Audiology Rehab Midterm
1/53
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
54 Terms
What is Aural Rehabilitation?
Intervention aimed at minimizing and alleviating the communication difficulties associated with hearing loss.
Who does AR serve?
Individuals with difficulty hearing and hearing loss
What is the purpose of AR?
Aimed to restore or optimize participants in activities, enhance conversational fluency and reduce hearing-related disability
Who can provide AR services?
Audiologist and SLP and Deaf educators
What is an audiogram?
A graph that visually represents the results of a hearing test.
Sensorineural Hearing loss:
Air conduction and Bone conduction thresholds are essentially the same
Conductive Hearing loss:
Air conduction showing hearing loss but Bone conduction show normal threshold
Mixed Hearing loss:
Air conduction and Bone conduction show hearing loss but Bone conduction better than Air conduction thresholds
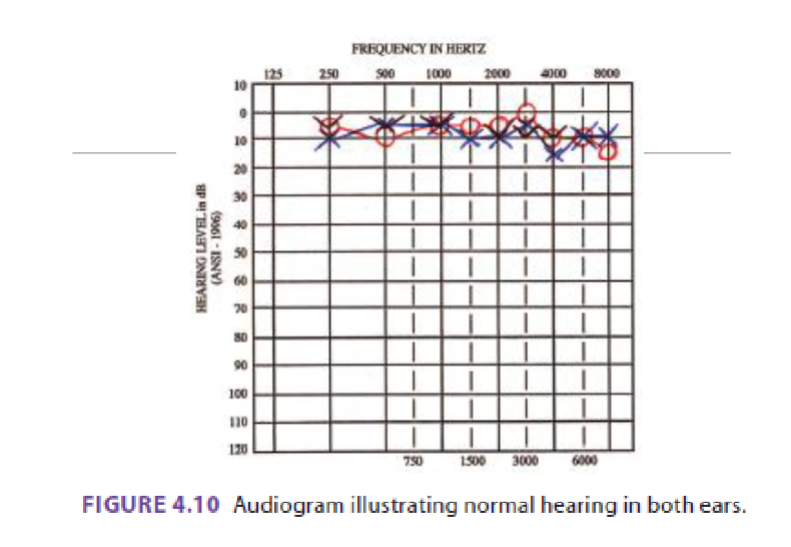
What type of hearing loss is this
Normal Hearing
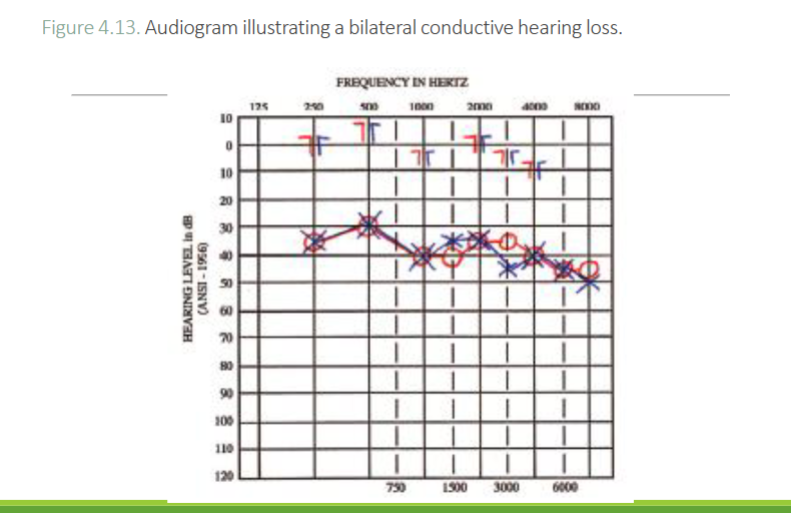
What type of hearing loss is this
Bilateral Conductive Hearing Loss
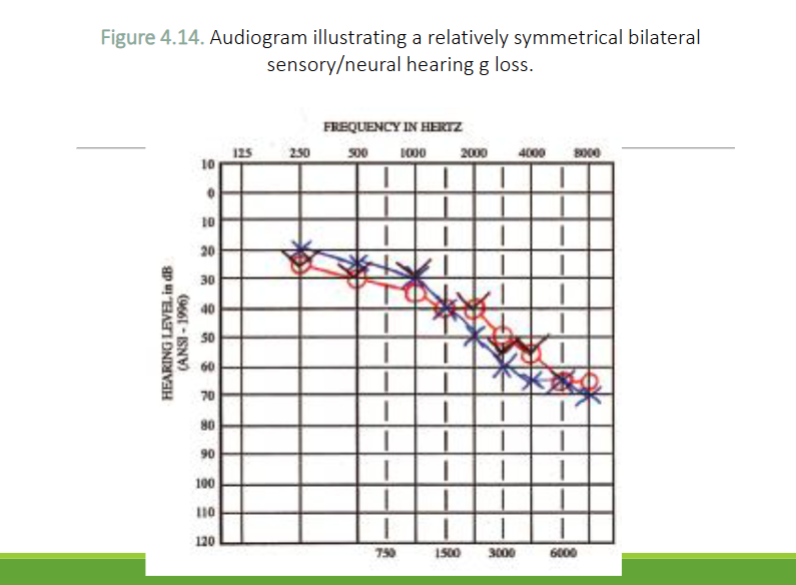
What type of hearing loss is this
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
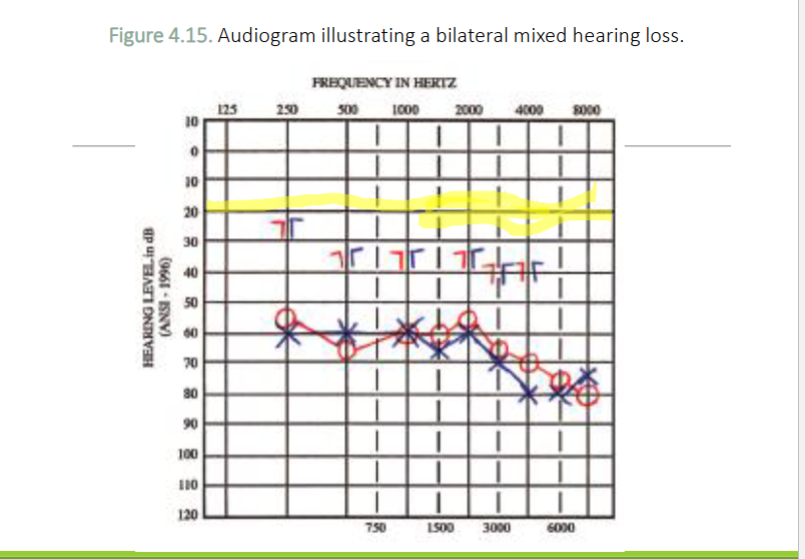
What type of hearing loss is this
Mixed Hearing Loss
What is the goal of a communication assessment?
Determine the communication demands placed in individuals in their everyday life
Impact of hearing loss on daily activities
Identify the settings in which communication problems likely arise
Assess how effectively people use communication strategies in a variety of settings
What is conversational fluency?
The ability for someone to comfortably and effectively participate in everyday conversation. From exchanging info and ideas and holding conversations.
What are some methods of assessing conversational fluency and communication needs?
Interviews, questionnaires, daily logs, group discussions, Structured Communication Interaction, unstructured communication interactions
The importance of a communication partner in evaluating conversational fluency and/or communication needs
It is important to have partner give an evaluation they can answer the questionnaires, daily logs, group discussion and structured communication interactions
What are the implications of hearing loss – financially, emotionally, socially, etc.?
Emotional: can include shame, guilt, anxiety, anger, frustration
Cognitive: inattentiveness, reduced concentration, low self-esteem, low confidence and increased effort to listen
interpersonal : includes bluffing, social withdrawal, dominating conversations
Behavioral: limitation of activities or social isolation
Physical: fatigue, muscle tension, headaches, sleep problems
Financially: feeling priced out of the market
What are some counseling strategies when it comes to working with those with hearing loss?
Informational Counseling; information is provided to a person regarding hearing loss, associated problems and the recommended steps of management. It is used to inspire patients and family to be active in the AR plan and to help promote healthy hearing. Clinicians listen to patients' concerns.
Personal Adjustment Counseling: Focuses on imparting to patients the reality of hearing loss and social, psychological and emotional ramification of HL. helps individuals accept that hearing loss is a part of their life and how to incorporate the Hl into their self image.
Rational Emotive Behavior Therapy: approach focused on resolving specific problems using cognitive, behavioral and affective elements; emotions result from beliefs rather than events or circumstances
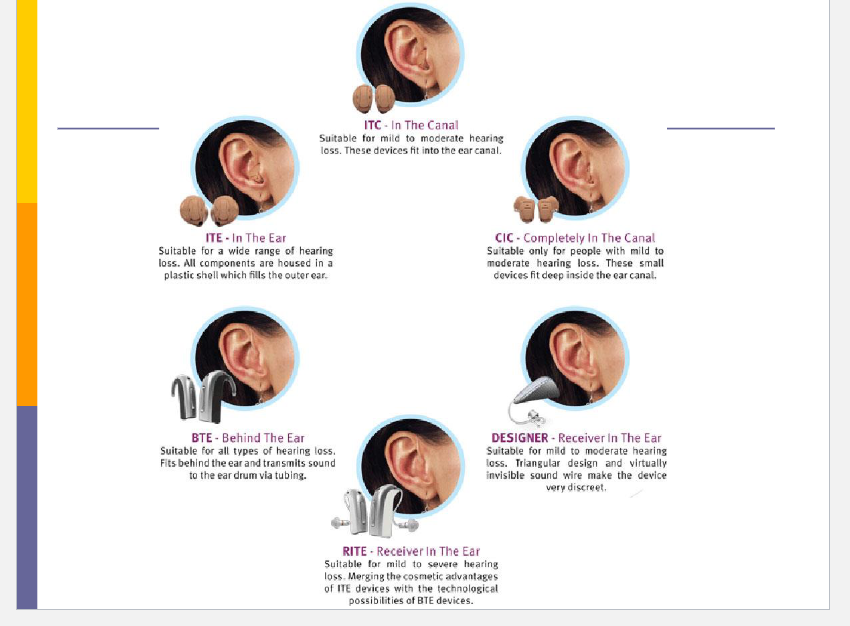
What are the different types of hearing aids (RIC (open-fit) vs BTE vs ITE (full-shell vs half-shell vs in-the-canal) vs CIC.
RIC: Receiver-in-canal hearing aids, offering a discreet design with the receiver placed in the ear canal for enhanced sound quality.
BTE: suitable for all hearing types; fits behind the ear
ITE: In the Ear; (full shell) fills the outer ear, provides good amplification. (half shell) covers only a portion of the outer ear for a less visible option.
ITC: (in-the-canal) sits in the ear canal for a custom fit but may offer less power.
CIC: Completely-in-canal is nearly invisible, designed for mild to moderate hearing loss.
What are some of the similarities of all hearing aids?
Assist the individual in hearing in some capacity, are placed in ear in some way
What are some of the differences of all hearing aids?
Where they are located within or around the ear, who they might help mild to moderate or moderate to severe. Different functions they might be able to offer
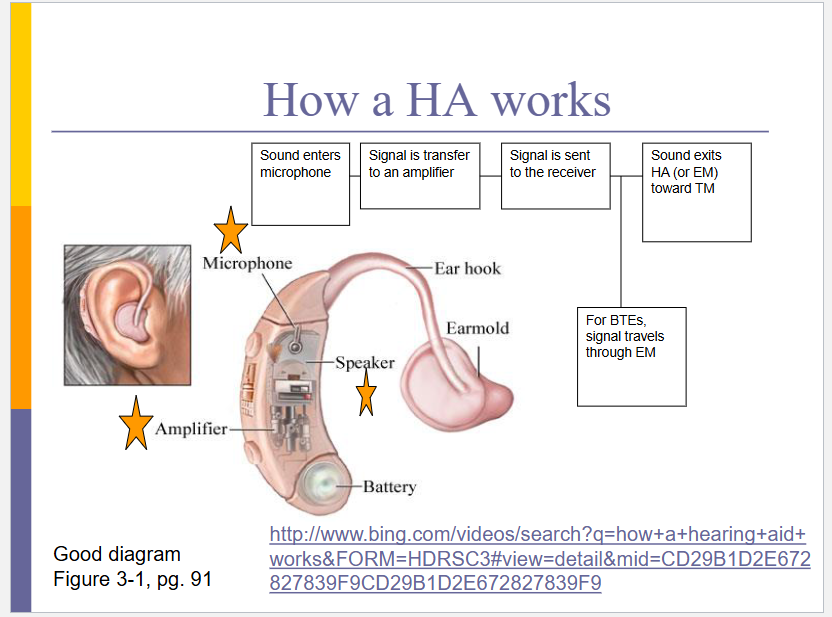
How does sound get processed through a HA?
Sound enters through microphone
Signal is transferred to amplifier
Signal is sent to receiver
For BTE signal travels through EM
Sound exits Hearing aid or EM and towards tympanic membrane
What is a cochlear implant?
Cochlear implants are designed to bypass damaged hair cells and stimulate the auditory nerve directly through the application of electrical current. The cochlear implant replaces damaged hair cells in the cochlea and does their job for them
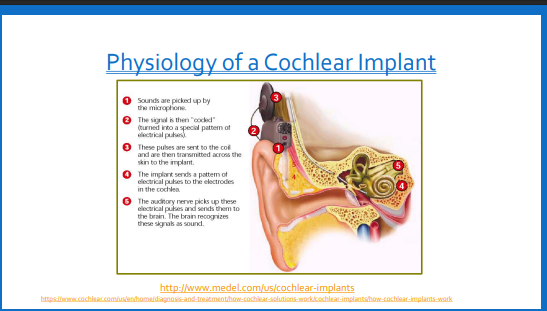
How are Cochlear implants different from a HA
Hearing aids are designed to make sound louder. These amplified sounds are then sent through the damaged part of the cochlea
Who qualifies for a cochlear implant
People with severe to profound hearing loss
What are earmolds?
Piece placed inside of the ear canal to assist with hearing aid
What purpose(s) do earmolds serve?
They connect to the hearing aid and seal and modify sound and hold hearing aid to patients ear
What are some of the issues that adults and older adults experience with hearing loss?
Turning up the volume,
difficulty on the telephone,
decrease in work performance,
increase rate of asking for repetitions
What are some reasons why a person would NOT pursue a hearing evaluation/hearing aid?
Fear and denial
Perceived cost
Stigma
Negative experiences
Lack of awareness
What are some reasons why a person WOULD pursue a hearing evaluation/hearing aid?
Family members suggested getting a hearing test
Having a hard time hearing in noisy environments
Feeling that people are mumbling
Trouble hearing speech through telephone
What role does the communication partner play when designing an AR plan for the patient with hearing loss?
The communication partner can give insight on the patient and their hearing and difficulties. Can engage in communication strategies that are given and motivate the patient. They also help facilitate understanding and support the patient's rehabilitation goals.
How are the communication partners a part of the assessment and evaluation of the impact hearing loss has on a patient?
Communication partners provide valuable feedback about the patient's hearing challenges in daily life, including observations of difficulties in social situations and overall impact on communication. Their perspectives help tailor assessment protocols and rehabilitation strategies. Partner can do daily logs, questionnaires, self-report measures and interview as well
What is speech reading?
“Reader” uses both the speakers provided visual and auditory cues as well as contextual cues
Are people with hearing loss naturally better at it than those with normal hearing?
No, it is difficult to speechread even if a person has a hearing loss due to the complexity of visual cues and the need for practice and familiarity with the speaker's lip movements.
What factors can impact speechreading ability?
Visibility of sound: sound not visible via mouth movements
Rapidity of speech: sounds occur faster than eye can resolve them
Co-articulations and stress effects: appearance of words vary depending on how spoken
Visemes and homophones: sounds/words appear similar on face
Talker effect homophonous: different talkers have different mouth movements
What are some communication strategies that people can use to improve speech understanding and/or communication?
Expressive Repair Strategies: used when the sender produces unintelligible utterance and the communication partner cannot understand it
Receptive repair strategy: used when a person has not understood the message
nonspecific repair: simply indicates a lack of understanding (huh)
Write
Fingerspell
Rephrase message
What is assertiveness training?
A communication strategy aimed at helping individuals express their needs and desires confidently and respectfully, improving interactions in various social situations.
What are some communication breakdowns that can occur for a person with hearing loss?
when conversation deviates from chosen topic
Asking to repeat than ask to simplify message
Use non-specific repair strategies saying “what”
What are conversational rules?
Rules followed when having a conversational some include
Ensure that no single person does all the talking
Take turns in organized fashion
Try to be relevant to the topic of conversation
3 courses of action for a person with HL to have when detecting communication breakdown: use repair strategy, disregards utterance, and bluffing. What happens when each of these strategies are used?

What are the 4 conversational styles?
Passive
Aggressive
Passive-aggressive
Assertive
What is the main aim of aural rehabilitation?
To restore/optimize participation in daily life activities
What 3 things can an audiogram tell us?
The relationship between air and bone conduction thresholds
The amount of hearing loss via bone conduction
The amount of hearing loss via air conduction
Which of the following is NOT something that defines conversational fluency?
monopolizing speaking time
Why should you avoid the use of "why" questions during an interview with a patient, particularly one that is asking about any communication difficulties they have?
Asking "why" questions may give the impression that you are judging them
Which style of hearing aid is best suited for severe to profound hearing loss as it offers the most power/output?
BTE (Behind the Ear)
How is a cochlear implant different from a traditional prescription hearing aid?
CI stimulation/signal is electrical rather than acoustical
Which of the following is NOT one of the three (3) main cochlear implant companies we discussed in class?
Medtronics
Which of the following is NOT a troubleshooting tip for fixing a hearing aid?
Check to see if the magnet is being placed properly on the patient's head
A cochlear implant patient should return to their audiologist for troubleshooting and/or reprogram and/or repair if experiencing all of the following EXCEPT which scenerio?
The patient keeps forgetting to charge the batteries
Which of the following conditions is a patient most suitable for a bone-anchored hearing aid (BAHA)?
They have microtia
What assistve listening device would work best in a closed setting in which it might be difficult for a person to see the talker's face and/or will experience distracting noise, such as in a car ride?
personal FM or remote microphone system
Which of the following is NOT a type of Counseling that might be used during an audiological appointment, particularly during an aural rehabilitation session?
reset counseling
Which type of training helps patients and their communication partners ways in which to better manage communication situations?
assertiveness training