BIOL 300 Discussion: Mobile Genetic Elements
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
28 Terms
What are Transposons?
Movable DNA elements found in prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
Where are Transposons distributed?
All throughout the genome
Which organisms can have transposons?
Both Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes have transposons
What can silence Transposons?
Methylation and RNAi can silence transposons.
What is an Insertion Sequence (IS)?
A type of transposon that is found in bacteria.
What is Transposase?
An enzyme that recognizes inverted repeats, excises the sequence, and transports it to a new location
When Transposase moves a sequence to a new location what tends to occur?
The new location consists of a target sequence, it tends to become duplicated during insertion
Is excision via Transposase precise?
It is rarely precise, it will usually take nearby information and/or genes that can interrupt genes or promoters.
Composite Transposons: Sequence on arm of DNA?
Insertion Sequences
Composite Transposons: Genes
Transposase as well as additional genes carried away
Composite Transposons: Other genes
Carry other genes, such as antibiotic resistance genes
What are Terminal Inverted Repeats?
Sequences that are palindromes, jumps together with the transposon, and is the element recognized by the transposase.
What are Autonomous Transposons?
Transposons that contain ORF(s) that expresses transposase
What are Nonautonomous Transposons?
Transposons that do not contain ORF(s) or the ORF doesn't express functional transposase. utilizes LINEs enzymatic machinery for transposition.
What is a Palindrome?
a region of DNA in which the sequence of nucleotides is identical with an inverted sequence in the complementary strand: GAATTC is a palindrome of CTTAAG.
What is a Non-Replicative Transposition Mechanism?
It's a cut and past mechanism where a single copy remains.
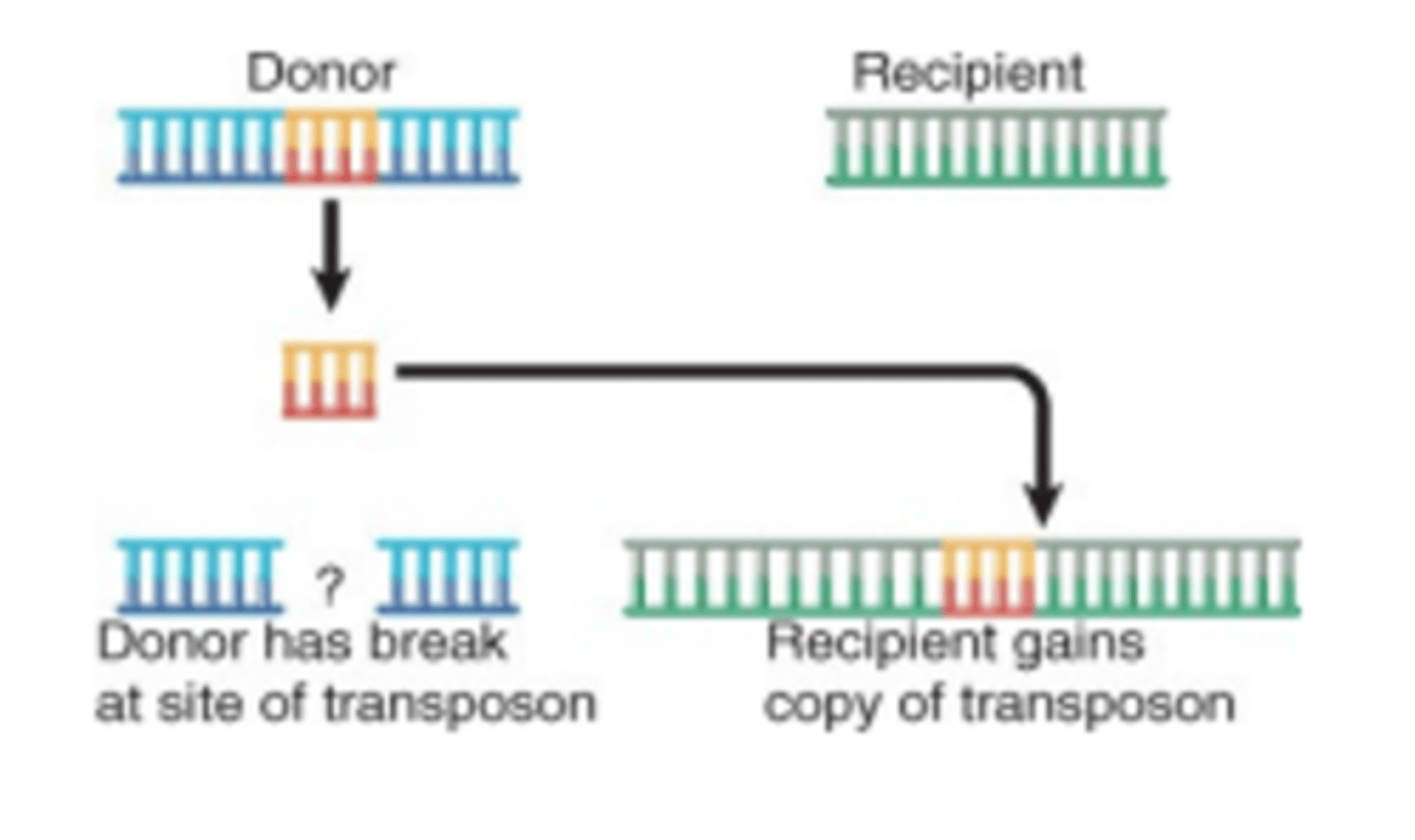
What is a Replicative Transposition mechanism?
It is a copy and paste mechanism that ends with more than one copy. Required Resolvase which is rare.
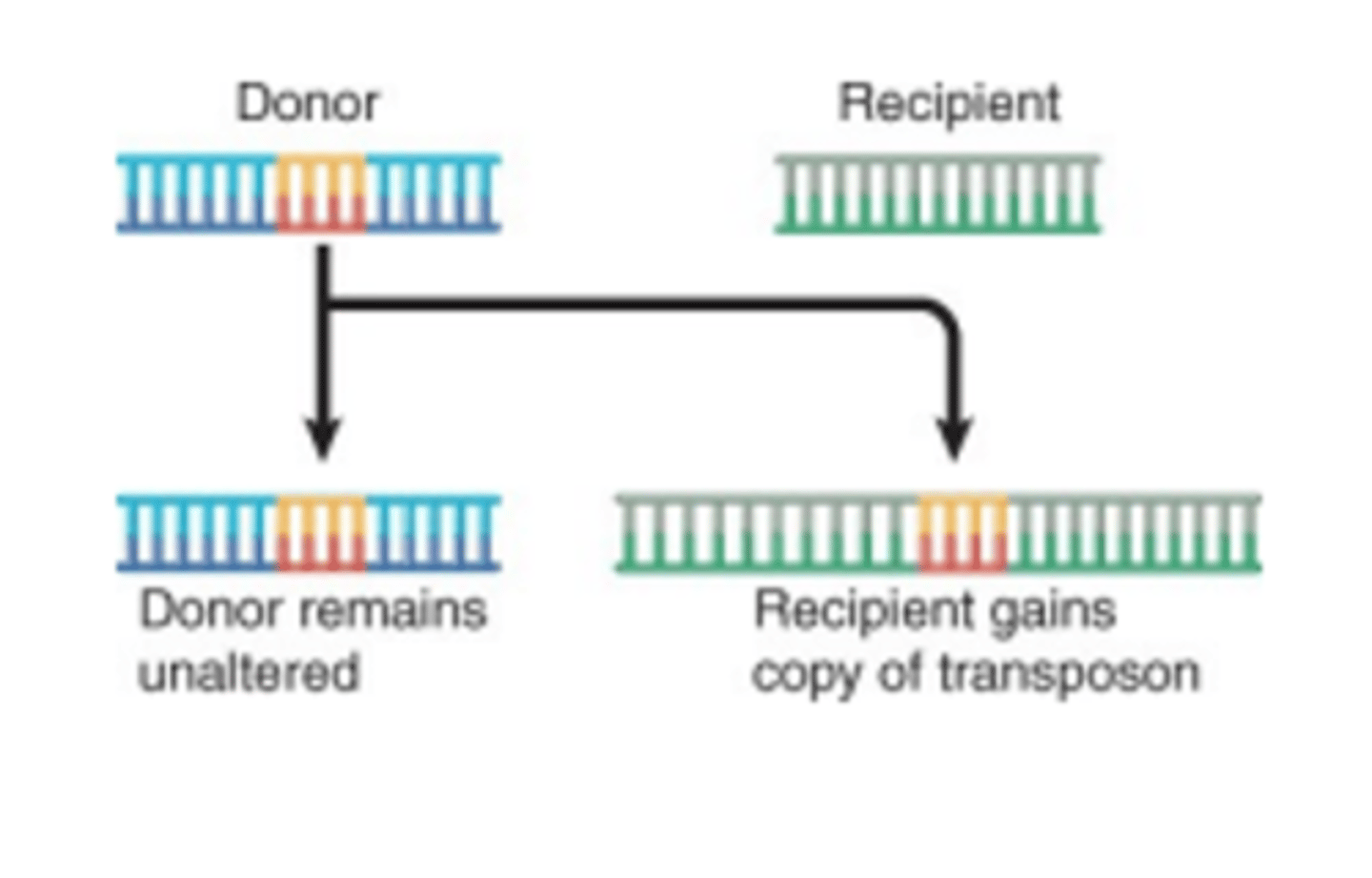
What is Resolvase?
Enzyme that assists in copy and paste mechanism which allows for duplication of transposon
What are Retroviruses?
Infections virus whose genome is RNA (ss or ds) that can recognize Long Terminal Repeats (LTRs) and converts RNA to DNA inside the host cells.
What is Reverse Transcriptase?
An enzyme that converts ssRNA to dsDNA
What is Integrase?
An enzyme that inserts the DNA copy of the viral RNA into the host genome.
What is a Gene Cassette?
Genes that have the same function and are located near one another
What are the 3 major gene cassettes
Gag, Pol, Env
What is gag?
Functions for packaging; in the matrix, capsid, and nucleocapsid
What is Pol?
Enzymes that are needed to process the retroviral genome into a state where it can be integrated; reverse transcriptase, integrase, and proteases
What is Env?
Signaling Proteins; Surface and Transmembrane proteins
What are Retrotransposons?
Genetic elements that can amplify themselves using an RNA intermediate.
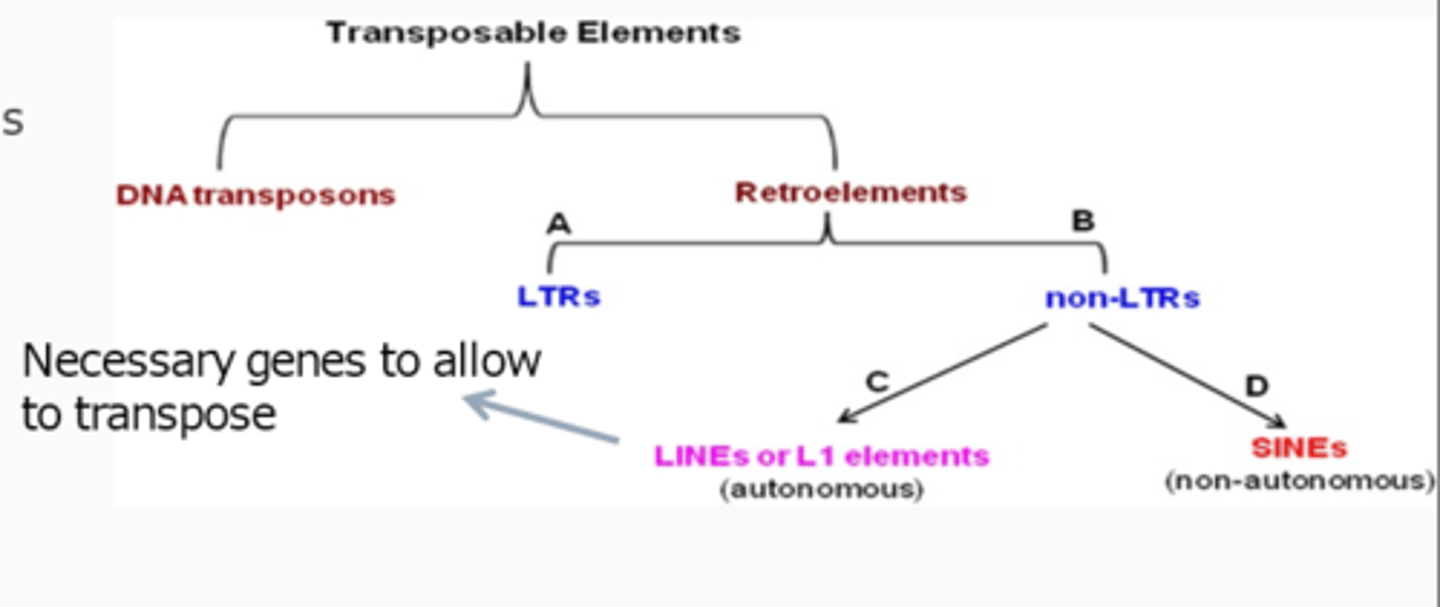
Structure of Insertion Sequence (IS)
Transposase gene Elements by inverted repeats (Palindromes)