Biology: Seedless Plants, Fungi, and Plant Reproduction
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
What are the main characteristics of plants?
Plants are multicellular, non-motile, eukaryotic organisms that are mostly autotrophic (photosynthetic), containing chlorophylls a and b, and some are parasitic or non-photosynthetic.
What is meant by 'alternation of generations' in plants?
It refers to the life cycle of plants where they alternate between a haploid gametophyte stage and a diploid sporophyte stage.
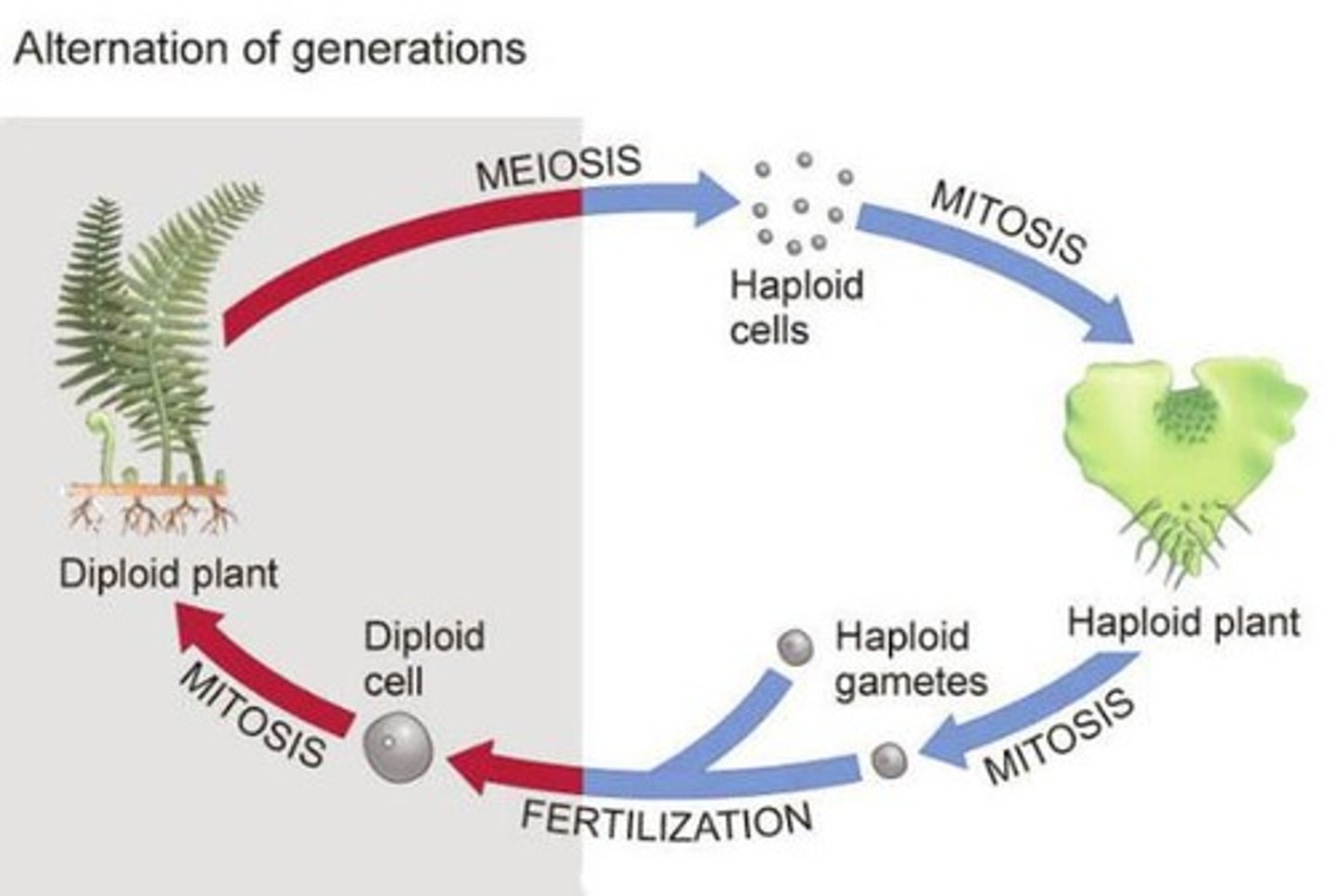
What are the two main life stages in the alternation of generations?
The gametophyte (haploid, multicellular) produces gametes by mitosis, while the sporophyte (diploid) produces spores via meiosis.
How do animals and plants differ in gamete production?
Animals produce gametes within internal organs, while plants grow external structures to produce gametes.
What are the two main groups of seedless plants?
Nonvascular plants (Phylum Hepatophyta and Bryophyta) and seedless vascular plants (Phylum Pterophyta).
What is the dominant life stage in nonvascular plants?
The gametophyte stage is dominant in nonvascular plants.
What is the function of rhizoids in nonvascular plants?
Rhizoids anchor the plant to the substrate.
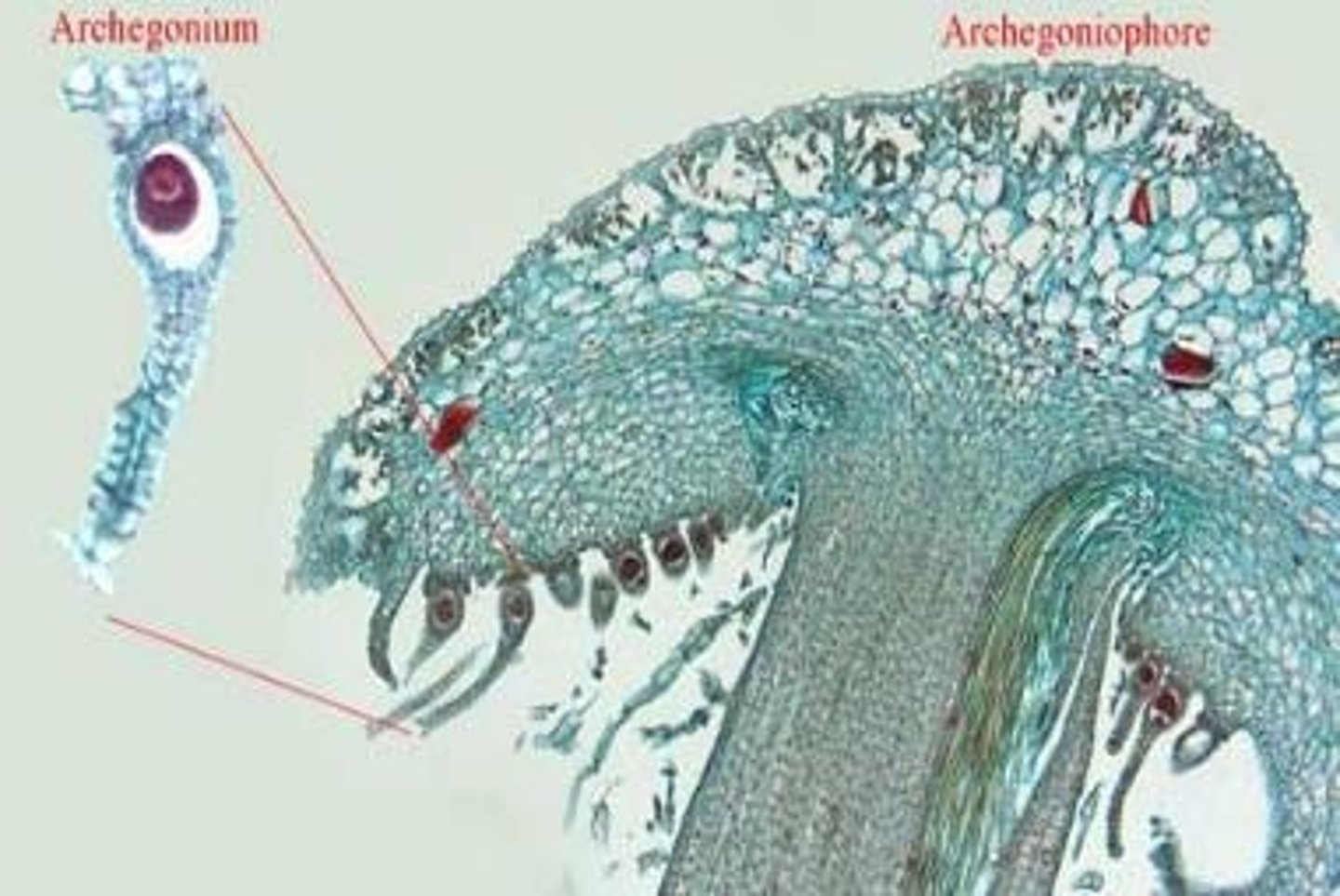
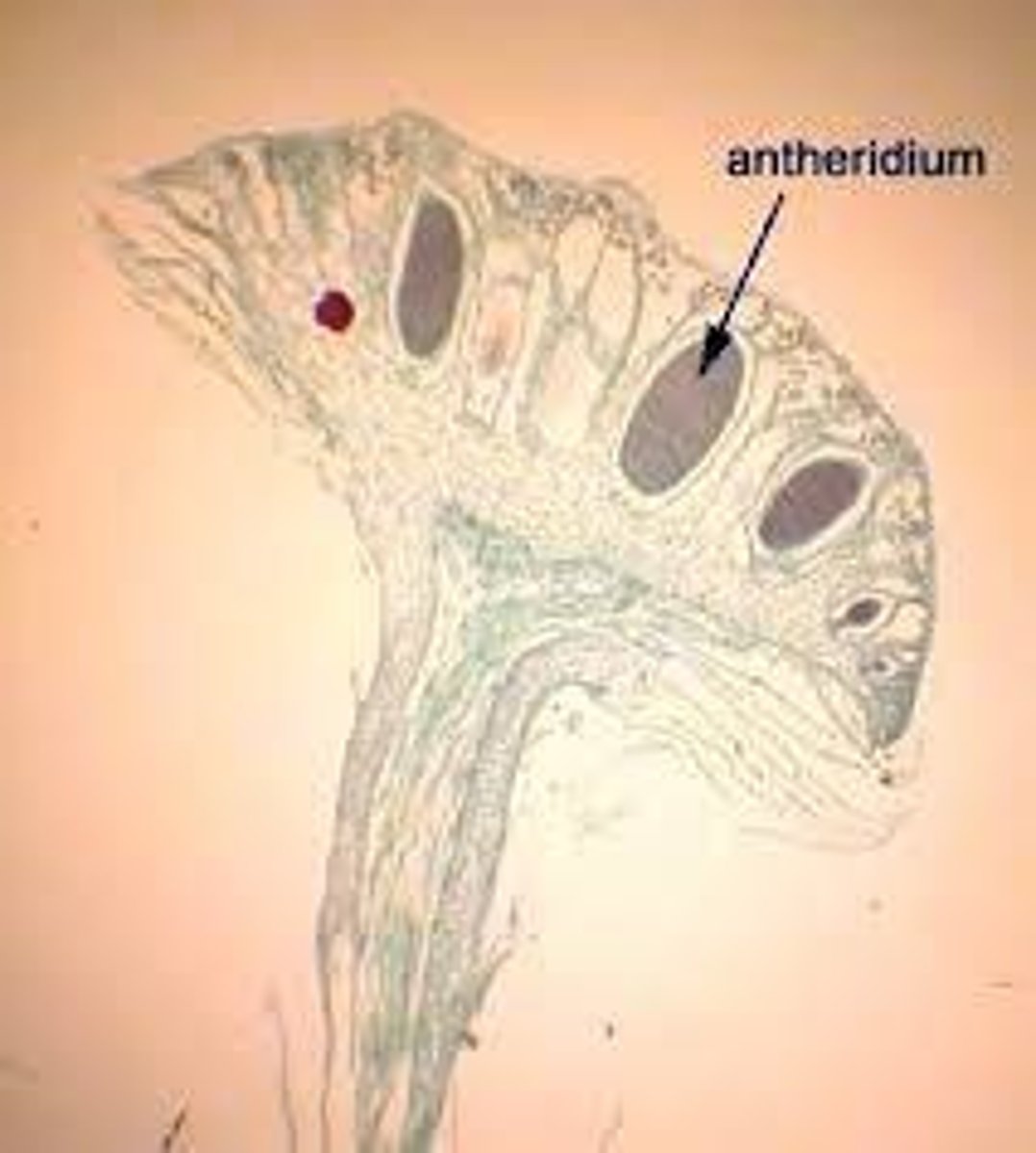
What is the reproductive structure of male and female liverworts?
Male liverworts have antheridiophores that house antheridia, while female liverworts have archegoniophores that house archegonia.
What is the dominant life stage in seedless vascular plants?
The sporophyte stage is dominant in seedless vascular plants.
What is the role of water in the reproduction of seedless plants?
Water is required for sperm transport during reproduction.
What distinguishes Phylum Chytridiomycota from other fungal phyla?
Chytridiomycota are the only fungi with a motile life stage (flagellated spores and gametes) and exhibit alternation of generations.
What type of hyphae do molds in Phylum Zygomycota have?
Zygomycota have aseptate hyphae.
What are the reproductive structures in Phylum Ascomycota?
Ascomycota have ascocarps that house asci, which produce ascospores.
What is a characteristic feature of Phylum Basidiomycota?
Basidiomycota produce basidiospores in structures called basidia.
What is the ecological role of fungi in symbiotic relationships?
Fungi can form mutualistic relationships, such as lichens (with algae) and mycorrhizae (with tree roots), benefiting both organisms.
What is the main function of mycorrhizae?
Mycorrhizae increase the surface area for absorption of water and minerals for tree roots.
What is the significance of the humongous fungus in Phylum Basidiomycota?
It covers 37 acres, weighs 21,000 lbs, and is approximately 1,500 years old, demonstrating the extensive growth of a single organism through asexual reproduction.
What is the purpose of the annotated bibliography assignment?
To summarize and critically analyze two scientific articles about the effects of salinity on seed germination.
What are the components required in each paragraph of the annotated bibliography?
Each paragraph should include a summary of the main points, a critical analysis of the article, a statement of relevance, and a complete bibliographic citation in APA format.
What is the next topic to be covered in class after fungi?
The Seed Plants: Gymnosperms.
What is the expected activity for next week in class?
Start the seed germination activity.
What is the significance of chlorophylls a and b in plants?
They are essential for photosynthesis, allowing plants to convert light energy into chemical energy.
What type of plants are included in Phylum Hepatophyta?
Liverworts, which lack vascular tissues and true roots, stems, or leaves.
What is the role of gemmae in liverworts?
Gemmae are asexual reproductive structures housed in gemma cups that help in the asexual reproduction of liverworts.
What is the function of the protonema in mosses?
The protonema is a filamentous structure that develops from spores and houses reproductive structures.
What is the role of spores in the life cycle of seedless plants?
Spores are produced through meiosis in the sporophyte generation and disperse to grow into gametophytes.