1. Crime in Canada
1/38
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Ch.1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
39 Terms
Intra- vs. Inter-Individual Differences
Intra-: variations in criminal conduct within an individual across time
Inter-: variations in criminal conduct b/w groups of individuals
Define: Forensic Psychology
application of psychology to the legal system, intended to guide legal decision-making
Define: Correctional Psychology
application of psychology to the understanding of the assessment & management of individuals who engage in criminal behaviour
There are a variety of definitions & explanations of crime.
List four types of definitions
legal → acts prohibited by the state & punishable under the law
moral → violation of norms of religion & morality that are punishable by supreme beings
social → violation of certain norms & customs that are punishable by the community
psychological → acts that are rewarding to the perpetrator but harmful to others
Bartol & Bartol Definition of Crime
crime is intentional behaviour that violates a criminal code, intentional in that it did not occur accidentally or w/o justification or excuse
What is the Criminal Code of Canada (CCC)?
is federal law that defines criminal offences → conduct, determining guilt, defenses if charged, punishments if convicted, powers/procedures for investigation & prosecution
List the Six Types of Offences Under the CCC
offences against the person
offences against property
offences against the administration of law & justice
sexual offences
terrorism offences
hate propaganda offences
Provincial/Territorial Courts Deal With…
most criminal offences (except the most serious ones
family law matters (child support, adoption, etc. → not divorce)
young persons (12-17) in conflict w the law
Role of Superior Courts (King’s Bench)
courts of inherent jurisdiction → hear cases in any area except when a statute/rule limits that authority
hear the most serious cases
act as court of first appeal for the provincial/territorial courts
Role of the Court of Appeal
hear appeals from the superior & provincial courts
usually heard by panel of three judges
also hear constitutional questions that may be raised in appeals involving individuals, gov’ts, or gov’t agencies
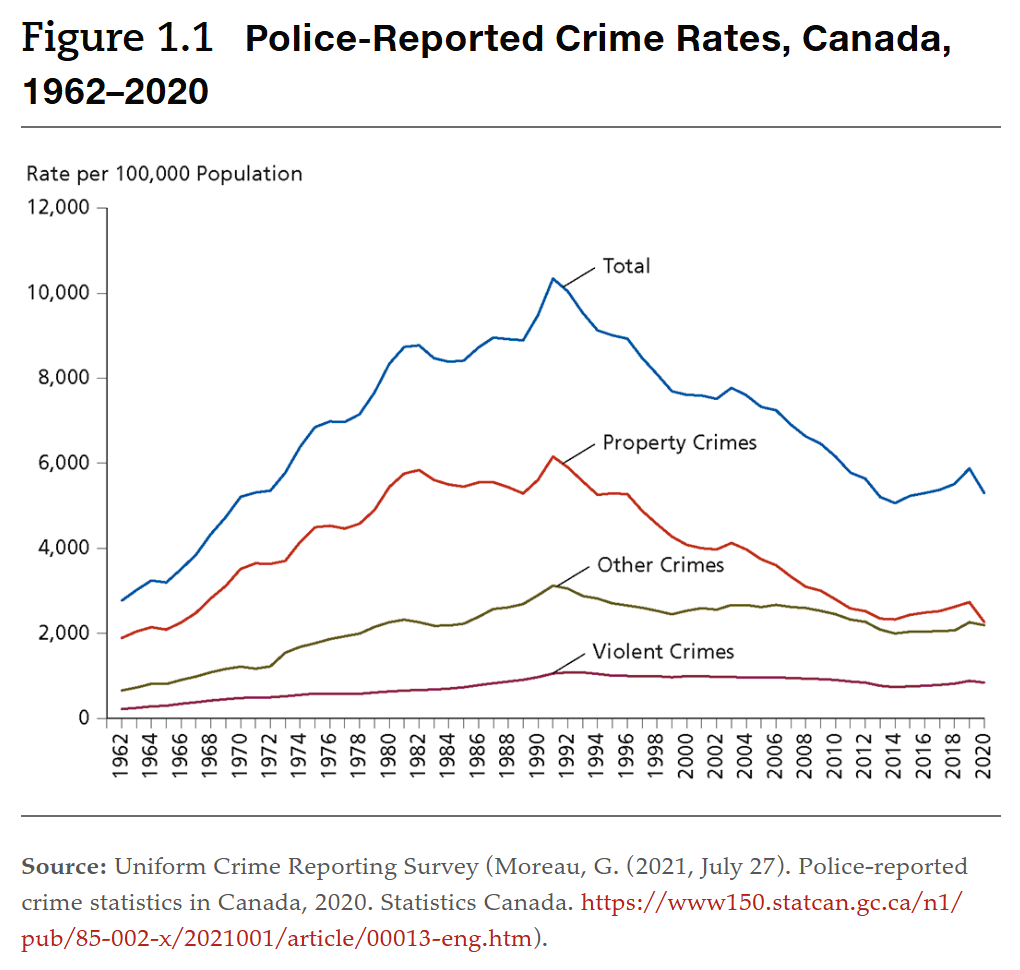
General Trend in Crime Rates
Crime peaked in the 90s → dec. → slight inc. 2012-2020 → dec.
likely underestimates crime b/c only reflects what was reported
Define: Incidence Rates
the number of criminal incidents reported to the police as a function of the population
e.g. X number of [incidents] per number of people
Define: Prevalence Rates
the proportion of the population found to be involved in crime
e.g. X% arrested for [incident]
In 2020, 76% of crime reported was ____ violent
non-violent
e.g. technical offences (failure to comply or attend), property-related crimes (theft), mischief/fraud
Crime Severity Index
tracks changes in the severity of police-reported crime from year to year → considered the change in volume of a particular crime & the relative seriousness of that crime
more serious → heavier weight → more impact on index
Two Factors Determining the Weight of an Offence for the Crime Severity Index
incarceration rate → proportion of those convicted who are sentenced to prison time
average length of a prison sentence (in days)
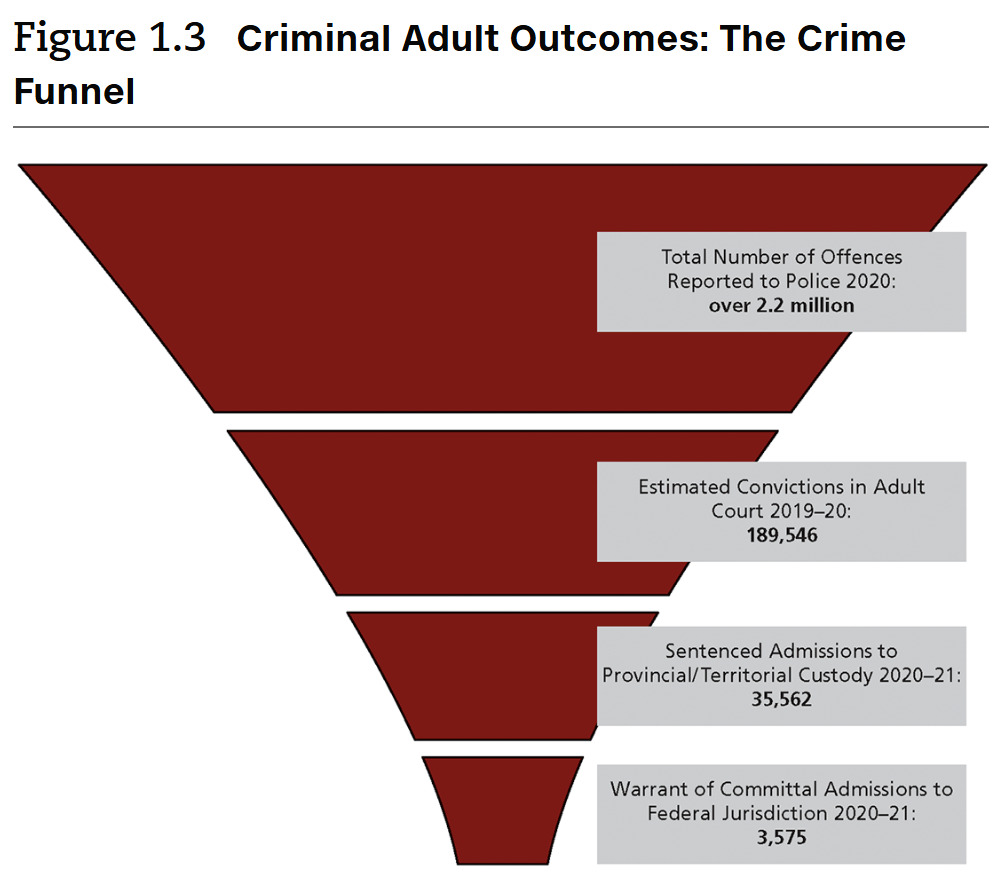
The Crime Funnel
a way to consider crime rates & severity based on how many people eventually go to prison following a police-reported criminal incident
total reported offences > estimated convictions > provincial sentence > federal sentence
Length of Sentences & the Implications of this for Assessment/Treatment
majority of sentences carried out in community
~47% adult custodial sentences are <1month
sentences for men usually > women
only 3.2% federal sentences (2+ years)
thus limits time to assess & treat → limits comprehensiveness
General Trend in Variation Across Provinces
(2)
crime increases as you move further west & north
there is an over-representation of Indigenous in the Canadian criminal justice system
International Context of Canadian Incarceration Rates
2020 → incarceration rate: 104 per 100,000
modest compared to the USA
above the median observed in 223 Western & European countries (143 out of 223)
Crime Victimization Surveys
gives an idea of the crime rate not reported to police
is administered to a random sample every 5 years
typically yielder higher rates than police-reported
Two General Findings of the 2019 Crime Victimization Survey
few people report crime (only 30%) → even lower for certain crimes (e.g. 6% sexual assault)
certain groups have greater risk of victimization (youths, women, indigenous)
Direct & Indirect Costs of Crime (6)
direct: (1) police costs (2) court costs (3) corrections costs
indirect: (4) victim (5) victim’s family & friends (6) perpetrator + their families
Provincial/Territorial vs. Federal Corrections
Provincial: < 2 years → includes remand centers, provincial jails, conditional sentence, probation & responsible for youths
Federal (CSC): > 2 years +1 day → includes maximum, medium, and minimum security prisons & parole
General Population of Incarcerated Individuals Under the Correctional Service Canada (CSC)
(1) serving life (2) serving for violent crimes (3) race
25% (not majority) serving life or indeterminant sentences
72% serving in custody & community for violent crime(s)
Indigenous incarceration still increasing → make up 26% of those in CSC but only 5% of pop (very high %)
A majority of provincially sentenced individuals are serving in/on…
probation
General Personality & Cognitive Social Learning (GPCSL) Perspective (Bonta & Andrews)
is an integrative & situational model of criminal cause
recognizes the influence of both historical & immediate factors on an individual who decides to engage in a criminal act
Define: Meta-Analysis
use of statistics to aggregate the results of individual studies to develop one averaged effect size for all the studies combined
combining & synthesizing summaries and conclusions to detect/evaluate trends
Define: Effect Sizes
outcome measure indicating the degree of the relationship b/w two variables OR the impact of an intervention
info about the magnitude of diff b/w groups
Measuring Predictive Accuracy: Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Analysis
measures the accuracy of risk assessments by examining false and true positives across decision thresholds
for each possible cut-off value (score) → can plot the false pos. rate (x-axis) as a fxn of the true pos. rate (y-axis) then can measure the AUC to get measure
good b/c less influenced by decision thresholds & base rates
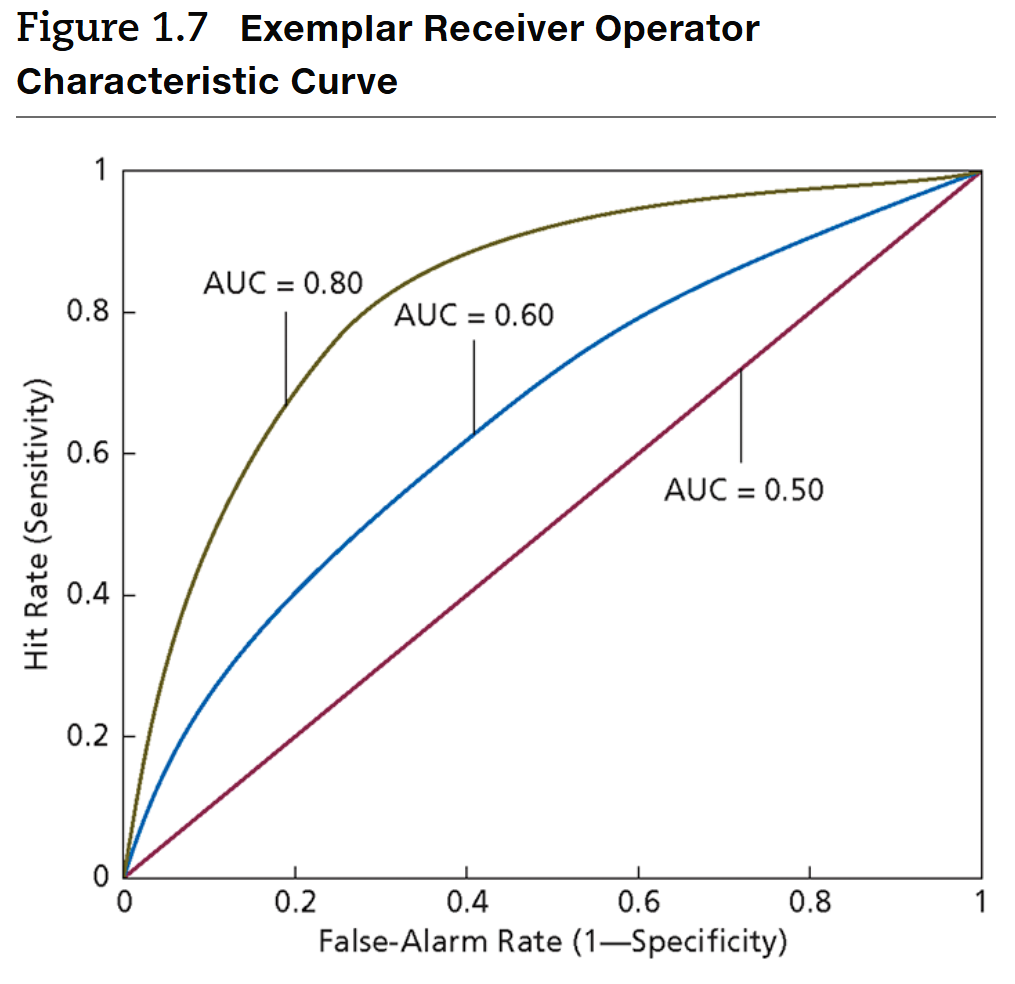
Area Under the Curve (AUC) Values
values range from .50 (chance accuracy) to 1.00 (perfect accuracy)
e.g. AUC of .80 indicates that 80% of the time, a randomly selected recidivist will have a higher risk score than a randomly selected non-recidivist
AUC >.80 considered very good
Define: Cross-Sectional / Correlational Research Design
diff groups of people who differ on variable of interest (involvement in crime) are observed at one point in time to determine how they differ on other variables
looks at factors at one point in time to see if they are correlated to crime at that same point in time
Define: Longitudinal Research Design
a particular group of individuals are followed over time & repeatedly observed
Define: Risk Factors
measurable constructs that predict criminal offending
Define: Risk Assessment
the determination of risk or probability of reoffending through the systematic review of static & dynamic factors (criminogenic needs)
Define: Protective Factors
pos. attributes a person possesses that dec. the probability of reoffending or inc. the likelihood of success
internal (e.g. high intelligence) or external (e.g. prosocial supports)
Define: Specific Responsivity Factors
non-criminogenic facilitators & barriers
Define: Risk-Need-Responsivity (RNR) Model
model of offender rehabilitation used throughout Canada & the world
intervention & supervision strategies should be matched to recidivism risk
greater risk → more program hours/supervision
prioritize criminogenic needs
responsivity principle = general + specific responsivity
General vs Specific Responsivity Principle
General: interventions work best when they are matched to the learning styles of justice-impacted people → usually CBT
Specific: recognized that individuals are unique → treatments should be tailored to address individual diffs (e.g. gender, race, culture, personality, age. etc.)