Bio 2 final
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/147
Last updated 11:37 PM on 12/19/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
148 Terms
1
New cards
Groups of cells that are similar in both structure & function are known as \______.
Tissues
2
New cards
The type of tissue that functions to protect, support, & bind together body tissues are classified as\_____.
Connective tissues
3
New cards
\_______ glands possess ducts that transport secretions onto epithelial surfaces.
Exocrine
4
New cards
The specific type of epithelial tissue found lining organs of the digestive system such as the small intestine are \_______.
Simple columnar
5
New cards
Tendons & ligaments are classified as \______.
Dense connective (fibrous) tissue
6
New cards
\______ tissue is commonly called fat.
Adipose
7
New cards
\_____ muscle tissue has no visible striations & is found in the walls of hollow organs.
Smooth
8
New cards
Irritability & conductivity are the two major functional characteristics of \_____.
Nervous tissue
9
New cards
The structural & functional unity of all living things is the \______.
Cell
10
New cards
A tissue constructed as a single layer of flattened cells is known as \______.
Simple squamous epithelium
11
New cards
Which type of tissue conducts electrochemical impulses via cells called neurons?
Nervous tissue
12
New cards
Which type of tissue is situated in the lining of the urinary bladder & urethra where stretching occurs?
Transitional epithelium
13
New cards
Which of the following epithelial tissues is composed of many layers of cells?
Stratified squamous epithelium *key word: stratified
14
New cards
Bone is best described as\______.
Osseous tissue
15
New cards
Glands, such as the thyroid, that secrete their products directly into the blood rather than through ducts are classified as \______.
Endocrine
16
New cards
What characteristic is shared by both cardiac & smooth muscle tissue?
Involuntary contractions
17
New cards
The type of muscle found in the walls of hollow organs, such as the stomach, & in the walls of blood vessels is \______.
Smooth muscle
18
New cards
The presence of chondrocytes indicates that a tissue is \______.
Cartilage
19
New cards
Damaged tissues that are repaired by the same kind of cells experience a replacement process known as \_______.
Regeneration
20
New cards
Due to the cast placed on her broken leg, Kinsley's muscles have decreased in size. Which term best describes how her muscles have been affected?
Atrophy
21
New cards
Jacinda tore her Achilles (calcaneal) tendon during a recent track meet. She has injured\______.
Dense connective tissue
22
New cards
Which of the following tissues is constructed of many collagen fibers?
Scar tissue
23
New cards
The hypodermis, or subcutaneous tissue is represented by:
D
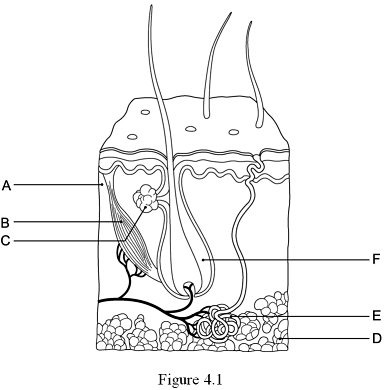
24
New cards
The hair follicle is indicated by:
F
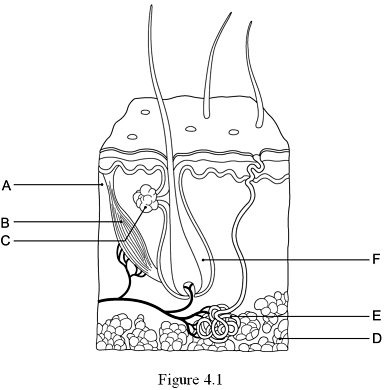
25
New cards
The layer responsible for whorled ridges on the epidermal surfaces is indicated by:
A
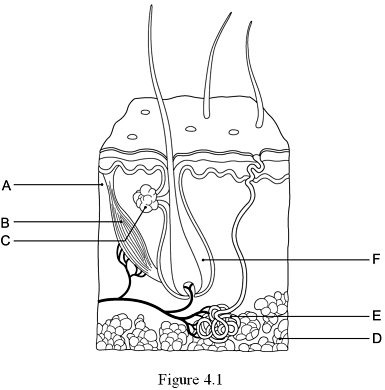
26
New cards
The arrector pili muscle is represented by:
B
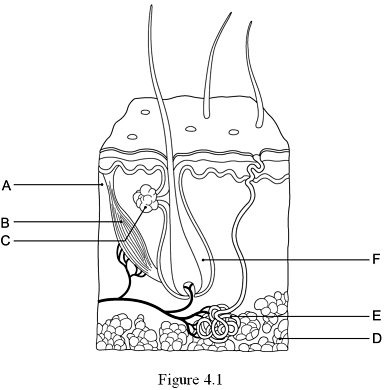
27
New cards
The gland that produces a mixture of oily substances and fragmented cells is indicated by:
C
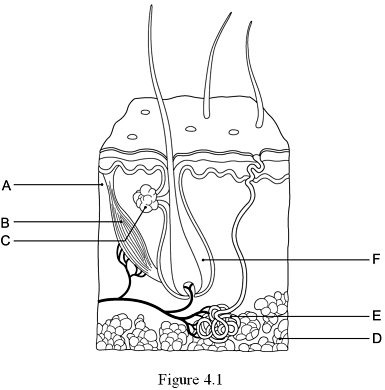
28
New cards
The gland that produces sweat is indicated by:
E
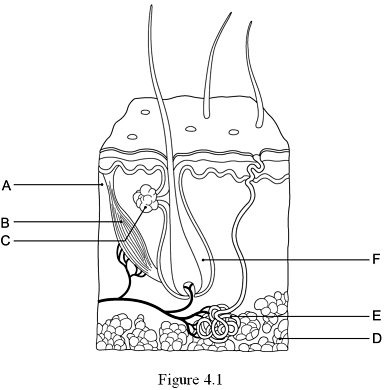
29
New cards
The pleura and pericardium are examples of \____________ membranes that cover organs in a body cavity closed to the exterior
serous
30
New cards
The \________ membrane lines the fibrous capsule surrounding joints
synovial
31
New cards
When James shaves his face, which portion of the hair is removed?
hair shaft
32
New cards
The sebaceous and sweat glands associated with skin are classified as \_________ glands because they release secretions to the skins surface via ducts
exocrine
33
New cards
\____________ is a lubricant that keeps skin soft and moist and also contains chemicals that kill bacteria
sebum
34
New cards
What type of burn only involves injury to superficial epidermis?
first degree
35
New cards
Hair color is due to a pigment known as \________.
melanin
36
New cards
The white crescent area located over the nail matrix
lunule
37
New cards
A nurse tends to a patient with a sunburn. Upon examination, she sees blisters and red skin. What type of burn is it?
second-degree
38
New cards
Staphylococcus infection of the skin that causes pink, water-filled, raised lesions is known as:
impetigo
39
New cards
\___________ is a skin cancer that accounts for 80% of all skin cancer causes and affects the cells stratum basale
basal cell carcinoma
40
New cards
Which of the following letter in ABCDE rule for recognizing melanomas is incorrect?
A) A stands for asymmetry
B) B stands for border irregularity
C) C stands for color
D) D stands for diagnosis
A) A stands for asymmetry
B) B stands for border irregularity
C) C stands for color
D) D stands for diagnosis
~~D~~
41
New cards
\___________ lines the body cavities that are open to the exterior
mucous
42
New cards
\___________ reduces friction in movable joints such as the knee
synovial fluid
43
New cards
The only dry membrane is the:
cutaneous membrane
44
New cards
The skin an its derivatives( nails, glands, hairs) form:
integumentary system
45
New cards
Although you get wet while swimming, a tough protein within the skin prevents it from soaking up moisture like a sponge. This substance is:
keratin
46
New cards
The epidermis is composed of
stratified squamous epithelium
47
New cards
Two main layers of skin
epidermis and dermis
48
New cards
¨Tanning¨ effect that occurs when someone is exposed to the sun is due to the increased presence of:
melanin
49
New cards
Which layer of the epidermis is composed of flattened, dead, keratin-filled cells?
stratum corneum
50
New cards
\____________ results from liver disorders
jaundice
51
New cards
A physician estimates the volume of fluid lost in a severely burned patient by:
rule of nines
52
New cards
cancer of melanocytes
malignant melanoma
53
New cards
skin inflammation
dermatitis
54
New cards
dry, dead flakes of stratum corneum
dandruff
55
New cards
Virus that produces cold sores
Herpes simplex
56
New cards
malignancy of the lowest epidermal layer
basal cell carcinoma
57
New cards
cancer of stratum spinosum cells
squamous cell carcinoma
58
New cards
burn in which only the epidermis becomes red and swollen
first-degree
59
New cards
Inflammation of the hair follicles and sebaceous glands is called:
boils and carbuncles
60
New cards
staphylococcus bacterial infection causing water-filled lesions, commonly around mouth and nose
impetigo
61
New cards
full thickness burn of the skin in which the skin blackens or blanches
third-degree
62
New cards
infection of the sebaceous glands accompanied by skin pimples
acne
63
New cards
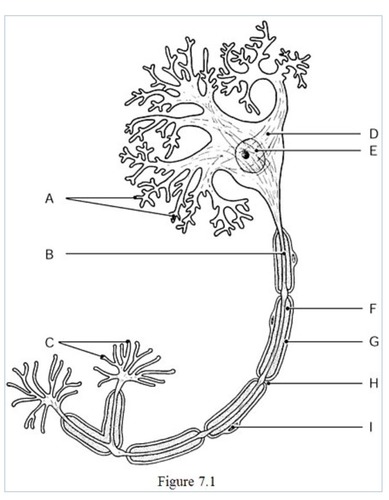
the neural processes that convey incoming messages toward the cell body are indicated by
label A (dendrites)
64
New cards
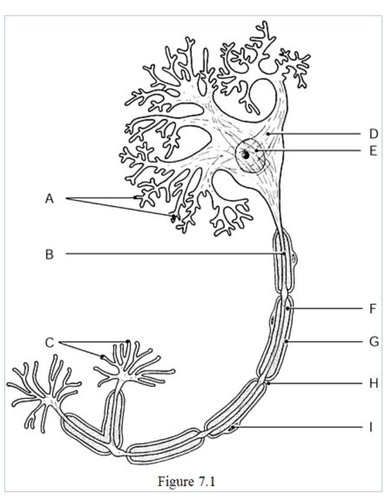
The metabolic center on the neuron is indicated by
label D (cell body)
65
New cards
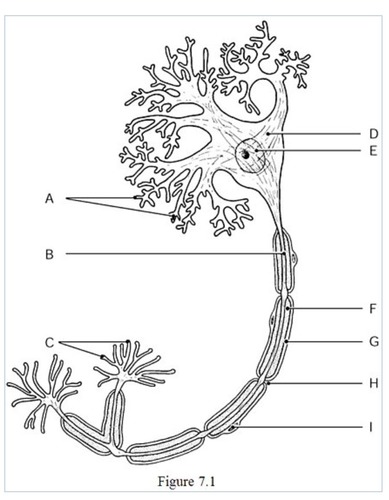
The axon terminals are indicated by
label C
66
New cards
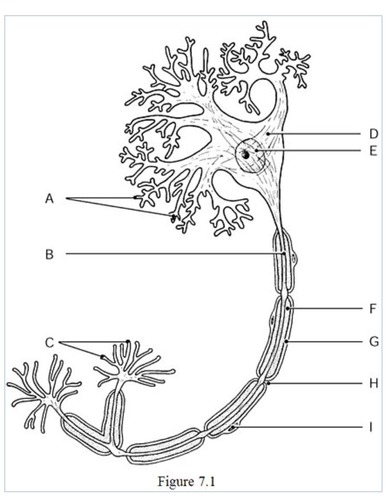
The axon is indicated by
label B
67
New cards
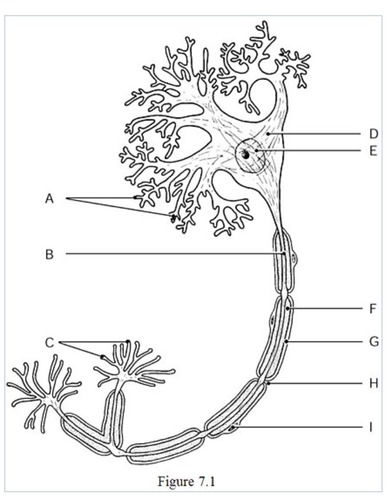
The gaps between Schwann cells are indicated by
label H
68
New cards
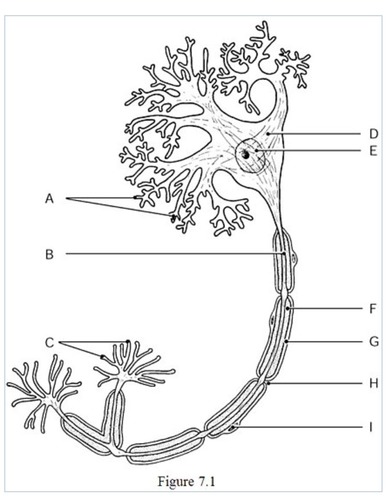
The nucleus of the neuron is indicated by
label E
69
New cards
What are the two main functional subdivisions of the nervous system?
central and peripheral
70
New cards
What cells form the myelin sheaths around nerve fibers in the PNS?
Schwann cells
71
New cards
Support cells in the central nervous system are collectively called \__________
neuroglia
72
New cards
The part of the neuron that typically conducts nerve impulses away from the cell body is the \_____
axon
73
New cards
The gaps between Schwann cells found at regular intervals in the PNS are called \______
nodes of ranvier
74
New cards
Mr. Warren has spinal cord damage that prevents nerve impulses from being carried from the CNS to muscles or glands. What specific type of neuron has been damaged?
motor neuron
75
New cards
What are the major positive ions situated outside the neuron when it is polarized?
sodium ions
76
New cards
During repolarization, what ions are pumped out of the cell?
potassium
77
New cards
What reflexes stimulate skeletal muscles?
somatic
78
New cards
How are neurons with several processes branching off the cell body, such as motor neurons and interneurons, structurally classified?
multipolar
79
New cards
What are the two major functional properties of neurons?
irritability and conductivity
80
New cards
Impulse conduction is faster in neurons that are
myelinated
81
New cards
The gap between two communicating between neurons is termed
synaptic cleft
82
New cards
Fibers that carry information from the skin, joints, and skeletal muscles to the central nervous system are
somatic
83
New cards
What type of neuron connects sensory and motor neurons in neural pathways?
interneurons (association neurons)
84
New cards
The thalamus, hypothalamus, and epithalamus collectively constitute the \_______
diencephalon (interbrain)
85
New cards
What brain dysfunction results when blood supply to a region (or regions) of the brain is blocked and vital brain tissue dies, as by a blood clot or a ruptured blood vessel?
cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or stroke
86
New cards
the brain and spinal cord are protected by three connective tissue membranes called
meninges
87
New cards
In what cerebral lobe is the primary somatic sensory cortex located?
parietal
88
New cards
In which of the following is one of the major functions of the pons
breathing
89
New cards
What fissure separates the cerebral hemispheres?
longitudinal fissure
90
New cards
The hypothalamus regulates the
pituitary gland
91
New cards
The large fiber tract that allows communication between the two cerebral hemispheres is called the
corpus callosum
92
New cards
What portion of the diencephalon acts as a relay station for sensory impulses travelling upward to the sensory cortex?
thalamus
93
New cards
Hemiplegia and aphasia characterize those patients who have experienced a \________.
CVA or stroke
94
New cards
How many pairs of spinal nerves emerge from the spinal cord
31
95
New cards
Progressive, degenerative disease of the brain that results in dementia and is associated with a shortage acetylocholine
alzheimers disease
96
New cards
which of the following isn't a major region of the brain: brain stem, ventral ramus, diencephalon, cerebrum, cerebellum
ventral ramus
97
New cards
which of the following indicates damage to the primary motor area?
* inability to form complex memories
* inability to say words properly
* inability to recognize patterns
* inability to voluntarily move skeletal muscles
* inability to involuntarily move smooth muscles
* inability to form complex memories
* inability to say words properly
* inability to recognize patterns
* inability to voluntarily move skeletal muscles
* inability to involuntarily move smooth muscles
inability to voluntarily move skeletal muscles
98
New cards
A stroke in the primary motor area has caused Don to lose control over his skeletal muscles on the right side of his body. What lobe was affected?
frontal lobe
99
New cards
Wendy had a few alcoholic drinks, then found walking and maintaining her balance difficult. Which part of her brain was affected?
cerebellum
100
New cards
The gland that produces thymosin is?
Label E (Thymus)
Explore top notes
Explore top flashcards
Foundations of govt, British history, DOI, Articles of Confederation
Updated 881d ago