Development and Biological Tools
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Natural selection has favored alleles that increase…
SA, leading to features like branched alveoli
John Gurdon Experiment
Replaced egg nucleus with skin cell nucleus and skin cell DNA can still function
If all cells have the entire genome, why do different cells express different proteins?
Alternative splicing, Different parts of genome activated and repressed, different TF being active, Translational regulation, Translational degradation
Translational Regulation
Blocking ribosomes from binding, using miRNAs, Alternating mRNA structure so ribosome can’t bind, controlling initiation factors
Translational degradation
Newly synthesized proteins or corresponding mRNA’s are broken down while translation is still occuring
What do model organisms need to have/do
Grow easily, easy to study (able to genetically modify, sequenced genome), quickly reproducing, research community
Examples of model organisms
mouse, fruit fly, yeast, arabidopsis
Mutagenesis Screens
Take plants and induce lots of mutations using (UV, EMS which induces a bunch of substitiutions), results: lots of plants with lots of mutations —→ look at phenotypes, mutations that affect plant development
How do I know which gene mutations are in
Next Gen Sequencing (PCR), we need to identify the specific mutation that is causing the messed up phenotype (pick candidate genes and rank genes based on what it involves)
Expression Pattern
Is the gene turned on in the right organs at the right place and right time
If the gene is necessary for the process..
Outcome will not occur without factor
If the gene is sufficient
Factor will ALWAYS cause outcome
In Situ Hybridization
Fluorescently label RNA/DNA complementary to the mRNA of target gene, add it to cells, see mRNA expression (only happens in dead tissues (have to open the cell to immobilize)
When do we use in situ hybridization
To find out where mRNA is, or if regulation is happening via degradation of protein
Fluorescent antibody staining
Antibodies (immune system proteins that can be easily developed to bind to any specific protein) with fluorescent markers against target gene, add them to cells, look for protein expression
3 ways to test expression patterns
fluorescent protein expression
Genes encoding fluorescent proteins can be fused to the gene of interest (or regulatory DNA) to see protein expression
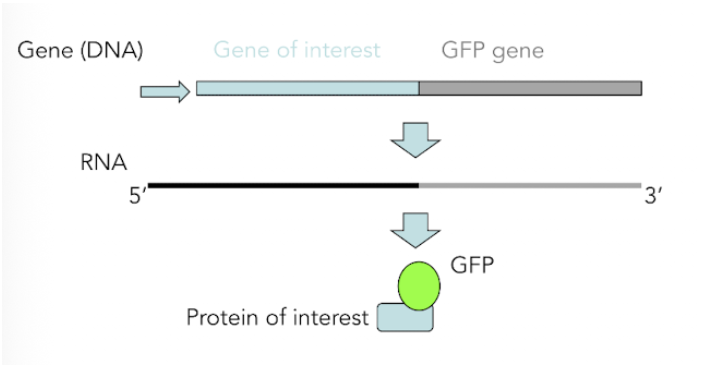
GFP
Wherever gene is expressed so if GFP (fusion of protein + GFP)
AP3
Part of a group of genes that tells us how flowers form different parts in specific positions
AAP3 is expressed in
the ring of cells in the developing flower (Helps plants make petals and stamens
What happens if we remove AP3
No petals form necessary for development

CRISPR
Can cut DNA at any sequence guided by 20 bp of guide RNA
How does the CRISPR method work
After cut, the mechanism to repair the DNA would ligate the broken ends together without a template, errors occur and the repair can add/remove bases causing a frameshift mutation that disrupts the gene
Overexpression
Forcing a gene to be expressed more than usual in places where its not normally active. Done by inserting a copy of the gene under a strong promoter in plants genome, adding regulatory DNA
By forcing AP3 into new areas we can see which
organs can be converted into petals/stamens
If we add AP3 gene with AP3 regulatory DNA, where will it be expressed?
Its expression is controlled by its regulatory DNA so the gene will be expressed in the same domain
PAX6
Transcription factors responsible for initiating eye development across many animals
Overexpression of PAX6 results in
Formation of whole eyes in wrong places
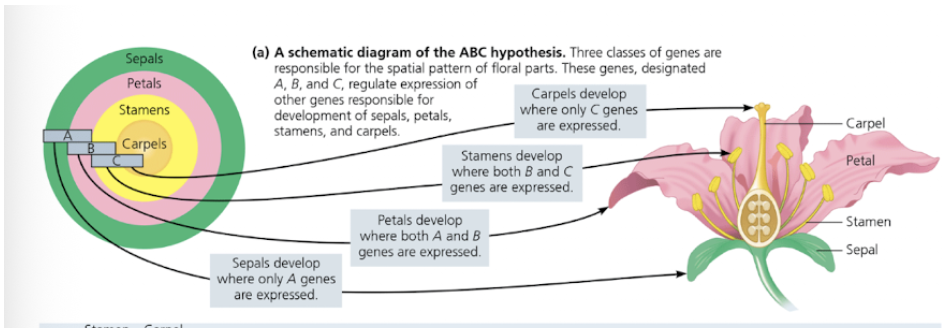
3 classes of genes responsible for the spatial pattern of floral parts
A, B, C regulate expression of other genes responsible for sepals, petals, stamens, and carpals
Combinatorial Control
TF work together to regulate expression of other genes, by combining in different ways, a small number of factors can regulate a large number of genes
Cells can integrate multiple signals through turning on
Combinations of TF
Stem Cells
They are able to make more cells like themselves (can self renew) and they can become other cells that have differen functions (differentiation), found in almost all tissues in the body
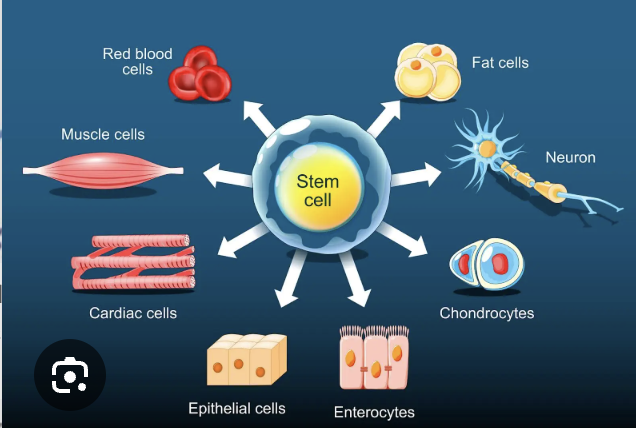
Stem cells are needed for
maintenence of tissues as well as repair after injury
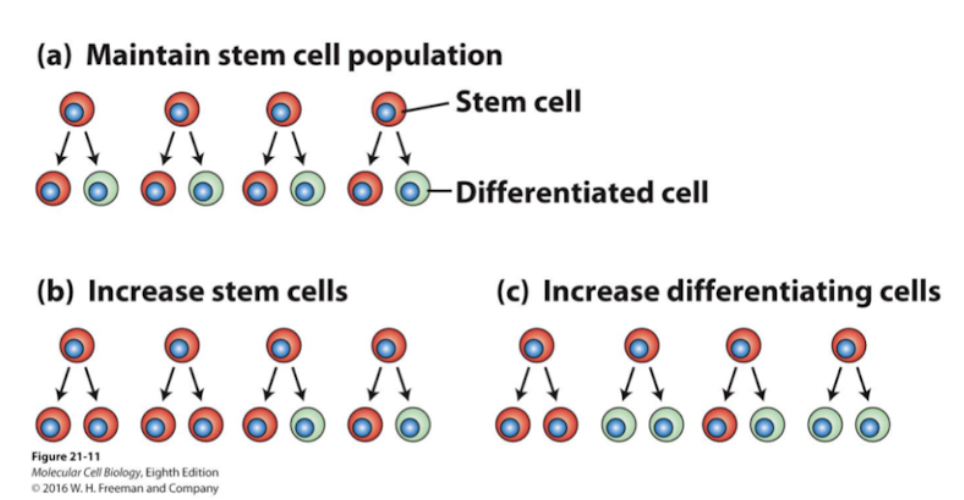
if the body needs more stem cells it will divide in a specific way to
result in 2 stem cells (usually during development/injury)
Different ways stem cells can divide
1 stem cell → 1 stem cell + 1 differentiated cell (increases differentiation)
1 stem cell → 2 differentiated cells (reduces the stem cell pool and increases differentiated cells quickly (used when tissues needs lots of mature cells fast
Anatomy
study of the biological form of an organism
Physiology
Study of the biological functions an organism performs
Proximate level of causation
Researchers who focus on the physical/chemical mechanisms responsible for function
Ultimate Level of Causation
Researchers who focus on how physiological systems evolved and how they impact fitness