APES-Unit 9: Global Change
1/246
Earn XP
Description and Tags
-Review -AP Classroom MCQ -Test -Knowt Flashcards
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
247 Terms
greenhouse gases that contribute to climate change
One important drawback of the use of HCFCs as a replacement for CFCs is that HCFCs
Leaking of refrigeration and air-conditioning units
HCFCs were originally introduced as a solution to help phase out the use of CFCs. Which of the following most likely contributed to the increased levels of HCFCs in the stratosphere over the past 30 years?
The Northeast and the Gulf of Mexico
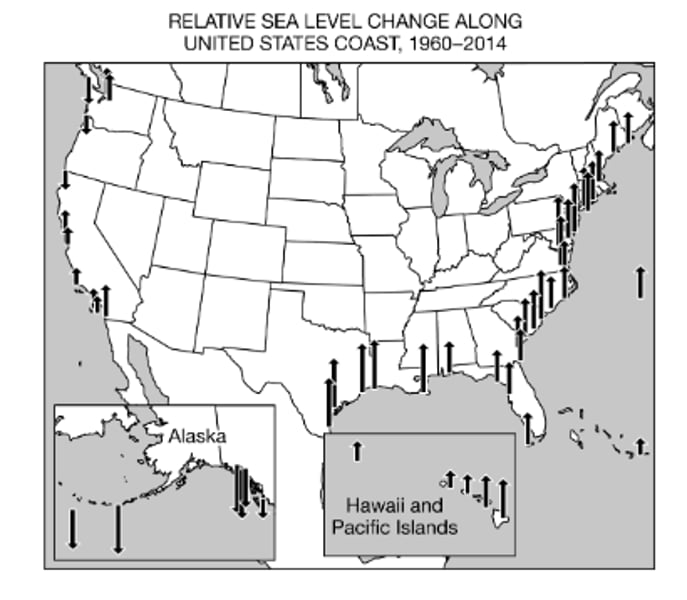
Based on the information in the map, which areas in the United States have experienced the greatest sea level rise?
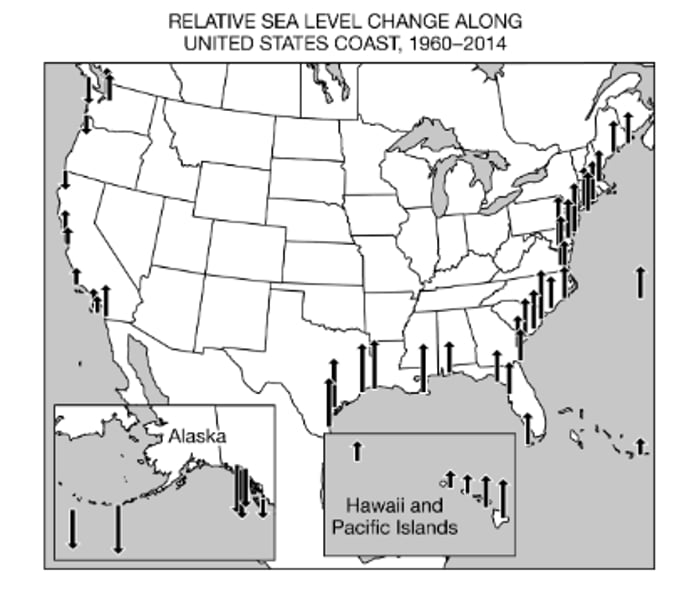
There will be in an increase in the number of individuals who live in flood prone regions, and there will be an increase in the number of properties at risk of flooding.
Based on the information in the map, which of the following is a likely consequence for the human population if the sea level continues to change in the same pattern?
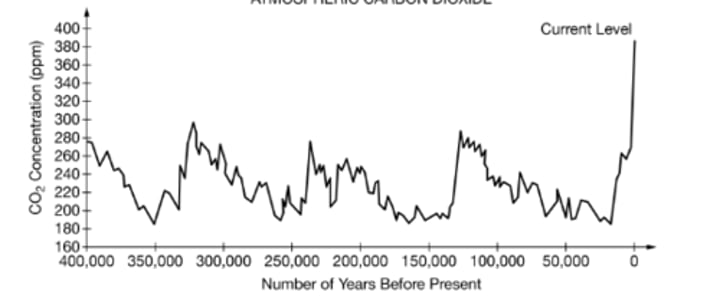
Temperatures were warmer 125,000 years ago than the average temperature over the past 400,000 years.
Which of the following hypotheses is best supported by the graph?
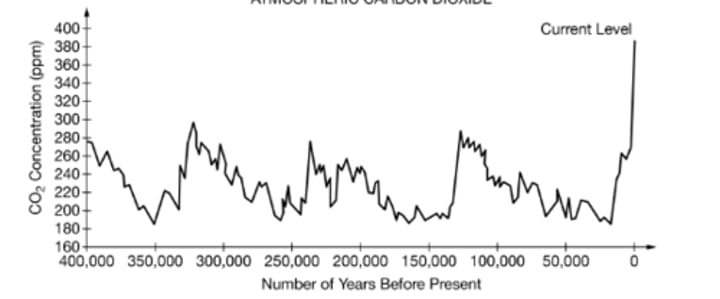
Four glacial periods occurred in the past 400,000 years.
Based on the data shown in the graph, which of the following is the most plausible hypothesis about the number of glacial periods that occurred in the past 400,000 years?
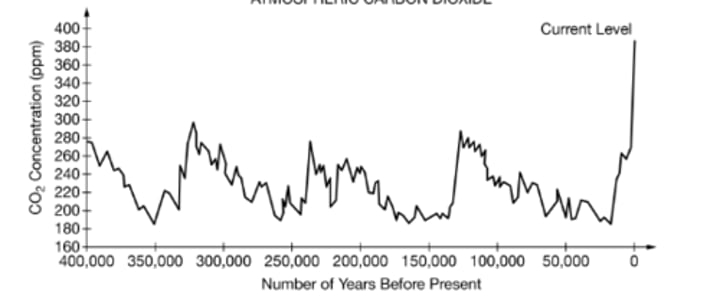
Human activity, especially the burning of fossil fuels, has led to an increase in anthropogenic carbon dioxide emissions. This has caused a doubling in the concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere.
Based on the data shown in the graph, which of the following is the most plausible hypothesis for the cause of the trend in CO2 levels from about 5,000 years ago to the present?
The increasing use of coastal areas by human has destroyed much of the habitat of the species.
Which of the following best describes how the American crocodile has become endangered in the state of Florida?
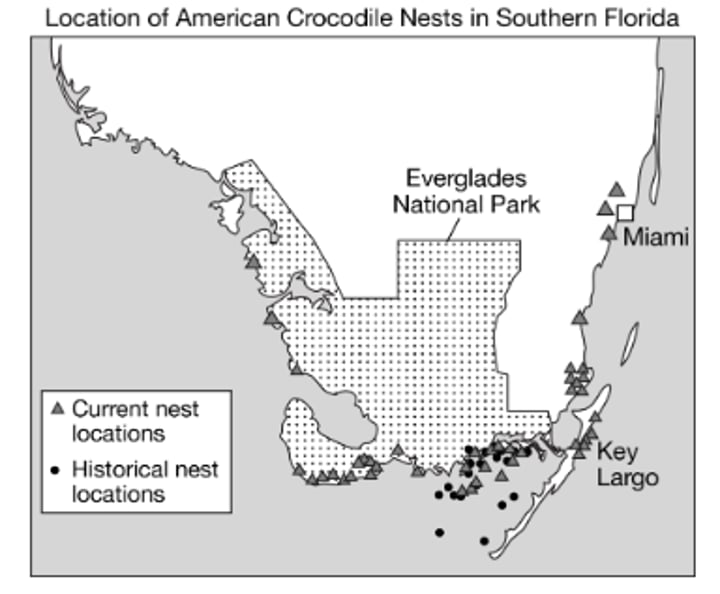
Crocodiles now nest in areas where they did not nest historically as a result of restoration projects at public beaches, county parks, and other areas.
Which of the following claims about crocodile nests is best supported by the data in the maps?
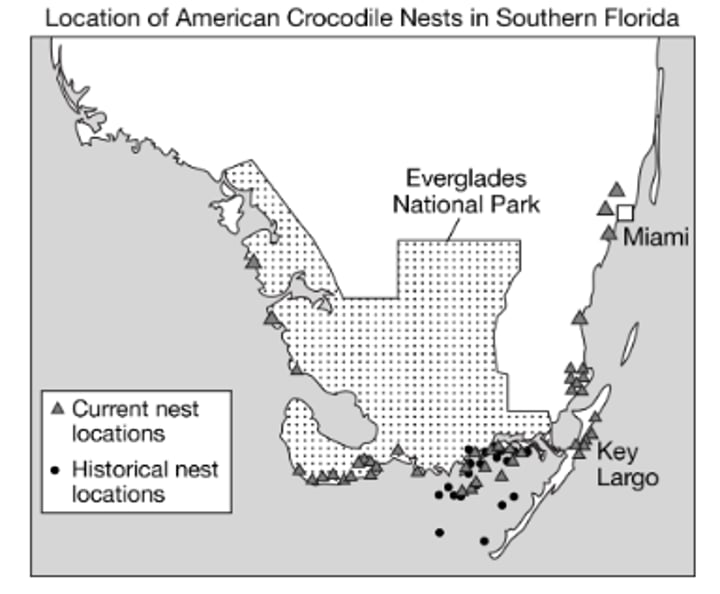
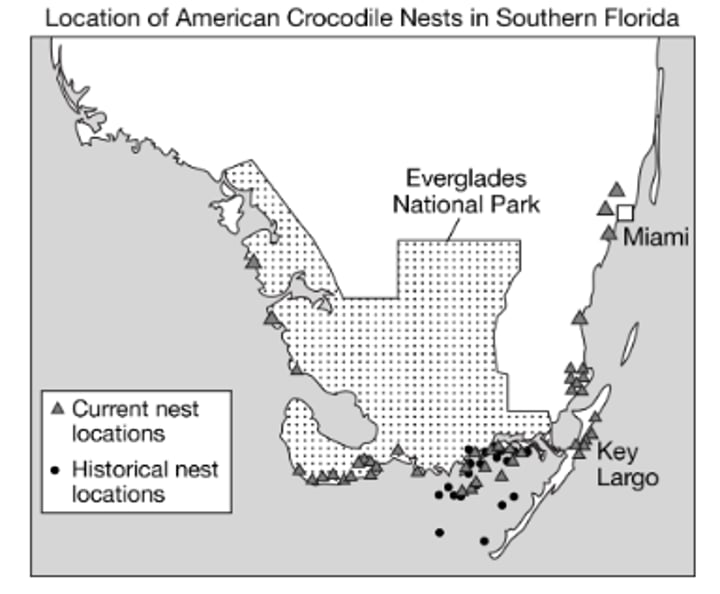
There will be an increase in the number of human and crocodile interactions in coastal areas.
Which of the following best describes a likely unintended consequence of the restoration plan based on the data in the map?
Chlorine atoms in CFCs
Which of the following is the primary cause of stratospheric ozone depletion?
absorbing 99% of incoming UV-B and UV-C radiation
The stratospheric ozone layer benefits life on Earth by
b
Which of the following correctly identifies the three main characteristics associated with the hole in the ozone layer?
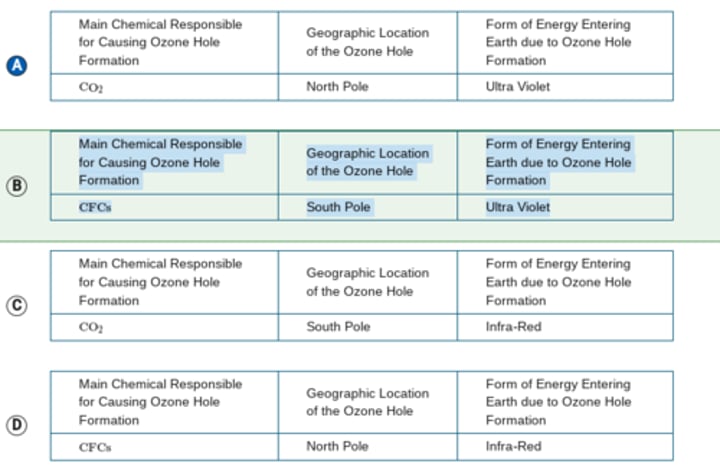
A global plan to decrease CFCCFC emissions was enacted by signing the Montreal Protocol.
Which of the following best describes why there has been a reduction in ozone depletion over the last half of the twentieth century?
Carbon dioxide is the largest contributor to anthropogenic greenhouse gas emissions.
Which of the following best describes why carbon dioxide has a significant effect on global climate change?
Gases in the atmosphere absorb infrared radiation and radiate the energy back toward Earth's surface.
Which of the following best describes the cause of the greenhouse effect on Earth?
Chlorofluorocarbons
Which of the following gases has the greatest impact on global climate change as a result of having the highest global warming potential (GWP)
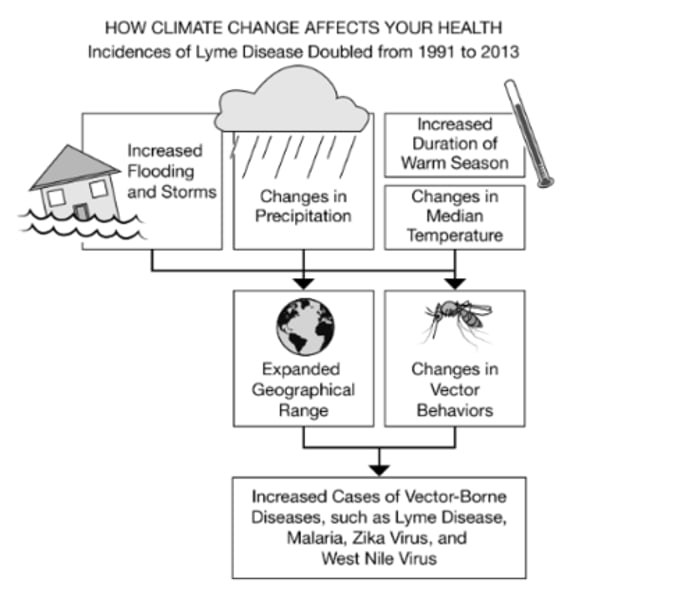
Increased temperatures provide an expanded breeding range and duration, which will likely increase the size of vector populations.
Based on the information in the diagram, which of the following best supports the claim that a change in the duration of warm seasons would result in a higher prevalence of vector-borne diseases?
Elevated levels of atmospheric CO2
Sea surface temperatures in the Caribbean Sea have increased over the past 30 years.
Which of the following is the most likely cause for the warming trend?
Algae that live symbiotically with the corals leave the reef, causing coral bleaching.
Which of the following best describes the effect of increasing global temperature on coral ecosystems?
An increase in metabolism in marine species and a decrease in dissolved oxygen in ocean water
Which of the following changes are linked to an increase in ocean water temperature?
Carbon dioxide emissions from the combustion of fossil fuels
Which of the following best identifies the primary cause of increasing acidity in the oceans?
Acidification decreases the amount of carbonate ions, which leads to a decline in the formation of reef infrastructure.
Which of the following best describes how ocean acidification harms coral reefs?
Reliance on fossil fuels for electricity generation emits carbon dioxide to the atmosphere, which is absorbed by the ocean, leading to a decrease in the pH in the ocean.
Which of the following actions best explains a cause of increasing ocean acidification?
Mangrove forests are removed as part of a beach development project.
Which of the following could directly lead to a loss of biodiversity as an unintended consequence of human actions?
Asian carp outcompete native fish species in rivers in the United States.
Which of the following best describes an example of a harmful effect of an invasive species on biodiversity?
Increased use of habitat corridors between fragmented ecosystems
Which of the following would most likely promote biodiversity in a given area?
Fertilizer use
________ is the primary source of nitrous oxide emissions.
Higher air temperatures
________ have been proven to result in higher incidences of heat- related deaths caused by cardiovascular disease, heat exhaustion, heat stroke, hyperthermia, and diabetes.
Dutch elm disease
________ is transmitted to elm trees by elm bark beetles — killing over half of them elm trees in the northern US.
commercial fisheries
European green crabs found their way into the San Francisco Bay area in 1989 threatening __________.
global climate
As the oceans store a large amount of heat, even small changes in these currents can have a large and lasting effect on the ________.
Water hyacinth
It forms dense mats, reducing sunlight for submerged plants and aquatic organisms, crowding out native aquatic plants, and clogging waterways and intake pipes.
Zebra mussels
They can attach to almost any hard surface—clogging water intake and discharge pipes, attaching themselves to boat hulls and docks, and even attaching to native mussels and crayfish.
thermal expansion
The amount of energy absorbed and stored by the oceans has an important role in the rise of sea levels due to _____.
Arctic
The _____ region is a large natural source of methane.
stratosphere
Volcanic gases that reach the ______ have a long-term effect on climate.
tectonic plates
The movement of _______ causes volcanoes and mountains to form, which can also contribute to changes in the climate
mosquitoes
Due to global warming, ______ have more places to breed, which increases malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and yellow fever rates.
Antarctica
The main ice-covered landmass is ________ at the South Pole, with about 90% of the world’s ice and 70% of its freshwater.
50%
The total surface area of glaciers worldwide has decreased _____ since the end of the 19th century.
Sea-level rise
________ threatens to inundate many coastal wetlands, threatening biota that cannot move inland due to coastal development.
absorb
As the oceans _______ more heat from the atmosphere, sea surface temperatures rise and ocean circulation patterns change.
store
As the oceans _____ a large amount of heat, even small changes in these currents can have a large and lasting effect on the global climate.
carbon dioxide
The world’s oceans contain more _______ than the atmosphere.
methane
Agricultural activities, waste management, and energy use all contribute to _______ emissions.
nitrous oxide
Fertilizer use is the primary source of _________ emissions.
infrared radiation
When sunlight strikes Earth’s surface, some of it is reflected back toward space as ________ (heat).
Greenhouse gases
It absorb this infrared radiation and trap the heat in the atmosphere.
global warming
Due to ________, mosquitoes have more places to breed, which increases malaria, dengue fever, Zika virus, and yellow fever rates.
Ocean currents
________ carry heat around the Earth.
Atomic oxygen
________ can combine with oxygen molecules to form ozone.
Stratosphere
Contains approximately 97% of the ozone in the atmosphere, and most of it lies between 9 and 25 miles (15-40 km) above Earths surface
UVA
It is closest to blue light in the visible spectrum and is the form of ultraviolet radiation that usually causes skin tanning
UVB
It causes blistering sunburns and is associated with skin cancer
UVC
It is found only in the stratosphere and is largely responsible for the formation of ozone
Ozone Layer
A belt of naturally occurring ozone gas that sits between 9 and 19 miles (15-30 km) above Earth and serves as a shield from the harmful ultraviolet B radiation emitted by the sun
Ozone
A highly reactive molecule and is constantly being formed and broken down in the stratosphere
Chlorofluorocarbons
These are nonflammable chemicals that contain atoms of carbon, chlorine, and fluorine
Halocarbons (halons)
These are organic chemical molecules that are composed of at least one carbon atom with one or more halogen atoms; the most common halogens are fluorine, chlorine, bromine, and iodine
Agriculture
Mostly comes from the management of agricultural soils
Commercial and residential buildings
On-site energy generation and burning fuels for heat in buildings or cooking in homes
Energy supply
The burning of coal, natural gas, and oil for electricity and heat is the largest single source of global greenhouse gas emissions
Industry
Primarily involves fossil fuels burned on-site at facilities for energy; cement manufacturing also contributes significant amounts of CO2 gas
Land use and forestry
It includes deforestation of old-growth forests (carbon sinks), land clearing for agriculture, strip-mining, fires, and the decay of peat soils
Transportation
It involves fossil fuels that are burned for road, rail, air, and marine transportation
Waste and wastewater
Landfill and wastewater methane (CH4), and incineration as a method of waste management
Carbon dioxide (CO2)
It is an important heat-trapping (greenhouse) gas, and is released through human activities such as deforestation and burning fossil fuels, as well as natural processes such as respiration and volcanic eruptions
Fluorinated gases
Industrial processes, refrigeration, and the use of a variety of consumer products all contribute to this gases, which include hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF6)
Black carbon (soot)
It is a solid particle or aerosol, not a gas, but it also contributes to the warming of the atmosphere
Ocean acidification
It occurs when atmospheric carbon dioxide reacts with seawater to form carbonic acid,
Kyoto Protocol (2005)
A plan created by the United Nations to reduce the effects of climate change, which results in a reduction in the pH of ocean water over an extended period of time
Montreal Protocol (1987)
An international treaty designed to phase out the production of substances that are responsible for ozone depletion
Paris Agreement (2016)
It deals with greenhouse gas emissions and mitigation
Adaptation
The ability to survive in changing environmental conditions
Acclimatization
The process by which an individual organism adjusts to a gradual change in its environment allowing it to maintain performance across a range of environmental conditions
Invasive species
These are animals and plants that are transported to any area where they do not naturally live
Endangered Species
A species considered to be facing a very high risk of extinction in the wild
Which is classified as an infectious disease?
I. Pneumonia
II. Malaria
III. Measles
A. I only
B. II only
C. I and II
D. I and III
E. I, II, and III
E. I, II, and III
Risk assessment is...
The scientific process of using statistical methods to estimate how much harm a particular hazard can cause to human health or to the environment.
A pathogen is a/an...
Organism that can cause disease in another organism
The atmospheric layer where ozone is helpful is
Stratosphere
Brown urban smog it is not emitted directly from specific sources, but formed in the atmosphere from nitrogen oxides and...
Volatile organic compounds (VOC)
Photochemical smog is formed when primary pollutants interact with...
Sunlight
______, a highly toxic pollutant, was phased out of gasoline in the U.S. during the 1970's
Lead
Which of the following is not one of the results of the UV filtering effect of the ozone layer?
a. Allows human and other forms of life to exist on land
b. Protects human from sunburn
c. Protects our immune system from damage
d. Prevents the formation of photochemical ozone near the ground
e. Reduces the amount of water vapor in the troposphere
E. Reduces the amount of water vapor in the troposphere
Harmful chemicals emitted directly into the air from natural processes and human activities are called
primary pollutants
Which of the following is not one of the major air pollutants?
a. Suspended particulate matter
b. Sulfur dioxide
c. Nitrogen oxides
d. Formaldehyde
e. Ozone
D. Formaldehyde
What is the difference between point and nonpoint source water pollution?
Point sources can be targeted for reduction
A secondary pollutant:
Forms in the stratosphere
How do CFCs affect ozone production?
UV radiation frees a chlorine atom, which breaks down ozone
Acid rain, snow, fog, and cloud vapor typically have a pH of...
5.6
The biggest air pollution threat to poor people is
indoor air pollution
All of the following are volatile organic compounds (VOCs), except
carbon monoxide
Which of the following would NOT be a reason for sick building syndrome?
a. Faulty ventilation systems
b. Emissions from carpets and furniture
c. Contamination from outdoor air
d. Contamination from molds and pollen
e. CFC's
C. Contamination from outdoor air
Sick Building Syndrome is linked to all of the following, except
a. Headaches
b. Coughing and sneezing
c. Lung cancer
d. Inability to concentrate
e. Skin irritation
C. Lung cancer
Climate Change would most likely have the greatest impact on which of the following groups of species
Organisms in extreme environments
Which is not considered to be a greenhouse gas?
a. Carbon dioxide
b. Water vapor
c. Nitrogen
d. Nitrous oxide
e. Methane
C. Nitrogen
Which of the following organizations was created by the UN to monitor, understand, and estimate the global impact of climate change?
a. Montreal Protocol
b. EPA
c. IUCN
d. IPCC
e. Peace Corps
D. IPCC
A thermal (temperature) inversion, which can lead to serious pollution events, occurs when:
Cool air stays close to the surface and is blanketed by a layer of warm air that traps pollutants