Bio307 - Ch. 21 - Digestion
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/22
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
1
New cards
Gastrointestinal Tract (GI)
moves nutrients, water, electrolytes from external environment to the internal environment
2
New cards
Chyme
soupy substance created as ingested food is broken down by mechanical and chemical digestion
3
New cards
Salivary Glands
add exocrine secretions containing enzymes and mucous to the lumen
ex: amylase, which helps digest carbohydrates
ex: amylase, which helps digest carbohydrates
4
New cards
Digestion
chemical AND mechanical breakdown of foods into absorbable units
5
New cards
Absorption
The transfer of substances from the lumen of the GI tract to the ECF
6
New cards
Proenzyme
a biologically inactive precursor to an enzyme, which can be modified into an active enzyme when conditions are right
7
New cards
Motility
movement of food from mouth through the pharynx (throat), esophagus, stomach, small and large intestines and out of the body.
8
New cards
peristalsis
involuntary muscle contractions that create waves of movement, pushing the contents of the GI tract forward
9
New cards
segmentation
contractions of circular muscles, which involves mixing of the food to aid in digestion and absorption
10
New cards
lipase(s)
pancreatic enzyme that catalyzes the breakdown of fats to fatty acid + glycerol
11
New cards
amylase
enzyme that converts starch/glycogen to simple sugars
12
New cards
protease (endopeptidase)
endopeptidase: cleaves peptide bonds within the protein
exopeptidase: cleaves bonds at either terminal of a protein, resulting in cleavage of peptide bonds
exopeptidase: cleaves bonds at either terminal of a protein, resulting in cleavage of peptide bonds
13
New cards
gastroesophageal reflux (GERD)
when stomach acid repeatedly flows back into esophagus, and this backwash irritates the lining of the esophagus
14
New cards
gastric
relating to the stomach
15
New cards
diarrhea
feces is discharged frequently and in liquid form, a loose watery stool 3 or more times in a day
16
New cards
Recognize that the GI tract is a tube that is continuous with the external environment, is not subject to homeostatic regulation.
...
17
New cards
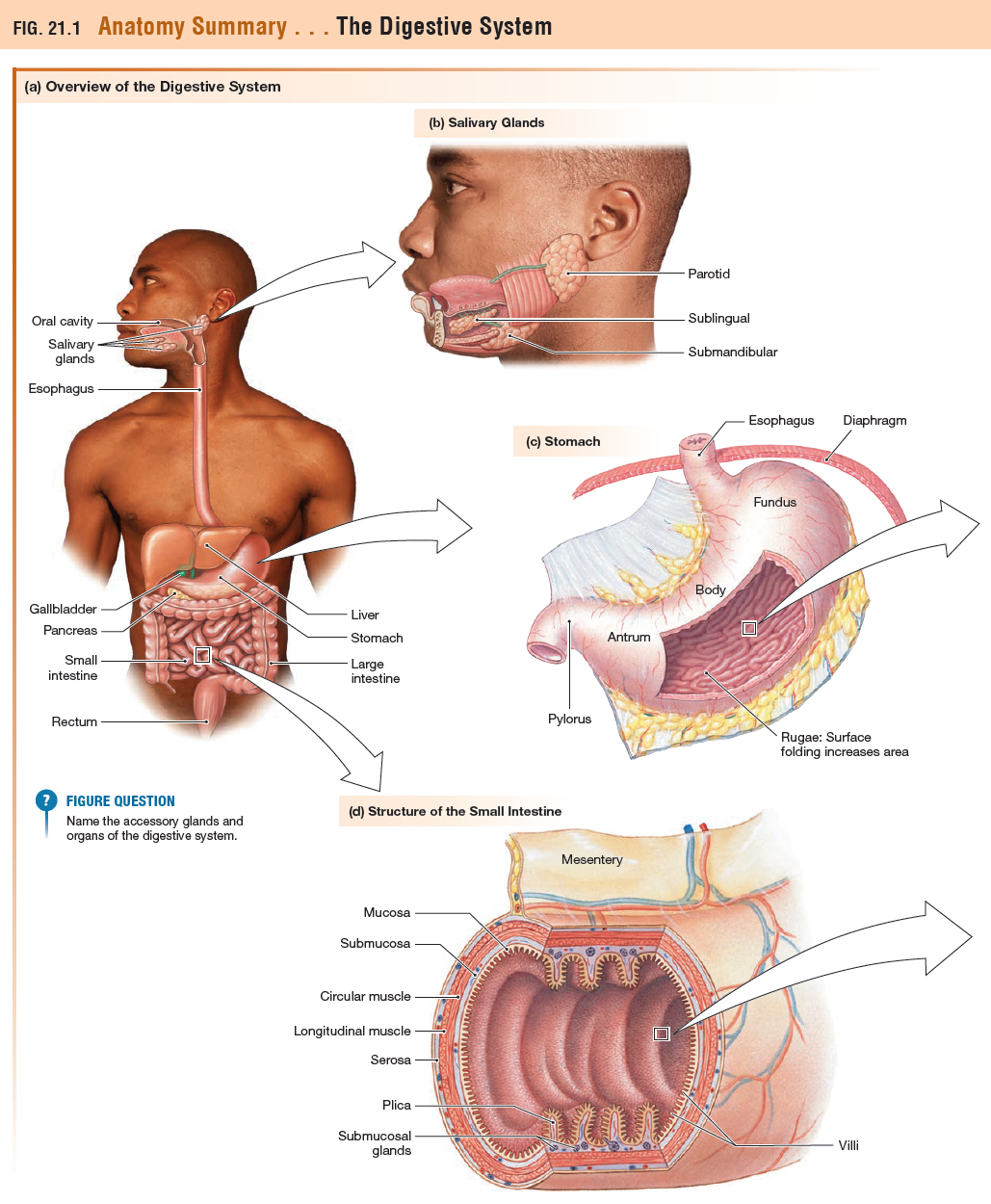
Label Figure 21.1a and 21.1d
...
18
New cards
List the 4 layers of the GI tract, inner to outer
Mucosa - epithelial
Submucosa - connective
Muscularis Propia (externa) - 2 layers of smooth muscle
Serosa - connective tissue
Submucosa - connective
Muscularis Propia (externa) - 2 layers of smooth muscle
Serosa - connective tissue
19
New cards
Provide the major functions of:
Saliva
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
Stomach
Gastric Acid
Pepsin
Small Intestine
Bicarbonate Secretion (into small intestine)
Brush Border enzymes
Bile Salts
Pancreas (digestive function)
The Liver (digestive functions)
gallbladder
large intestine
bacterial flora
Saliva
Lower Esophageal Sphincter
Stomach
Gastric Acid
Pepsin
Small Intestine
Bicarbonate Secretion (into small intestine)
Brush Border enzymes
Bile Salts
Pancreas (digestive function)
The Liver (digestive functions)
gallbladder
large intestine
bacterial flora
Saliva: contains enzymes (amylase) which help initiate breakdown of food
Lower Esophageal Sphincter: region of high muscle tension that acts as a barrier between the esophagus and the stomach, where the tension relaxes allowing bolus to pass into the stomach:
Stomach: storage, digestion, defense
Gastric Acid: releases pepsin (enzyme which breaks down proteins), triggers somatostatin release from D cells, HCl denatures proteins by breaking bonds, helps kill bacteria, and inactivates salivary amylase, stopping breakdown of carbohydrates
Pepsin: breaks down proteins
Small Intestine: 95% of absorption of nutrients
Bicarbonate Secretion (into small intestine): acid buffer, maintain pH balance
Brush Border enzymes: anchored to luminal cell membrane, degrade of nutrients into absorbable units
Bile Salts: breakdown of fats
Pancreas (digestive function): enzymes for sugar, fat, starch digestion
The Liver (digestive functions): secrete bile, purify blood containing the newly absorbed nutrients
Lower Esophageal Sphincter: region of high muscle tension that acts as a barrier between the esophagus and the stomach, where the tension relaxes allowing bolus to pass into the stomach:
Stomach: storage, digestion, defense
Gastric Acid: releases pepsin (enzyme which breaks down proteins), triggers somatostatin release from D cells, HCl denatures proteins by breaking bonds, helps kill bacteria, and inactivates salivary amylase, stopping breakdown of carbohydrates
Pepsin: breaks down proteins
Small Intestine: 95% of absorption of nutrients
Bicarbonate Secretion (into small intestine): acid buffer, maintain pH balance
Brush Border enzymes: anchored to luminal cell membrane, degrade of nutrients into absorbable units
Bile Salts: breakdown of fats
Pancreas (digestive function): enzymes for sugar, fat, starch digestion
The Liver (digestive functions): secrete bile, purify blood containing the newly absorbed nutrients
20
New cards
GI Tract: mouth to anus
1) Mouth
2) Esophagus
3) Stomach
4) Small Intestine
5) Large Intestine
6) Anus
2) Esophagus
3) Stomach
4) Small Intestine
5) Large Intestine
6) Anus
21
New cards
Why digestive enzymes are synthesized and secreted as proenzymes
localized activation, can be transformed into the active state when needed
22
New cards
Contraction Mechanism:
Peristalsis: pushes the food forward
Segmentation: mixes and combines the food
Segmentation: mixes and combines the food
23
New cards
How the small intestine provides a large amount of surface area on which nutrient absorption can occur
microvilli amplifies the surface area of diffusion