Quiz 5: SBAS/ACS - St Peter
1/80
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
81 Terms
How much higher is the rate of end-stage kidney disease (ESKD) in racial/ethnic minorities compared with Whites?
Up to 3.9 times higher in racial/ethnic minorities, especially among Black, Native American, and Hispanic populations
What trends were observed in the CARDIA study comparing Black and White young adults?
Black individuals developed reduced GFR at a younger age than White individuals, showing faster kidney function decline
Which two chronic conditions most strongly contribute to higher CKD rates in Black persons?
Hypertension (most prevalent) and earlier onset of type 2 diabetes
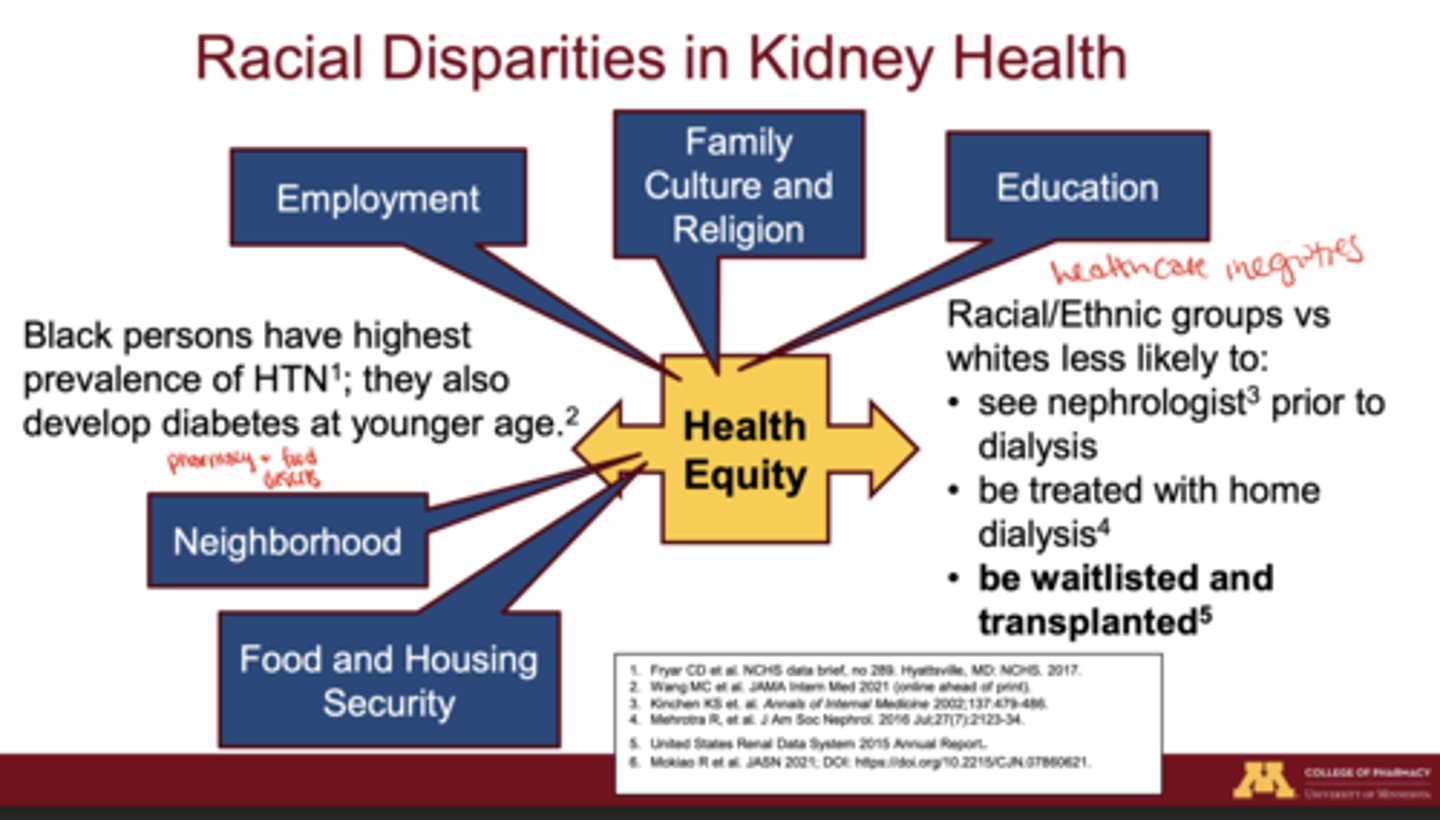
What healthcare inequities contribute to racial differences in kidney disease outcomes?
People of color are less likely to:
1. see a nephrologist before dialysis
2. be treated with home dialysis
3. be waitlisted for or receive transplant
What are 3 SDOH influencing CKD progressions in communities of color?
Neighborhood safety, food and housing security, education level, cultural and religious influences, and employment access
What medication use disparities exist among older Black patients with CKD and type 2 diabetes?
less likely to start SGLT2 inhibitors or GLP-1 receptor agonists and more likely to receive sulfonylureas
What are the clinical consequences of these prescribing disparities?
Greater risk for hypoglycemia and reduced protection against CKD progression and cardiovascular events
What may explain the lower initiation of newer diabetes drugs among minority populations?
High drug cost, limited insurance coverage, provider bias, and systemic access barriers
Why is assessing kidney function critical in CKD management?
It guides CKD staging, tracks disease progression, and informs dosing, initiation, and discontinuation of renally cleared medications
What are the three components of total kidney clearance?
Glomerular filtration + tubular secretion - tubular reabsorption
What is the "gold standard" for measuring GFR? Why isn't it commonly used?
EXOGENOUS Measured GFR using inulin, iohexol, or iothalamate is the gold standard but is too expensive and time-consuming for routine clinical
What are the main endogenous biomarkers used to estimate GFR?
Serum creatinine (sCr) and serum cystatin C (sCys)
What factors affect serum creatinine production?
Muscle mass, age, sex, diet (especially red meat), creatine supplements, and protein ingestion
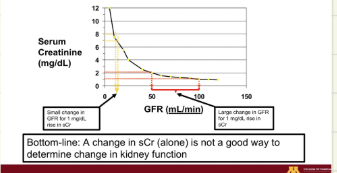
Why is serum creatinine alone a poor marker of kidney function?
Small changes in sCr can reflect large or small GFR changes, and sCr is influenced by non-GFR factors such as diet, muscle mass, and medications
What are examples of non-GFR determinants of serum creatinine?
Muscle mass, diet, tubular secretion, and medications such as trimethoprim or cimetidine
Why might cystatin C be preferred over creatinine in certain cases?
It's less affected by muscle mass and diet, making it a better reflection of filtration in individuals with extreme muscle mass or creatinine-altering drugs
When is cystatin C particularly useful for kidney function assessment?
In bodybuilders, amputees, patients on trimethoprim, or those with low muscle mass
What are non-GFR determinants that can affect cystatin C?
Smoking, obesity, inflammation, hyper/hypothyroidism, and glucocorticoid therapy
What are the limitations of cystatin C testing in practice?
High cost, limited lab availability (<10%), and lack of inclusion in standard autoanalyzer panels
What was found about African ancestry and serum creatinine?
Black individuals have higher average serum creatinine independent of age, sex, BMI, or comorbidities
Why was the "Black race factor" originally included in older eGFR equations?
studies showed higher serum creatinine at the same measured GFR in Black participants
What are problems with using "race" in clinical algorithms?
Race is a social, not biological construct
- clinicians often misidentify race
- pop. mixing makes race categories less meaningful
What are the three major modern eGFR estimating equations that removed race as a factor?
2021 CKD-EPIcr (creatinine)
2012 CKD-EPIcys (cystatin C)
2021 CKD-EPIcr-cys (combined)
Which eGFR equation provides the best balance of accuracy and lowest bias across racial groups?
2021 CKD-EPIcr-cys equation
Why is the Cockcroft-Gault equation less ideal for diverse populations?
derived from a small group of White men and tends to overestimate GFR in both Black and non-Black individuals
How can using race-adjusted equations impact patient care?
They may overestimate GFR in Black patients, delaying CKD diagnosis and transplant eligibility
What is the "balanced bias" observed in race-free equations, and why is it problematic for drug dosing?
New equations may slightly underestimate GFR in Blacks and overestimate in non-Blacks
**acceptable for CKD staging but risky for renally dosed medications
What are the pros and cons of using the 2021 CKD-EPIcr equation?
Pro: Balanced bias
Con: Underestimates mGFR in Black patients, risking underdosing
What are the pros and cons of using the 2021 CKD-EPIcr-cys equation?
Pro: Most accurate and least biased
Con: Higher cost and limited cystatin C availability
What is the clinical implication of removing race from eGFR equations?
equitable CKD diagnosis and treatment decisions while relying on biologically valid biomarkers
What non-genetic factors may influence higher sCr among Black individuals?
Epigenetic influences from stress, diet, and socioeconomic disadvantage
When is combined creatinine-cystatin C eGFR most accurate?
When creatinine or cystatin C alone is unreliable
e.g., extremes of body size or chronic illness
What is the equation used for drug dosing?
Cockcroft-Gault (CrCl = [(140 - age) × weight] / (72 × sCr) × 0.85 if female
What are limitations of the Cockcroft-Gault equation?
Developed in 249 White men, uses actual body weight, may overestimate in obesity and underestimate in frailty
Which equations are used for CKD staging (not dosing)?
CKD-EPI 2021 (eGFRcr), CKD-EPI 2021 (eGFRcr-cys), and CKD-EPI 2012 (eGFRcys)
Why did KDIGO and NKF eliminate race from CKD-EPI 2021 equations?
To improve equity; race is a social construct and adds bias to kidney staging
Which CKD-EPI equation provides the least bias across groups?
2021 CKD-EPI creatinine + cystatin C combined equation
Why is eGFR indexed to 1.73 m² body surface area (BSA)?
To standardize kidney function across different body sizes
When should eGFR be un-indexed (converted to actual mL/min)?
When adjusting drug doses, because dosing depends on absolute filtration capacity, not normalized values
How do you convert indexed eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m²) to non-indexed (mL/min)?
Multiply by (patient BSA ÷ 1.73) eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m²)× Patient BSA/1.73
What weight should be used in Cockcroft-Gault for obesity?
Use Adjusted Body Weight (AdjBW) if BMI ≥ 30; otherwise, use IBW or Actual depending on context
What are common causes of discrepancies between eGFR and CrCl?
Differences in standardization (BSA vs non-BSA), body composition extremes, and drug effect on creatinine secretion
What defines CKD?
Kidney damage or GFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m² or Albuminuria: UACR > 30mg/g for ≥ 3 months
Bottom-line: For CKD diagnosis, need 2 instances of evidence for kidney
damage (typically UACR) OR 2 GFRs ≤60; obtained at least 3 months apart
How often should kidney function be monitored in CKD?
At least annually; more frequently (2-4×/yr) in advanced stages or on nephrotoxic drugs
Why must drug dosing consider kidney function?
Reduced clearance increases toxicity risk for renally eliminated drugs
Which method do FDA labeling and most trials use for renal dosing?
Cockcroft-Gault (CrCl mL/min)
When could eGFR be used instead of CrCl for dosing?
If drug labeling or clinical data support eGFR use (e.g., newer nephrology guidelines)
What drugs require special caution or contraindication in low GFR?
Metformin (< 30), SGLT2 inhibitors (< 20-25), NSAIDs, aminoglycosides, DOACs (varies)
How can misclassification of kidney function affect dosing?
Overestimation → toxicity
Underestimation → subtherapeutic dosing
What steps ensure safe dosing in CKD?
Use correct equation, verify chronicity, trend labs, review drug labels, and reassess after major GFR changes
In the "Oskar" case, which equation gave the most accurate GFR for staging?
2021 CKD-EPI creatinine + cystatin C
Which value was used for Oskar's drug dosing?
Cockcroft-Gault (rounded to mL/min using AdjBW for obesity).

Why might cystatin C-based eGFR be prioritized in clinical practice moving forward?
Reduces racial bias, improves risk prediction, and aligns with 2021 NKF/ASN consensus
What are "measured" vs. "estimated" kidney function values?
Measured (mCrCl or mGFR) use urine collection or tracer studies.
Estimated (eGFR or C-G CrCl) use serum biomarkers and are population-based approximations.
Which body size-related factor makes serum creatinine (sCr) unreliable?
sCr production depends on muscle mass, not fat mass
- obesity, sarcopenia, or amputation distort its interpretation

Why is cystatin C less affected by body composition?
It’s produced by all nucleated cells, filtered (not secreted) by glomeruli, and minimally affected by muscle mass or diet

In what clinical situations is cystatin C preferred over creatinine?
- muscular or athletic patients
- high-protein diets or creatine supplements
- amputation or paralysis
- muscle wasting or prolonged ICU stay
When is the combination equation (CKD-EPIcr–cys, 2021) recommended?
When both biomarkers are distorted
e.g., obesity, chronic illness, corticosteroid therapy, or mixed muscle/inflammation conditions
What non-GFR factors raise cystatin C levels?
Obesity (inflammation), smoking, thyroid disease, uncontrolled hyper/hypothyroidism, and high glucocorticoid exposure
How does obesity affect cystatin C vs. sCr?
Obesity directly increases cystatin C via inflammation and indirectly increases sCr by slightly increasing lean mass
For Class I obesity (BMI 30–34.9), what equation is preferred?
eGFRcrBSAadj (preferred) or C-G using adjusted body weight (ABW × 0.4)
For Class II–III obesity (BMI ≥35), what equation is most accurate?
eGFRcr-cysBSAadj (preferred)
What's the preferred method for kidney function estimation in obesity or underweight?
Use eGFRBSA-adjusted (mL/min) rather than unindexed eGFR
For underweight adults, which method should be used?
eGFRcys BSAadj or eGFRcr-cysBSAadj (mL/min) for greater accuracy
Why should clinicians standardize using BSA-adjusted eGFR?
To improve dosing consistency and comparability between individuals of different body sizes
How does aging affect creatinine metabolism?
Both creatinine production (from reduced muscle mass) and creatinine excretion decline
***GFR naturally decreases ~1 mL/min/year after age 30
Why can elderly patients have "normal" sCr despite impaired kidney function?
Low muscle mass reduces creatinine generation, masking a true GFR decline
When is eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73m² not necessarily CKD in older adults?
If albuminuria is absent and eGFR remains stable at 45–59 mL/min, risk of kidney failure is minimal
What eGFR thresholds in the elderly predict increased kidney-failure risk?
<45 mL/min/1.73m² indicates a higher risk across all age groups
Which equations perform better in adults ≥70 years old?
GFRcr-cys (2021) or eGFRcys (2012)
- cys C is unaffected by muscle mass
Should pharmacists round up low serum creatinine in older adults?
No.
Rounding to 0.8 or 1.0 mg/dL decreases accuracy and introduces bias; use the actual sCr value
What is the best practice for drug dosing in elderly patients?
Use eGFRBSAadj (mL/min) for dosing; consider mGFR or mCrCl for narrow-therapeutic-index drugs
Is CKD common in children?
No, it is rare, but must be recognized in those with congenital or glomerular disease
What happens to GFR and sCr during normal growth?
GFR remains stable (111-127 mL/min/1.73m²), but sCr rises as muscle mass increases, especially in adolescent males
What is the current pediatric equation for eGFR?
bedside CKiD equation: eGFR = 0.413 × (Height in cm / sCr
Why does the pediatric equation use height instead of weight?
Height correlates best with kidney growth and muscle development in children
Should BSA adjustment be used for drug dosing in pediatric patients?
No, BSA adjustment isn’t needed for dosing with the CKiD formula
What is the "U25 eGFR" and when is it used?
A newer calculator for ages ≤25 years
- it bridges the gap between pediatric (CKiD) and adult (CKD-EPI) equations
What's the overall limitation of eGFR and eCrCl equations?
population estimates and may be inaccurate in individuals at extremes of weight or age
When should measured GFR or CrCl be obtained?
In cases needing precise drug dosing (e.g., chemotherapy, aminoglycosides, narrow-therapeutic-index drugs)
What's the standard recommendation for adult special populations if no specific study data exist?
Use CKD-EPIcr (2021), CKD-EPIcr–cys (2021), or CKD-EPIcys (2012) depending on context
Use eGFRBSAadj for underweight/obese
For Class II–III obesity, use eGFRcr–cysBSAadj or C-G (ABW × 0.4)