Sleep
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Normal sleep
__ is defined as the cyclic temporary and physiologic loss of consciousness that is readily, promptly, and completely reversed with appropriate stimuli
Rule of three
3 weeks w/out food
3 days w/o water
3 hours in extreme environments
3 minutes w/o oxygen
Fatigue reasons
• Chronotype: are you an early bird or night owl?
If your a night owl and don't fall asleep early enough to get your 7-8 hours of restful sleep, your fighting your natural circadian rhythm.
• Fragmented sleep/ snooze alarm
• Bedroom environment/ blue light
• Spouse behavior
• Alcohol / caffeine
STOP-BANG questionnaire
S = Snoring
T= Tiredness
O = Observed apnea
P = Pressure (HTN)
B = BMI (>35)
A = Age (>50yo)
N = Neck circumf (>40cm)
G = Male gender
Snore
(S) have you been told that you
Tired
(T) are you often __ during the dya
Observed
(O) Has anyone ___ you stop breathing while sleeping
Pressure
(P) do you have or are you being treated for high blood pressure
BMI
(B) is your __ more than 35 kg/m2
Age
(A) is your __ 50 or older
Neck
(N) is your __ circumference greater than 17" if male or 16" if female
Gender
(G) is your __ male
One
Each positive score is __ point in stop bang
0-2
low risk for obstructive sleep apnea
3-4
intermediate risk for obstructive sleep apnea
5-8
high risk for obstructive sleep apnea
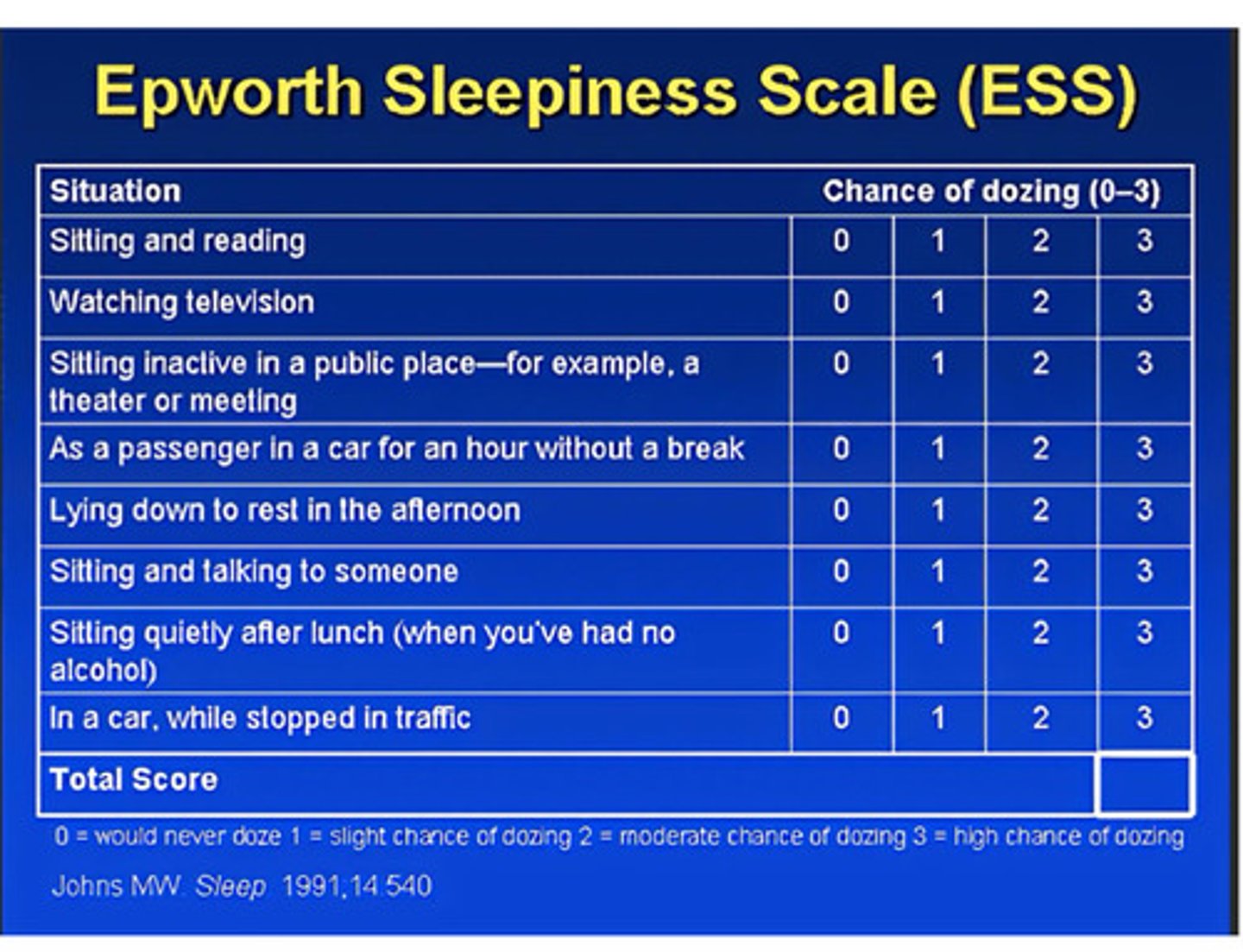
Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS)
An index of sleepiness during the day as perceived by patients, derived from the answers to 8 questions
sleep study
Only a __ interpreted by a medical sleep
specialist in conjunction with a medical exam can rule in or out benign snoring
Polysomnogram
__ (sleep study) may be hospital
based or take home models are becoming
increasingly popular
C-PAP
Highly effective, low compliance treatment
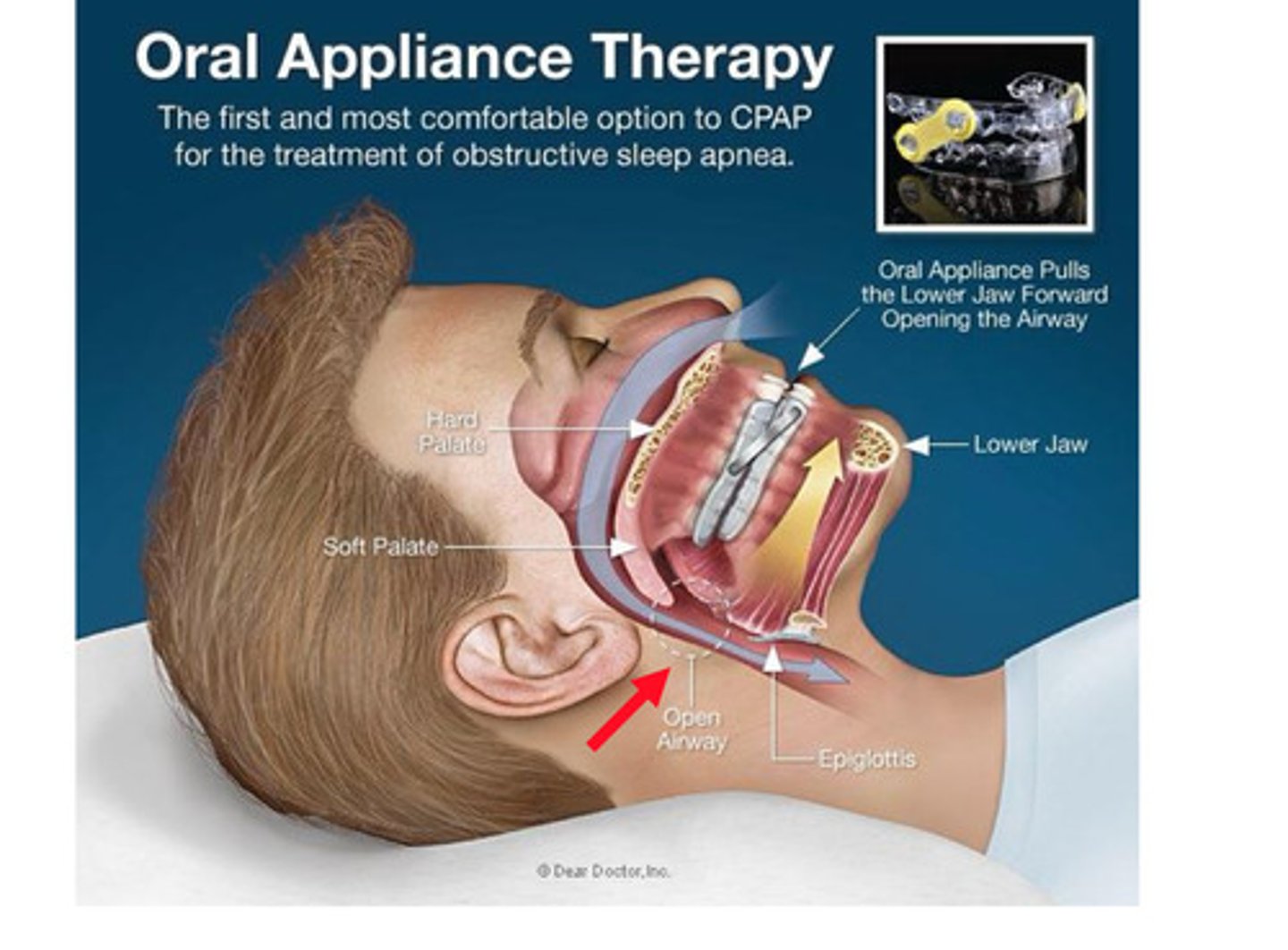
MAD
Slightly lower effect, high compliance treatment
Mandibular Advancement Device
This custom made oral device is indicated for sleep apnea if CPAP cannot be used. Brings mandible forward to open airway
2 am
Deepest soee0
4:30 am
Lowest body temp
6:45 am
sharpest blood pressure rise
7:30
Melatonin secretion stops
2:30
Best coordination
Suprachiasmatic nucleus
__ regulates the Circadian Rhythm
hr circadian rhythm
Your 24 /__ is one of two factors determining wake and
asleep
adenosine
Second is sleep pressure due to a buildup of __ which turns down the effect of wake promoting regions of the brain
Caffeine
the most widely used psychoactive stimulant in the world blocks
the adenosine effect
Orexin
A neurotransmitter associated with narcolepsy

Adenosine

Sleep cycle
a period of sleep lasting about 90 minutes and including one or more stages of NREM sleep, followed by REM sleep
sleep cycle stage 1
interim between consciousness and sleep
5-15 mins
How long between stage 1-2
Sleep cycle stage 2
Heart rate slows, brain does less complicated tasks (non rem)
15 mins
How long between stage 2-3 (non rem-delta)
Sleep cycle stage 3
Body makes repairs (delta stage)
Sleep cycle stage 4
Body temperature and blood pressure decreases
90 minutes
How much time between first feeling sleepy to rem
Sleep cycle stage 5
REM, paradoxical sleep, but voluntary muscles are paralyzed, dreaming occurs, triggered by the pons, 15-30 minutes, visual cortex and limbic system are active
4-6
how many sleep cycles per night
Sleep disturbed breathing snoring
Upper airway resistance also related to GERD- vacuum created (can turn into obstructive sleep apnea)
Apnea
breathing cessation with decreased air flow of 70% or greater for 10 seconds or more
Hypopnea
reduced breathing by
30% or more lasting 10 sec or
more with O2 desaturation of 4%
or greater
Apnea hyponea index (AHI) is calculated by
Number of Apneas plus
Hypopneas per hour defines the
5-15
Moderate AHI index
15-30
Severe AHI index
Insomnia
recurring problems in falling or staying asleep
- treatment but no cure (sedatives, antihistamines, antidepressant)
Benefits of sleep

fatigue
One person dies every hour in a traffic accident due to __, greater than deaths from alcohol and drugs combined.
dementia
Longer naps during the day could be a sign of early
__
Alzheimers
Older adults that napped at least once for over an hour
had a 40% higher chance of developing __
disease than those that did not nap or napped for less
than 1 hour per day
Depression; Melatonin
__ can cause a decrease in Seratonin which helps with moods, thinking. Seratonin is a precursor to __, the neurotransmitter that promotes sleep
Dementia tests
The sage test
Mini cog test
Mini mental test
Montreal cognitive assessment
inflammatory
Sleep supports normal production of stem cells which are the building blocks of the immune system. Good sleep reduces the body's __ burden
Obesity
A major cause of OSA
Ghrelin
hormone secreted by empty stomach; sends "I'm hungry" signals to the brain
Leptin
A hormone produced by adipose (fat) cells that acts as a satiety factor in regulating appetite.
ghrelin
Sleep deprivation increases __, increases appetite,
especially carbohydrates
bulimia nervosa
an eating disorder characterized by episodes of overeating, usually of high-calorie foods, followed by vomiting, laxative use, fasting, or excessive exercise
anorexia nervosa
an eating disorder in which an irrational fear of weight gain leads people to starve themselves
Telomeres
dna at tips of chromosomes which is difficult to replicate, protect and worsen with lack of sleep
testosterone
In men, decreased sleep results in
decreased __ levels and
ages a man 10-15 /yrs
Type two Diabetes
Decreased sleep results in increased
eating (ghrelin). Body can not handle increased sugar
in the blood with an increased
probability of developing
Ozempic
semaglutide (Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 (GLP-1) agonist; antidiabetic)