Chapter 14 U.S. History Vocabulary: Industrialization
1/27
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
28 Terms
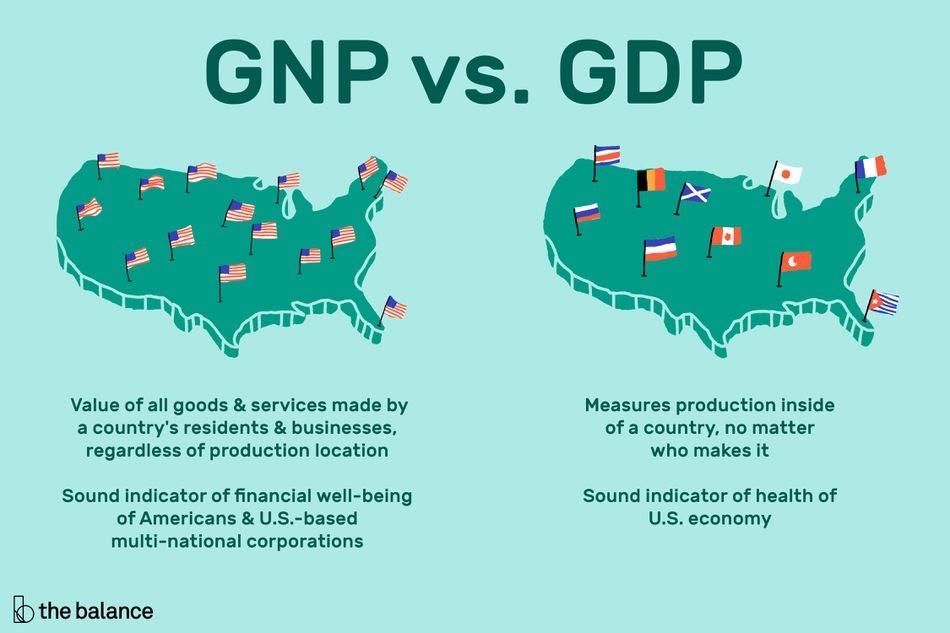
What is Gross National Product (GNP)?
Gross National Product (GNP) is the total value of all goods and services produced by a country's residents, regardless of where they are located, in a given period. It includes income earned by domestic residents from abroad and excludes income earned by foreign residents domestically.
Laissez-faire
Policy that government should interfere as little as possible in the nation's economy

Entrepreneurs
People who start and run their own businesses, taking on risk for profit

Alexander Graham Bell
Invented the telephone in 1876

Thomas Edison
Inventor of the phonograph, lightbulb, and motion picture

Leland Stanford
Railroad tycoon and founder of Stanford University

Cornelius Vanderbilt
Wealthy businessman, who built a railroad and shipping empire

Time zone
Standard divisions of the Earth created to make train schedules more reliable.

Corporation
A business owned by many investors through shares of stock

Economies of Scale
When producing more goods lowers the cost per unit

Fixed cost
Expenses a business always pays no matter how much it produces
Operating cost
Expenses that change depending on production levels

Pools
Agreements between businesses to set prices or divide markets to reduce competition

Andrew Carnegie
Steel industry leader, who used vertical integration to grow an empire

Vertical integration
Controlling all steps of production from raw materials to sales

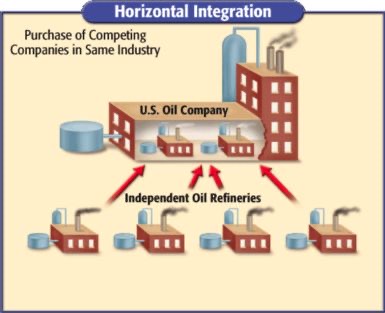
Horizontal integration
Buying out competitors to control a single part of an industry
Monopoly
Total control of a type of industry by one person or one company

Trust
A combination of firms or corporations formed by a legal agreement, especially to reduce competition

Holding company
A company that owns stock in other companies, but doesn’t produce goods itself

Stock
A share of ownership in a company

Trade Unions
Group of workers with the same skill who joined together for better pay and conditions

Deflation
A drop in prices, often causing the purchasing power of money to increase.

Industrial unions
Unions that include all workers in an industry, regardless of skill

Lockout
When employers close a workplace to force workers to accept their terms

Marxism
Economic and political ideas of Karl Marx promoting a classless society

Women’s Trade Union League
Organization supporting women workers and pushing for better treatment and reforms

Land grants
Land from the government given to people or companies in exchange.

Knights of Labor
Labor union that welcomed skilled and unskilled workers advocating for reforms.
