exam 4 assignments o chem
1/59
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
60 Terms
How many chiral ketones are there that have the molecular formula C6H12O?
2
How many achiral aldehydes are there that have the molecular formula C6H12O?
5
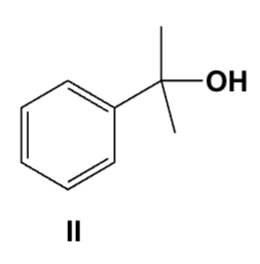
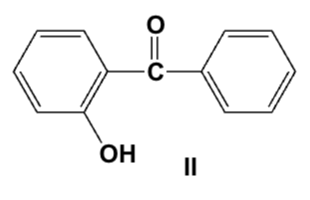
Which is the correct structure for 2-hydroxybenzophenone?
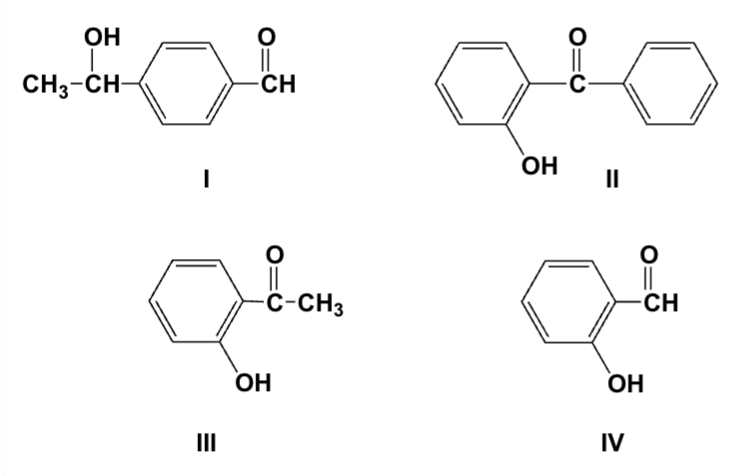
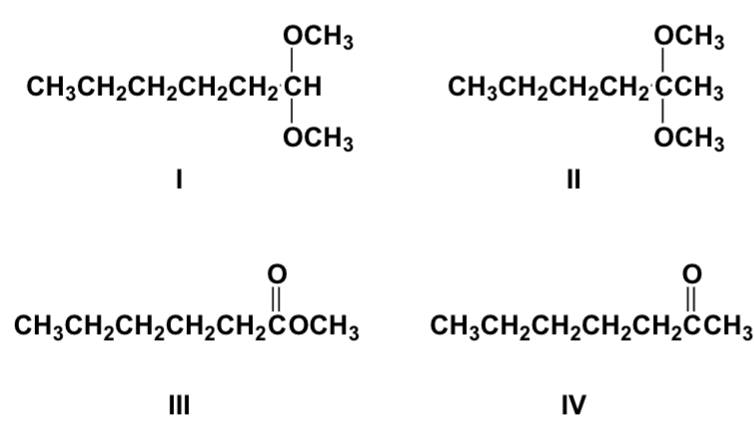
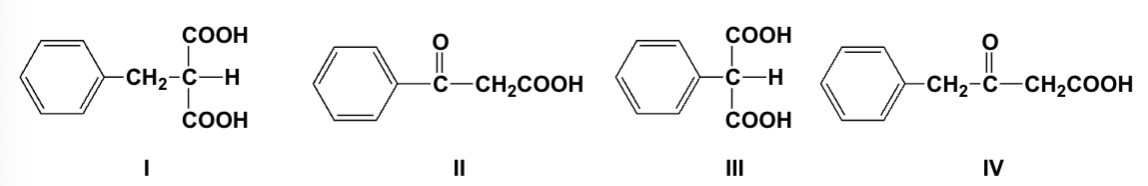
Arrange the compounds in order of increasing solubility in water (least first).
III, IV, I, II
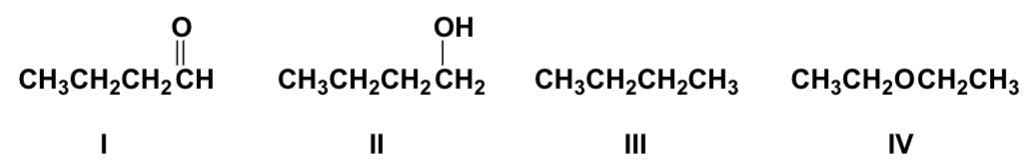
Arrange the compounds in order of increasing boiling point (lowest first).
IV, III, I, II
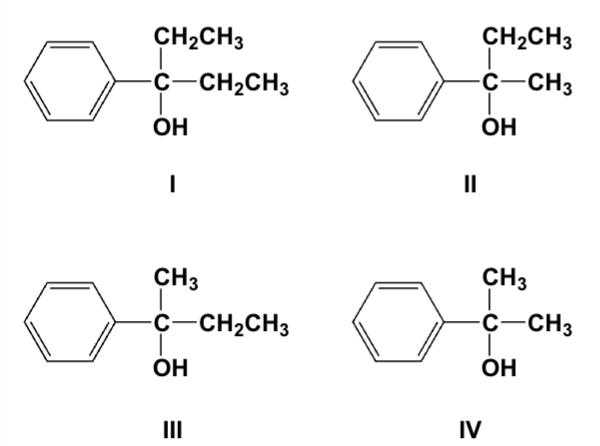
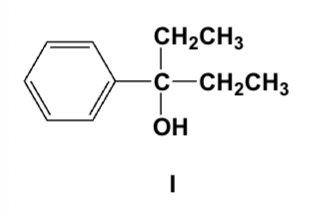
Which is the major product of the reaction of ethyl Grignard and propiophenone (ethyl phenyl ketone)?
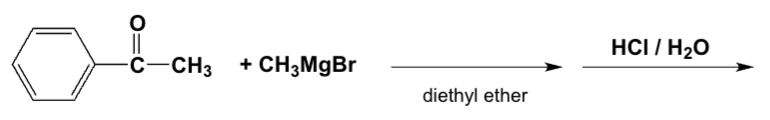
Which is the major product of the following reaction?
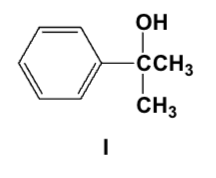
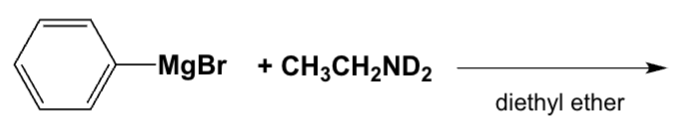
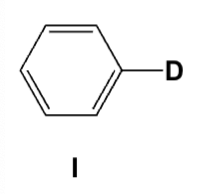
Which is the major product of the following reaction?
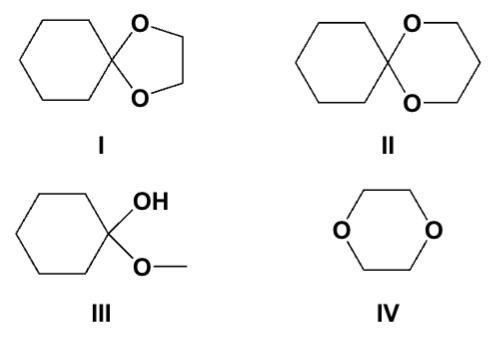
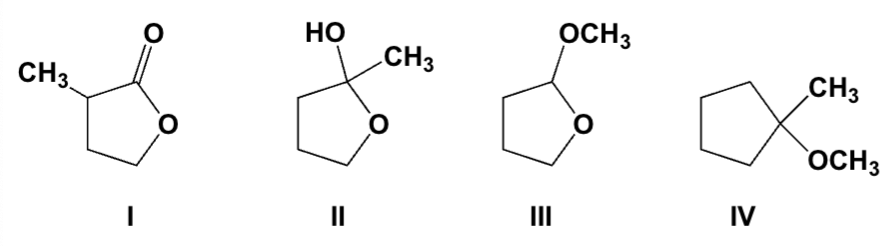
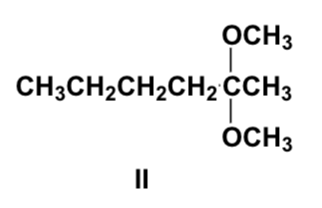
Which compounds are acetals?
I, II
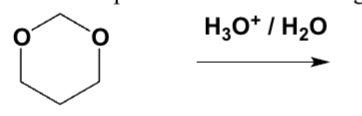
Which is the product of the following reaction?
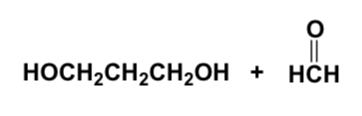
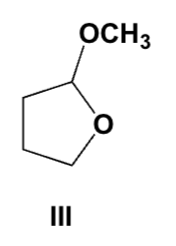
Which compound reacts with aqueous acid to give an aldehyde?
1-Hexene was treated with dilute sulfuric acid. The product of that reaction was reacted with potassium dichromate in sulfuric acid. This product was then treated with methanol in hydrochloric acid. What is the major product of this series of reactions?
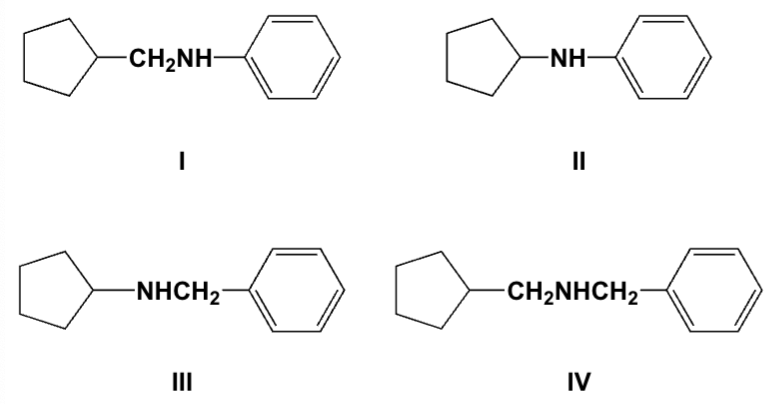
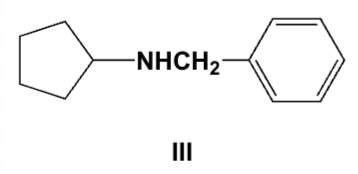
Which is the major product of the reaction of cyclopentylamine and benzaldehyde followed by nickel and hydrogen?
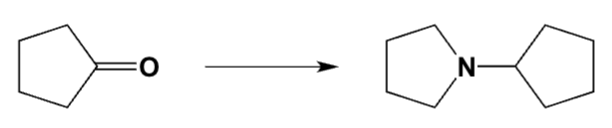
Which is the best procedure for the following preparation?
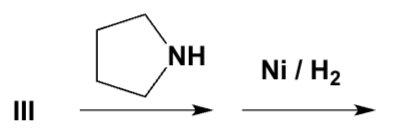
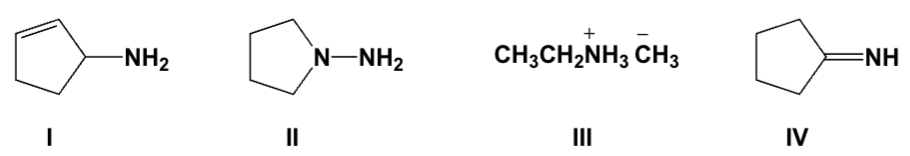
Which compound is a Schiff base?
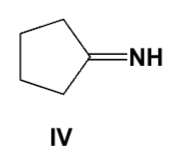
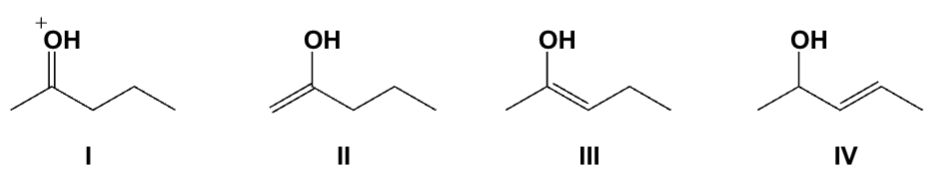
Which structure is the major tautomer of 2-pentanone in aqueous acid?
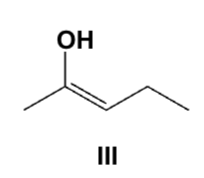
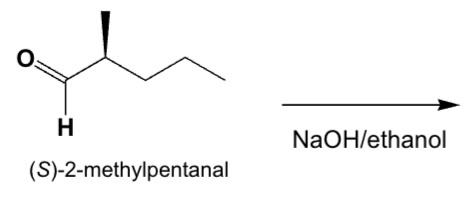
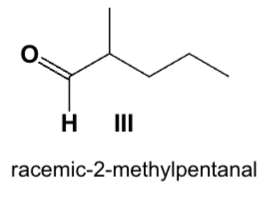
Which is the main product from the reaction of (S)-2-methylpentanal with an aqueous base?
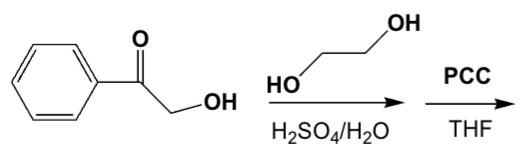
Which is the product of the following sequence of reactions?
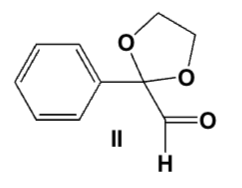
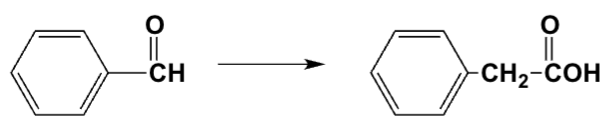
Which is the best procedure for the following preparation?
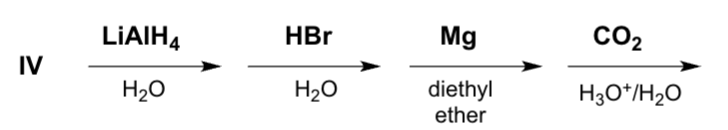
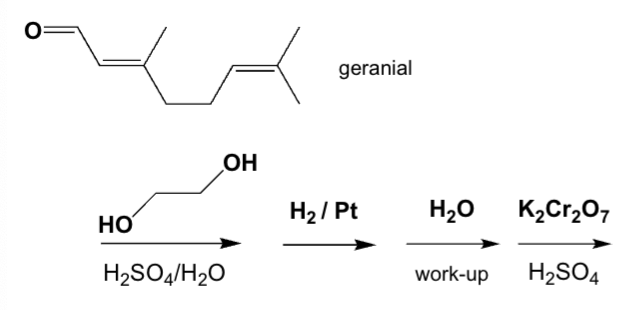
Geranial reacts according to the following reaction sequence. Which product is formed?
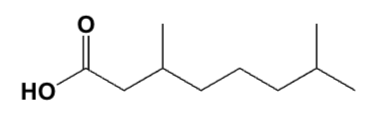
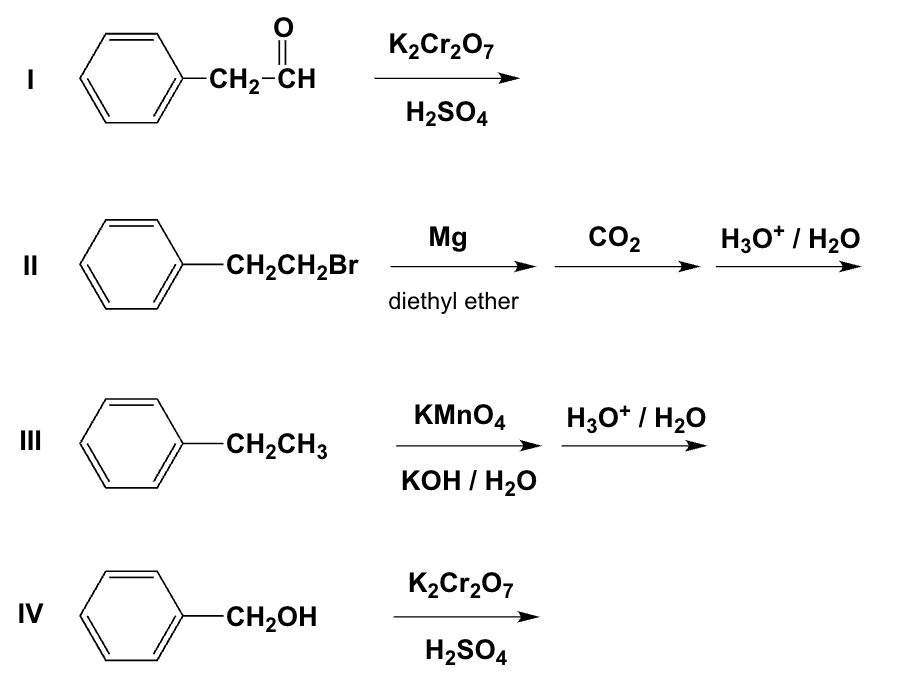
Which reactions yield the same carboxylic acid?
I, III, IV
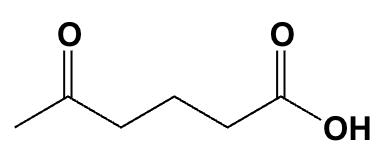
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
5-oxohexanoic acid
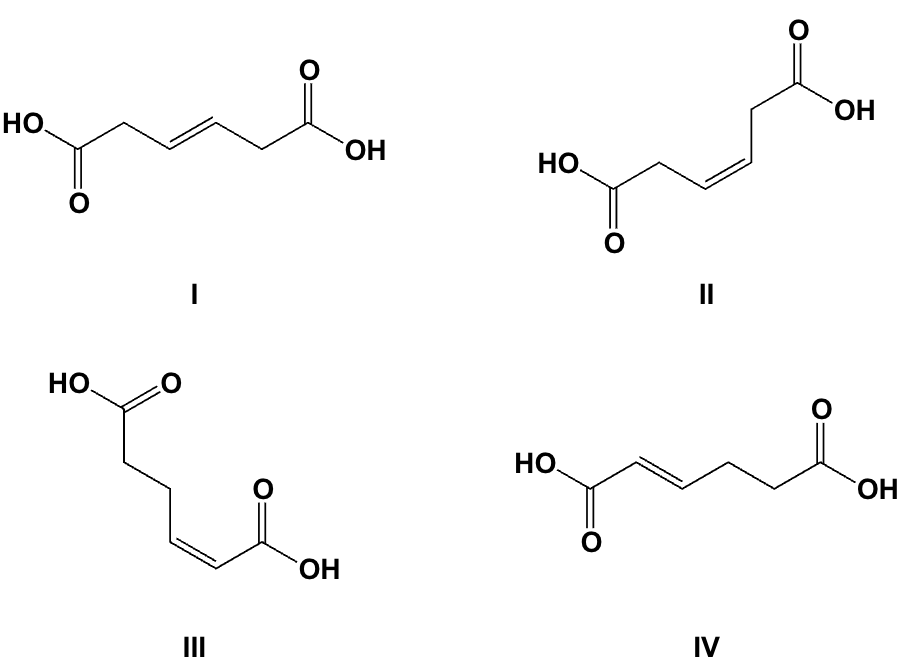
Which is the correct structure for Z-3-hexenedioic acid?
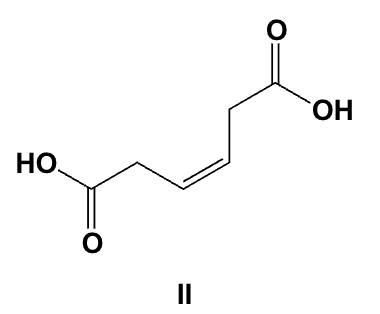
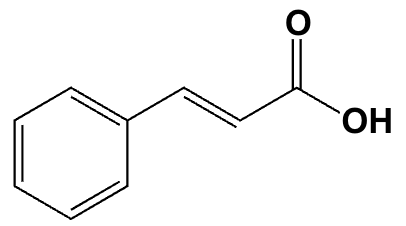
What is the IUPAC name for the following compound?
trans-3-phenylpropenoic acid
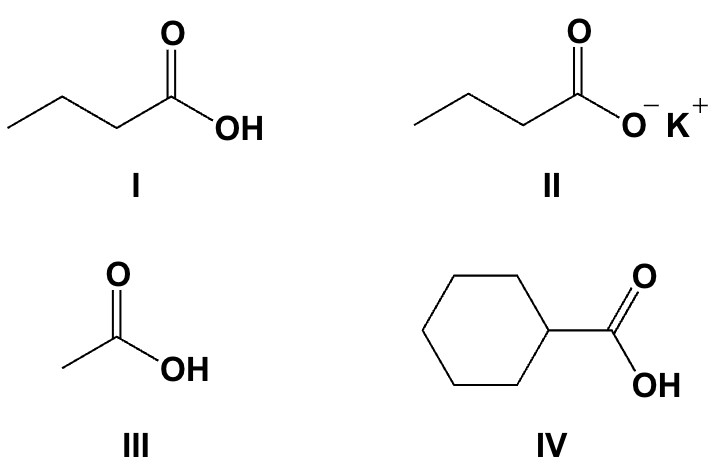
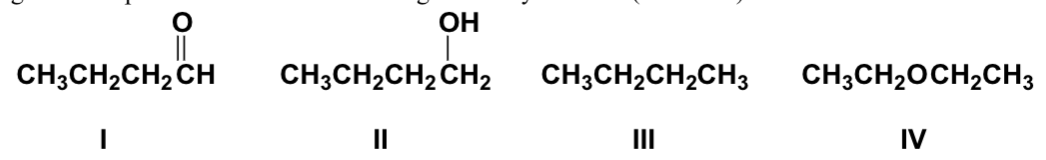
Arrange the compounds in order of increasing solubility in water (least soluble first).
IV, I, III, II
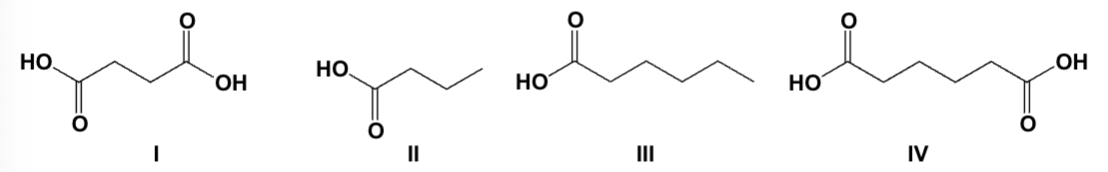
Arrange the compounds in order of increasing boiling point (lowest first).
II, III, I, IV
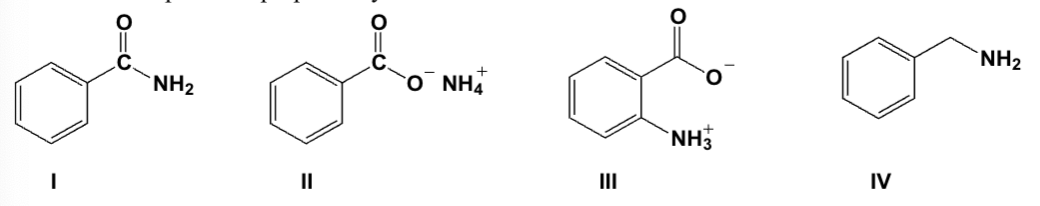
Which compound is prepared by reaction of benzoic acid with ammonia and water?
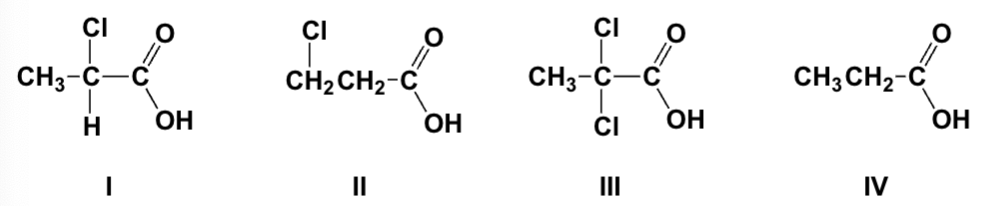
Arrange the compounds in order of increasing acidity (lowest first).
IV, II, I, III

Which reactions proceed nearly to completion as written?
I, II
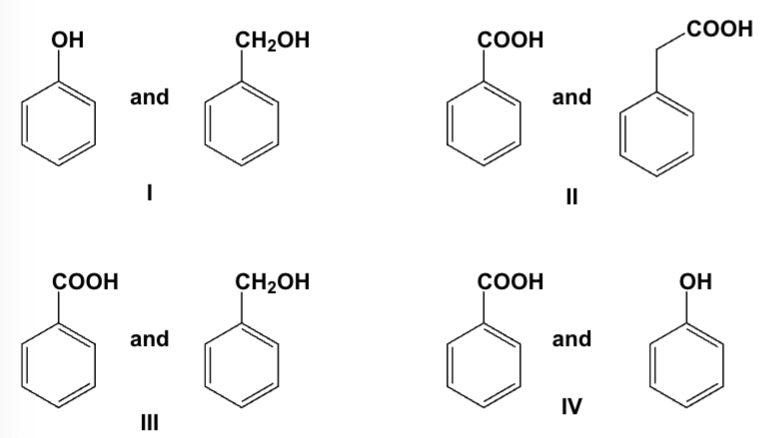
Which mixtures can be separated by treatment with aqueous NaOH?
I, III
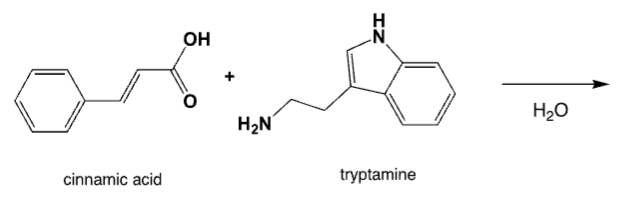
What is the major product of the reaction between cinnamic acid and tryptamine in water?
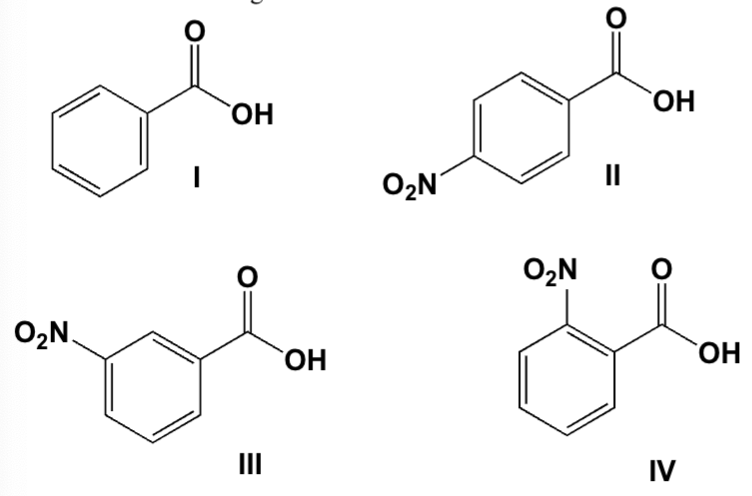
Which acid is strongest?
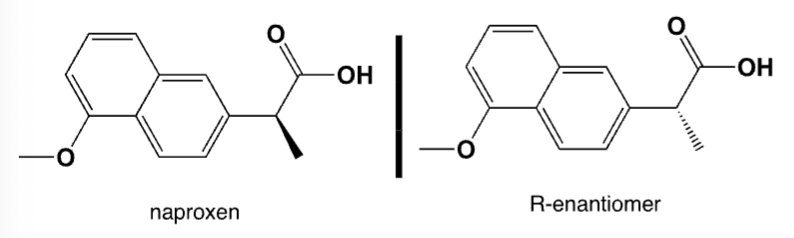
Only the S-enantiomer of naproxen inhibits the COX-1 and COX-2 enzymes, the R-enantiomer is a strong liver toxin. Therefore, only enantiomerically pure naproxen is sold in US pharmacies. Unfortunately, the classic synthesis leads to a racemic mixture. Which base do you use to separate the two enantiomers by recrystallization?
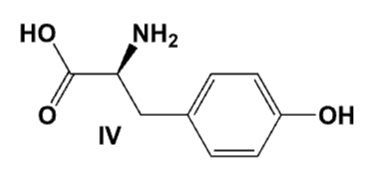
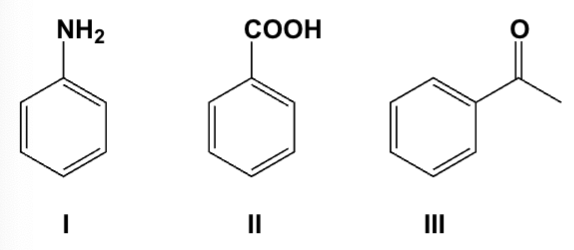
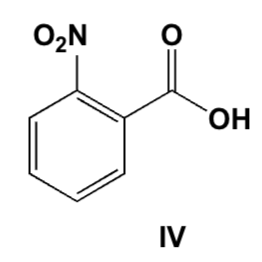
An ether solution containing all of the following compounds was extracted first with 1M HCl, then with 1M NaOH. Which compound was extracted into the basic layer?
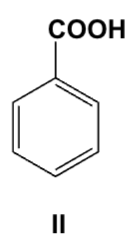
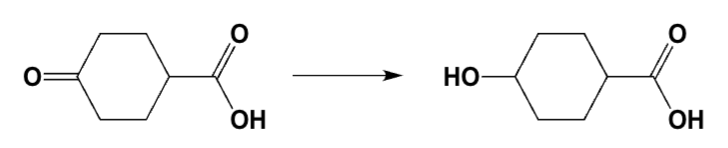
Which conditions are best for the transformation?
NaBH4
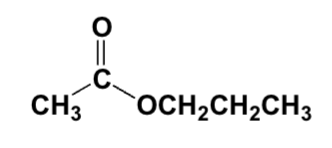
Which conditions are best for making the following compound?
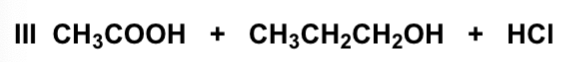
Which conditions will convert pentanoic acid to pentanoyl chloride?
SOCl2
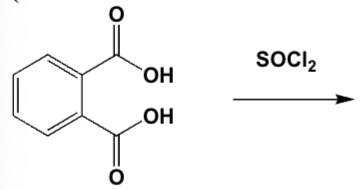
1 Mol of benzene-1,2-dicarboxylic acid reacts with 1 Mol of thionyl chloride. Which product is formed? (HINT: 2 Mols of HCl and 1 Mol of SO2 are released)
Acetophenone (methyl phenyl ketone) is the product from thermal degradation of which compound?
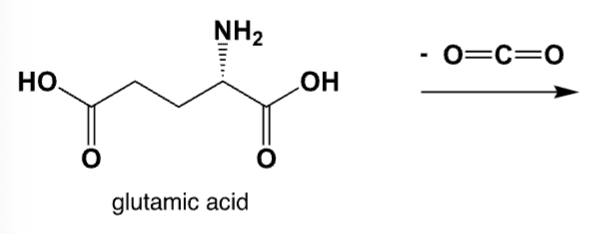
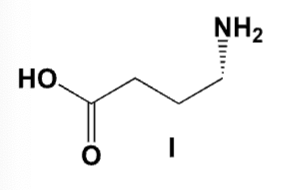
The enzyme-catalyzed decarboxylation of glutamic acids lead to gamma-amino-butyric acid (GABA), which is a common neurotransmitter in the human brain. What is the chemical structure of GABA?
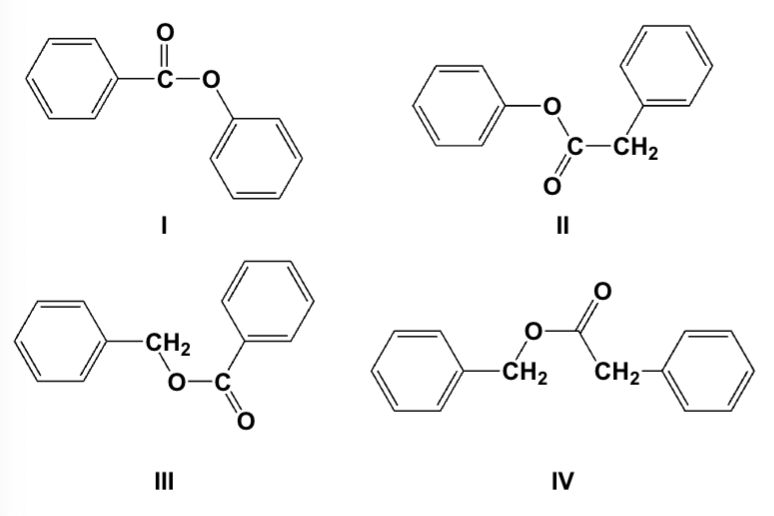
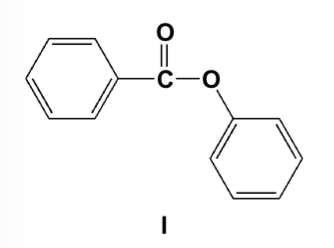
Which is the correct structure for phenyl benzoate?
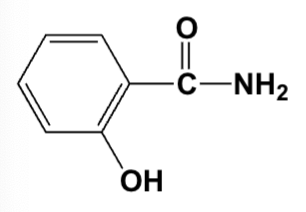
What is the common name for the following compound?
Salicylamide
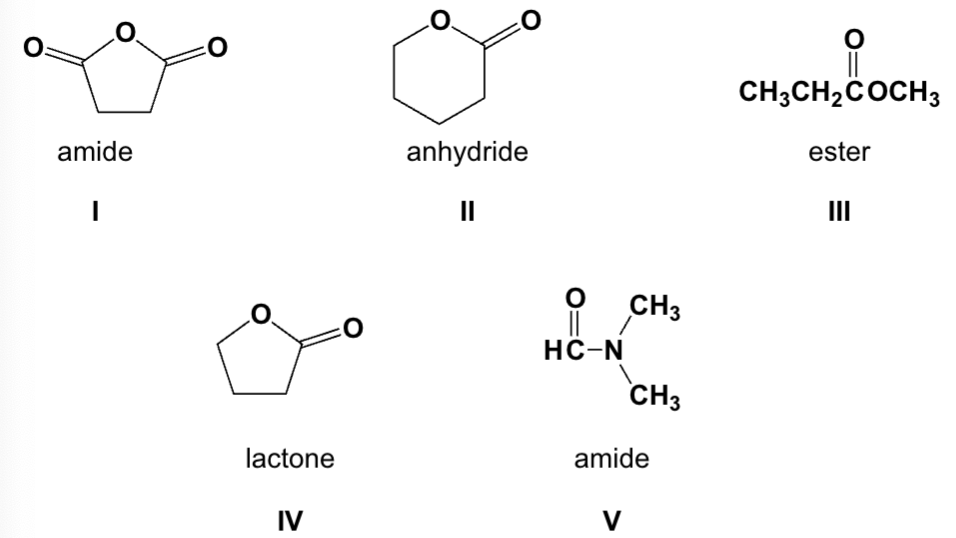
Which functional groups are correctly named?
III, IV, V
Carboxylic acids and amides have in general higher boiling points than esters and anhydrides because of which property?
Hydrogen Bonding
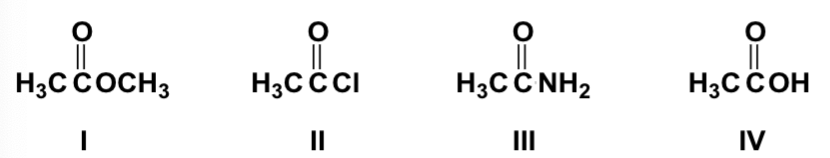
Which is the order of increasing boiling point of the following compounds (lowest first)?
II, I, IV, III
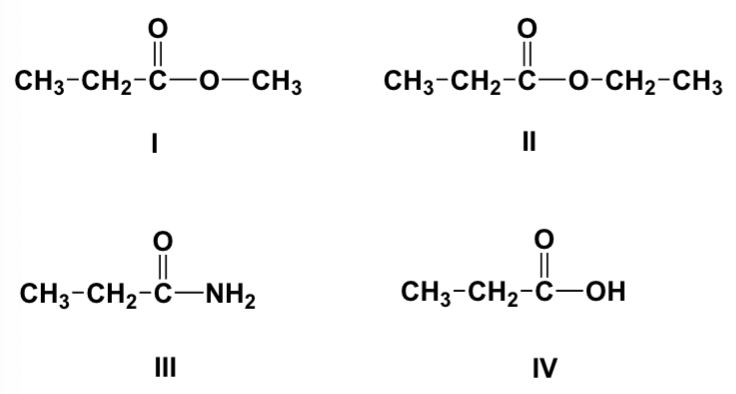
Which is the order of increasing solubility in water of the following compounds (least first)?
II, I, III, IV
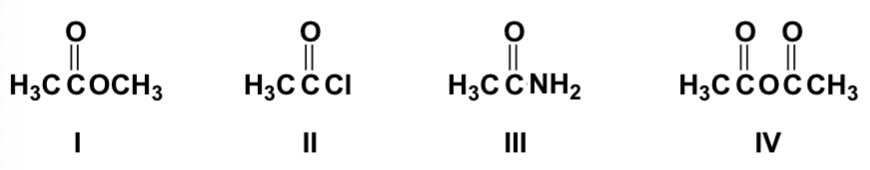
What is the order of decreasing reactivity toward nucleophilic acyl substitution for these carboxylic acid derivatives (most reactive first)?
II, IV, I, III

Which compounds will yield benzoic acid when hydrolyzed?
II, IV
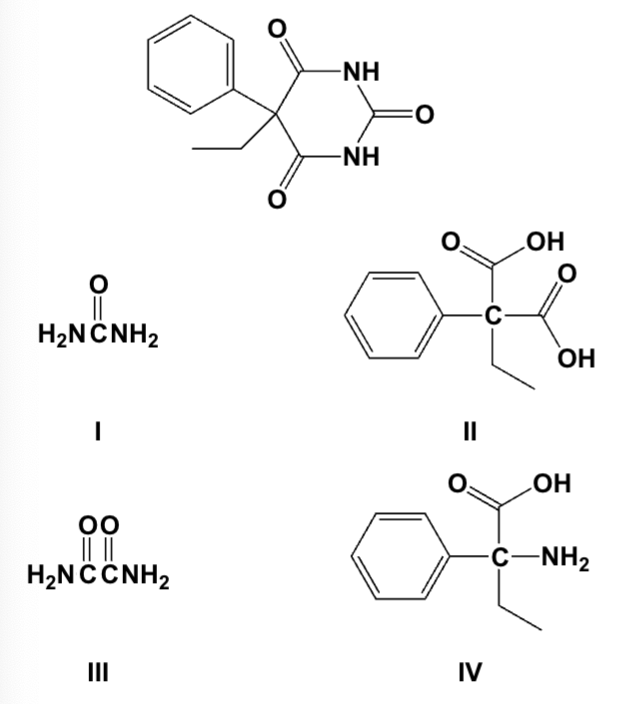
Partial hydrolysis of phenobarbitol gives which compounds?
I, II
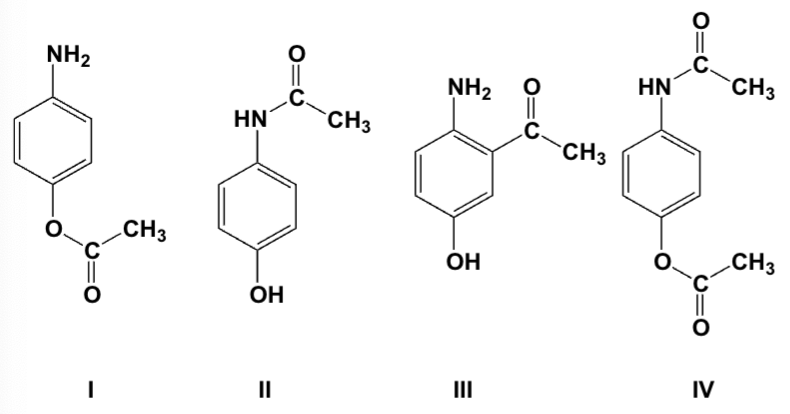
Which is the major product of the reaction of 4-aminophenol with 1 equivalent of acetic anhydride?
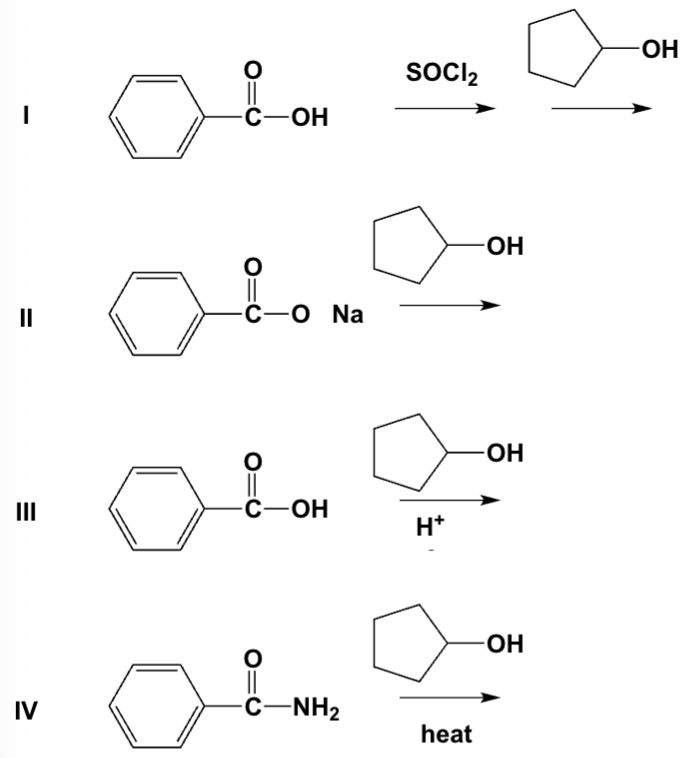
Which reactions can be used to prepare an ester?
I, III
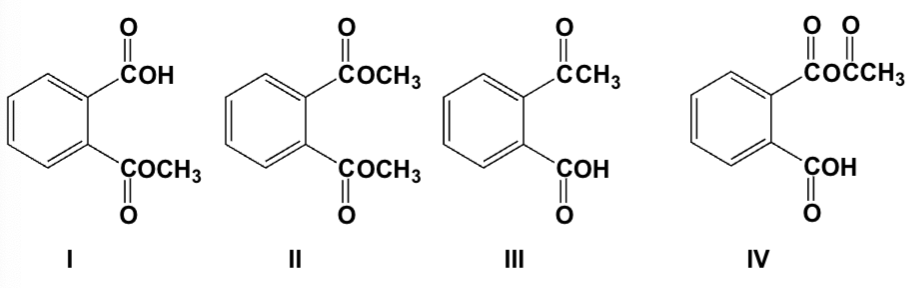
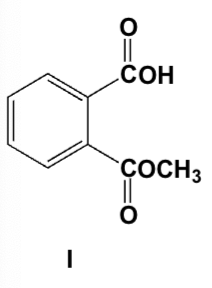
Which is the product of the reaction of phthalic anhydride with 1 equivalent of methanol?
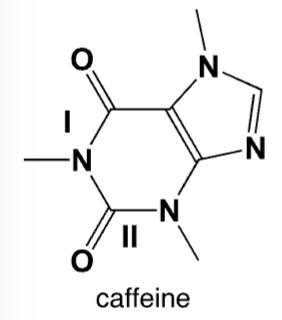
Characterize the amides I and II in caffeine.
I is a tertiary amide, II is a tertiary amide
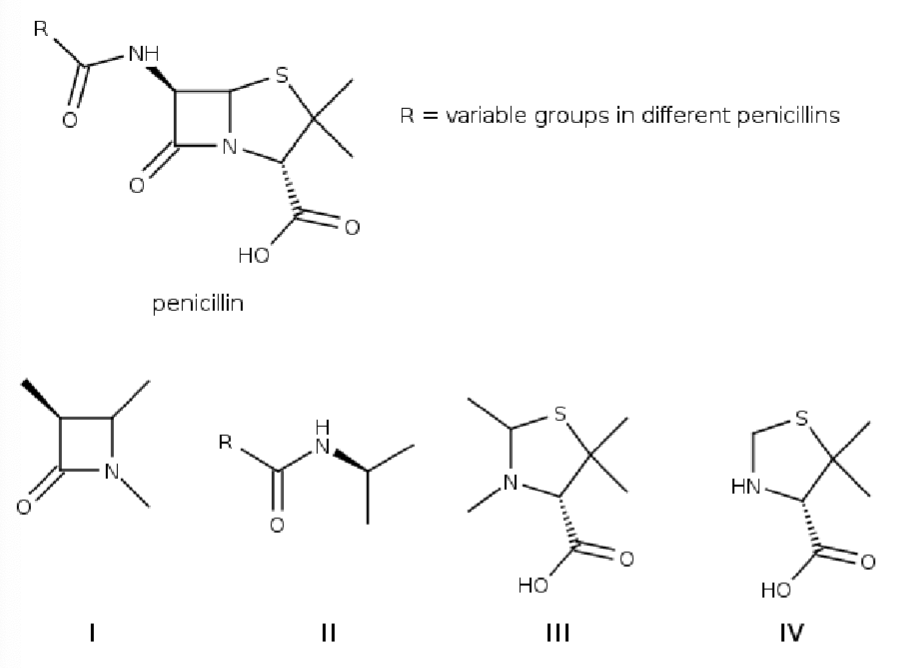
Penicillins derived from Penicllium fungi were the first available B-lactam antibiotics, which inhibit the biosynthesis of the peptidoglycan layer of bacterial cell walls. Which detail of the structure of penicillin is the “lactam-unit”?
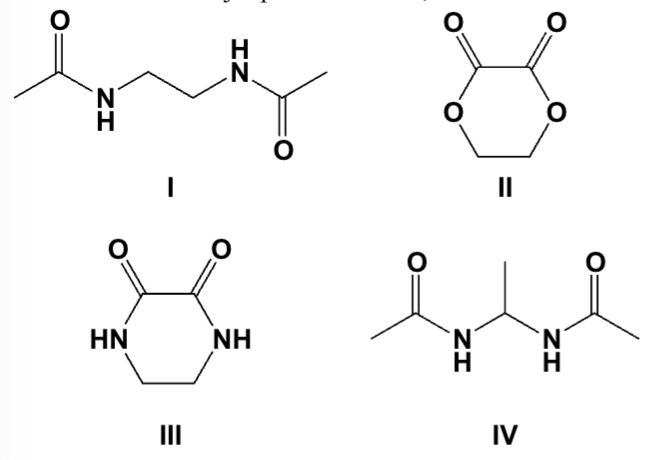
Which is the major product when 1,2-diaminoethane is heated with dimethyl oxalate?
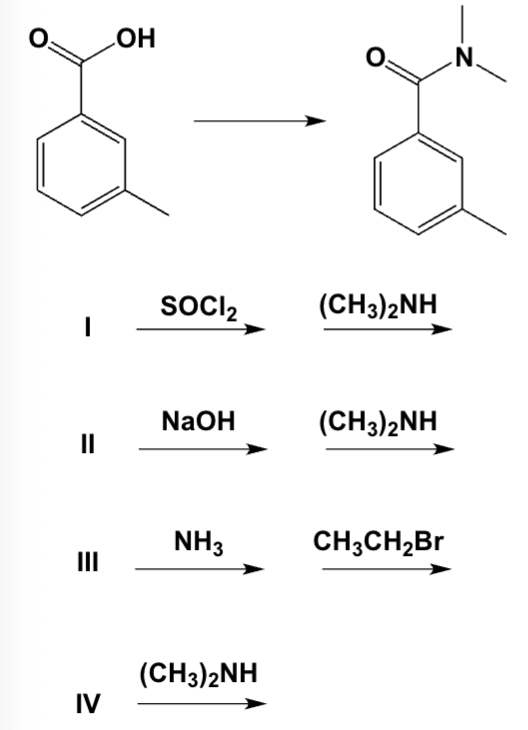
Which are the best conditions for the following preparation?
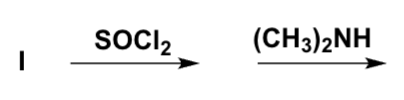

Why are the amino acids in proteins connected by means of amide and not ester bonds?
I, IV
Which is the product from the reaction of sodium benzoate and acetyl chloride?
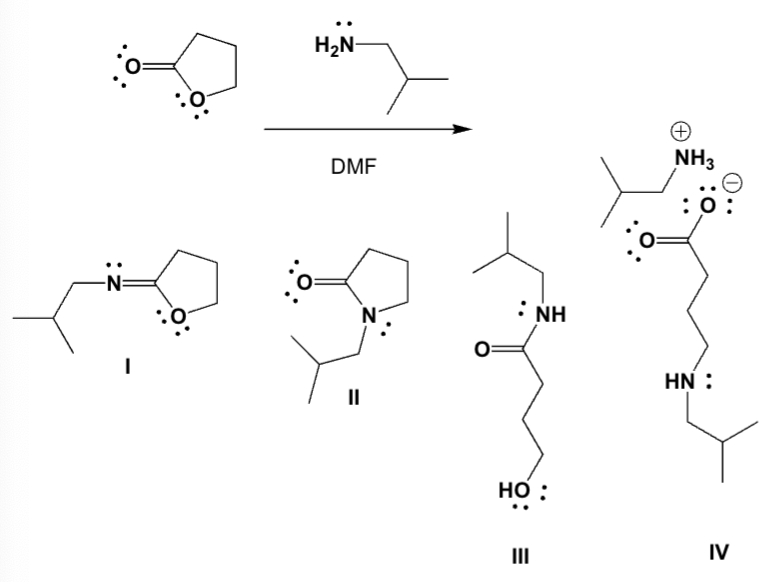
Butyrolactone reacts with 2-methylpropan-1-amine in DMF (dimethylformamide). Which is the major product?
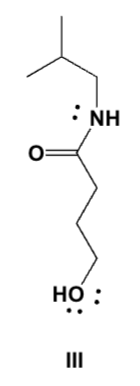
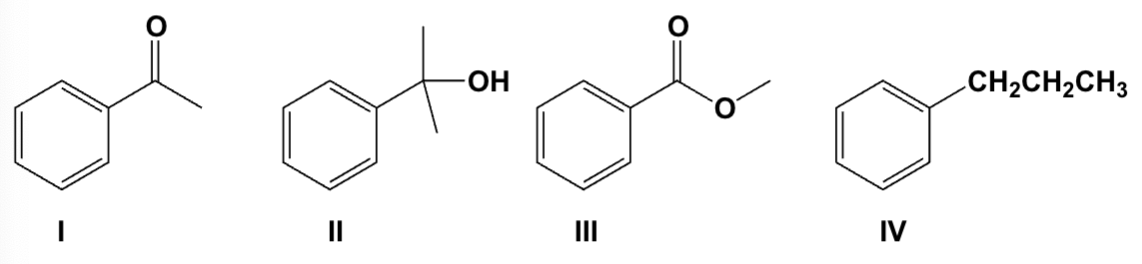
Which is the product of the reaction of ethyl benzoate with 2 equivalents of methyl Grignard followed by aqueous acid?