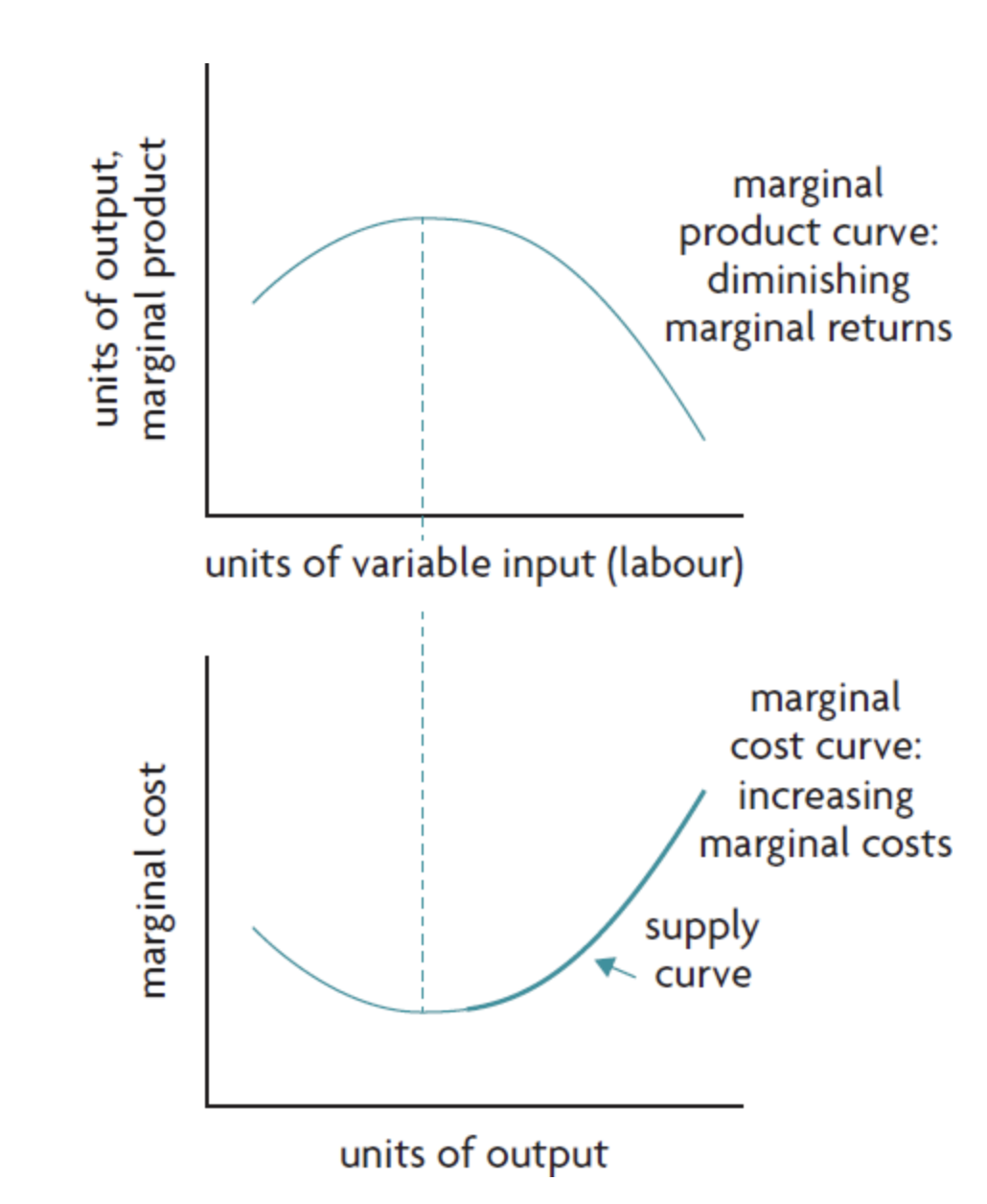
marginal costs and the firms supply curve
upward sloping part of MC curve = supply curve
the firm can only produce more output if the price of the good increases to cover the extra cost of each extra unit produced
explicit vs implicit costs
explicit - direct, out-of-pocket payments that businesses actually make, e.g wages, rent, materials, and utility bills.
implicit - opportunity costs - value of resources the firm already owns but could have used elsewhere (not used when calculating accounting profit)
profit formulas
revenue - costs of production
economic profit = total revenues - economic costs
total revenue - sum of explicit costs - implicit costs
(economic costs = implicit + explicit costs)
profit maximization
producing a level of output where the difference between total revenue and total costs is the largest
largest amount of profit
rewards for f.o.p
land - rent
labour - wages
capital - interest
enterprise - profit
→ the costs of a business
normal profit
the minimum amount of revenue that the firm must receive in order to keep the business running
TR=TC
normal profit also = the opportunity cost of running the business instead of doing something else.
abnormal/supernormal profit
TR>TC
more than normal profit is made
losses
TR<TC
less than normal profit is made
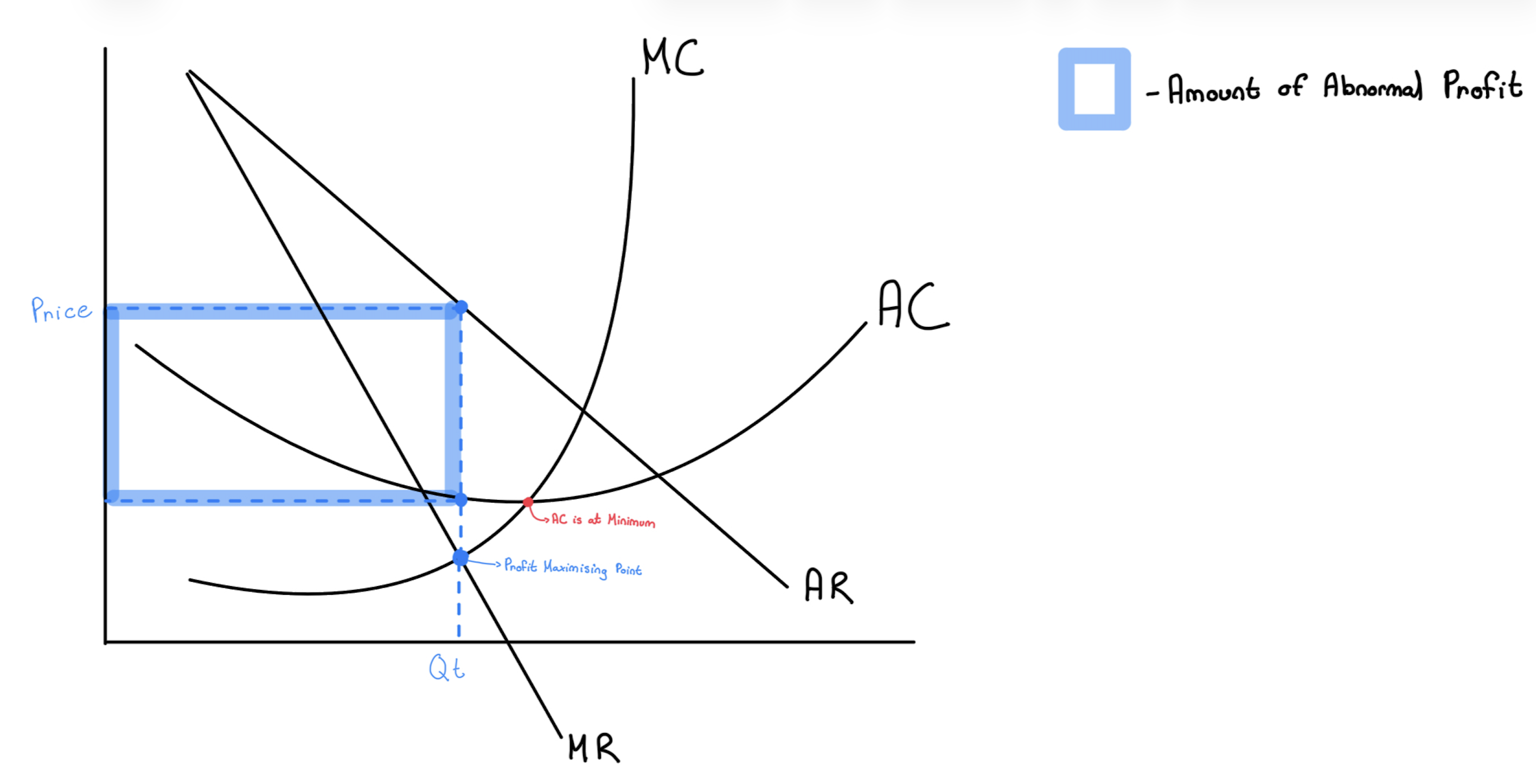
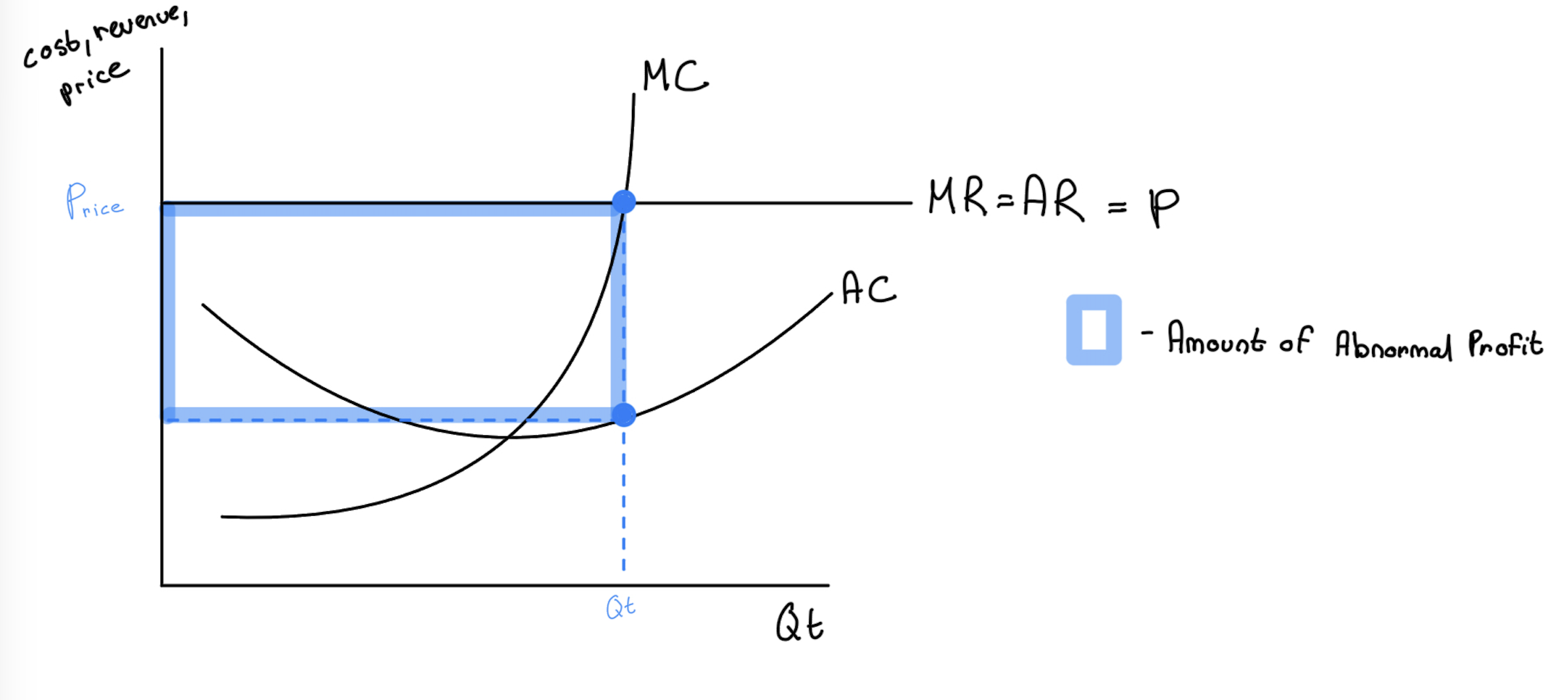
profit maximization - price takers
AR>AC → abnormal profit
AR=AC → normal profit
MC=MR → profit maximization
minimizing loss - price takers
when AR<AC
MC=MR → minimize loss

profit maximization - price makers
MR=MC
as long as MR>MC the profit can be increased by producing more units until the last unit of output brings not more profit (MC=MR)