Male & Female Reproductive 2402
1/107
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
108 Terms
What happens during meiosis I?
- Homologous chromosomes separate **
- Reduces the diploid cell to haploid
Know the sequence of meiosis I:
1.) Prophase 1
2.) Metaphase 1
3.) Anaphase 1
4.) Telophase 1
- PMAT
What is synapsis?
- Pairing of homologous chromosomes
What phase does synapsis occur?
- Prophase 1
At the end of meiosis I, how many chromosomes are present?
- 23 chromosomes
Number of possible chromosome combinations in a gamete of a human?
- 8 million (8,000,000)
What is the gubernaculum?
- Fibrous cord that is attached to each developing testis
What is the function of the gubernaculum?
- Helps guide the descent of the testes **
- Passes through the inguinal canal **
Seminiferous tubules are lined with what specific type of cells?
- Stratified cuboidal epithelium
- Contains sustentacular cells **
- Includes spermatogenic cell (sperm cells)
1 primary spermatocyte will produce how many sperm cells?
- 4 sperms for each primary spermatocyte
What is the function of Sertoli cells?
- Throughout the development of spermatogenic cells:
~ Support
~ Nourish
~ Regulate
What is a vasectomy and how does it act as birth control?
- Removing, cutting, and tying a small section of ductus deferens
- Prevents sperm cells from leaving epididymis
List the parts of the sperm cell and describe each.
- Head: nucleus; acrosome (helps penetrate oocyte/egg)
- Midpiece: mitochondria (allow sperm to swim)
- Tail: Uses midpiece (ATP of mitochondria/midpiece) to propel around
Does the male or female have a prostate gland?
- Males
How many prostate glands are present?
- 1 ONLY
What type of fluid is secreted by the bulbourethral glands secrete?
- Mucus-like fluid
What is the function of bulbouretheral glands?
- Lubricates the end of the penis in preparation for sexual intercourse
What does seminal fluid contain?
- Nutrients (fructose)
- Prostaglandins
Number of sperm cells in an ejaculate.
- 120 million per mL
What is circumcision?
- Surgical procedure that removes the prepuce (covering) from the glans penis
What are some causes of erectile dysfunction?
- Diabetes mellitus **
- Paralysis
- Prostate surgery
- Certain drugs
- Alcohol consumption
- Cigarette smoking
The epididymis transports sperm from the ____________ to the ____________?
- Rec Testes to the Ductus (Vas) Deferens
The ductus deferens transports sperm to the ____________?
- Ejaculatory duct
What occurs in the epididymis?
- Maturing of sperm cells
What is spermatogonia?
- Undifferentiated spermatogenic cells
What glands expel the first fluid during ejaculation?
- Bulbourethral glands
- Lubrication
How many lobules in the testes?
- 250 lobules
How many tubules are in the lobules?
- 1 to 4 tubules per lobule
Which neurotransmitter causes vasodilation?
- Nitric oxide
-Dilates arteries in erectile tissue (penis/vagina)
Do you think an erection would be controlled by the parasympathetic or sympathetic system?
- Parasympathetic
Male reproductive functions are controlled by hormones secreted by what structures?
- Hypothalamus
- Anterior pituitary
- Testes
What hormone is responsible for secondary sex characteristics?
- Testosterone
What body fluids would be needed to study testosterone?
- Blood
- Urine
List some male secondary characteristics.
** - Increased growth of body hair
** - Growth on the scalp may slow
** - Deeper Voice (enlargement of larynx & thickening of vocal cords)
** - Thickening of the skin
** - Increased muscular growth
** - Thickening and stretching of bones
** - Increased rate of RBC production
** - Increased cellular metabolism
- Broader shoulders
- Narrower waist
What are androgens?
- Male sex hormones
Where are androgens produced?
- MAJORITY in interstitial cells of the testes
- FEW in the adrenal cortex
Which hormones control the release of testosterone?
- LH (Luteinizing Hormone)
- ISCH (Interstitial Cell Stimulating Hormone)
- Same thing**
Why is the hormone FSH important? (MALE)
- Stimulates sustentacular cells of testes
- Mature and respond to effects of testosterone
- In presence of FSH, testosterone, and sustentacular cells will stimulate spermatogenesis which give rise to sperm cells
How would you describe the size of the prostate gland?
- Walnut
- Chestnut
Why is it important for the testes to descend?
- Can cause infertility if not descended correctly
What happens to the penis (internally) when an erection take place? I want to know what is happening physiologically-not the physical appearance.
- Parasympathetic impulses
- Release vasodilator nitric oxide (NO) which causes vasodilation of arteries (in penis).
- Increasing blood flow (+ veins constrict) into erectile tissues
What are the regions of the uterus?
- Fundus (dome-shaped top)
- Body (upper ⅔)
- Cervix (lower ⅓); extends to vaginal canal **
What is a secondary oocyte?
- Ovum (egg cell) that may be fertilized by sperm
Why would a woman have a pap smear?
- Detect variants of HPV (human papillomavirus)
- CAN cause cervical cancer
-If HPV+, there is a high risk of cervical cancer
What is the zona pellucida?
- Layer of glycoprotein that forms between primary oocyte and granulose cells
Where is the location of the uterine tube?
- Between uterus and ovaries
Where does fertilization take place?
- Uterine (Fallopian) tubes **
- Ectopic pregnancy is fatal due to the fetus growing in the fallopian tubes (bursting of uterine tubes as the fetus develops)
What is the labia minora?
- Minor part of labia that protects urethral & vaginal opening
- Skin that forms around clitoris tissue **
What are the layers of the uterine wall? (list from inner to outer)
- Endometrium (inner mucosa layer)
- Myometrium (middle muscular layer)
- Perimetrium (outer serosal layer)
What does the primary oocyte divide into?
- Large secondary oocyte
- Small first polar body
What is the function of polar bodies?
- Allow for formation of egg cell w/ large amounts of cytoplasm & organelles
- Supports zygote through the first cell division, ensuring enough organelles & nutrients **
Which female structure is analogous to the male penis?
- Clitoris
Look at a sagittal view of the female reproductive system. Which structure is anterior to the vagina?
- Urethra
Why does menopause occur?
- Less estrogen
- Less progesterone
- Ovaries are aging
- Secondary sex characteristics decrease
Why is estrogen important-what role does it have in a female body?
- Maintain secondary sex characteristics which are important for childbearing:
~ Breast & mammary glands
~ Duct enlargements
~ Increase adipose tissue in breast & buttocks
~ Increase vascularity of skin
- Cause endometrium to thicken (preparation of environment for baby)
- Enlargement of accessory reproductive organs
What is ovulation?
- Release of an oocyte from a mature ovarian follicle
- Stimulated by LH
Where is LH released from?
- Anterior pituitary gland
What role does LH play in the female body?
- Triggers ovulation (menstrual cycle) **
- Endometrium weakens & ruptures
- Follicle fluid, wall, and secondary oocyte is released from ovary's surface
What happens to specific hormones during menopause?
- Decreased estrogen
- Decreased progesterone
- FSH & LH are slightly increased
What might happen to the secondary sex characteristics during menopause?
- Breast, vagina, uterus, & uterine tubes may shrink
- Pubic, axillary, scalp hair may thin
What happens to hormones in an athlete?
- Lower GnRH (gonadotropin-releasing hormone) from hypothalamus
- Lower blood estrogen levels
- Affects fertility (child development)
What do the hormones estrogen and progesterone do in the reproductive cycle?
- Help thicken uterus wall
- Endometrium becomes more granular & vascular (more enriched in blood vessels)
- Helps develop the fetus
* THINK OF UTERUS WALL AND FETUS *
What treatment can be used to limit the symptoms of menopause?
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) **
- Specifically: Estrogen Therapy **
- Treatment for hormonal changes/menopausal hot flashes
How many lobes does a mammary gland contain?
- 15 to 20 lobes
Each mammary gland lobe contains what glands?
- Alveolar glands
What duct do the mammary gland lobes drain into?
- Alveolar ducts
Where does the alveolar duct drain into?
- Lactiferous duct
- Leads to nipple, which opens to the outside
The drainage of the mammary gland occurs in the following sequence:
1.) Alveolar glands
2.) Alveolar ducts
3.) Lactiferous ducts
What synthetic chemicals are most commonly found in combined hormonal contraceptives?
- Estrogen
- Progestin
What are examples of chemical barriers used as birth control?
- Creams
- Foams
- Jellies
- Chemical barriers consist of spermicidal properties (kills off sperms)
What are examples of mechanical barriers used as birth control?
- Male & female condoms
- Prevent semen (+ sperms) to enter vagina
What are some side effects of oral contraceptives?
- Minor side effects:
~ Nausea **
~ Retention of body fluids **
~ Increased skin pigmentation **
~ Breast tenderness **
~ Menstrual changes
- Major side effects:
~ Increased risk of blood clots **
~ Development of liver disorders
~ High BP (blood pressure)
What is anovulation?
- Inability to ovulate (have menstrual periods)
What would cause anovulation as it pertains to infertility?
- Hyposecretion of gonadotropic hormones (LH & FSH) from anterior pituitary gland
What are androgens?
- Male sex hormones
- Prevent over secretion of GnRH & LH
How do you think an overproduction of androgens would affect the female body?
- Irregular periods
- Deeping of voice
- Receding hairline
- Facial/body hair growth increase
- Tumors may occur
What are the hormones of the female body?
- GnRH
- FSH
- LH
- Estrogen
- Progesterone
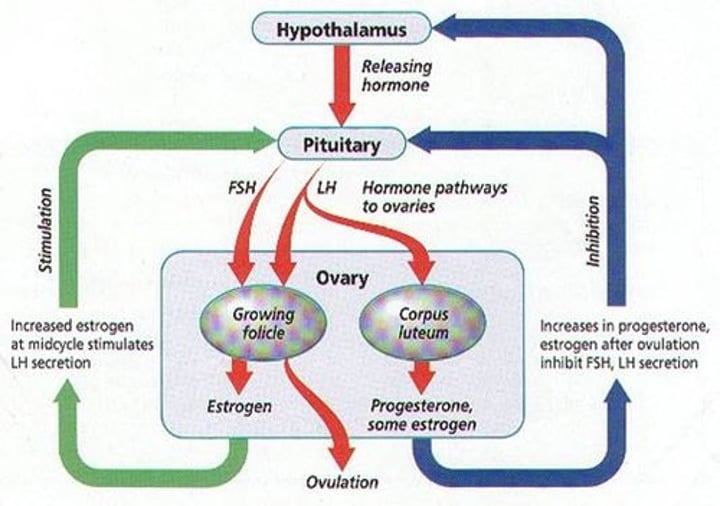
What is the function of GnRH? (FEMALE)
- From hypothalamus
- Stimulates release of FSH & LH from anterior pituitary
What is the function of FSH? (FEMALE)
- Stimulates maturation of primordial follicles
- Primary oocytes to secondary oocytes
What is the function of LH? (FEMALE)
- Stimulate ovulation
- Release of secondary oocyte
What is the function of estrogen? (FEMALE)
- Controls the development of secondary sex characteristics **
- Enlargement of reproductive organs (i.e.- vagina, uterine tubes, ovaries, etc.)
- Thickening endometrium
What is the function of progesterone? (FEMALE)
- Affects mammary glands
- Promote changes in uterus
- Regulates secretion of FSH & LH
What is endometriosis?
- Tissue resembling inner lining of uterus (endoterium) grows in the wrong area or in abdominal cavity
- May lead to scarring
- Fertility issues may occur
How does Tamoxifen and raloxifene work?
- Blockage of estrogen receptors
- Half of patients’ w/ breast cancer have estrogen receptors on cancer cells
What is the cause of HIV?
- Human Immunodeficiency Virus
What are the symptoms of HIV?
- Fever
- Weakness
- Fatigue
- Infections
What are the effects on fetus when one has HIV?
- Exposure to HIV
- Other infections
Are there any treatments for HIV?
- Drugs to treat/ delay symptoms
Are there any complications of HIV?
- AIDS is acquired from HIV
What are the causes of gonorrhea?
- Neisseria gonorrhoeae bacteriaterm
What are the symptoms of gonorrhea?
- Women: none
- Men: painful urination
What are the effects on the fetus when one has gonorrhea?
- Stillbirth
- blindness
What are the treatments possible for gonorrhea?
- Antibiotics
- Dual drug therapy for resistant strains
What are some complication of gonorrhea?
- Arthritis
- Rash
- Infertility
- Pelvic inflammatory disease
What are the symptoms of genital warts?
- Warts on genitals
What are the effects on the fetus when one has genital warts?
- None known
Are there any treatments for genital warts?
- Chemical or surgical removal of warts
Are there any complications for genital warts?
- Increased risk of cervical cancer (in women)
What are the causes of genital warts?
- Human papillomavirus
When the secondary oocyte is fertilized it becomes a _______.
- Zygote