434 Unit 2 Lec 13-14
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/30
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
31 Terms
1
New cards
Monogenic Diseases
•Large effect gene variants
•Clearly traced through family pedigrees
•The huntington associated variant was identifying by cutting human DNA with a sequence specific enzyme
•Clearly traced through family pedigrees
•The huntington associated variant was identifying by cutting human DNA with a sequence specific enzyme
2
New cards
Genetic Locus
site on the DNA, contains multiple genes
3
New cards
Genome wide association studies
•Goal is to associate genes with traits
•Individual genes likely only have small effects
•scan for markers across entire genomes
•current approach to understanding polygenic diseases
•Individual genes likely only have small effects
•scan for markers across entire genomes
•current approach to understanding polygenic diseases
4
New cards
Population
For disease, you want people with and without the disease, and for traits, you want people along the continuum of that trait
\
•Certain traits have less or more of a genetic impact- need a large population size
\
•ancestry is a critical factor to consider - compare people from the same ancestry to get the right SNPs
\
•Certain traits have less or more of a genetic impact- need a large population size
\
•ancestry is a critical factor to consider - compare people from the same ancestry to get the right SNPs
5
New cards
GWAS compares….
Compare SNPs in people with and without disease to see if theres a difference between them
6
New cards
Do SNPs cause disease?
\
SNPs dont necessarily cause disease, they’re just associated with the disease
SNPs dont necessarily cause disease, they’re just associated with the disease
7
New cards
Next gene sequencing
needed for finding rare SNPs (find your own SNPs) but its more expensive
8
New cards
Whole Exome Sequencing
Selective sequencing of exons (coding)
→misses out on changes to introns
→misses out on changes to introns
9
New cards
Polygenic Risk Scores
•attempt to determine the relative risk for complex diseases
•consdiers potentially hundreds of genetic variants that modulate disease risk
•Can assess risk for individuals or populations
•Can identify cohorts for further analysis of gene-disease connections
•Can include environmental risk or utilize biomarkers
•consdiers potentially hundreds of genetic variants that modulate disease risk
•Can assess risk for individuals or populations
•Can identify cohorts for further analysis of gene-disease connections
•Can include environmental risk or utilize biomarkers
10
New cards
Polygenic Risk Scores incorporate information from…
GWAS studies

11
New cards
How do non coding variants contribute to genetic disease
•Non coding genome can alter the amount of RNA or protein produced by a gene (gene expression)
→Promoters, enhancers, silencers, insulators
→Promoters, enhancers, silencers, insulators
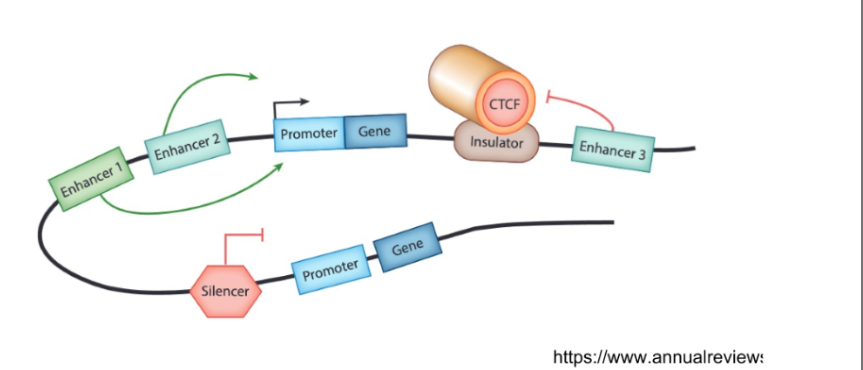
12
New cards
\
Promoters
Promoters
initiate gene expression
13
New cards
Promoters are acted on by
Enhancers, Silencers, Insulators
14
New cards
Enhancers
increase gene expression
15
New cards
Silencers
reduce gene expression
16
New cards
Insulators
block the effect of enhancers at adjacent genes
17
New cards
Personalized Genomics:
“One size fits all” approaches don’t work for everyone
•Using genomics to define or predict disease
•Based on individuals DNA sequence or other biomarkers
•Using genomics to define or predict disease
•Based on individuals DNA sequence or other biomarkers
18
New cards
Precision Medicine
•Allows for more accurate treatment and prevention strategies
•Use of polygenic risk scores to improve patient outcomes is an example
•Use of polygenic risk scores to improve patient outcomes is an example
19
New cards
Pharmacogenomics, PGx
how a persons genetic background effects drug response is a subfield of precision medicine
20
New cards
Uses of precision medicine
•Make a diagnosis
•Plan a treatment
•Determine treatment efficacy
•Make a prognosis
•Plan a treatment
•Determine treatment efficacy
•Make a prognosis
21
New cards
Biomarkers
DNA/RNA/protein features that correlate with disease risk or therapy efficacy, can be used to specify treatment
22
New cards
Pembrolizumab(Keytruda)
•Targets tumors based on two biomarkers: tumor microsatellilite (short DNA repeats) instability (MSI) and DNA mismatch repair deficiency(dMMR)
1)T cells normally attack tumor cells
2)T cells can be inactivated by tumors that express the PD-L pathway
3)Prembrolizumab blocks PD1 receptors on T cells, allowing T cells to attack the tumor
1)T cells normally attack tumor cells
2)T cells can be inactivated by tumors that express the PD-L pathway
3)Prembrolizumab blocks PD1 receptors on T cells, allowing T cells to attack the tumor
23
New cards
Actually personalized medicine:
•mRNA vaccines can be reprogrammed to target tumors from specific patients
•engineerred mRNAs express neoantigens: new proteins found on the outside of tumor cells due to DNA mutations
1)Tissue samples
2)Next generation sequencing
3)Vaccine design
4)Manufacturing
5)Administration
•engineerred mRNAs express neoantigens: new proteins found on the outside of tumor cells due to DNA mutations
1)Tissue samples
2)Next generation sequencing
3)Vaccine design
4)Manufacturing
5)Administration
24
New cards
PGx Goals
•Avoid adverse reactions
•Decide dosage
•Overall patient health improvement
•Decide dosage
•Overall patient health improvement
25
New cards
Pharmacogenes:
•Genes with variants that affect drug pharmacokinetics or pharmacodynamics
•Pharmacokinetic genes:
→normal metabolziers
→poor metabolziers
→intermediate metabolizers
→ultrarapid metabolizers
•Pharmacokinetic genes:
→normal metabolziers
→poor metabolziers
→intermediate metabolizers
→ultrarapid metabolizers
26
New cards
Pharmacodynamic genes
positive or negative for high risk allele
27
New cards
Drug receptors
Varying numbers of drug receptors on cells can produce varying responses
28
New cards
Drug uptake
Drug entry into target cells can be impacted by genotype
29
New cards
Drug breakdown
Genotype impacts the rate of drug breakdown, which affects dosing
30
New cards
Allele specific
•Variant specific therapy
•Pharmacodynamic effect
•Pharmacodynamic effect
31
New cards
CYP2D6
•Structural variants or large scale deletions or duplications affect drug metabolism
•Deletion of CYP2D6 created a null allele that has no activity or less drug metabolism
•Duplications CYP2D6 have increased activity
•Deletion of CYP2D6 created a null allele that has no activity or less drug metabolism
•Duplications CYP2D6 have increased activity