Health Assessment
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 1:36 AM on 9/10/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
131 Terms
1
New cards
Purposes of a Health Assessment
* Establishment of nurse-patient relationship
* Gather data of pt general health status
* Identify pt strengths
* Identify actual and potential health problems
* Establish base for nursing process
* Gather data of pt general health status
* Identify pt strengths
* Identify actual and potential health problems
* Establish base for nursing process
2
New cards
Different Types of Health Assessment
* Comprehensive
* Ongoing/Partial/Follow Up
* Focused
* Emergency
* Ongoing/Partial/Follow Up
* Focused
* Emergency
3
New cards
Comprehensive Health Assessment
A health assessment done upon admission, a broad health assessment that includes a complete health history and a physical assessment.
4
New cards
Ongoing/Partial/Follow Up Health Assessment
A type of health assessment done at regular intervals. This assessment concentrates on specific problems to monitor positive or negative trends and evaluate interventions effectiveness. These assessments are also used to find new problems.
5
New cards
Focused Health Assessment
A type of health assessment done to assess a specific health issue and focuses on pertinent history and body regions, usually involving 1 or 2 systems. Thus type of assessment can also be used to address immediate and highest priority concerns.
6
New cards
Emergency Health Assessments
A type of focused assessment done when addressing life-threatening or unstable conditions.
7
New cards
What are some ways that you may prepare a patient for a physical assessment?
* Consider physiologic and psychological needs of patient
* Explain general process to patient to decrease fear and anxiety
* Explain each procedure more in depth as you do them
* Have patient change into a gown and empty bladder
* Answer questions directly and honestly
* Explain general process to patient to decrease fear and anxiety
* Explain each procedure more in depth as you do them
* Have patient change into a gown and empty bladder
* Answer questions directly and honestly
8
New cards
How would you prepare the environment for a physical assessment?
* Ensure privacy and respect
* Agree on specific time for assessment
* Ensure patient is free of pain
* Prepare bed/examination table
* Provide gown and drape
* Gather needed supplies beforehand
* Agree on specific time for assessment
* Ensure patient is free of pain
* Prepare bed/examination table
* Provide gown and drape
* Gather needed supplies beforehand
9
New cards
Standing
Position used to assess posture, balance, and gait. Do not use for pt who are weak, dizzy, or fall-risk.
10
New cards
Sitting
Position that allows for visualization of upper body, full lung expansion, VS assessment, and assessment of the body above the abdomen.
11
New cards
Supine
Position that allows for relaxation of abdominal muscles, assessment of VS, and assessment of the anterior body.
12
New cards
Dorsal Recumbent
Position used for patients that have difficulty maintaining supine position. Used for assessment of the anterior body with exception to the abdomen as this position causes abdominal muscle contraction.

13
New cards
Sim’s
Position used for assessment of rectum or vagina.
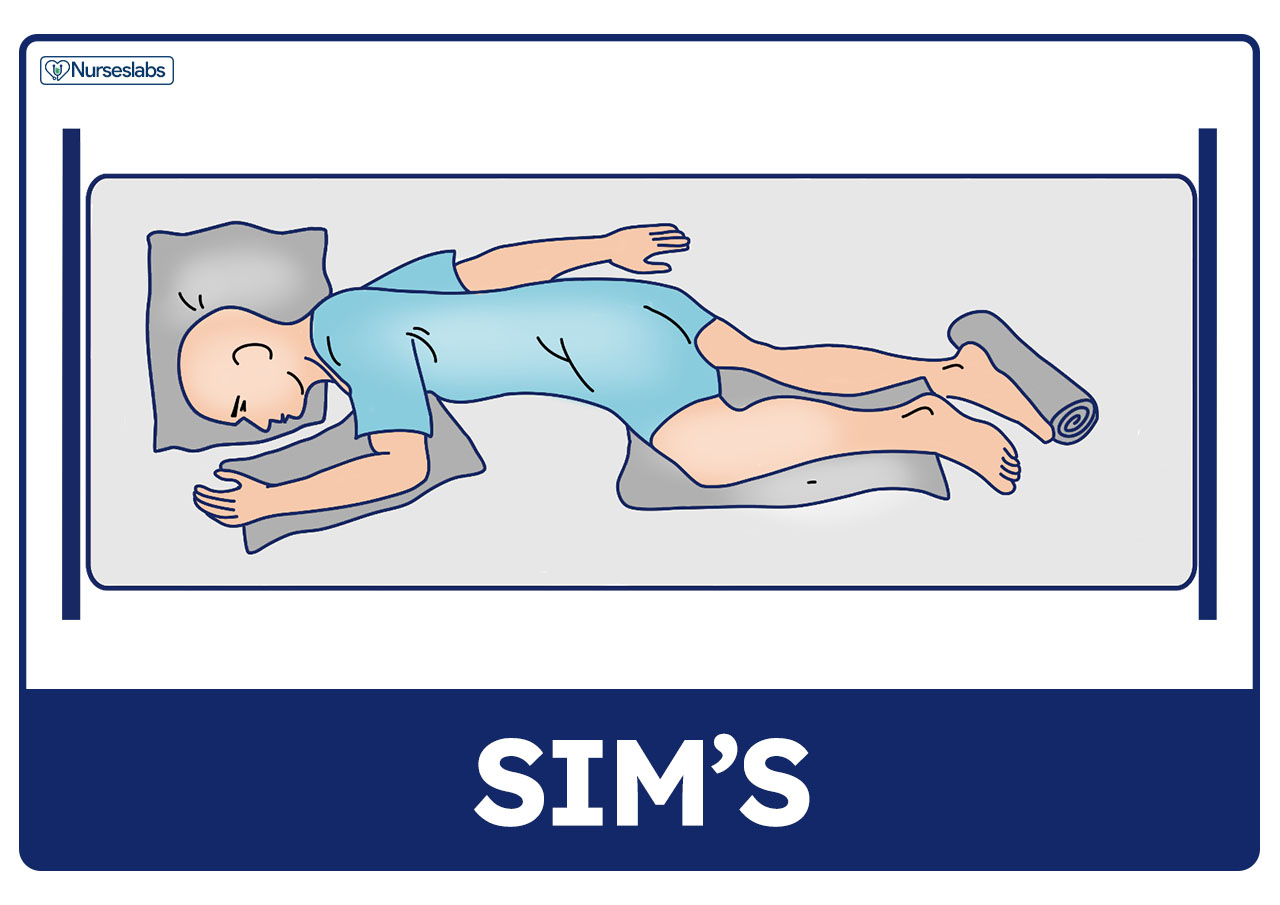
14
New cards
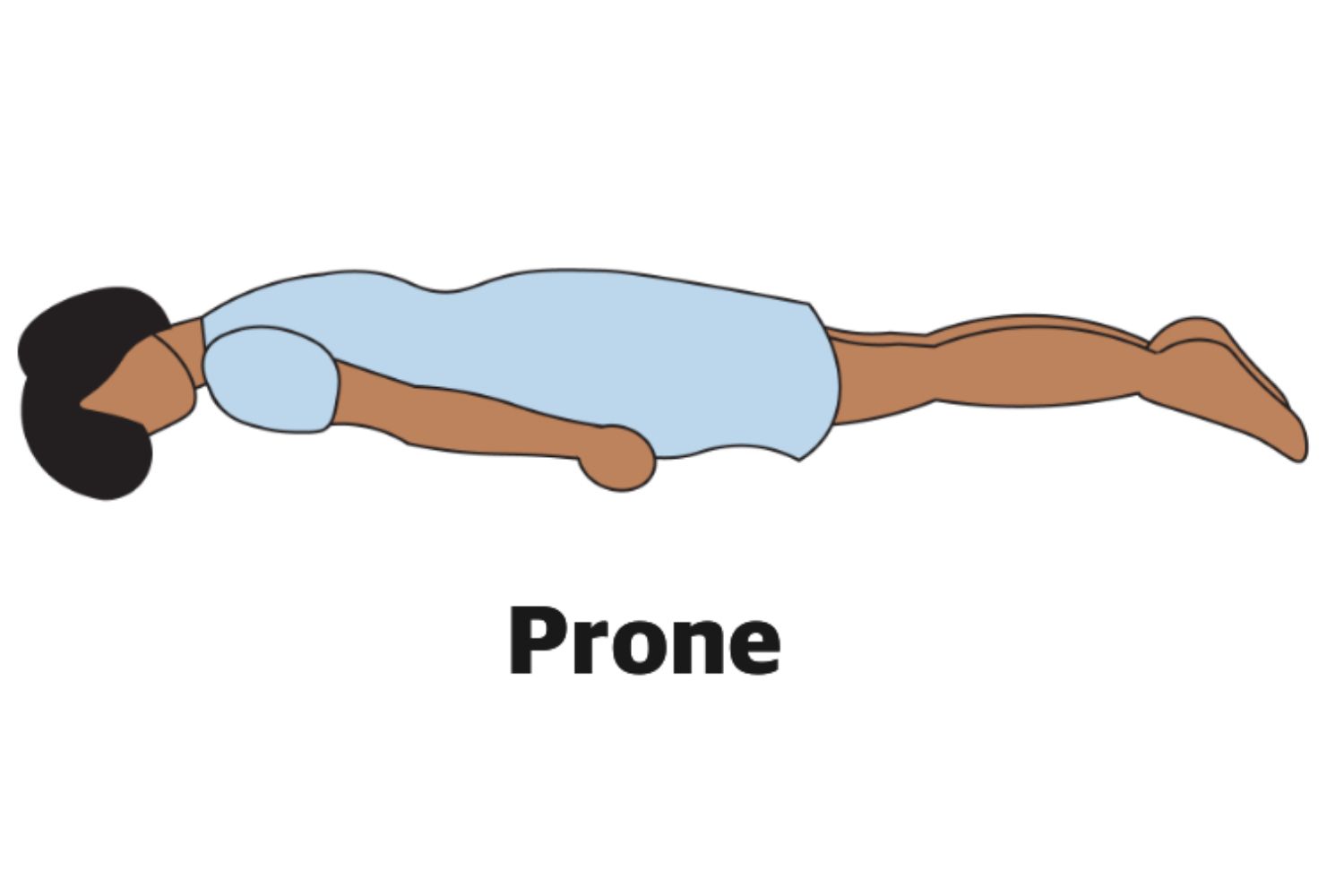
Prone
Position used to assess hip joint and posterior thorax.
15
New cards
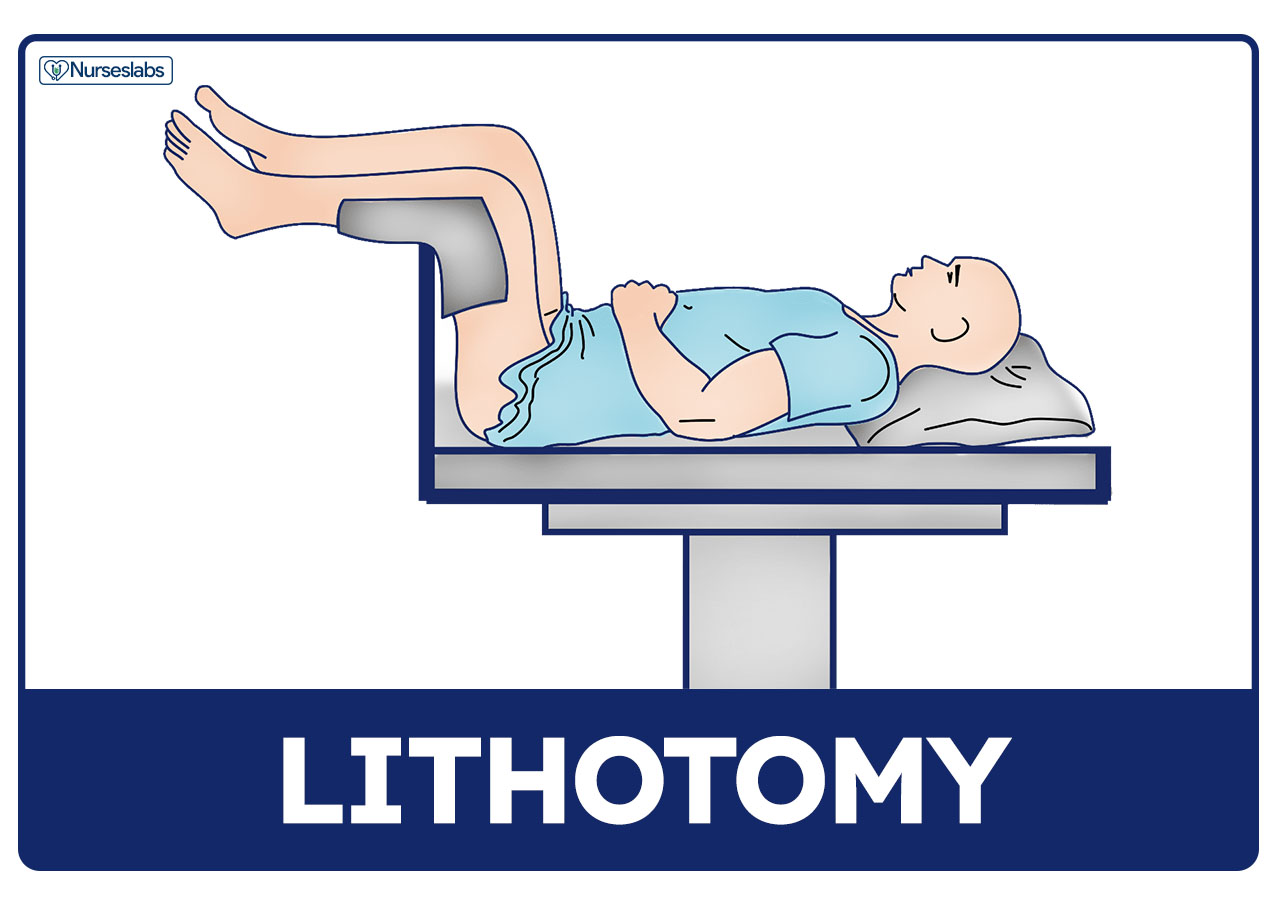
Lithotomy
Position used for assessment of female genitalia and rectum.
16
New cards
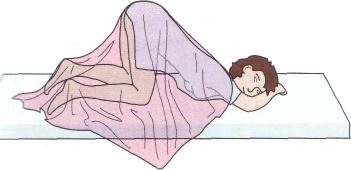
Knee-Chest
Position used for assessment of anus and rectum.
17
New cards
What factors should you assess during a health history?
* Biographical data
* Reason for seeking care
* History of present illness
* Past medical history
* Family history
* Functional health
* Psychosocial and lifestyle factors
* Review of systems
* Reason for seeking care
* History of present illness
* Past medical history
* Family history
* Functional health
* Psychosocial and lifestyle factors
* Review of systems
18
New cards
What type of questions would you ask regarding present health history?
Questions that are directly related to the primary problem the patient is complaining of.
19
New cards
What type of questions would you ask regarding past health history?
Questions related to the patient’s health in the past (Ex. childhood injuries) or simply not related to the illness the patient is currently presenting with (Ex. Prescribed medications).
20
New cards
What types of questions would you ask regarding family history?
Health history of the patient’s family that can be explicitly or implicitly related to the patient.
21
New cards
What type of questions would you ask regarding functional health?
Questions regarding the daily/typical life of the patient.
22
New cards
What are the techniques used during a physical assessment?
1. Inspection
2. Palpation
3. Percussion
4. Auscultation
23
New cards
Inspection
A technique used in a physical assessment that starts upon initial contact and continues throughout the assessment. Appearance, behavior, movement, size, color, shape, position, and symmetry are assessed.
24
New cards
Palpation
A technique used during a physical assessment that uses touch to assess for temperature, turgor, texture, moisture, vibrations, and sharp or structures. There are two types of palpation: light (1-2cm) and deep.
25
New cards
Percussion
A technique used during a physical assessment that assesses location, shape, size, and density of tissues. Fingertips are tapped over body tissues to produce sounds/vibrations.
26
New cards
Auscultation
A technique used during a physical assessment that assesses the four characteristics of sound: pitch, loudness, quality, and duration. Auscultation is performed using a stethoscope.
27
New cards
How would safety be assessed?
* Bed position
* Call light position
* Appropriate emergency equipment
* Assistive devices
* Fall risk/hazards
* Call light position
* Appropriate emergency equipment
* Assistive devices
* Fall risk/hazards
28
New cards
List the Vital Signs
* Temperature
* Pulse
* Respirations
* BP
* O2 sat
* Pain
* Pulse
* Respirations
* BP
* O2 sat
* Pain
29
New cards
How would you assess mental status?
* LOC
* A&O x? (Person, place, time, event)
* Speech
* A&O x? (Person, place, time, event)
* Speech
30
New cards
How would you assess the psychosocial status of a patient?
Assess behavior and affect.
31
New cards
How would you assess the head, eyes, ears, and nose of a patient?
Assess the following:
* Eyes
* Pupils
* Mouth
* Carotid arteries
* Swallowing
* Throat
* Neck and facial color
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Glasses?
* Hearing aids?
* Ability to hear
* Ability to see
* Eyes
* Pupils
* Mouth
* Carotid arteries
* Swallowing
* Throat
* Neck and facial color
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Glasses?
* Hearing aids?
* Ability to hear
* Ability to see
32
New cards
How would you assess the chest of a patient?
* Color
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Respirations and their quality
* Heart sounds
* Lung sounds
* Cough
* Sputum
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Respirations and their quality
* Heart sounds
* Lung sounds
* Cough
* Sputum
33
New cards
How would you assess the abdomen of a patient?
* Color
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Bowel sounds
* Tenderness
* Distention
* Pain/discomfort
* Ability to eat
* Urine elimination patterns
* Urine characteristics
* Bowel elimination pattern
* Stool characteristics
* Moisture
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Bowel sounds
* Tenderness
* Distention
* Pain/discomfort
* Ability to eat
* Urine elimination patterns
* Urine characteristics
* Bowel elimination pattern
* Stool characteristics
34
New cards
How would you assess the upper and lower extremities of a patient?
* Skin
* Color
* Pulses
* Temperature
* Tenderness
* Edema
* Capillary refill
* Strength
* Sensation
* ROM
* Lesions
* Wounds
* Color
* Pulses
* Temperature
* Tenderness
* Edema
* Capillary refill
* Strength
* Sensation
* ROM
* Lesions
* Wounds
35
New cards
How would you assess the activity of a patient?
Assess the following:
* Movement and ambulating
* Ability to move in bed
* Ability to get out of bed
* Ability to walk and distance walkers
* Gait
* Movement and ambulating
* Ability to move in bed
* Ability to get out of bed
* Ability to walk and distance walkers
* Gait
36
New cards
What is important about vital signs?
They indicate the general physiologic functioning and health status of a patient.
37
New cards
Can VS be delegated?
Yes, only if the patient is stable.
38
New cards
What is the responsibility of the RN regarding VS?
* Accuracy
* Interpretation
* Reporting of abnormal findings
* Interpretation
* Reporting of abnormal findings
39
New cards
Redness
Also known as erythema or flushing, a skin color that can be found on the face or in a localized area of skin. Can be caused by blushing, alcohol, fever, trauma, or infection.
40
New cards
Bluish
Also known as cyanosis, a skin color that can be noticed in exposed area, ears, lips, mouth, hands, feet, nail beds, and exposed areas in general. Can be caused by coldness or hypoxemia.
41
New cards
Yellowish
Also known as jaundice, a skin color that can be seen throughout the body. Can be caused by liver disease due to increased bilirubin levels.
42
New cards
Paleness
Also known as pallor, a skin color that can be seen in the face, lips, conjunctivae, mucous membranes, and exposed areas in general. Can be caused by anemia (Decreased hemoglobin) or shock (Decreased blood volume).
43
New cards
White patchy areas on skin
Also known as vitiligo, a skin color assessment that can be seen throughout the body. Usually caused by congenital or autoimmune conditions leading to depigmentation.
44
New cards
Tanned or Brown
A skin color assessment that can be seen in sun-exposed areas. Usually caused by overexposure causing increased melanin production or pregnancy.
45
New cards
Purplish
Also known as ecchymosis, a skin color assessment caused by collection of blood within subcutaneous tissue.
46
New cards
Small, nonblanchable purple spots
Also known as petechiae, a skin color assessment where there are small hemorrhagic spots that do not blanch when pressure is applied.
47
New cards
Excessive Perspiration
Also known as diaphoresis, a skin color assessment in which the patient is excessively wet with sweat.
48
New cards
Skin Tension
Also known as turgor, a skin assessment measuring skin tension which is dependent upon hydration.
49
New cards
Excessive extracellular accumulation of fluid
Edema
50
New cards
What assessment tool would you use for melanoma?
* A (Asymmetry)
* B (Border)
* C (Color)
* D (Diameter)
* E (Evolving)
* B (Border)
* C (Color)
* D (Diameter)
* E (Evolving)
51
New cards
Describe asymmetry when assessing for melanoma
If a line is drawn through a mole, both sides will not match.
52
New cards
Describe border when assessing for melanoma
Early melanoma borders are usually uneven with the edges possibly being scalloped or notched.
53
New cards
Describe color when assessing for melanoma
Color variety is a warning sign. Melanomas can be different shades of brown, tan, black, red, white, or blue.
54
New cards
Describe diameter when assessing for melanoma
Melanomas are usually larger than the size of a pencil eraser, but may be smaller when initially detected.
55
New cards
Describe evolving when assessing for melanoma
Any change in the mole/site points towards danger.
56
New cards
How would you test for pupillary reaction?
* Darken a room and have the pt look ahead
* Using a penlight, move light from the side of the pt head towards his/her eyes
* Observes for contraction and size
* Repeat on the other side
* Equal bilateral pupil size and constriction upon contact with light are normal results
* Using a penlight, move light from the side of the pt head towards his/her eyes
* Observes for contraction and size
* Repeat on the other side
* Equal bilateral pupil size and constriction upon contact with light are normal results
57
New cards
How would you assess for convergence?
* Hold an object 6-8 inches away from pt nose and have pt look at point/tip of object
* Move object closer to pt nose
* Eyes converging (Pt appearing cross-eyes) are normal results
* Move object closer to pt nose
* Eyes converging (Pt appearing cross-eyes) are normal results
58
New cards
How would you test for accommodation?
* Hold an object with a tip 4-6 inches away from pt nose
* Have pt look at object first ten a more distant object
* Finally, have pt refocus back on the near object
* Pt pupil constriction when looking at near object and pupil dilation when looking at distant object are normal results
* Have pt look at object first ten a more distant object
* Finally, have pt refocus back on the near object
* Pt pupil constriction when looking at near object and pupil dilation when looking at distant object are normal results
59
New cards
How would you test extraocular movements?
* Position pt 2 ft away facing you at eye level
* Have patient hold still and follow movement of penlight with eyes
* Move penlight through cardinal positions
* Pt following penlight with no lag in eyes are normal results
* Have patient hold still and follow movement of penlight with eyes
* Move penlight through cardinal positions
* Pt following penlight with no lag in eyes are normal results
60
New cards
How would you test peripheral vision?
* Have pt stand 2 ft away and face you at eye level
* Have pt cover one eye
* Have pt fix gaze upon your nose
* Outstretch your arm to one side so that neither you nor the pt sees your fingers
* Bring arm and fingers into your and the pts peripheral vision and tell pt to inform you when he/she sees tour fingers
* Repeat steps on other side
* Pt and you should see finger within peripheral vision around the same time for normal results
* Have pt cover one eye
* Have pt fix gaze upon your nose
* Outstretch your arm to one side so that neither you nor the pt sees your fingers
* Bring arm and fingers into your and the pts peripheral vision and tell pt to inform you when he/she sees tour fingers
* Repeat steps on other side
* Pt and you should see finger within peripheral vision around the same time for normal results
61
New cards
What are the characteristics of sound you can assess during auscultation?
1. Pitch
2. Loudness
3. Quality
4. Duration
62
New cards
Describe Pitch (Auscultation)
Ranges from high to low
63
New cards
Describe Loudness (Auscultation)
Ranges from soft to loud
64
New cards
Describe Quality (Auscultation)
Descriptions such as gurgling or swishing.
65
New cards
Describe Duration (Auscultation)
Short, medium, or long
66
New cards
What are the normal breath sounds?
* Bronchial/Tubular
* Bronchovesicular
* Vesicular
* Bronchovesicular
* Vesicular
67
New cards
What are the adventitious/abnormal breath sounds?
* Wheeze (Sibilant)
* Rhonchi (Sonorous wheeze)
* Crackles
* Strider
* Friction Rub
* Rhonchi (Sonorous wheeze)
* Crackles
* Strider
* Friction Rub
68
New cards
Bronchial/Tubular Lung Sounds
A normal lung sound characterized as blowing, hollow sounds. This sound is auscultated over the larynx and trachea and expiration sound is longer, lower, and higher pitched.
69
New cards
Bronchovesicular Lung Sounds
A normal lung sound that is medium-pitched, medium intensity, and is characterized by blowing sounds. This sound is auscultated over the anterior first and second intercostal space and over the scapula posteriorly. Inspiration and expiratory sounds are similar.
70
New cards
Vesicular Lung Sounds
A normal lung sound characterized by soft, low-pitched, whispering sounds. Heard over most lung fields, inspiration is longer, louder, and higher pitched.
71
New cards
Wheeze (Sibilant)
An abnormal lung sound characterized by musical/squeaking sounds that are high-pitched and continuous. This sound can be heard during inspiration and expiration and indicated air passing through narrow airways.
72
New cards
Rhonchi (Sonorous Wheeze)
An abnormal lung sound characterized by sonorous/coarse, low-pitched continuous sounds. This lung sound is heard during inspiration and expiration and indicated air passing through or around secretions. Coughing may somewhat clear this sound.
73
New cards
Crackles
An abnormal lung sound characterized by bubbling, crackling, or popping sounds that have a low- to high-pitch and is discontinuous. Heard during inspiration and expiration, this sound indicates opening of small deflated airways and alveoli with air passing thru fluid in these airways.
74
New cards
Stridor
An abnormal lung sound characterized by harsh, loud, and high-pitched sounds that are heard upon inspiration. This sound indicates a narrowing of the upper airway and/or presence of foreign body in airway.
75
New cards
Friction Rub
An abnormal lung sound characterized by rubbing or grating sounds that are lowest over the lower lateral anterior surface. This sound is heard upon inspiration and expiration and indicates inflamed pleura rubbing against chest wall.
76
New cards
What are the two normal heart sounds?
1. S1 (“lub”)
2. S2 (“dub”)
77
New cards
Describe the S1 heart sound
Normal heart sound that sounds like “lub”. This sound represents the closing off the mitral and tricuspid valves and initiation of ventricular contraction and is best heard in the tricuspid and apical areas.
78
New cards
Describe the S2 heart sound
Normal heart sound that sounds like “dub”. This heart sound indicates the closing of the aortic and pulmonic valves, termination of systole, and initiation of ventricular diastole. This sound is best heard over the aortic and pulmonic areas.
79
New cards
What extra heart sounds may you auscultate?
S3 and S4
80
New cards
Describe S3 heart sounds
An extra heart sound that may follow S2 and can be heard as “dee”. This sound is best heard over the mitral area and is considered normal in children and young adults, but abnormal in middle-age and older adults.
81
New cards
Describe S4 heart sounds
An extra heard sound that may precede S1 and can be heard as “dee”. This sound is considered normal in older adults, but is considered abnormal in all other age groups.
82
New cards
What are the five areas for listening to the heart?
* Aortic (Right second intercostal space, sternal border)
* Pulmonic (Left second intercostal space, sternal border)
* Eros Point (Left third intercostal space, sternal border)
* Tricuspid (Left fourth intercostal space, sternal border)
* Mitral (Left fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line)
* Pulmonic (Left second intercostal space, sternal border)
* Eros Point (Left third intercostal space, sternal border)
* Tricuspid (Left fourth intercostal space, sternal border)
* Mitral (Left fifth intercostal space, midclavicular line)
83
New cards
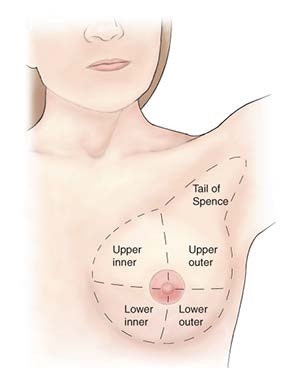
How is the female breast divided?
\
84
New cards
How would you assess a female breast using the circular technique?
Using the pads of your first three fingers, gently compress the breast against the chest wall beginning at the tail of spence and going in gradually smaller circles.
85
New cards
How would you assess a female breast using the wedge technique?
Using the pads of your first three fingers, gently compress the breast against the chest wall and palpate from the periphery towards the areola. Go in a clockwise fashion.
86
New cards
How would you assess a female breast using the vertical strip technique?
Using the pads of your first three fingers, gently compress the breast against the chest wall and begin at the outer edge of the breast and palpate up and down, eventually covering the whole breast.
87
New cards
What structures are in the right upper quadrant (RUQ)?
* Pylorus
* Duodenum
* Liver
* Right kidney and adrenal gland
* Hepatic flexure of colon
* Head of pancreas
* Duodenum
* Liver
* Right kidney and adrenal gland
* Hepatic flexure of colon
* Head of pancreas
88
New cards
What structures are in the left upper quadrant (LUQ)?
* Stomach
* Spleen
* Left kidney and adrenal gland
* Splenic flexure of colon
* Body of pancreas
* Spleen
* Left kidney and adrenal gland
* Splenic flexure of colon
* Body of pancreas
89
New cards
What structures are in the right lower quadrant (RLQ)?
* Cecum
* Appendix
* Right ovary and fallopian tube (Female)
* Right ureter and lower kidney pole
* Right spermatic cord (Male)
* Appendix
* Right ovary and fallopian tube (Female)
* Right ureter and lower kidney pole
* Right spermatic cord (Male)
90
New cards
What structures are in the left lower quadrant (LLQ)?
* Sigmoid colon
* Left ovary and fallopian tube (Female)
* Left ureter and lower kidney pole
* Left spermatic cord (Male)
* Left ovary and fallopian tube (Female)
* Left ureter and lower kidney pole
* Left spermatic cord (Male)
91
New cards
What structures are midline?
* Urinary bladder
* Urethra (Female)
* Urethra (Female)
92
New cards
What four things should you look for when assessing for scoliosis?
1. Head level and centered over trunk
2. Shoulders same height
3. Hips at same level
4. When bent forwards with arms drooping towards feet, is the rib cage level on both sides?
93
New cards
How would you assess grip?
Have pt squeeze your index and middle fingers.
94
New cards
How would you test knee flexion?
Have pt bend their knee and keep his/her foot on the table. Have the pt attempt to keep this position with foot down while you try to straighten his/her knee.
95
New cards
How would you test knee extension?
While you support pt knee and provide resistance at the ankle. Have patient attempt to straighten the leg.
96
New cards
How would you generally test for muscle strength?
Have patient move against resistance. Bilateral equal resistance should be present. Slightly high resistance on dominant side is normal.
97
New cards
How would you assess for shoulder flexion?
Have patient raise arm forward against resistance.
98
New cards
How would you test for wrist extension?
Pt makes fist and resists you attempt to pull wrist down.
99
New cards
How would you assess hip flexion?
Have pt raise thigh against resistance.
100
New cards
How would you assess ankle plantar flexion?
Have pt push using balls of feet against your resistance as if he/she was stepping on a pedal.