ap world history unit 3 (copy)
1/75
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
76 Terms
Qing Dynasty
☆ last imperial dynasty of China ☆ preceded by the Ming Dynasty and succeeded by the People's Republic ☆ founded in 1644 by the Manchus and ruled China for more than 260 years, until 1912 ☆ expanded China's borders to include Taiwan, Tibet, Chinese Central Asia, and Mongolia
Manchus
☆ Northeast Asian peoples who defeated the Ming Dynasty and founded the Qing Dynasty in 1644 ☆last of China's imperial dynasties
Mughal Empire
☆ Muslim state (1526-1857) exercising dominion over most of India in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries ☆ often had difficulties managing such a large, diverse empire

Ottoman Empire
☆ Islamic state of Turkic speaking peoples lasting from 1453-1922; conquered the Byzantine Empire in 1453 ☆ based at Istanbul (formerly Constantinople) ☆ encompassed lands in the Middle East, North Africa, the Caucasus, and eastern Europe.

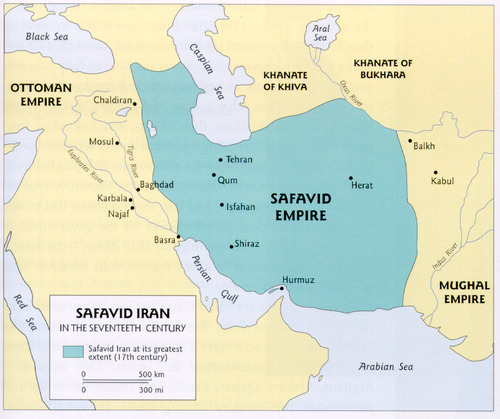
Safavids
A Shi'ite Muslim dynasty that ruled in Persia (Iran and parts of Iraq) from the 16th-18th centuries that had a mixed culture of the Persians, Ottomans, and Arabs.
Songhai
☆ an Islamic West African empire that conquered Mali and controlled trade from the 16th century ☆ eventually defeated by the Moroccans who were broke after fighting with Portugal

Devshirme
☆ 'Selection' in Turkish ☆ the system by which boys from Christian communities were taken by the Ottoman state to serve as Janissaries (elite military units)
Janissary
☆ elite Ottoman guard (trained as foot soldiers or administrators) recruited from the Christian population through the devshirme system, that often converted to Islam ☆ utilized gunpowder weapons

samurai
class of salaried warriors in feudal Japan who pledged loyalty to a noble called a daimyo (who in turned pledged loyalty to a shogun) in return for land or rice payments

Divine Right
☆ belief that a ruler's authority comes directly from God ☆ the idea that monarchs are God's representatives on earth and are therefore answerable only to God.

absolute monarchy
system of government in which the head of state is a hereditary position and the king or queen has almost complete power

Versailles
☆ Palace constructed by Louis XIV outside of Paris to glorify his rule and subdue the nobility ☆ late 17th-early 18th century (became his primary residence around 1670)

zamindars
Mughal empire's taxation system where decentralized lords collected tribute/taxes for the emperor
Taj Mahal
☆ beautiful mausoleum (tomb) at Agra (India) built by the Mughal emperor Shah Jahan (completed in 1649) in memory of his favorite wife ☆ illustrates syncretic blend between Indian and Arabic architectural styles
tax farming
☆ tax-collection system utilized by the Ottoman Empire to generate money for territorial expansion ☆ the government hired private individuals to collect taxes
Protestant Reformation
☆ religious movement begun by German monk Martin Luther who began to question the practices of the Catholic Church beginning in 1519 ☆ split the Roman Catholic Church and resulted in the 'protesters' forming several new Christian denominations: Lutheran, Calvinist, and Anglican Churches (among many others)

95 Theses
☆ arguments written by Martin Luther against the Catholic church. They were posted on October 31, 1517 ☆ ultimately led to Martin Luther's excommunication and the Protestant Reformation
Martin Luther
☆ a German monk who became one of the most famous critics of the Roman Catholic Church ☆ In 1517, he wrote 95 theses, or statements of belief attacking the church practices (spread by printing press) ☆ began the Protestant Reformation ☆ preached faith is the only way to salvation (spread individual interpretation)

Counter/Catholic Reformation
☆ the reaction of the Roman Catholic Church to the Protestant Reformation ☆ reaffirming the veneration of saints and the authority of the Pope (to which Protestants objected), ended sale of indulgences and simony, created Jesuits missionaries, but also the began the Inquisition
Jesuits
☆ also known as the Society of Jesus; a teaching and missionary order to resist the spread of Protestantism (a result of the Counter Reformation) ☆ sent to China, Japan, and the New World to gain Catholic converts

indulgence
☆ a pardon given by the Roman Catholic Church in return for repentance for sins and payment ☆ "a way to reduce the amount of punishment one has to undergo for sins"

Simony
the buying and selling of church offices, seen as a corrupt practice, this practice was outlawed by the Catholic Church during the Counter Reformation
Inquisition
Roman Catholic tribunal for investigating and prosecuting charges of heresy, a reaction to the Protestant Reformation

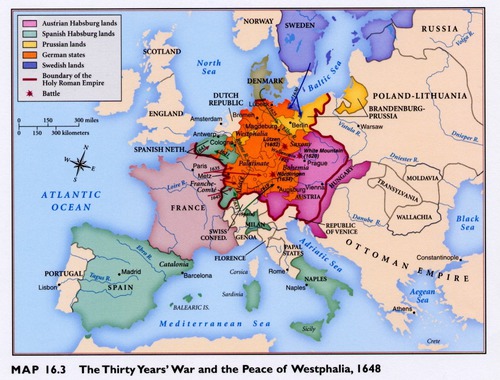
Thirty Years War
☆ a war that resulted from the Protestant Reformation (1618-1648 CE) ☆ occurred in the Holy Roman Empire between German Protestants and their allies (Sweden, Denmark, France) and the emperor and his ally, Spain who supported Roman Catholicism ☆ ended in 1648 after great destruction with Treaty of Westphalia
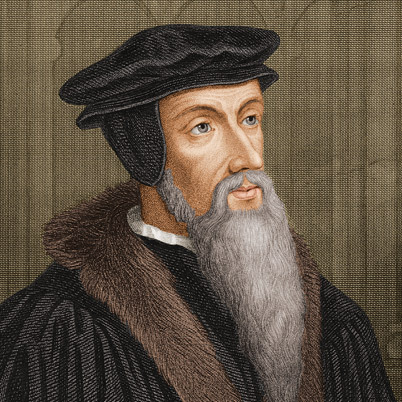
John Calvin
☆ 1509-1564 ☆ french theologian who developed the Christian theology known as Calvinism ☆ attracted Protestant followers with his teachings ☆ believed in predestined people go to heaven (elect)

Sikhism
☆ the doctrines of a monotheistic religion founded in northern India in the 16th century by Guru Nanak and combining elements of Hinduism and Islam ☆ a result of the presence of the Mughal Empire in India

Shogunate
Japanese system of government under a shogun (military warlord), who exercised actual power while the emperor was reduced to a figurehead

Daimyo
Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai; owed allegiance to the shogun

Jizya
☆ tax paid by Christians and Jews (and sometimes other faiths) who lived in Muslim communities to allow them to continue to practice their own religion ☆ often utilized by Islamic states to manage diverse populations within their empires
Ming Dynasty
☆ Succeeded Mongol Yuan dynasty in China in 1368 ☆ lasted until 1644 ☆ initially mounted huge trade expeditions to southern Asia and elsewhere, but later concentrated efforts on internal development within China
Kangxi
☆ Qing emperor (r. 1662-1722) ☆ He oversaw the greatest expansion of the Qing Empire.
Emperor Qianlong
☆ Emperor who refused to open more trading ports to Europe. ☆ He was known for his military skills, love of scholarship, and tolerance.
Gunpowder Empires
large multiethnic states in Southwest, Central, and South Asia that relied on firearms to conquer and control their territories
shah
☆ Persian word for king ☆ a title given to the emperors, kings, princes and lords of Iran
ghazi ideal
a model for warrior life that blended the cooperative values of nomadic culture with the willingness to serve as a holy fighter for Islam
castes
social groups into which people are born and cannot change
Ivan IV (the Terrible)
☆ Confirmed power of tsarist autocracy by attacking the authority of the boyars ☆ continued policy of expansion ☆ established contacts with western European commerce and culture.
Tamerlane
☆ a "second Genghis Khan" who united Mongols and led them in a series of conquests. His enemies called him "Prince of Destruction" ☆ he subdued Asia, Persia, Mesopotamia and India

Suleiman I
the Ottoman empire reached its peak under him, and he ruled from 1520-1566. His armies reached Hungary in 1526 and were at Vienna in 1529. Despite being unable to take Vienna, the Ottoman's ability to sent troops that far made Christian Europe scared.

Ismail
☆ A great Safavid ruler who, at the age of 14, conquered much of the territory that became the Safavid Empire ☆ He was a religious tyrant who made Shi'ia the state religion.
Shah Abbas I
☆ presided over Safavid Empire at its height ☆ He imported weaponry from Europe and relied Europeans to teach how to use these weapons.

Akbar
☆ The most famous Muslim ruler of India during the period of Mughal rule ☆ Famous for his religious tolerance, his investment in rich cultural feats, and the creation of a centralized governmental administration, which was not typical of ancient and post-classical India.
justices of the peace
English local officials in the shires appointed by the crown and given wide authority in local government.
English Bill of Rights
It guaranteed certain rights to English citizens and declared that elections for Parliament would happen frequently. By accepting this document, they supported a limited monarchy, a system in which they shared their power with Parliament and the people.
Louis XIV
☆ (1638-1715) Known as the Sun King, he was an absolute monarch that completely controlled France ☆ One of his greatest accomplishments was the building of the palace at Versailles.
Romanov Dynasty
Dynasty that favored the nobles, reduced military obligations, expanded the Russian empire further east, and fought several unsuccessful wars, yet they lasted from 1613 to 1917.
Peter I
☆ son of Alexis Romanov ☆ ruled from 1682 to 1725 ☆ continued growth of absolutism and conquest; included more definite interest in changing selected aspects of economy and culture through imitation of western European models.
daimyo
A Japanese feudal lord who commanded a private army of samurai
Tokugawa Ieyasu
☆ founder of the Tokugawa Shogunate which lasted from 1603 to 1867 ☆ reunified Japan and established political unity in Japan
Period of Great Peace
The Tokugawa Shogunate created this period in Japan known as the Edo Period by adopting a policy of isolation
Askia the Great
☆ Songhai ruler who made Islam official religion to unite his empire ☆ oversaw Songhai at its height
Shah Jahan
Mughal emperor of India during whose reign the finest monuments of Mogul architecture were built (including the Taj Mahal at Agra) (1592-1666)
tributes
wealth sent from one country or ruler to another as a sign that the other is superior
boyars
Russian nobles; landholding aristocrats
Henry VIII
☆ (1491-1547) King of England from 1509 to 1547 ☆ his desire to annul his marriage led to a conflict with the pope, England's break with the Roman Catholic Church, and its embrace of Protestantism ☆ established the Church of England (Anglican) in 1532

Charles V
☆ Holy Roman Emperor and Carlos I of Spain, tried to keep Europe religiously united, inherited Spain, the Netherlands, Southern Italy, Austria, and much of the Holy Roman Emperor from his grandparents, he sought to stop Protestantism and increase the power of Catholicism ☆ allied with the pope to stamp out heresy and maintain religious unity in Europe
Philip II
☆ King of Spain from 1556 to 1598 ☆ Absolute monarch who helped lead the Counter Reformation by persecuting Protestants in his holdings ☆ sent the Spanish Armada against England.
Spanish Armada
☆ "Invincible" group of ships sent by King Philip II of Spain to invade England in 1588 ☆ Armada was defeated by smaller, more maneuverable English "sea dogs" in the Channel ☆ marked the beginning of English naval dominance and fall of Spanish dominance
Edict of Nantes
document that granted religious freedom to the Huguenots
Peace of Westphalia
the peace treaty that ended the Thirty Years' War in 1648
Council of Trent
A meeting of Roman Catholic leaders, called by Pope Paul III to rule on doctrines criticized by the Protestant reformers.
shariah
Islamic law
Anne Boleyn
the second wife of Henry VIII and mother of Elizabeth I
1440
Gutenberg printing press
1453
Ottoman take Constantinople
1492
Columbus sails the ocean
1300-1600
the renissance
1517
Protestant reformation
examples of legitimizing rule through architecture
forbidden city (ming and Qing), Inca sun temple of Cuzco, Taj Mahal, versailles, suleymaniye mosque (ottoman)
ming eunuch officials
high-ranking civil servants that were castrated so they were not tempted to start another dynasty
vizier
a high official in the ottoman government
1644
ming dynasty fell to Manchu invaders that started the Qing dynasty (the ming were weak due to internal struggles of taxes and rebellion)
classical period art (500 BCE - 500)
☆ leaders, gods and goddesses ☆ idealized sculpture, active, faces without emotion ☆ little background or sense of perspective ☆ heroic figures and people living daily life
medival period art (500-1400 CE)
☆ to teach religion to people that couldn't read ☆ flat, stiff, 2D ☆ important figures were large and fully clothed ☆ solemn faces
renaissance art (1400-1650 CE)
☆ shows the importance of people and nature ☆ idealized, active ☆ expressive faces ☆ full, deep backgrounds ☆ symmetrical
vivtruvian man
by Leonardo da Vinci in about 1490, shows the ideal human proportions with geometry