GCSE geography - natural hazards (chapters 1, 2, 3, 4)
1/215
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
216 Terms
natural hazard
a natural event which has the potential to threaten both life and property
natural disaster
a natural hazard that has actually happened
how are natural disasters categorised?
are they geological (tectonic + geomorphological) or meteorological?
what is a meteorological natural disaster?
caused by weather conditions. this can be either over a short or long period of time. can affect a small or large area.
hazard risk
the chance or probability of being affected by a natural disaster
continental drift theory evidence (2)
the different continent borders and coastlines all fit together (e.g. east coast of south america and west coast of africa)
ores on the matching coastlines are the same
what is the earth’s crust divided into?
slabs called tectonic plates
what are these plates made of?
two types of crust- continental and oceanic
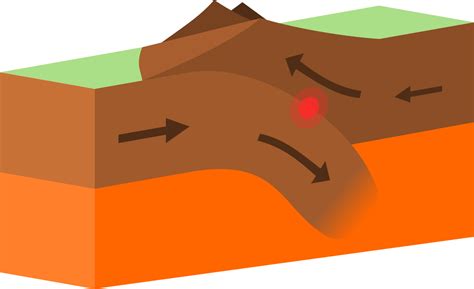
what will destructive/convergent plate margins result in?
earthquake / volcanic eruption
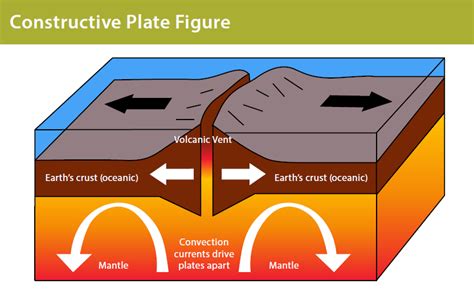
what will constructive/divergent plate margin result in?
earthquake / volcanic eruption
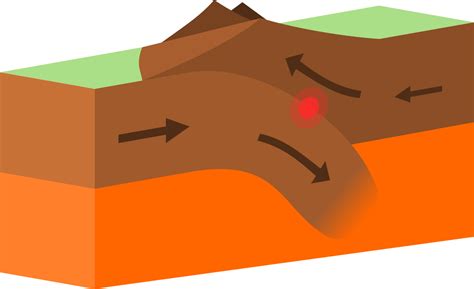
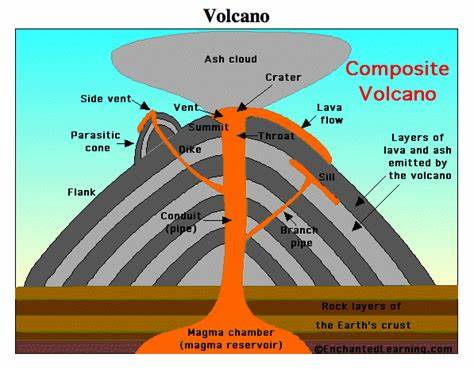
1. an oceanic plate (Nazca) is pushing towards a continental plate (south american)
2. oceanic plate is subducted beneath continental plate because it’s denser
3. the plate is destroyed in the mantle due to increased heat
4. continuous movement causes a build-up of friction and pressure
5. lava is forced into molten rock due to pressure, through the weakest point of the earth’s crust
6. this is repeated until lava cools and solidifies to become a composite cone volcano
7. if there is a volcanic eruption, it will be highly explosive, but they erupt less frequently than other volcanoes
8. it will be highly explosive due to a build up of carbon from the seabed, and a build up of pressure and friction
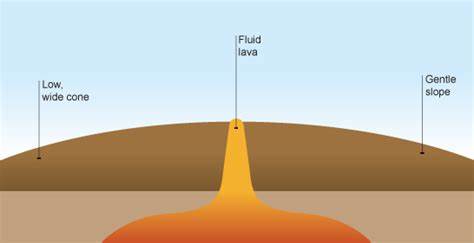
1. the tectonic plates are moving apart from eachother due to convection currents in the mantle
2. a gap is formed and immediately filled by magma rising from the mantle
3. this magma cools and solidifies to form rock or new volcanic crust
4. this repeats until many layers of magma build up to form wide, low volcanoes called shield volcanoes
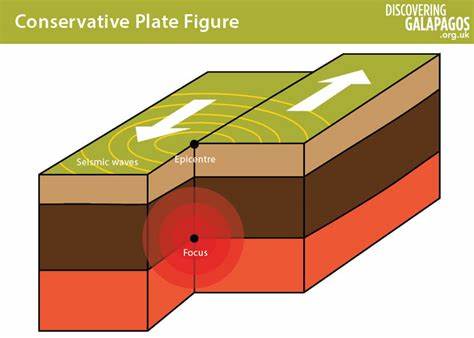
1. the plates can get stuck as they move apart, building stress
2. this can cause big cracks (faults) to be created on the moving plates
1. tectonic plates (in a slip fault) slide against each other either moving in the same or opposite direction (as a result of convection currents)
2. this creates friction which builds up in the focus spot
3. this friction is released in the form of seismic waves into the earth’s crust after a sudden slip
4. these seismic waves trigger earthquakes
1. no volcanoes are involved
2. no crust is destroyed or created
* flows for short distances
* viscous (thick + sticky lava)
* flows for long distances
* not viscous (hot + runny lava)
* Mount St Helens (USA)
* Heimay (Iceland)
1. Ash falls
2. Gas clouds
3. lava flows
4. pyroclastic flows
5. volcanic bombs
what are pyroclastic flows?
very hot flows of gas and ash, up to speeds of 700km/h
1. lahars
2. tsunamis
3. climate change
4. landslides
5. glacier bursts
1. many people killed/injured
2. farmland + buildings destroyed
3. communications damaged/disrupted (e.g. transport, water, electricity)
1. spread of disease due to no clean water/ broken sewers
2. hospitals are overwhelmed
3. shortage of necessities (e.g food, water, shelter, medicine)
4. local businesses have reduced income + food production
5. economic impact from cost of rebuilding + air travel disruption
1. set up exclusion (safe) zones
2. build volcano observatories
3. rebuild buildings + economy
1. richter scale (measures magnitude/energy of earthquakes)
2. mercalli scale (measures intensity/damage caused by earthquakes, 1-12 levels)
why do some people continue to live in areas at risk from tectonic hazards? (4)
well developed settlements would struggle to relocate
jobs/families in endangered areas
tourism creates jobs and opportunities in endangered areas (e.g. Blue Lagoon in Iceland)
land is fertile so opportunity for farmers
what is a LIC tectonic hazard?
Nepal (Ghorka) Earthquake
basic facts about the Ghorka earthquake? (4)
7.8 magnitude
8km deep focus point
on a convergent collision plate boundary
in April 2015
primary impacts of ghorka earthquake (4)
9000 dead (approx)
19000 injured
hundreds of thousands homeless
triggered an avalanche on the himalayas(20 dead)
secondary impacts of ghorka earthquake (3)
tourism rates dropped, $7 billion loss, main source of income
600,000 buildings destroyed
crops damaged, loss that harvest season
immediate responses to ghorka earthquake (2)
$1 million+ aid pledged from India + China
100+ search + rescue teams provided by the UK
long term responses to ghorka earthquake (1)
aid donated by many countries
what is a HIC earthquake case study?
New Zealand
basic facts about new zealand earthquake (4)
february 2011
12.51pm
5km deep focus point
6.3 magnitude
primary impacts of new zealand earthquake? (3)
185 dead
approx 2000 injured
10,000 houses needed to be rebuilt
secondary impacts of new zealand earthquake? (2)
liquefaction occurred, land cannot be rebuilt on
infrastructure severely damaged (roads, bridges etc)
immediate responses to new zealand earthquake (3)
search + rescue teams came globally
temporary housing provided
pop up hospitals
long term responses to new zealand earthquake (2)
unstable buildings were demolished
infrastructure was rebuilt
what is liquefaction?
when the ground shakes and causes water + mud to rise to the surface
what part of the earth is the sun concentrated at?
the equator
what part of the earth is the suns rays more spread out?
the polar regions
cold air …
sinks