CIE IGCSE Biology Unit 5: Enzymes
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
9 Terms
Enzymes
proteins that function as biological catalysts
Catalyst
a substance that increases the rate of a chemical reaction and is not changed by the reaction

Importance of Enzymes
Helps catalyse reactions that otherwise occurs too slowly to sustain life
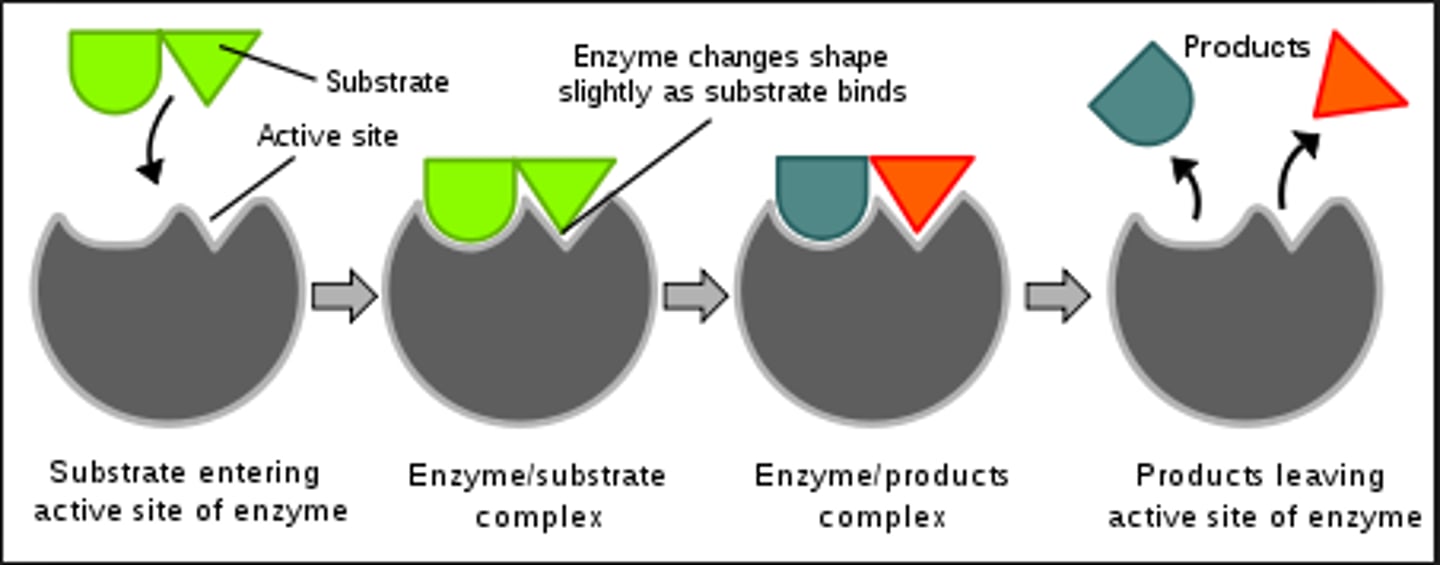
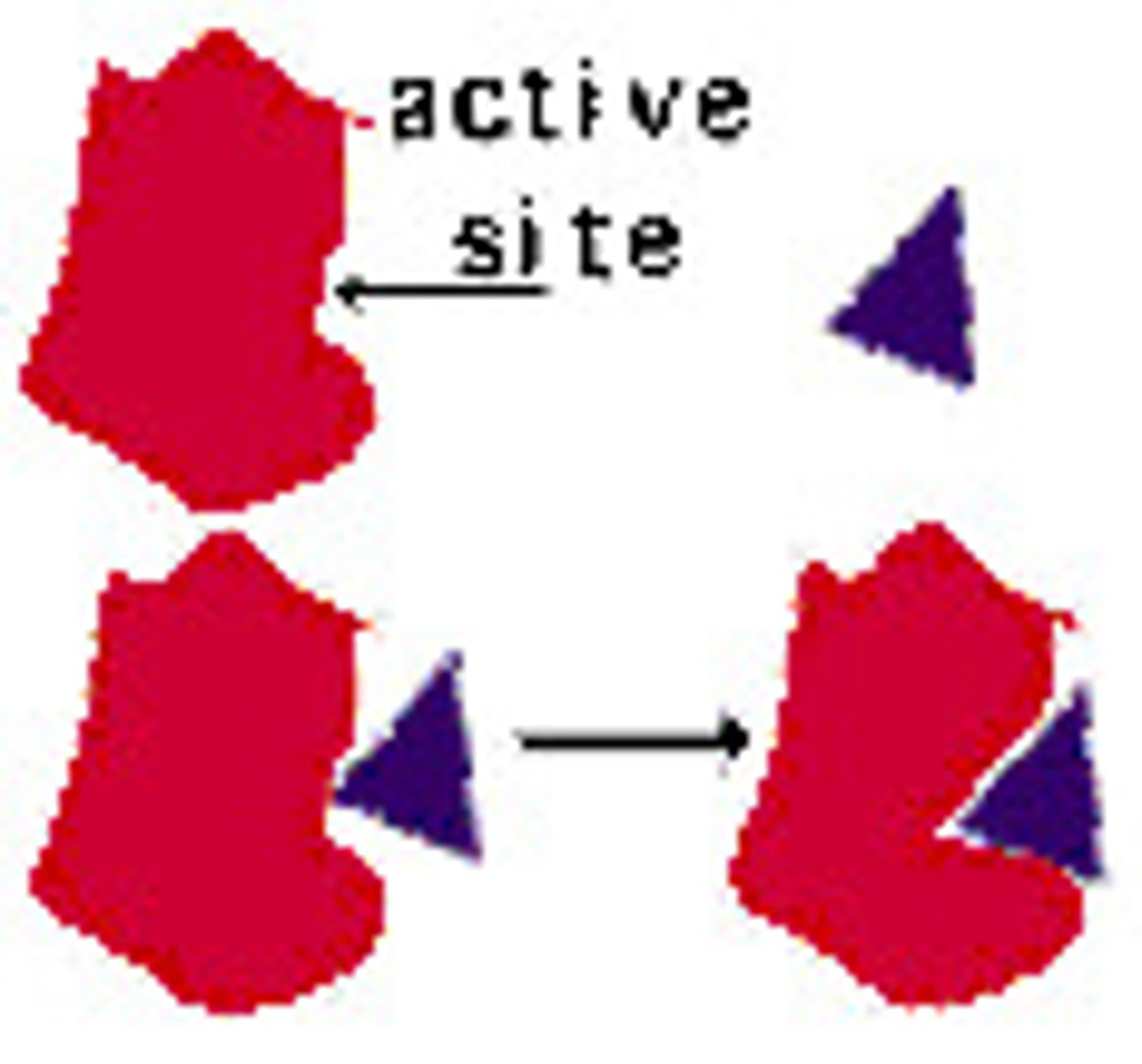
Enzyme Action
1. Specific substrate enters active site
2. Forms enzyme-substrate complex
3. Substrate becomes product and leaves active site
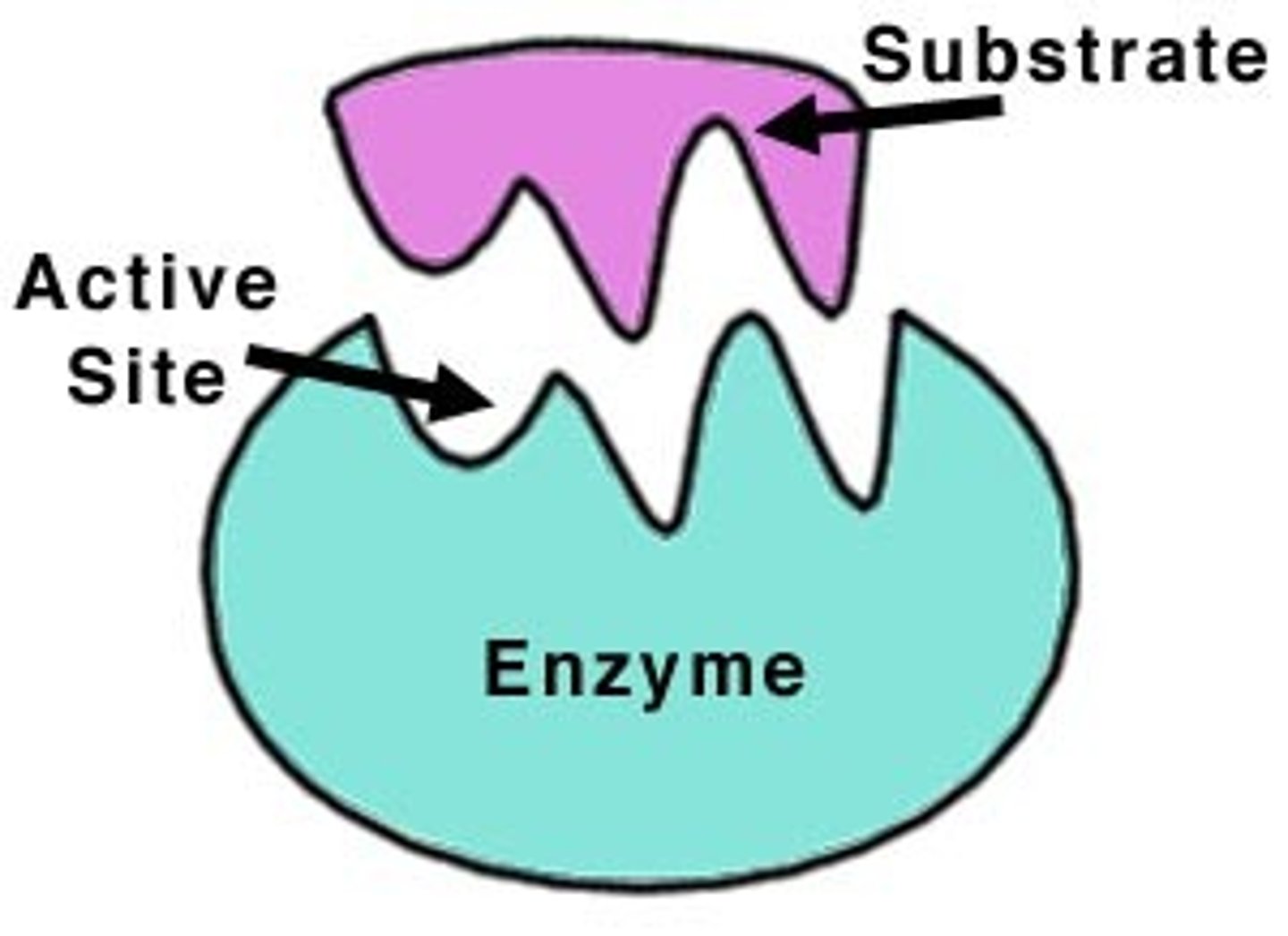
Substrate
Substance on which an enzyme converts to products by building up or breaking down
Active Site
Where the substrate fits and reaction take place
Temperature effect on enzymes
Enzyme activity increases as temperature increases up to optimum temperature due to greater kinetic energy increasing between enzymes and substrate.

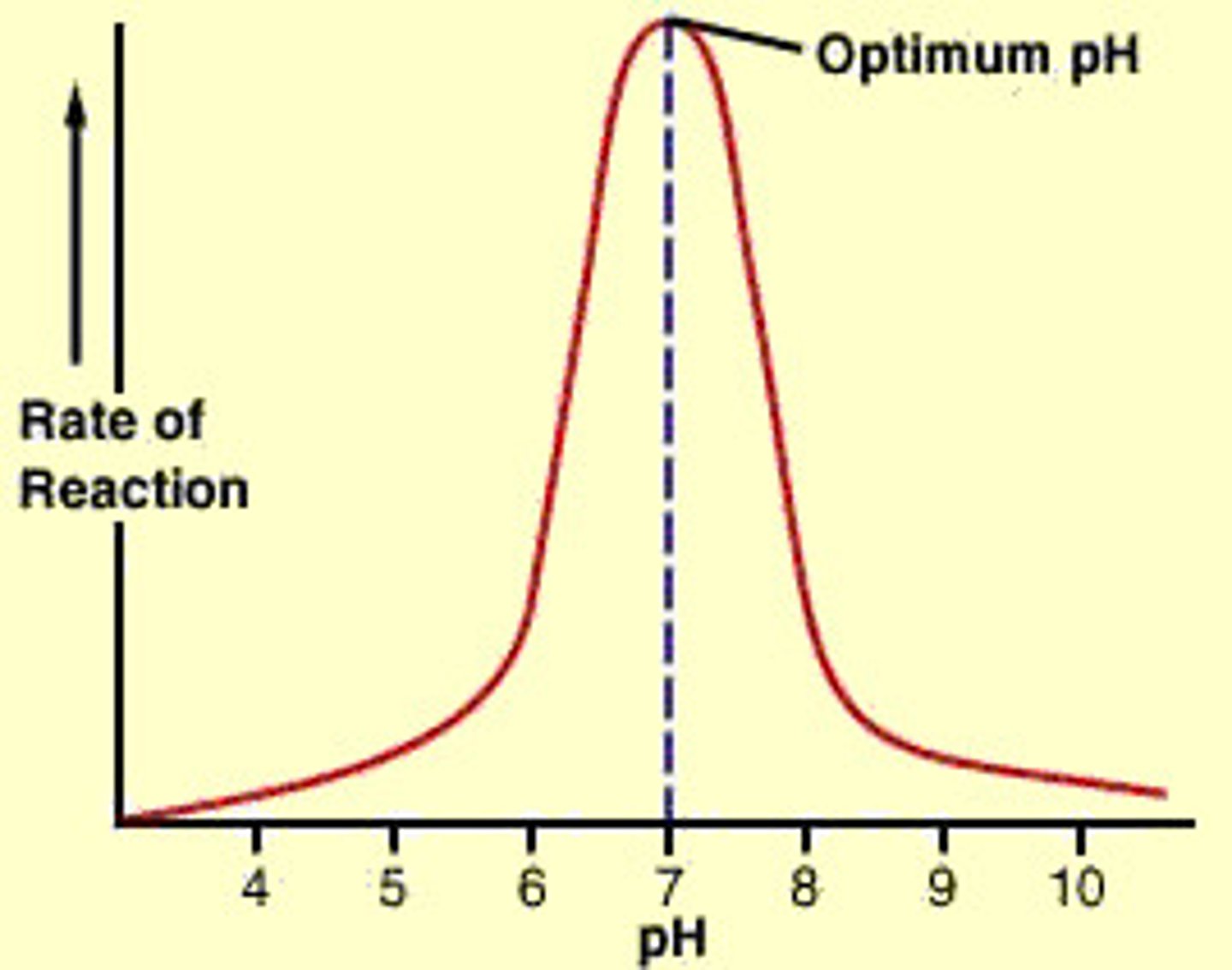
pH effect on enzymes
Enzyme activity optimizes at the optimum pH and decreases if pH is changed.
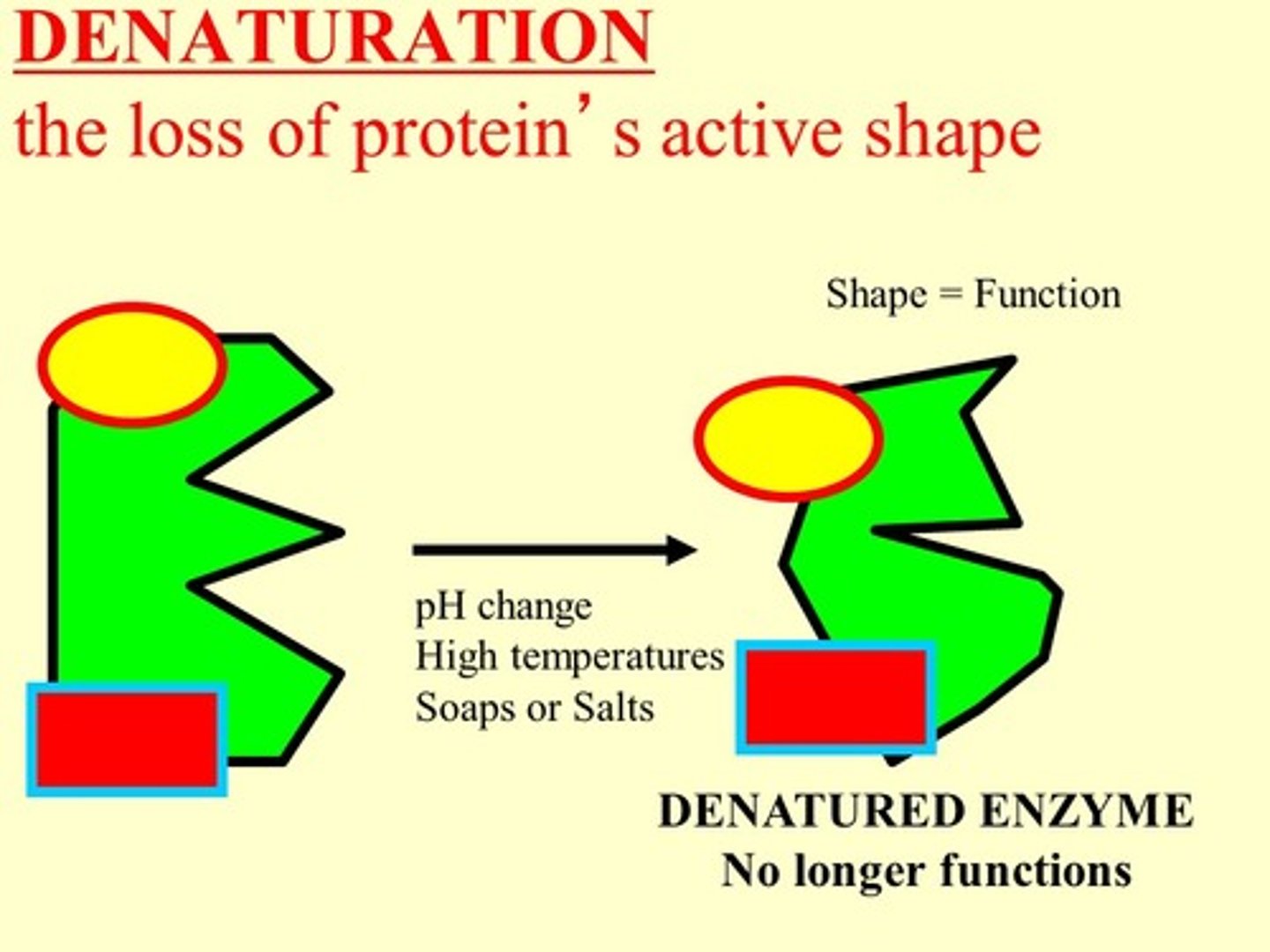
Denature
The loss of an enzyme's active site shape due to temperature, and pH and causes the enzyme to cease functioning