Cell division and stem cells
1/18
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Chromosone
Linear arrangements of genes
Why do chromosomes come in pairs
One gene from each parent
What does a gene code for?
Charecteristics
Allele
Different version of the same gene eg. Blue eyes
Stem cells
Undifferentiated cells that can differentiate into any other type of cell
2 sources of stem cells
embryonic tissue
Adult stem cells that occur in some tissue
Stem cell uses
Replaced damage or diseased tissue and so have many medical applications
Benefits of using your own stem cells
no rejection
No need to find a donor
No concern about using embryonic tissue
Benefits of embryonic cells
Embryonic stem cells can differentiate into a wider range of cell types
Issues of Embryonic cells
waste of ‘potential life.’
Clinical issues associated with the use of stem cells
no guarantee how successful eg. Stem cells used in Parkinson’s disease to replace nerve cells
Difficulty in finding suitable donors
Mutated stem cells can behave like cancer sells
Ethical issues associated with the use of stem cells
one source is produced by IVF, potential life
At what stage is an embryo regarded a person?
Social issues associated with stem cells in medicine
risks could out way benefits
Patients could be exploited by paying for expensive treatments, given false hope
Mitosis uses
growth
Replace cells
Repair cells
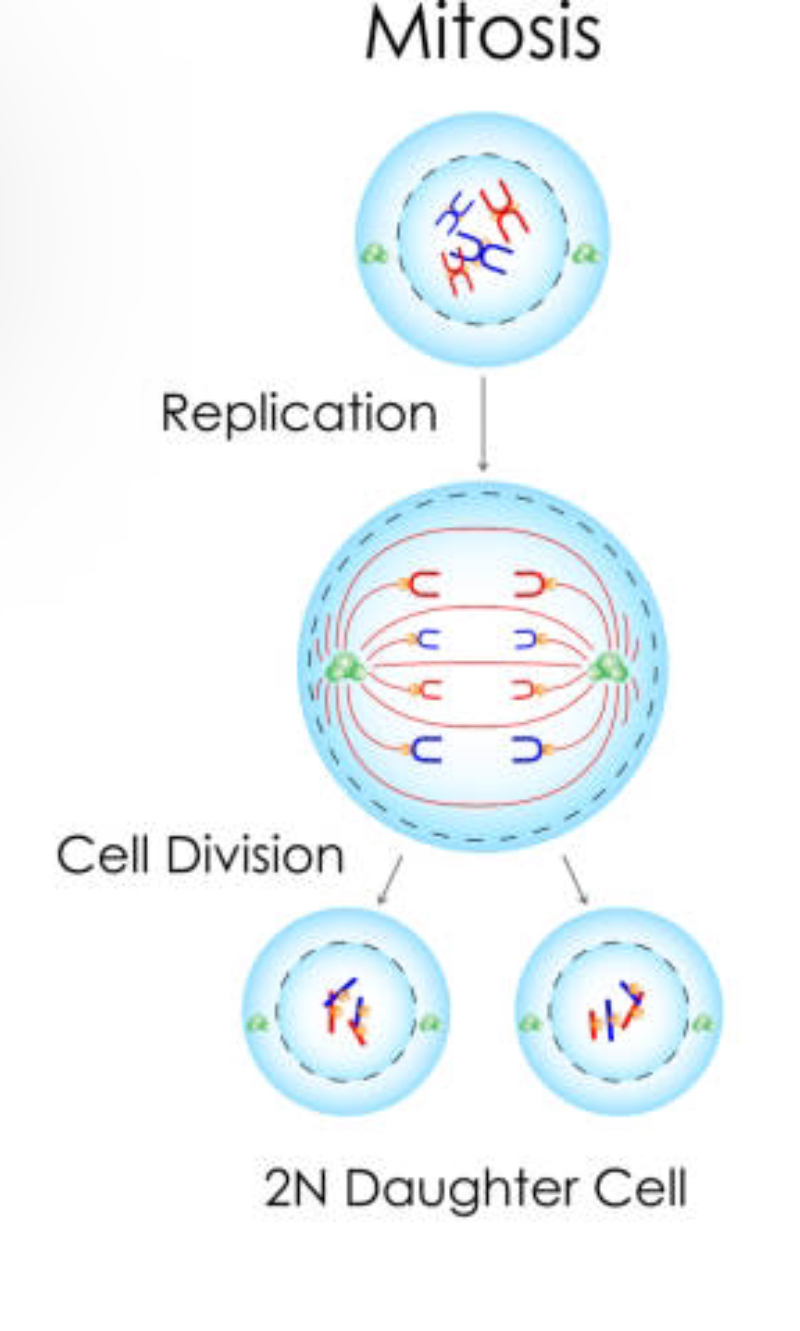
Mitosis
Mitosis mother cell has 4 chromosomes (2 pairs)
Produces 2 daughter cells, genetically identical
Has the same no. Chromosomes as the mother cell (4)
Problems of mitosis
Cancer is a result of uncontrollable mitosis
Use of meisos
Formation of sex cells, gametes
Meisos
Mother cell has 4 chromosomes [2 pairs - diploid]
2 divisions
4 new cells have formed
Each cells has half the chromosomes as the mother - haploid
Cells are not genetically identical
![<ul><li><p>Mother cell has 4 chromosomes [2 pairs - diploid]</p></li><li><p>2 divisions</p></li><li><p>4 new cells have formed</p></li><li><p>Each cells has half the chromosomes as the mother - haploid</p></li><li><p>Cells are not genetically identical </p><p></p></li></ul>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/791da65c-f361-4f49-b615-523bf3579b4d.jpg)