density and water masses
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
Density equation
mass/vol
density is a function of T,S,P
p (rho)= 1000kg/m3 for pure water, 1027 kg/m3 for avg ocean water
sigma= p-1000 => 27 kg/m3 for avg SW
Linear equation of state
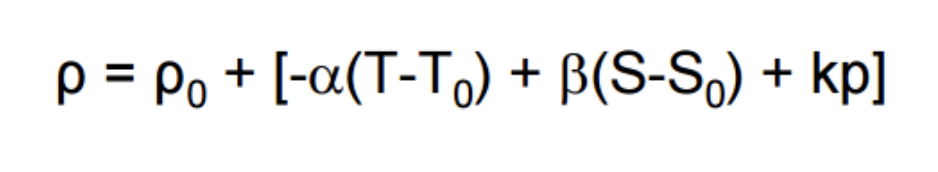
average values & expansion coefficients
P0= 1027 kg/m3, T0=10C, S=35%
Thermal expansion: a=0.15 kg/(m3C)
salinity contraction: B= 0.78 kg/(m3db)
When can we use a linear EOS?
if t,s,p have small variation
simple process studies
Effects of T and S on density
T range= 0-25C
S range= 34-36
density isopycnals
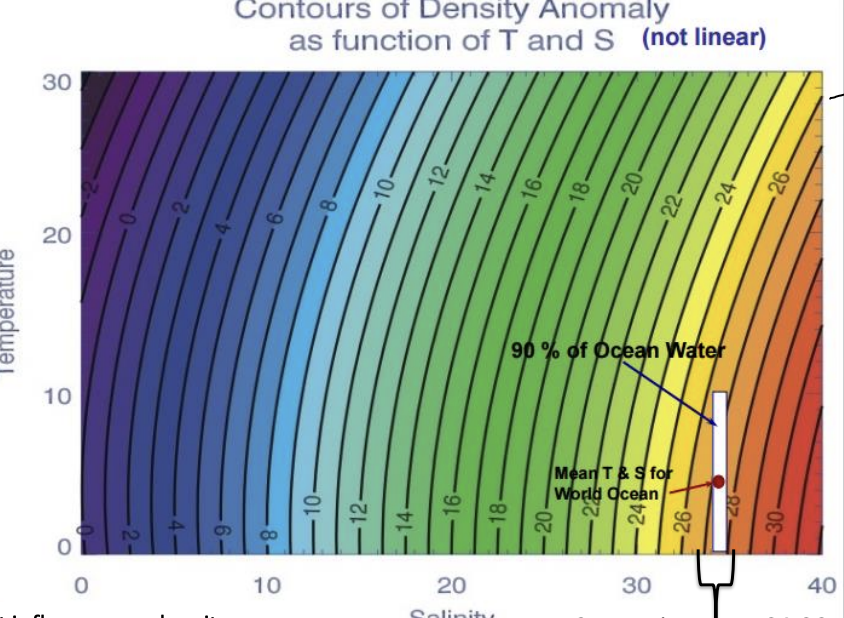
idealized density profile
Stable- less dense water atop more dense water
stratified- layered water column
hard to mix a water column if there are strongly stratified layers
easier to mix along isopycnals
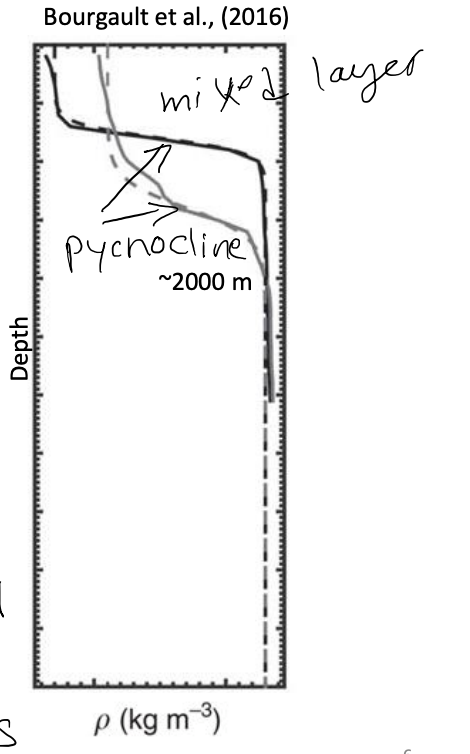
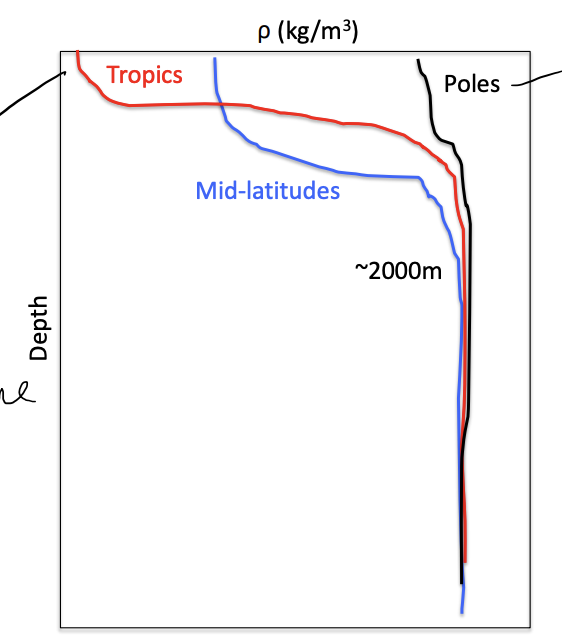
Latitudinal variability in density profiles
lowest density in tropics but connects to deep water via pycnocline
poles- little change between surface and deep
potential density
density usually calculated for a given pressure
SigmaT= P(T,S,0m)
density calculated with in situ T and S, but pressure at the surface
not really relevant so not used
Sigmatheta= potential T
Theta= density anomaly
what it would be if water mass brought to the surface
Adjusting for the impact of compressibility on volume, and pressure on temp
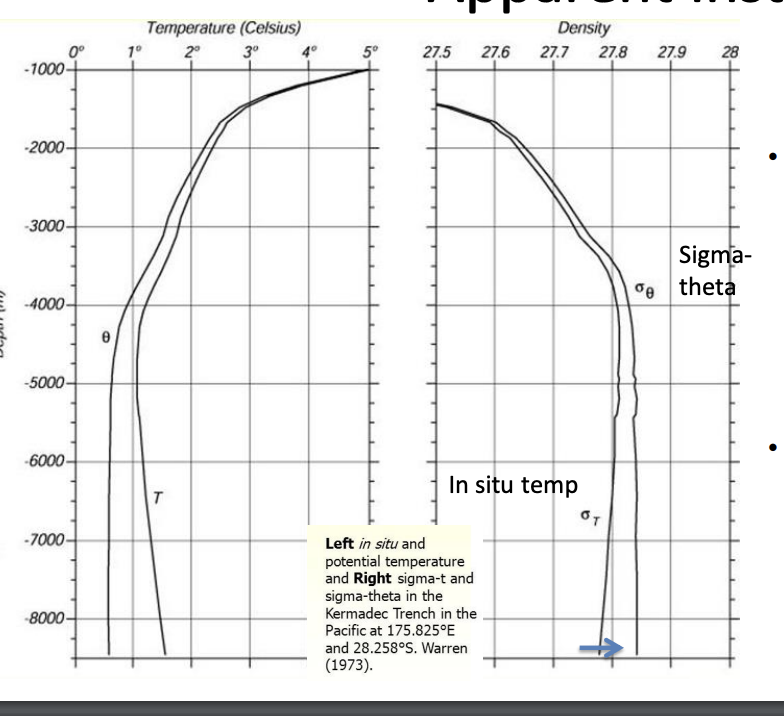
Apparent instability
potential temp
pressure increase cause T increase
does not represent change in heat content
allows comparison of T of water at one pressure with water at another pressure
identify water masses
potential density :S, 0, P=0
pressure increases cause volume decrease
Potential density all 3

T vs S theta
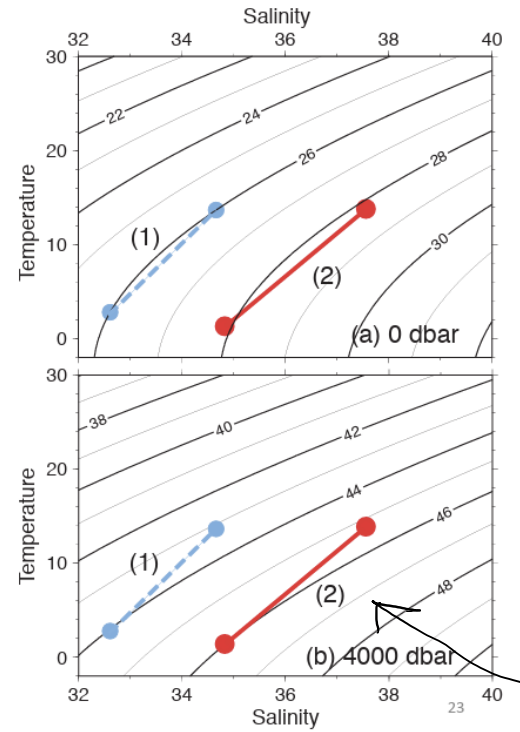
Blue- 2 parcels that are same density
warmer parcel is less dense at theta4
red- colder parcel is less dense, warmer parcel is more dense
b/c colder water more compressible, we find that parcel becomes more dense
Apparent Instability
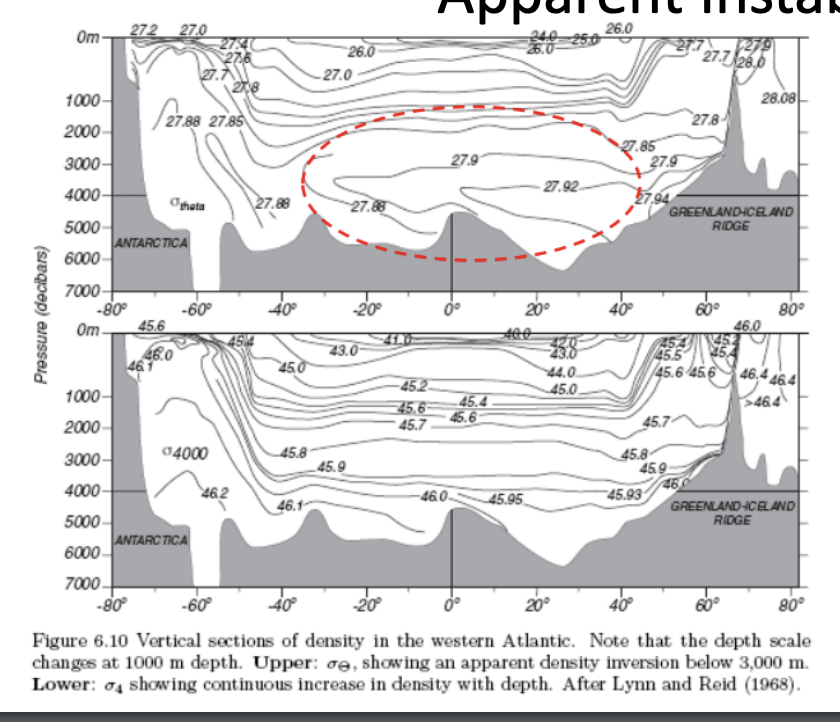
referenced to surface
good for identifying water mass
select a reference depth within 500m
when working in top 500m, reference depth is surface
when working within 500-1500m, reference pressure is 1000 dbar
Conservative water properties
changed by?
physical processes only
examples
T+S
major constituents
importance: can be used to identify water masses
non-conservative water properties
changed by?
changed by biological processes
examples: DO, nutrients
importance: can be used to determine age of water mass
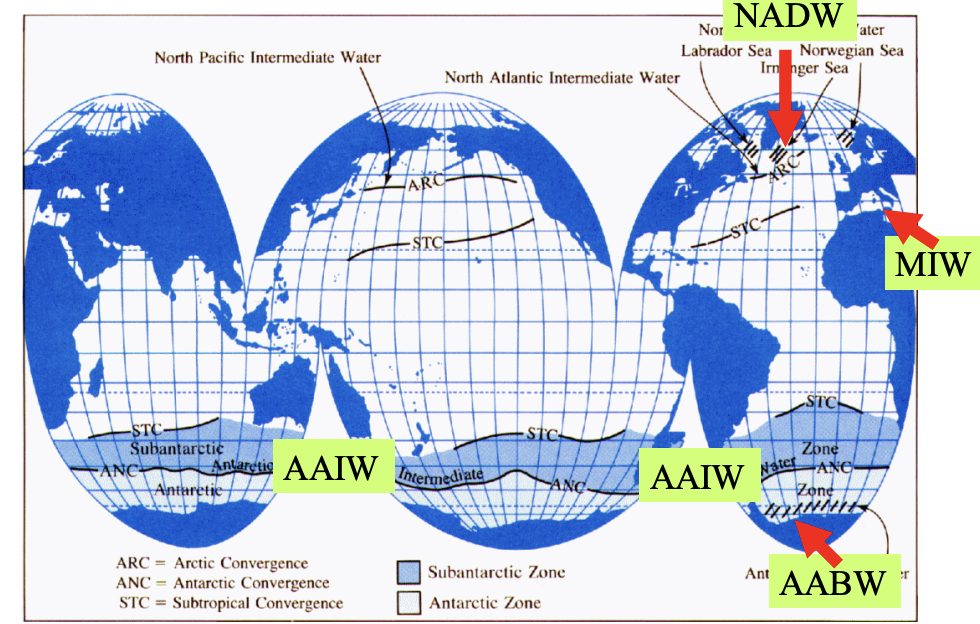
Water masses: Atlantic ocean
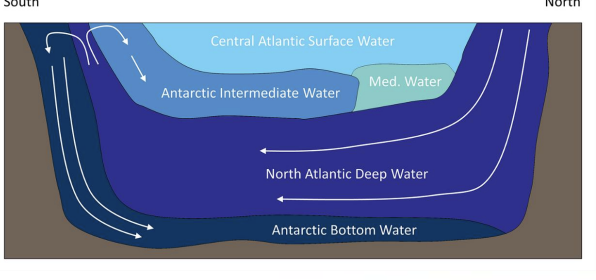
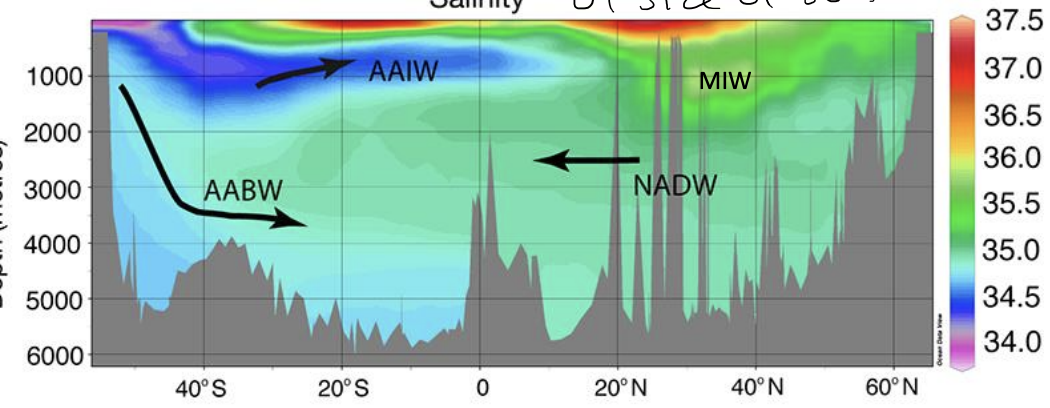
get signature T, S at surface
density controls depth of sinking
thickness+ horizontal extent of each layer is a function of size of the surface source + rate of formation
NADW
formed from salty GS water that cools and sinks
2-4 C
S= 34.9-35
2000-4000m
AAIW
forms in roaring 40s in S atlantic
sinks at convergent front
3-4C
S= 34.2-34.3
300-2000m
high Si signature
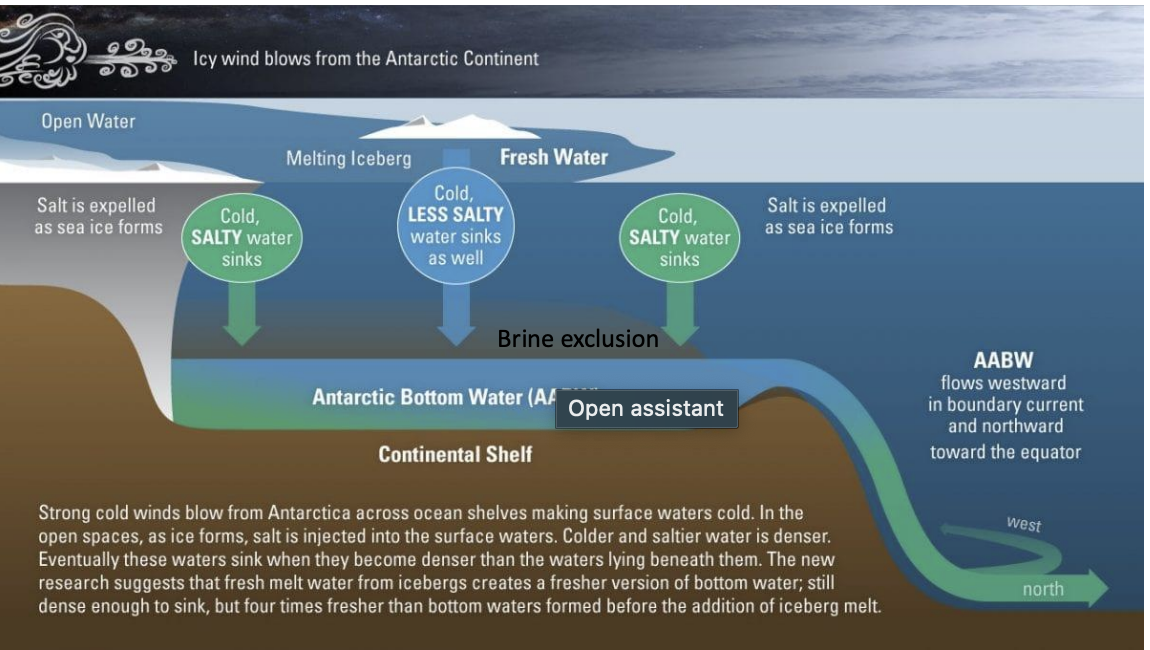
AABW
forms mostly in Atlantic sector of S. Ocean
-05.-1C
S=34.6-34.7
densest water
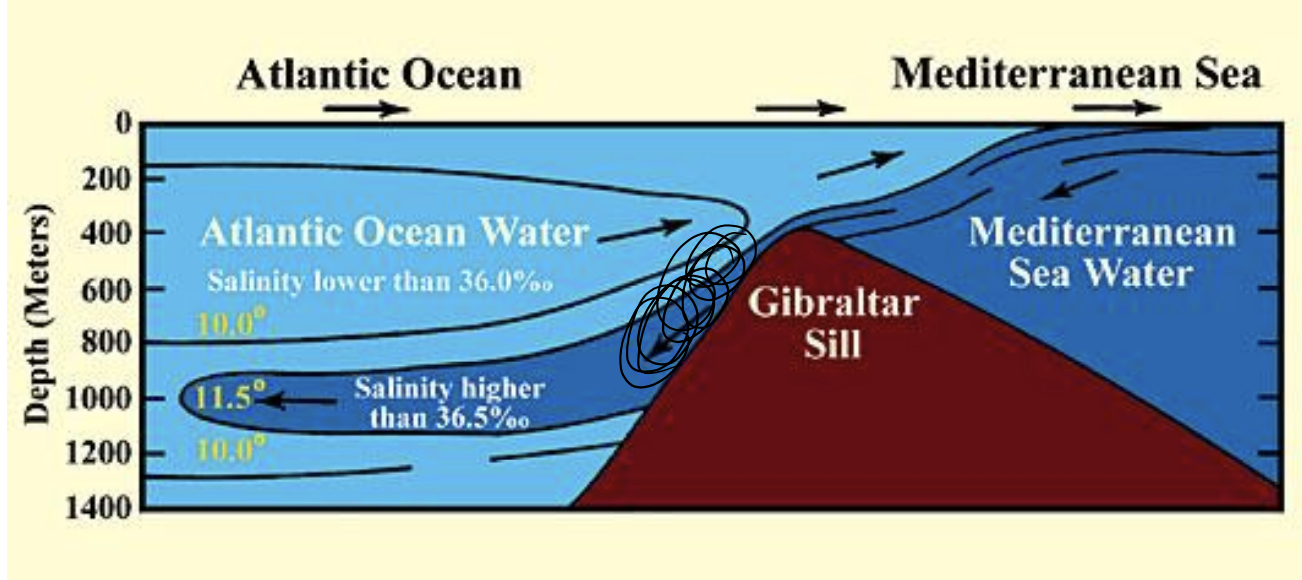
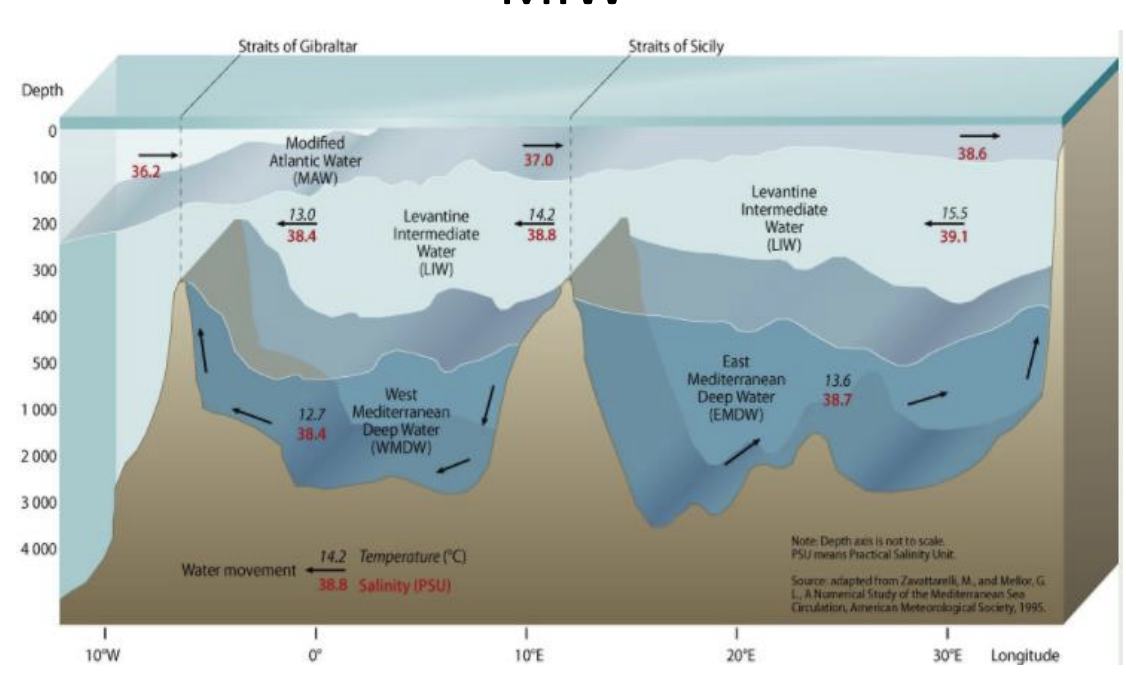
MIW
13C
S= 38.45
warm, salty
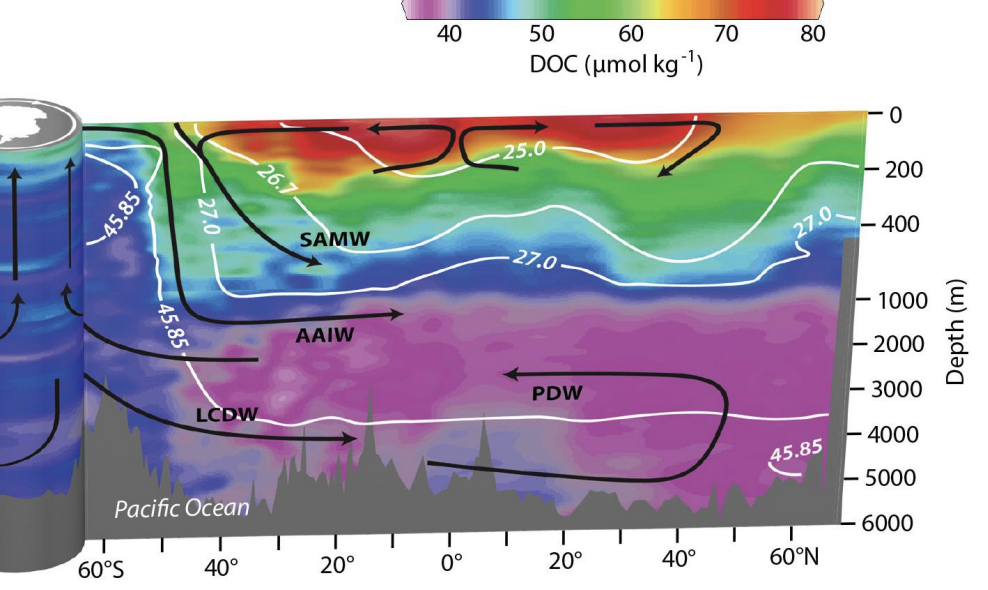
Pacific ocean water masses
no deep water forming in N pacific
Deep water formation areas