LRA 218-Radiographic Position
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
53 Terms
The bending or forcing of the hand laterally with the hand pronated in a posteroanterior (PA) projection is known as:
radial deviation.
ulnar deviation.
radial abduction.
ulnar extension.
ulnar deviation.
What is the distance between the tabletop and Bucky tray on most floating tabletop type of tables?
1/2 to 1 inch (1.3 to 2.5 cm)
1 to 2 inches (2.5 to 5.1 cm)
2 to 3 inches (5 to 7.6 cm)
3 to 4 inches (8 to 10 cm)
3 to 4 inches (8 to 10 cm)
Which special projection of the wrist will open up the interspaces on the ulnar side of the wrist?
Radial deviation
Ulnar deviation
Carpal canal
Carpal bridge
Radial deviation
How much CR angulation to the long axis of the hand is required for the tangential, inferosuperior projection to demonstrate the carpal sulcus (canal)?
10° to 15°
25° to 30°
35° to 45°
5° to 10°
25° to 30°
Which special projection of the wrist is ideal for demonstrating possible calcification in the dorsal aspect of the carpals?
Carpal bridge
Carpal canal
Ulnar deviation
Lateral wrist
Carpal bridge
A patient enters the emergency department (ED) with a Smith fracture. Which region of the upper limb must be radiographed to demonstrate this injury?
Trapezium
Elbow
Wrist and forearm
Hand
Wrist and forearm
A radiograph of a tangential, inferosuperior projection of the carpal canal reveals that the hamate is superimposed over the pisiform. Which of the following measures will correct this problem?
Rotate the wrist and hand 10° internally.
Increase the CR angle.
Decrease the CR angle.
Increase the extension of the hand and/or wrist.
Rotate the wrist and hand 10° internally.
A patient enters the ED with a possible scaphoid fracture. The patient is unable to assume the ulnar deviation position. Which of the following positions should be performed to confirm the diagnosis?
Gaynor-Hart
Jones
Modified Stecher
Coyle
Modified Stecher
A patient with a history of carpal tunnel syndrome comes to radiology. The physician wants to rule out abnormal calcifications in the carpal sulcus. Which of the following projections would best demonstrate this region?
Coyle method
Jones method
Carpal bridge
Gaynor-Hart method
Gaynor-Hart method
How many carpal bones are found in the wrist?
8
7
5
10
8
What is the most commonly fractured carpal bone?
scaphoid
hamate
capitate
lunate
scaphoid
Which wrist ligament is attached to the styloid process of the ulna and continues to the triquetrum and pisiform?
ulnar collateral ligament
palmar radiocarpal ligament
dorsal radiocarpal ligament
radial collateral ligament
ulnar collateral ligament
The two fat stripes of the wrist demonstrated radiographically are known as the scaphoid fat stripe and the ____ fat stripe.
pronator
pisiform
abductor
anterior
pronator
A general positioning rule is to place the long axis of the part ____ to the long axis of the image receptor.
parallel
axial
perpendicular
adjacent
parallel
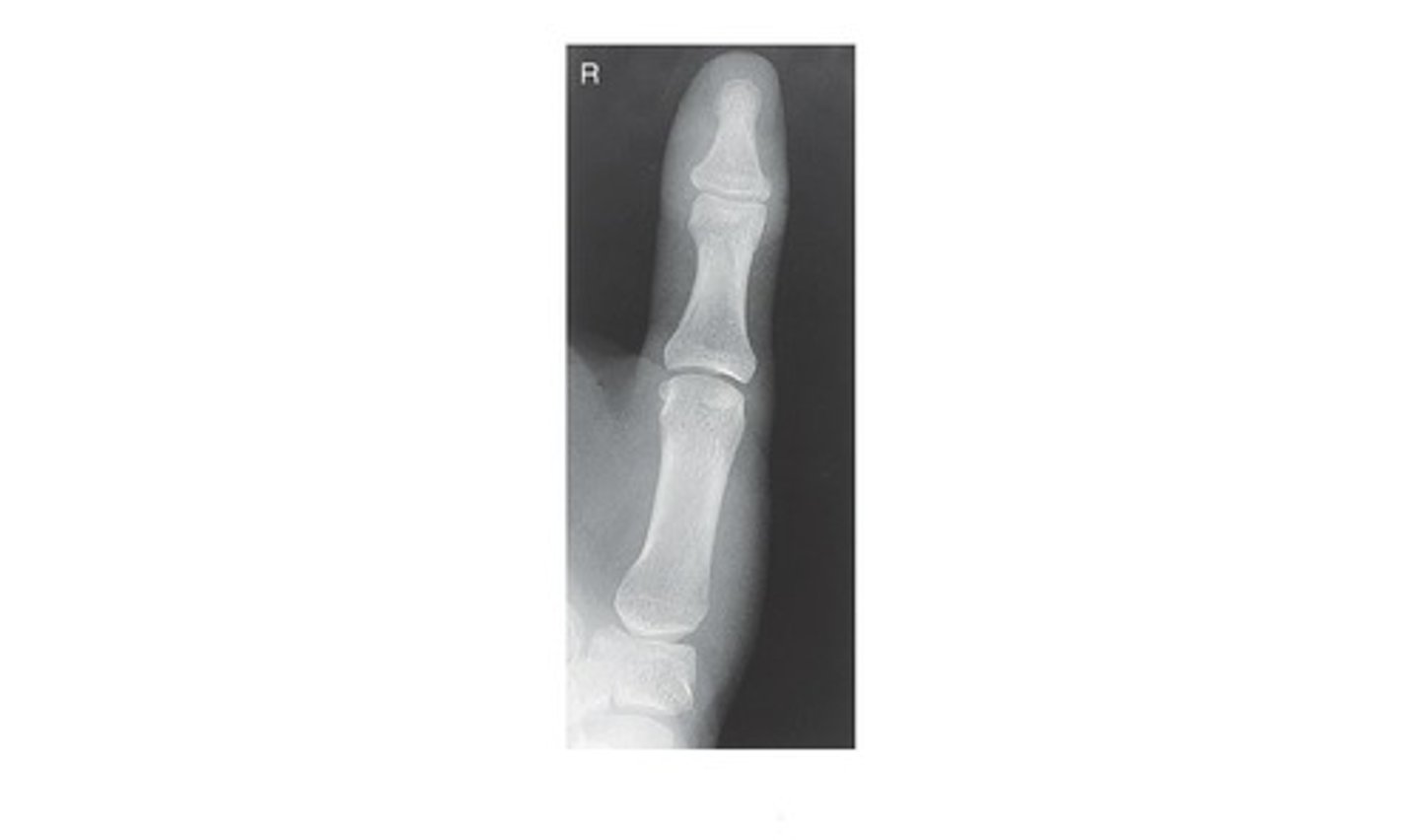
In which position is the following radiograph of the 1st digit (thumb) presented?
a. AP
b. PA
c. Lateral
d. Oblique
a. AP
The "Fan" lateral - lateromedial projection of the hand is the preferred lateral for the hand if phalanges are the area of interest.
True
False
True
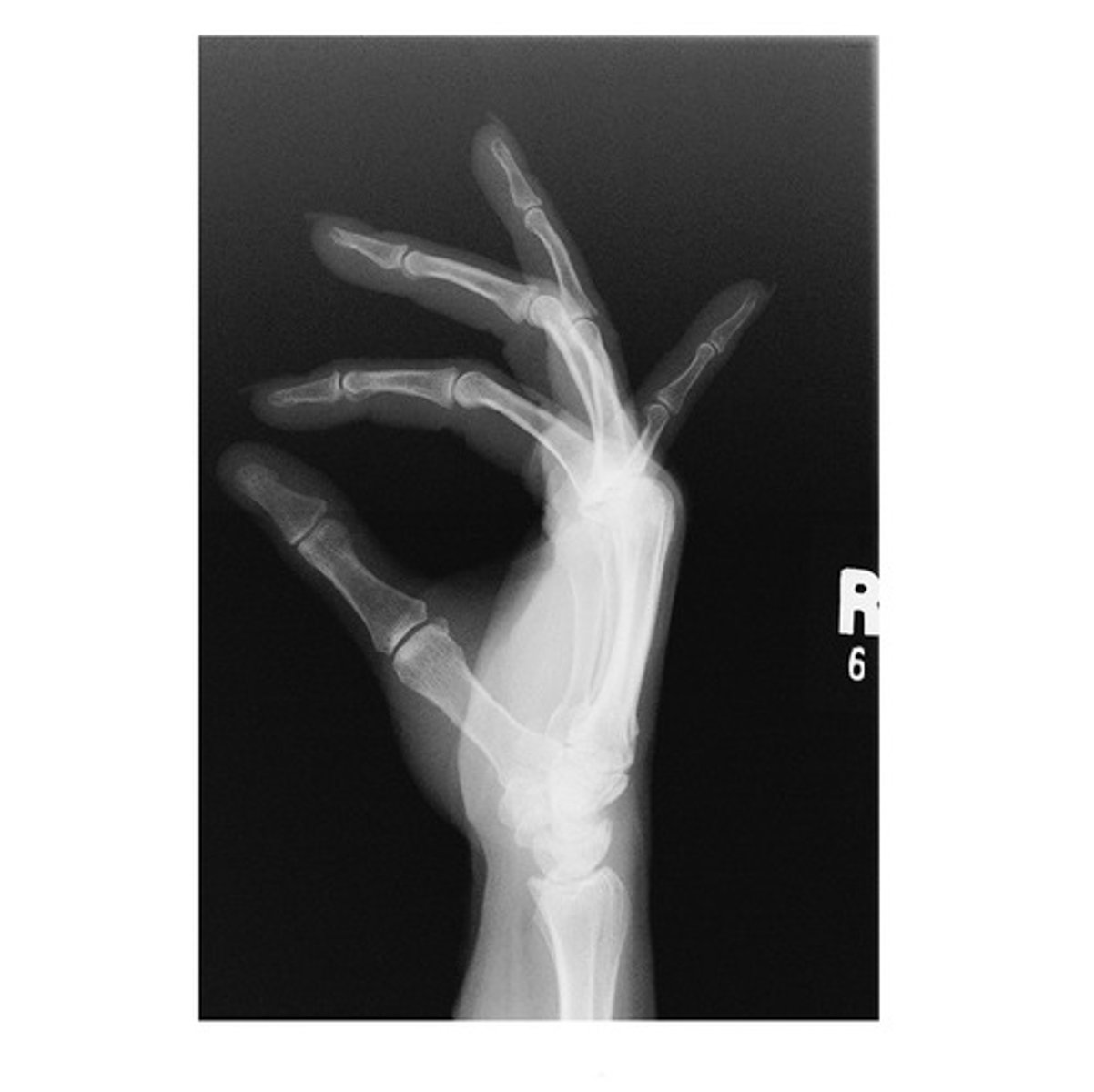
In which position is the following radiograph of the hand presented?
a. Lateral Flexion
b. Oblique
c. Lateral Extension
d. PA
c. Lateral Extension
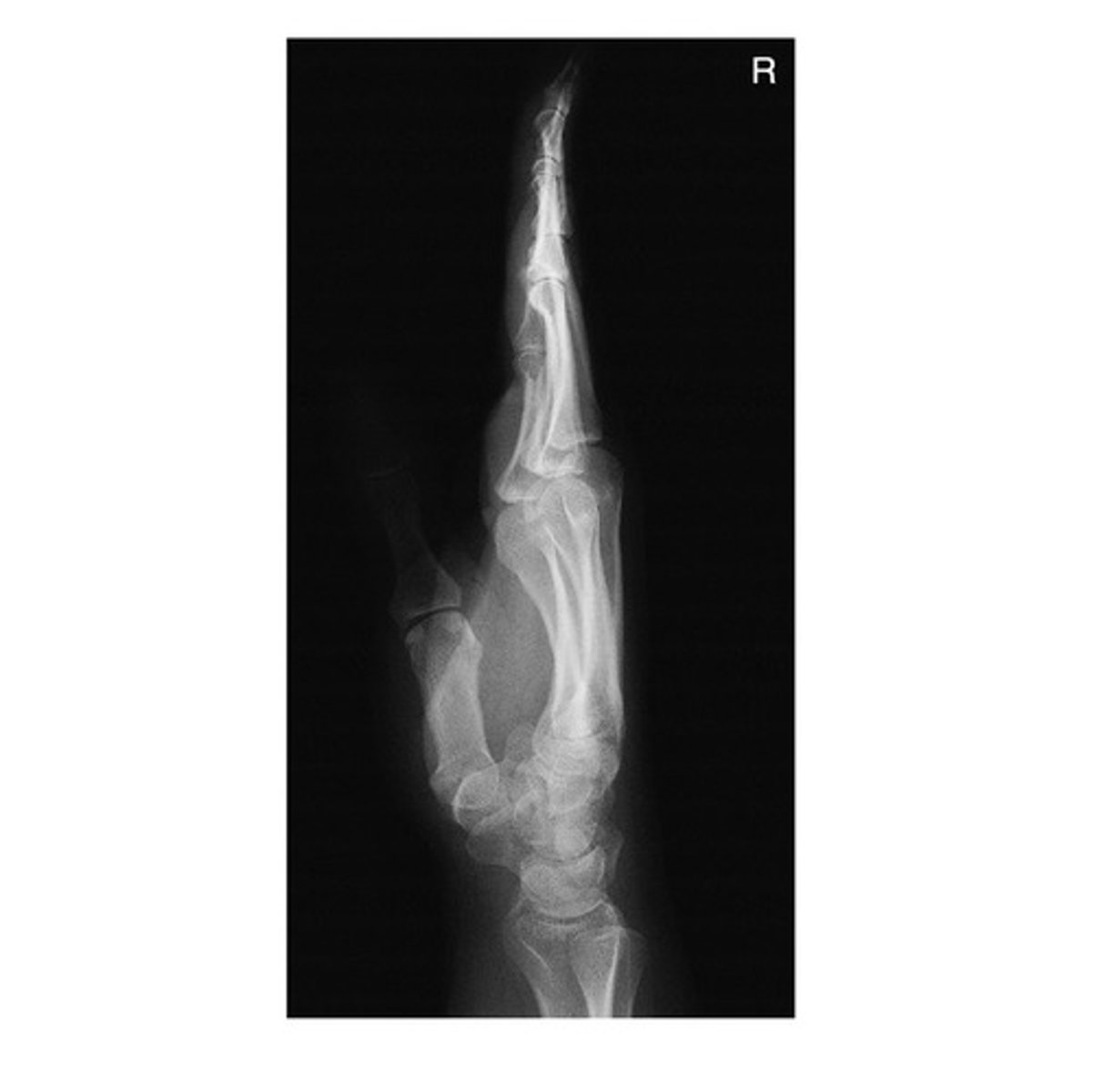
In which position is the following radiograph of the hand presented?
a. Lateral Flexion
b. Oblique
c. Lateral Extension
d. PA
a. Lateral Flexion
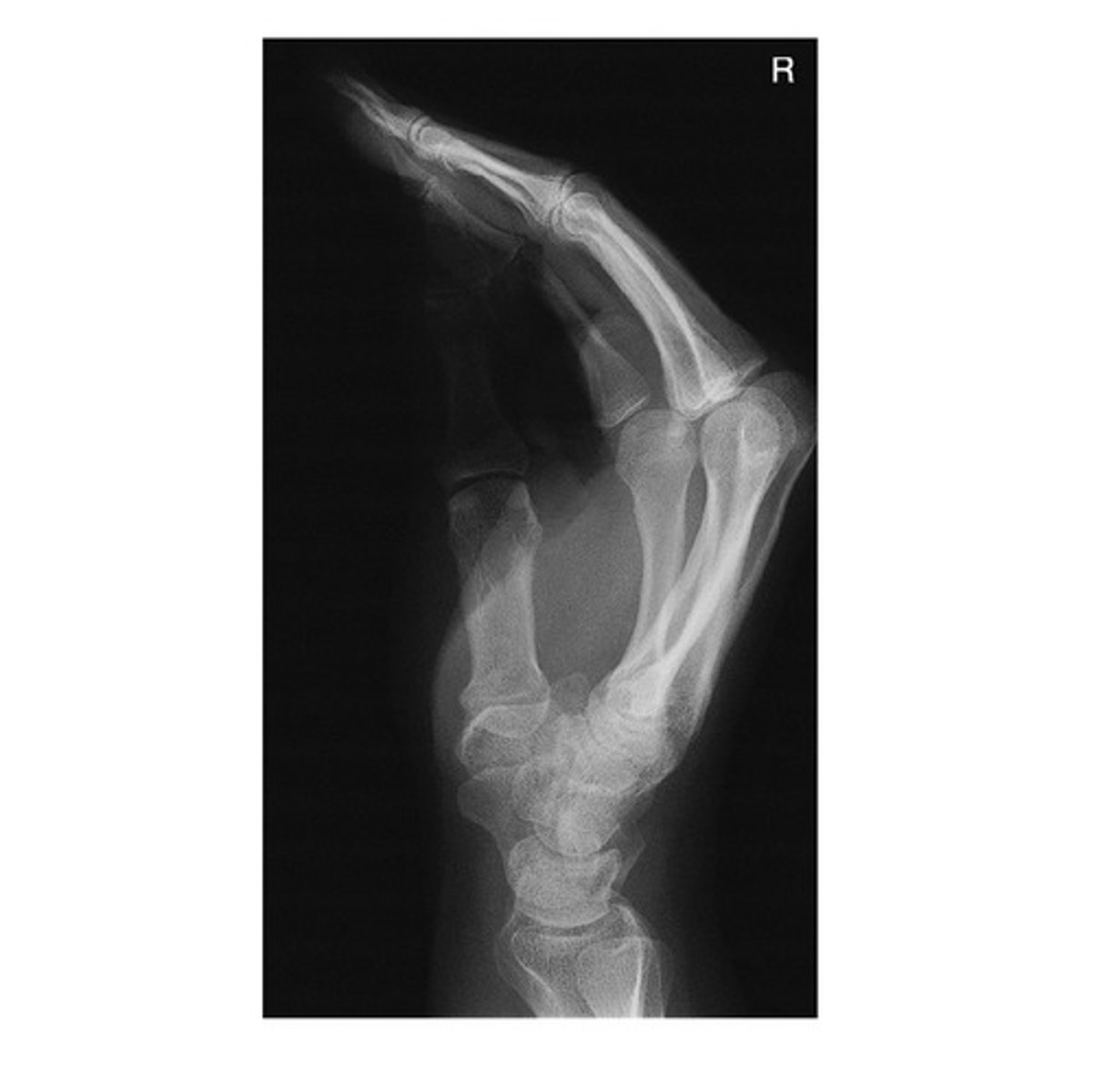
In order to obtain a PA Olique Hand image, the entire hand and wrist should be rotated _____ laterally.
a. 15 degrees
b. 25 degrees
c. 35 degrees
d. 45 degrees
d. 45 degrees
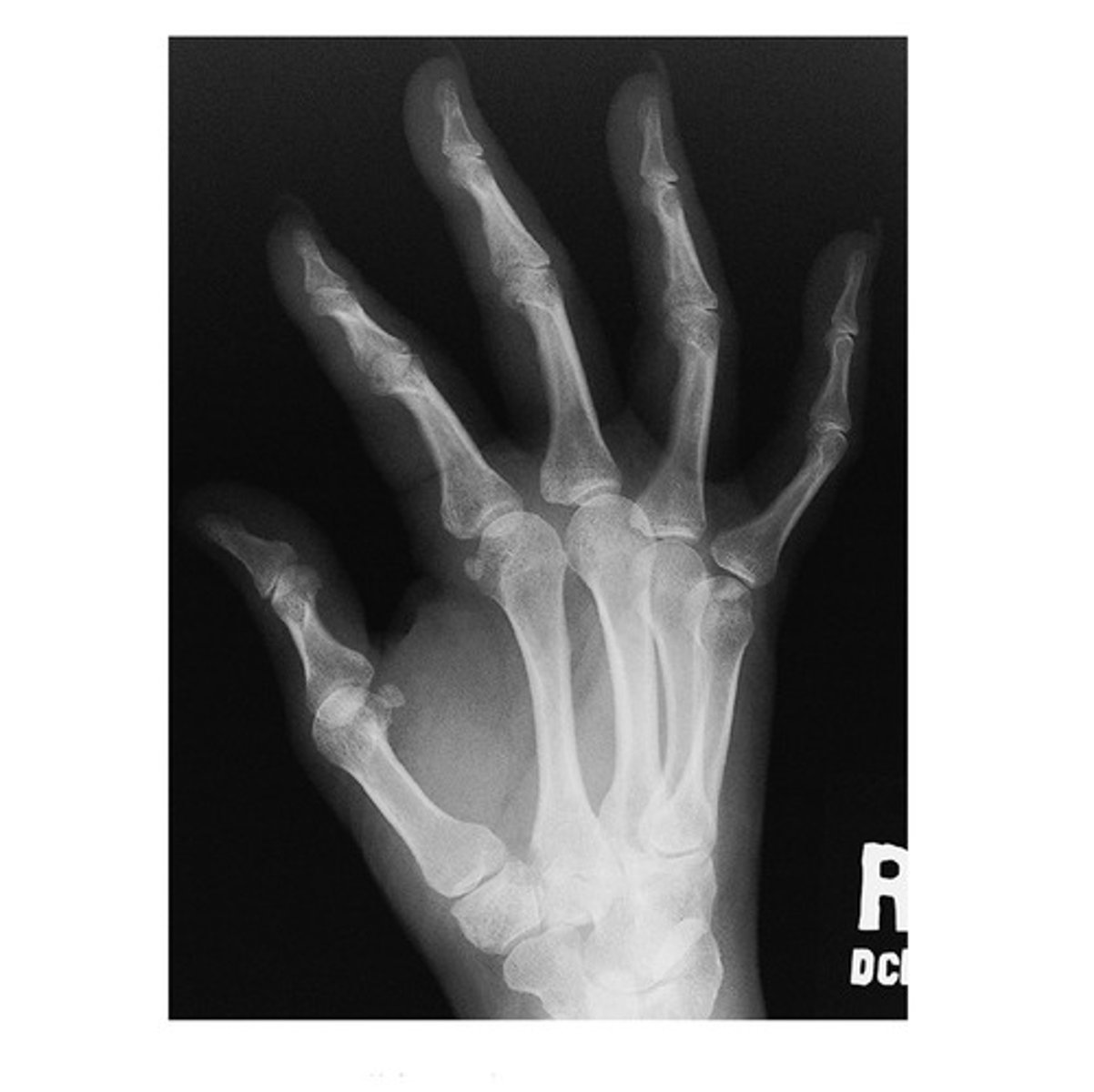
When performing a PA Finger examination, the CR (Central Ray) is perpendicular and centered to the _____ joint.
a. MCP
b. DIP
c. PIP
d. CMC
c. PIP
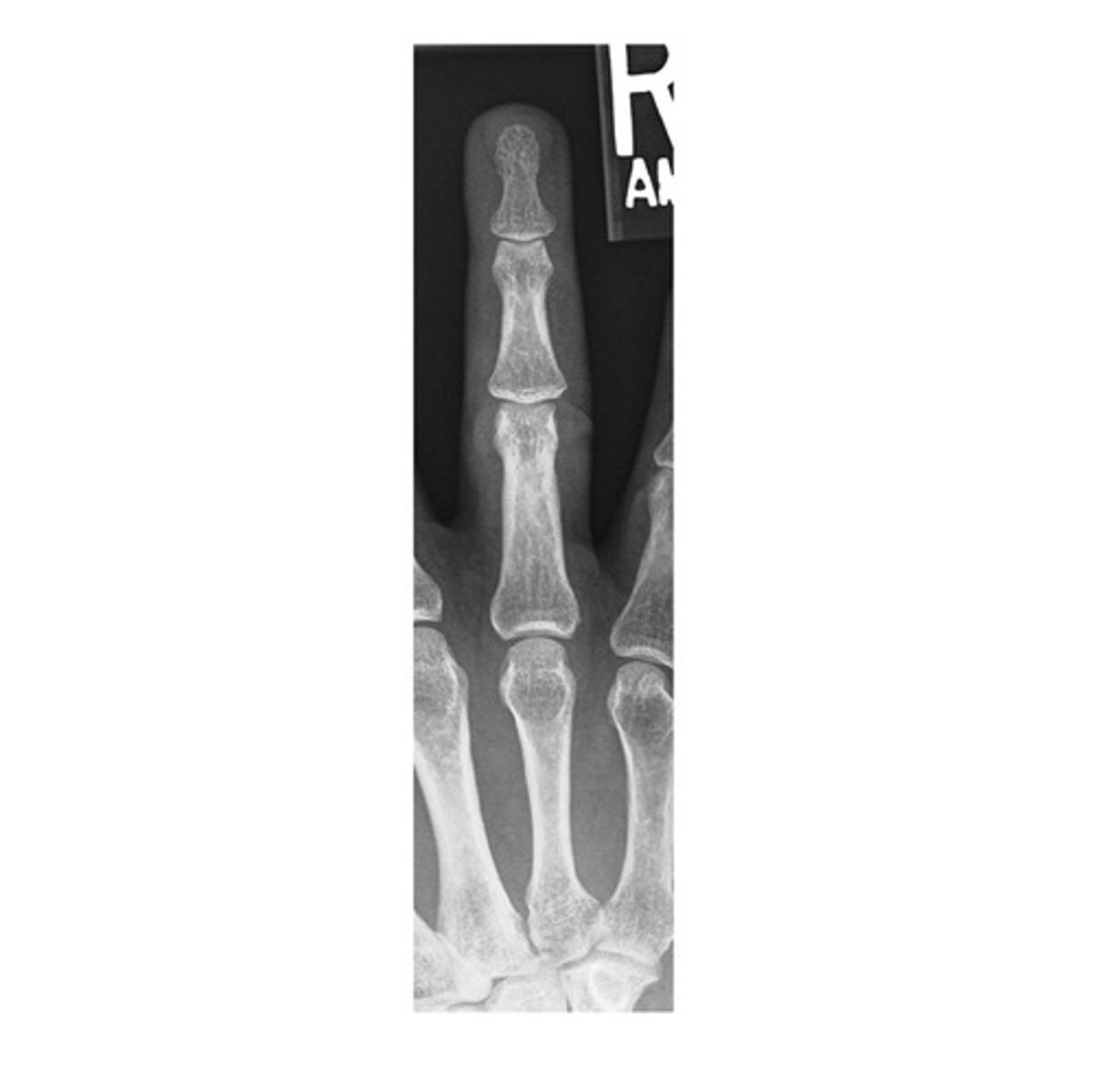
The minimum SID required to attain a radiograph of the second digit (mediolateral) is _____ inches.
a. 36
b. 40
c. 45
d. 72
b. 40
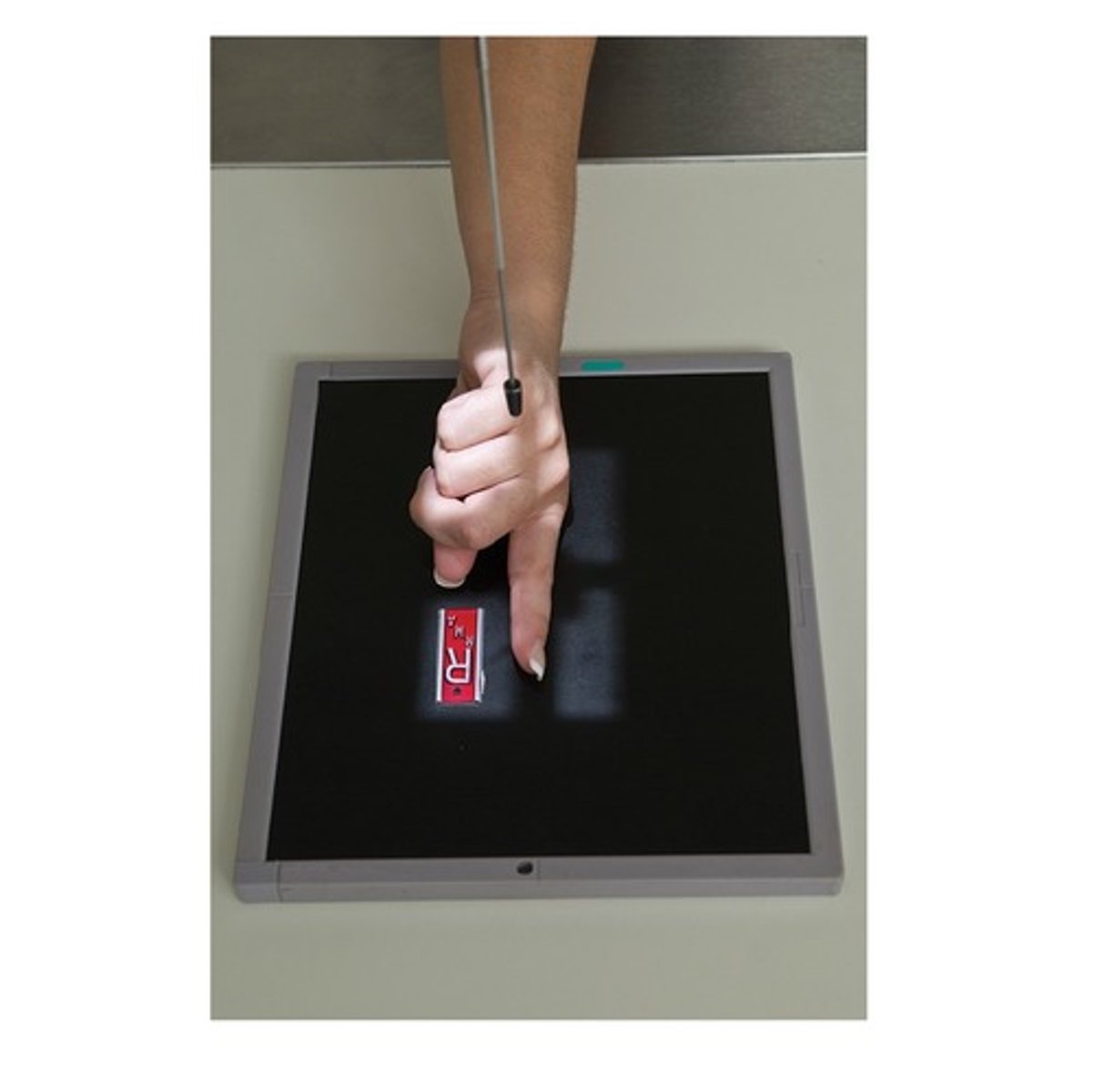

Which of the following statements is INCORRECT when positioning for an AP Axial Thumb (Modified Roberts) view:
a. The patient can be seated or standing with hand rotated internally placing posterior surface of thumb directly on IR.
b. Align thumb to long axis of portion of IR being exposed.
c. Extend fingers and hold back with other hand to prevent superimposing base of thumb and 1st CMC joint region.
d. All statements are correct
d. All statements are correct
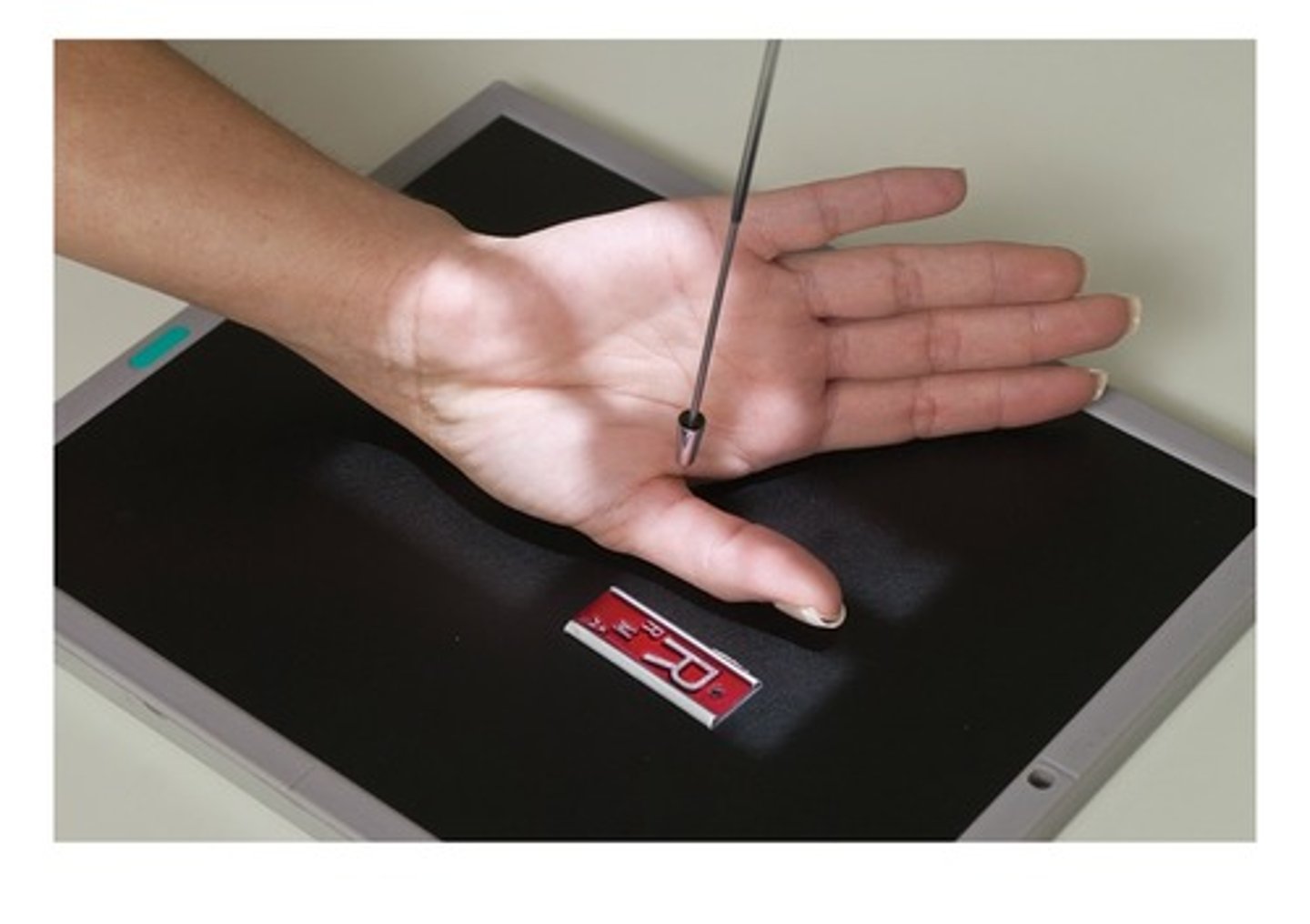

When performing a PA Hand radiographic examination, the central ray (CR) should be centered to the _____.
a. 2nd metacarpal shaft
b. 3rd PIP joint
c. 3rd MCP joint
d. 4th metacarpal shaft
c. 3rd MCP jointv
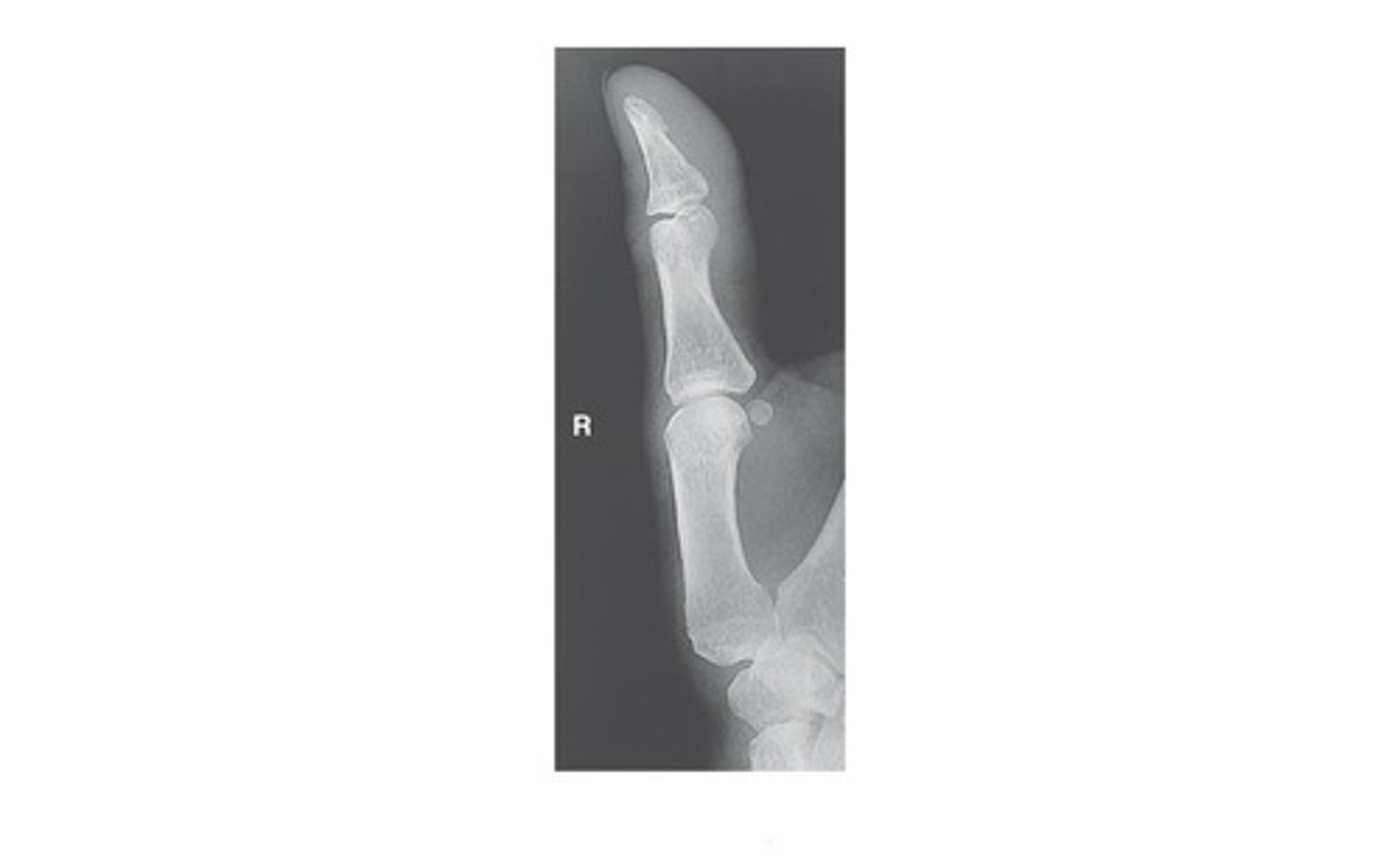
What radiographic image is demonstrated below?
a. AP Thumb
b. Oblique Thumb
c. Lateral Thumb
d. None of the above
b. Oblique Thumb
A patient arrives in radiology with a metal foreign body in the palm of the hand. Which of the following hand routines should be performed on this patient to confirm the location of the foreign body?
PA and lateral in extension projections
PA and lateral in flexion projections
Pa and fan lateral projections
PA and Gaynor-Hart method
PA and lateral in extension projections
A patient enters radiology with a possible Bennett's fracture. Which of the following routines should be performed to confirm the diagnosis?
thumb
finger
wrist
forearm
thumb
A radiograph of a PA projection of the hand reveals that the distal radius and ulna and the carpals were cut off. What should the technologist do to correct this problem?
Repeat the PA projection to include all the carpals and about 1 inch of the distal radius and ulna.
If the injury to the patient did not involve the carpal region and distal forearm, do not repeat it.
Make sure the carpals, distal radius, and ulna are included on the lateral projection.
Accept the radiograph. Carpals and distal radius and ulna are not part of a hand study.
Repeat the PA projection to include all the carpals and about 1 inch of the distal radius and ulna.
A radiograph of a PA oblique of the hand reveals that the midaspect of the fourth and fifth metacarpals is superimposed. What specific positioning error has been committed?
excessive rotation of the hand and/or wrist
fingers of the hand are not parallel to IR
incorrect CR angulation
insufficient rotation of the hand and/or rist
Correct Answer:excessive rotation of the hand and/or wrist
excessive rotation of the hand and/or wrist
Which of the following structures is considered to be most lateral?
capitulum
trochlea
proximal radioulnar joint
coronoid tubercle
capitulum
Which of the following structures is considered to be most proximal?
olecranon process
head of ulna
coronoid process
radial tuberosity
olecranon process
A nonvisible posterior fat pad on a well-exposed, correctly positioned lateral elbow radiograph generally suggests:
negative study for injury
fracture of one of the bones of the elbow
injury to the synovial joint
a congenital defect
negative study for injury
How much rotation of the humeral epicondyles is required for the AP medial oblique projection of the elbow?
45°
30°
15°
55°
45°
Which of the following actions will lead to the proximal radius crossing over the ulna?
pronation of the hand
external rotation of elbow
supination of the hand
placing epicondyles parallel to image receptor
pronation of the hand
What is the purpose of performing the AP partially flexed projections of the elbow?
to provide an AP perspective if patient cannot fully extend elbow
to provide a view of the radial head and capitulum
to separate the radial head from the ulna
to demonstrate any possible elevated fat pads
to provide an AP perspective if patient cannot fully extend elbow
Which routine projection of the elbow best demonstrates the radial head and tuberosity free of superimposition?
AP oblique with lateral rotation
lateral
AP oblique with medial rotation
AP
AP oblique with lateral rotation
Which routine projection of the elbow best demonstrates the olecranon process in profile?
lateral
AP
medial rotation oblique
lateral rotation oblique
lateral
Which basic projection of the elbow best demonstrates the trochlear notch in profile?
lateral
AP
medial rotation oblique
lateral rotation oblique
lateral
A radiograph of the elbow demonstrates the radius directly superimposed over the ulna and the coronoid process in profile. Which projection of the elbow has been performed?
medial rotation oblique
AP
lateral
lateral rotation oblique
medial rotation oblique
Which routine projection of the elbow will best demonstrate an elevated or visible posterior fat pad?
true lateral with 90° flexion
true AP with no rotation
lateral rotation oblique
coyle method
true lateral with 90° flexion
A patient with a fractured forearm had the fracture reduced and a fiberglass cast placed on the extremity. The orthopedic surgeon orders a postreduction study. The original kV was 60 kV. Which one of the following kV factors should be selected for the postreduction study?
63 kV
67 kV
70 kV
75 kV
63 kV
A patient enters the department in severe pain with a possible dislocation of the elbow. The patient has the elbow flexed more than 90°. Which one of the following routines should be performed to confirm the diagnosis?
partially flexed AP and limited lateral projections
Jones method and limited lateral projection
Coyle method and limited lateral projection
lateral elbow only
partially flexed AP and limited lateral projections
A lateral elbow radiograph demonstrates about half of the radial head superimposed by the coronoid process of the ulna. Which of the following occurred?
no positioning errors occurred
the hand was pronated rather than in a true lateral position
the hand and wrist were rotated laterally and not in a true lateral position
the shoulder was not dropped sufficiently to the tabletop level
no positioning errors occurred
A radiograph of an AP projection of the elbow reveals that there is complete seperation of the proximal radius and ulna. What positioning error has been committed?
excessive lateral rotation
excessive medial rotation
partial flexion of the joint
incorrect CR location and angle
excessive lateral rotation
Which rotation of the humerus will result in a lateral position of the proximal humerus?
A. Internal rotation (epicondyles perpendicular to image receptor)
B. Neutral rotation (epicondyles 45° to the image receptor)
C. External rotation (epicondyles parallel to the image receptor)
D. None of the above
A. Internal rotation (epicondyles perpendicular to image receptor)
Which AP projection of the shoulder and proximal humerus is created by placing the affected palm of the hand facing inward toward the thigh?
A. Internal rotation
B. Neutral rotation
C. External rotation
D. AP axial
B. Neutral rotation
Which of the following shoulder positions is considered a trauma projection (can be performed safely for a possible fracture or dislocation)?
A. AP apical oblique axial (Garth method) projection
B. Inferosuperior axial (Clements modification) projection
C. AP projection-internal rotation
D. None of the above
A. AP apical oblique axial (Garth method) projection
What medial central ray (CR) angle is required for the inferosuperior axial shoulder (Lawrence method)?
A. 5° to 10°
B. 40° to 45°
C. 25° to 30°
D. 10° to 15°
C. 25° to 30°
What additional maneuver must be added to the inferosuperior axial shoulder (Lawrence method) projection to best demonstrate a possible Hill-Sachs defect?
A. Increase medial CR angulation.
B. Angle the CR 10° to 15° downward or posteriorly in addition to the medial angle.
C. Perform exaggerated external rotation of the affected upper limb.
D. Increase abduction of the affected upper limb.
C. Perform exaggerated external rotation of the affected upper limb
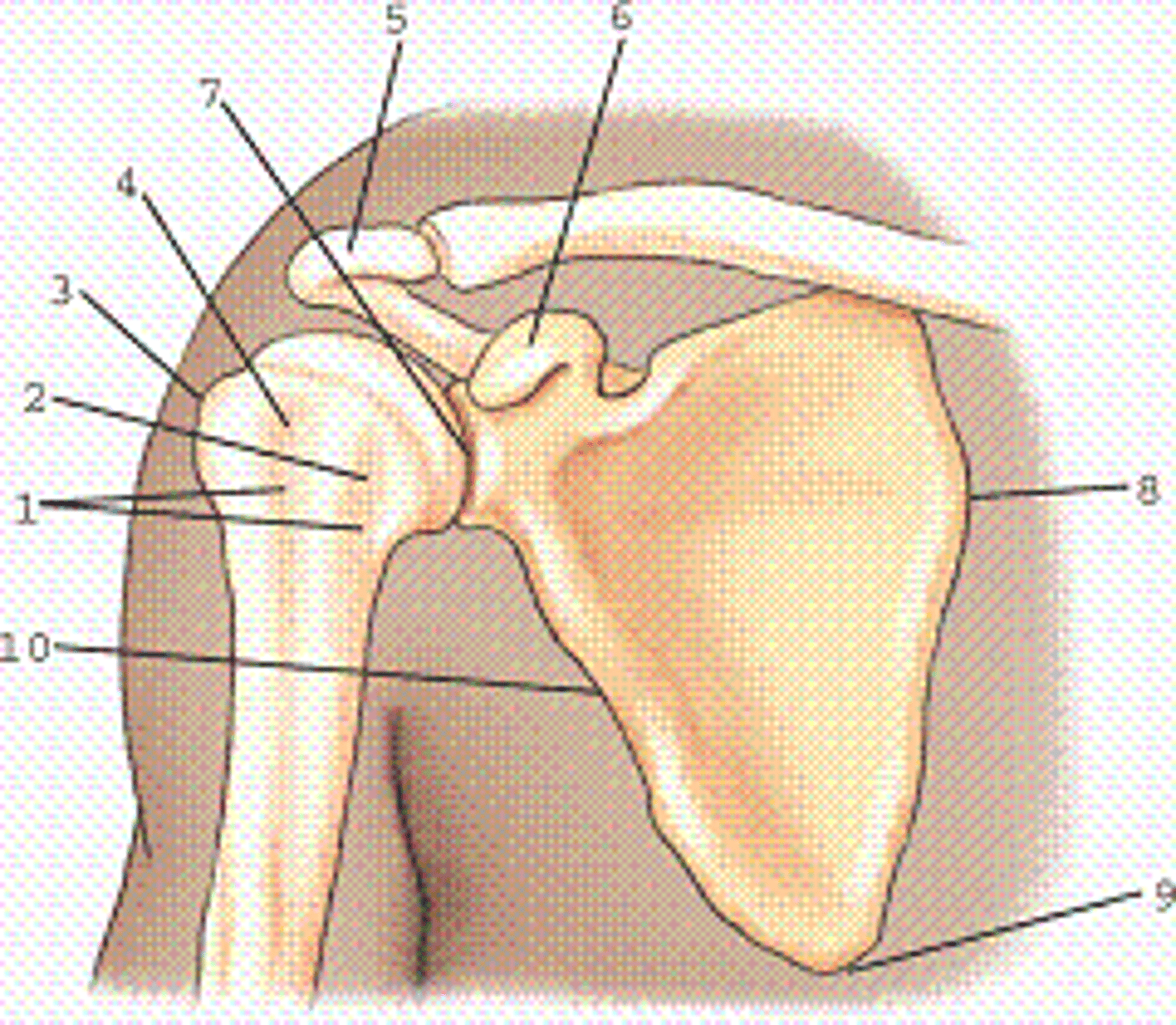
Which view and projection of the proximal humerus is represented in the figure?
A. External rotation, anteroposterior (AP) projection
B. Neutral rotation, AP projection
C. Internal rotation, AP projection
D. External rotation, lateral projection
A. External rotation, anteroposterior (AP) projection
The use of a grid during shoulder radiography will result in higher patient dose over nongrid procedures.
True
False
True
A radiograph of the inferosuperior axial projection (Lawrence method) demonstrates the acromion process of the shoulder to be located most superiorly (anteriorly).
True
False
True
Where is the CR centered for a transthoracic lateral projection for proximal humerus?
A. 1 inch (2.5 cm) inferior to the acromion
B. Level of the greater tubercle
C. Level of surgical neck
D. Midaxilla
C. Level of surgical neck
A referring physician suspects that a subacromial spur may be the cause for a patient's arm numbness. She asks the technologist for a projection that would best demonstrate any possible spurs. Which of the following projections would accomplish this objective?
A. PA scapular Y lateral with 10° to 15° caudal angle
B. PA scapular Y lateral with 10° to 15° cephalad angle
C. AP oblique shoulder with 45° caudal angle
D. AP shoulder with 10° to 15° caudal angle
A. PA scapular Y lateral with 10° to 15° caudal angle