A&P 1 Lab Practical 2
1/163
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
164 Terms
The interior of the cell becomes less negative due to an influx of sodium ions.
Depolarization
The specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in membrane permeability.
Repolarization
Immediately after an action potential has peaked, which of the following channels will open?
Voltage-gated potassium channels
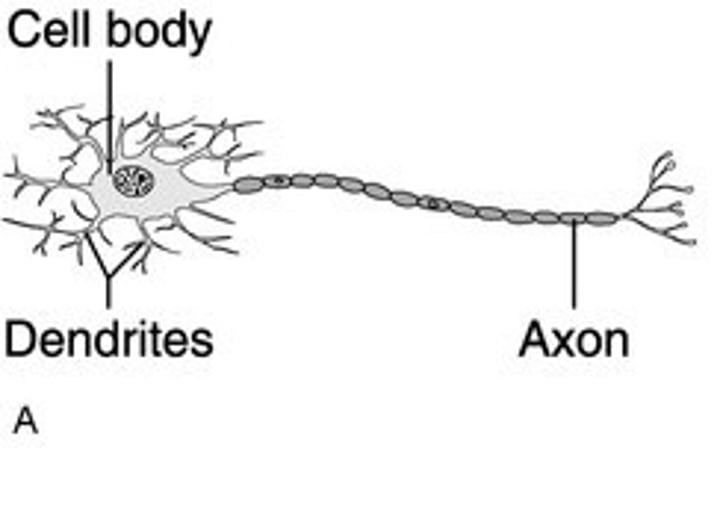
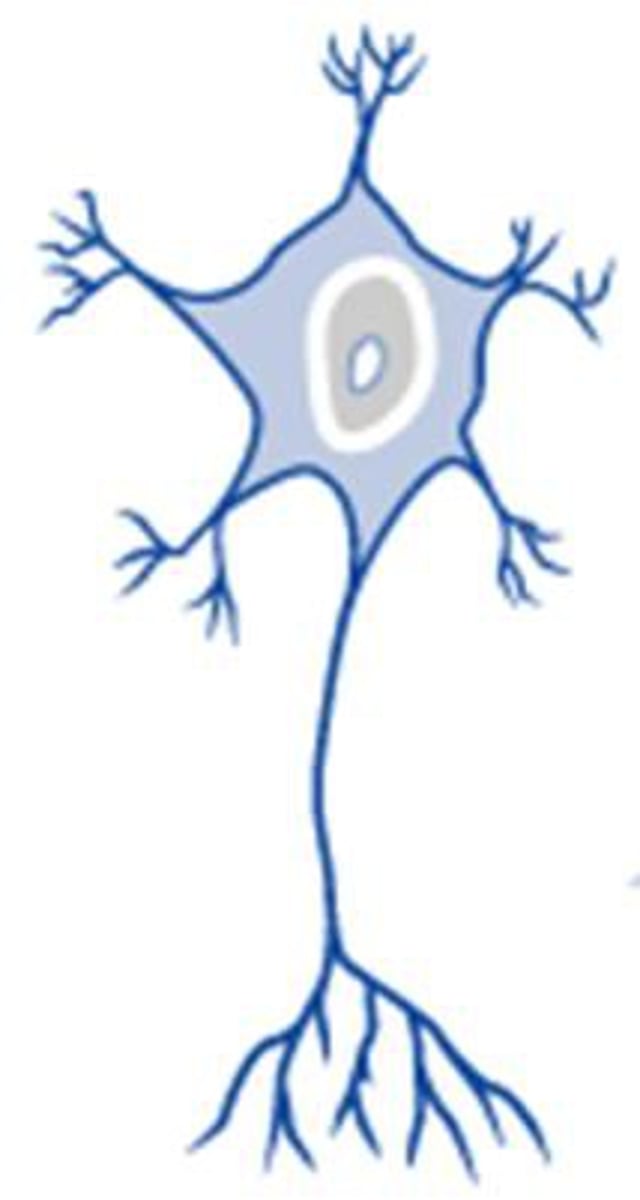
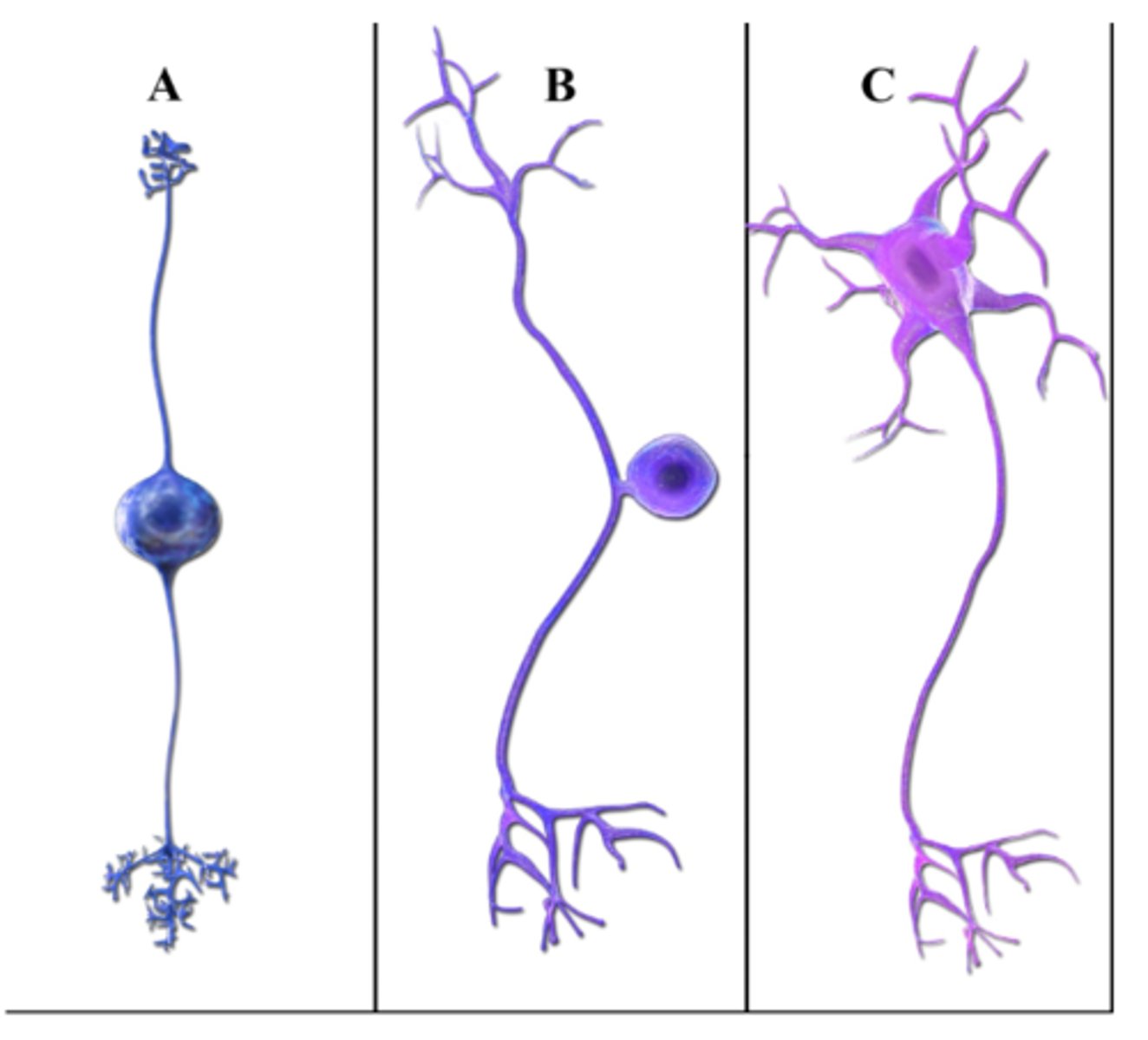
Which is by far the most common neuron type?
multipolar
Which neuron would be found in the retina of the eye?
Bipolar
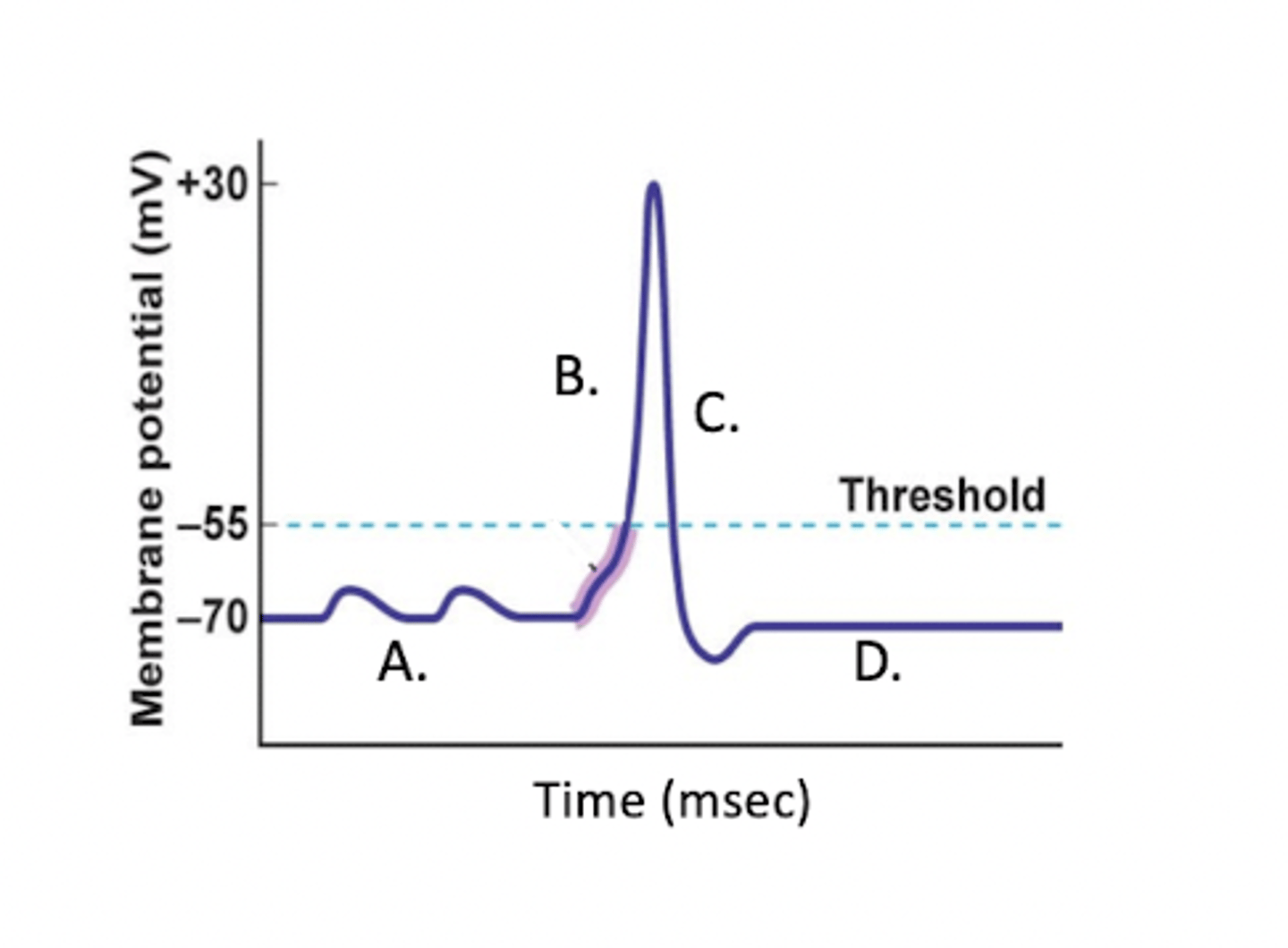
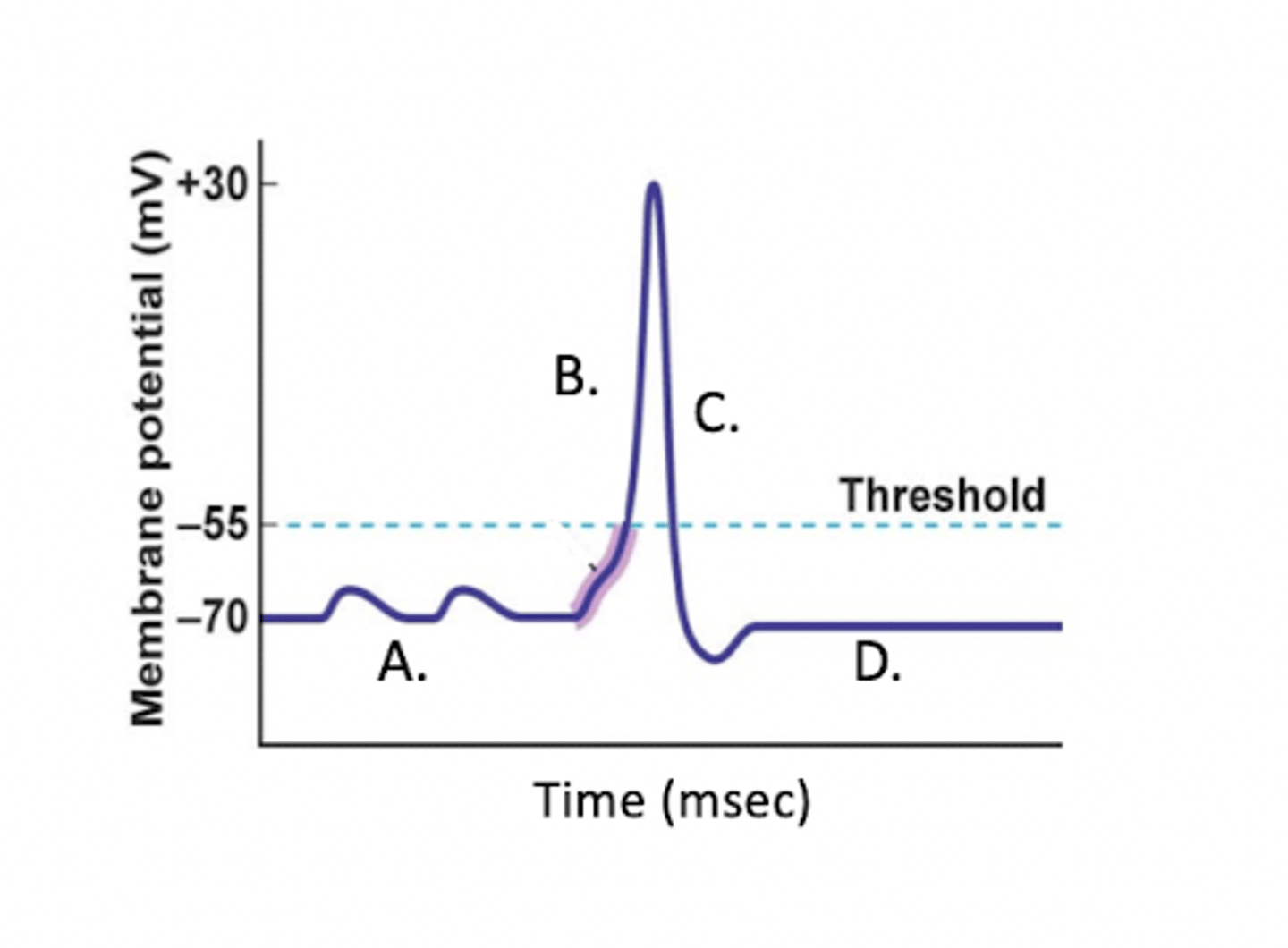
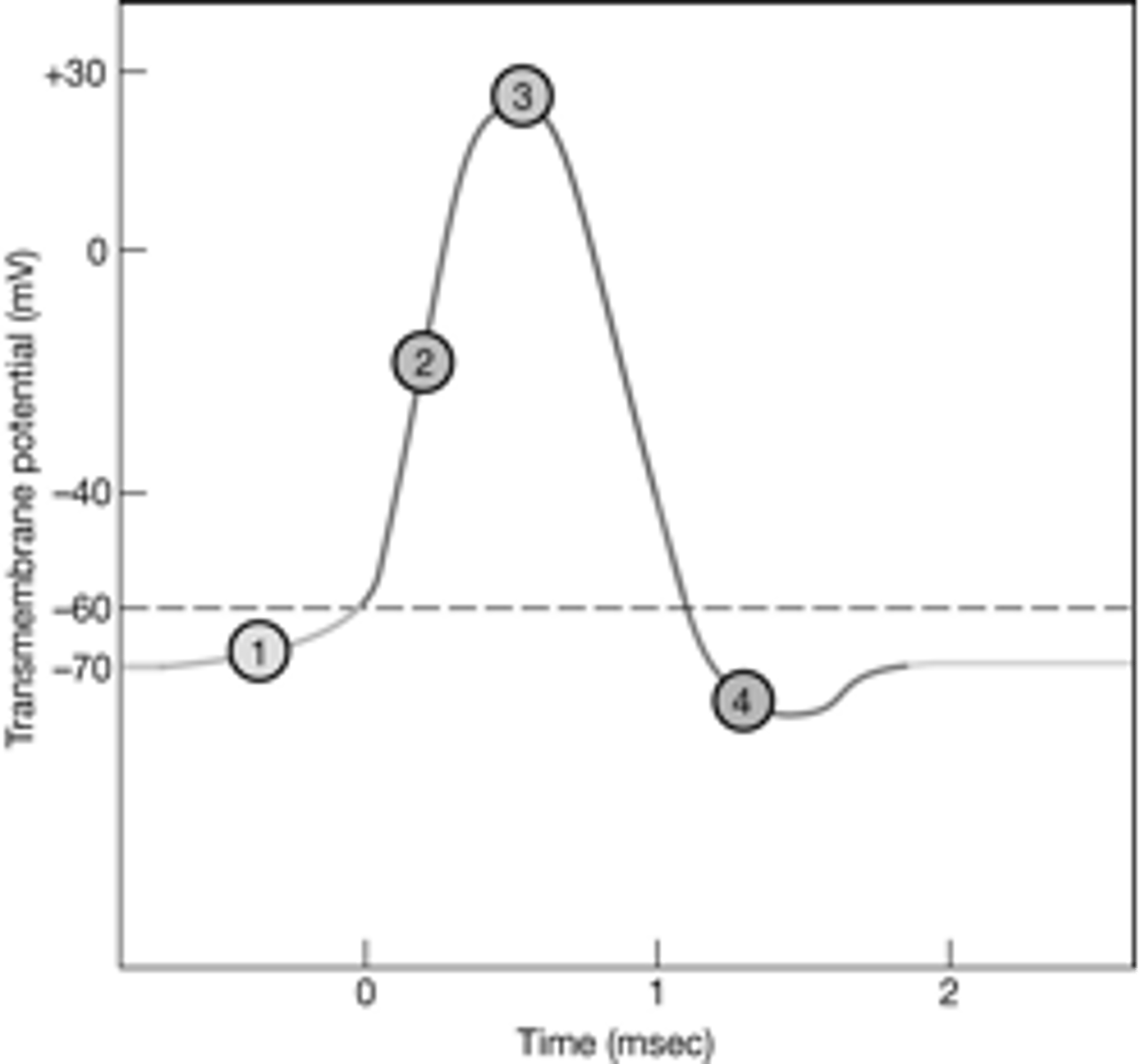
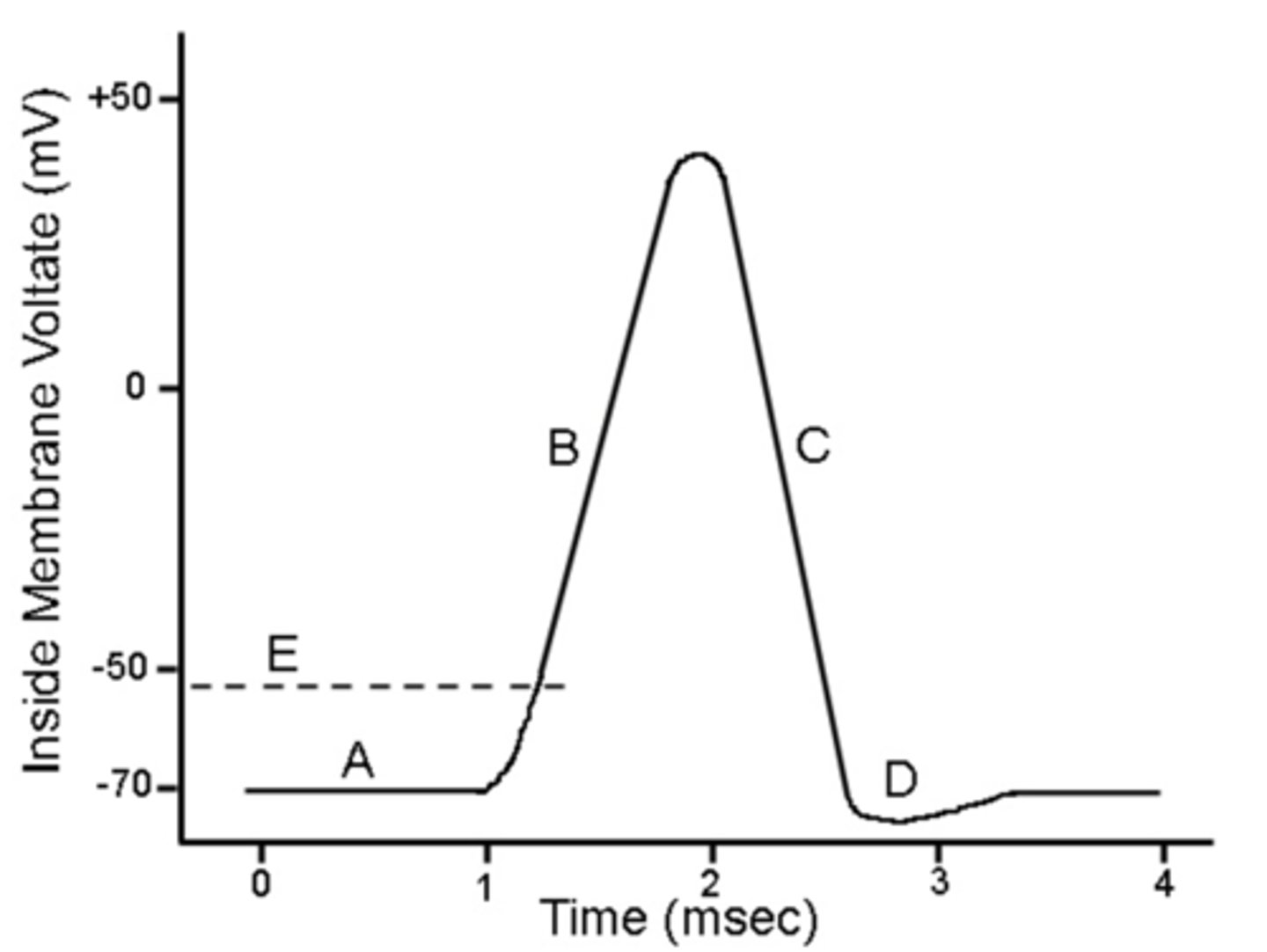
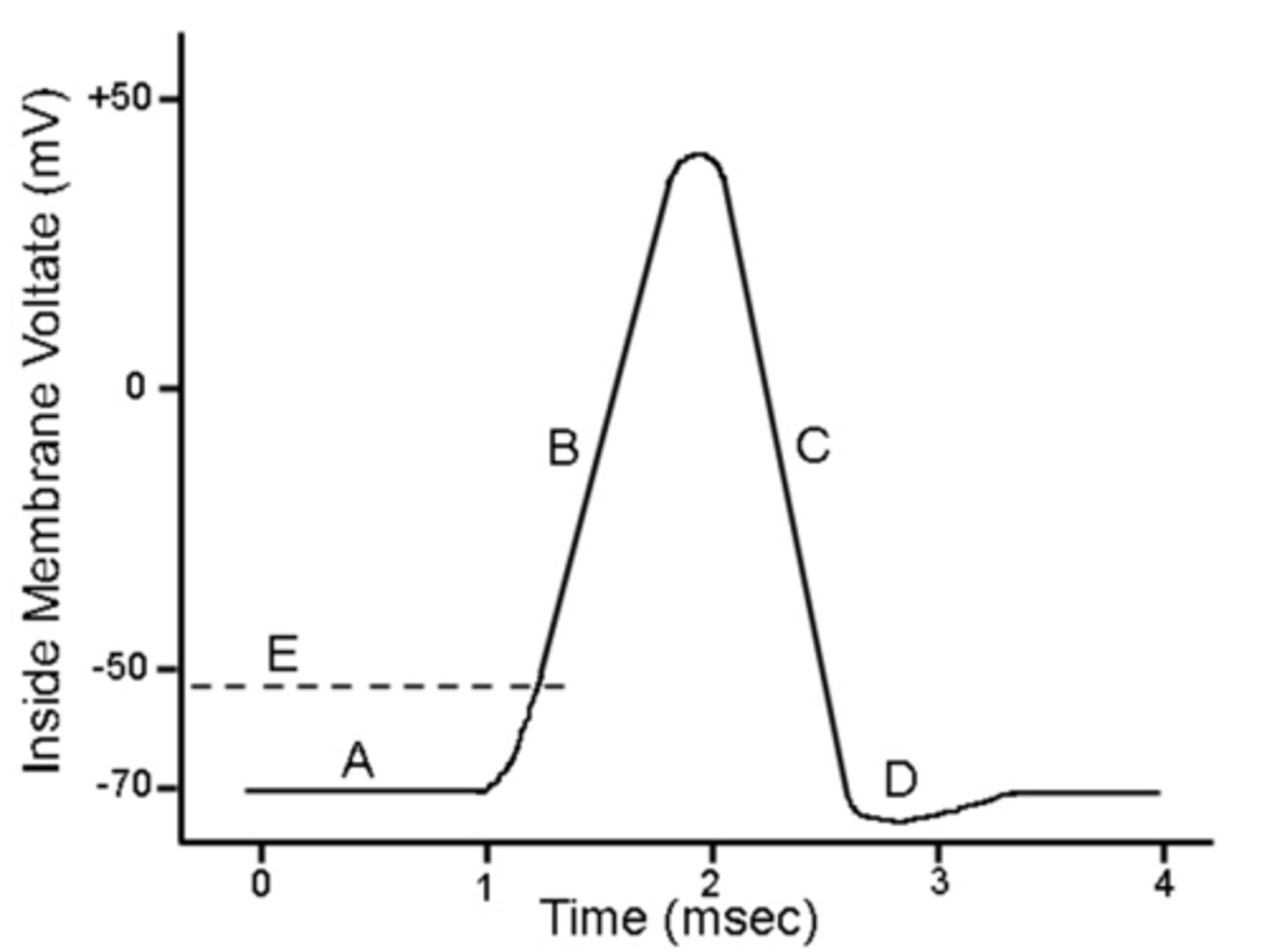
At which stage is the Na+ channel open?
B (hyperpolarization)
Involved in activating fibers of a skeletal muscle such as the biceps muscle.
Diverging circuit
Maybe involved in complex, enacting types of mental processing
Parallel after-discharging circuit
some K+ channels remain open and Na+ channels reset
Hyperpolarization
In myelinated axons the voltage-regulated sodium channels are concentrated at the nodes of Ranvier.
True
At which stage is the voltage approaching +30mV?
B (hyperpolarization)
Which synapse will have the largest impact?
Axoaxonal
Which neurotransmitter is blocked by botulinum toxin?
Acetylcholine
At which stage are both sodium and potassium channels closing?
4 (D/Repolarization)
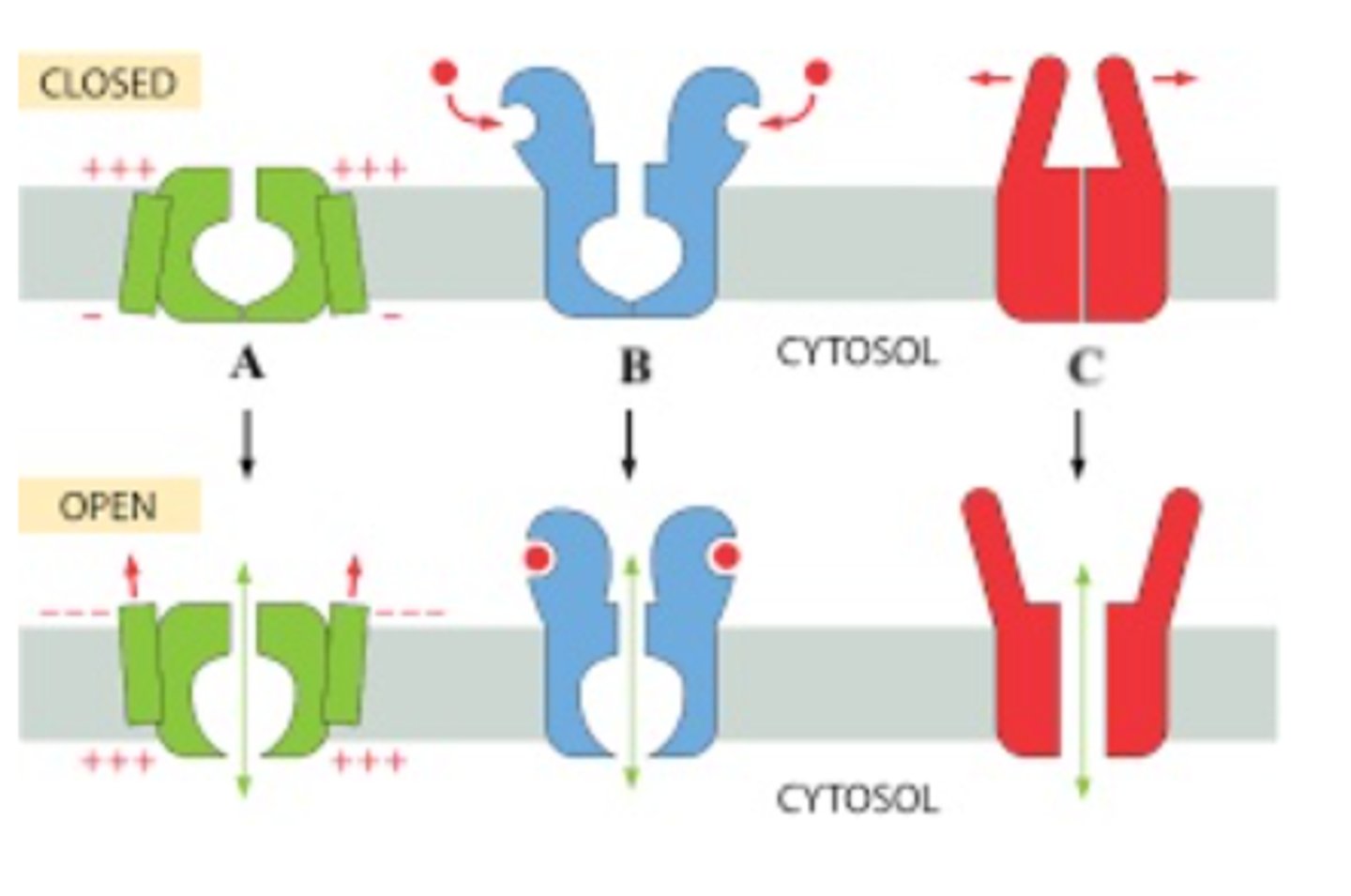
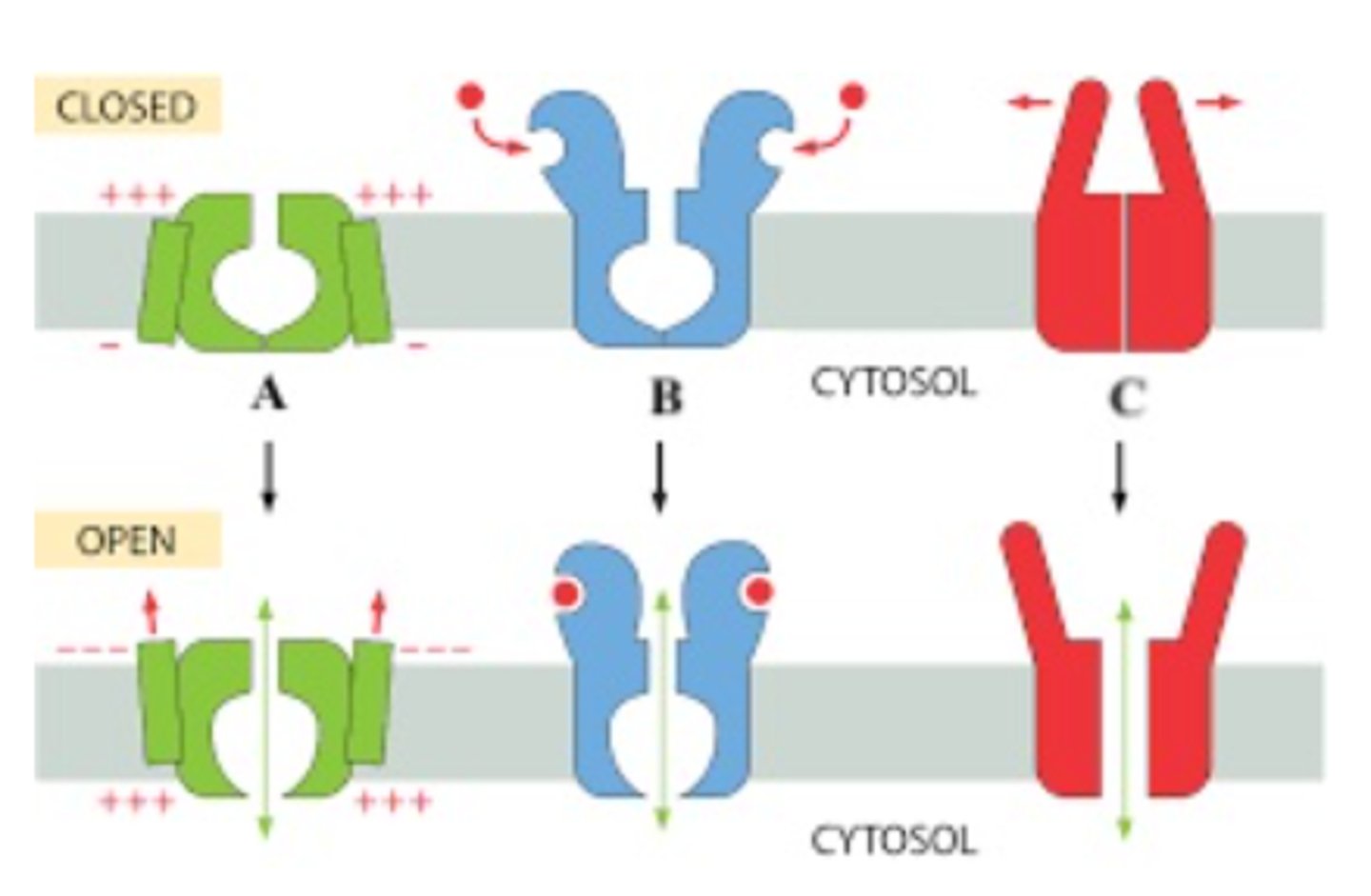
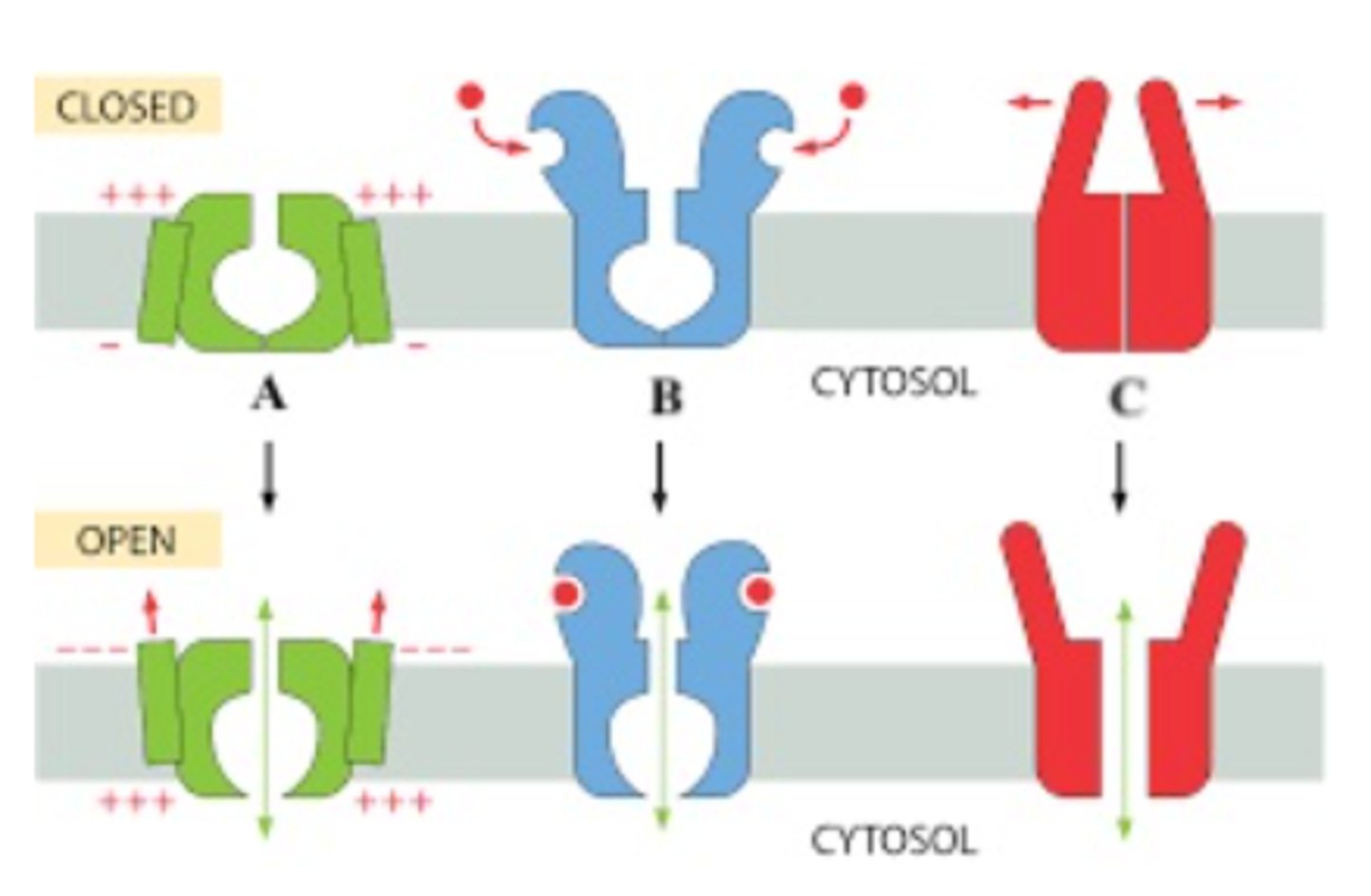
Which is channel is mechanically gated?
C
The term central nervous system refers to the ______.
Brain and spinal cord
Different types of sensory input can have the same ultimate effect.
Converging circuit
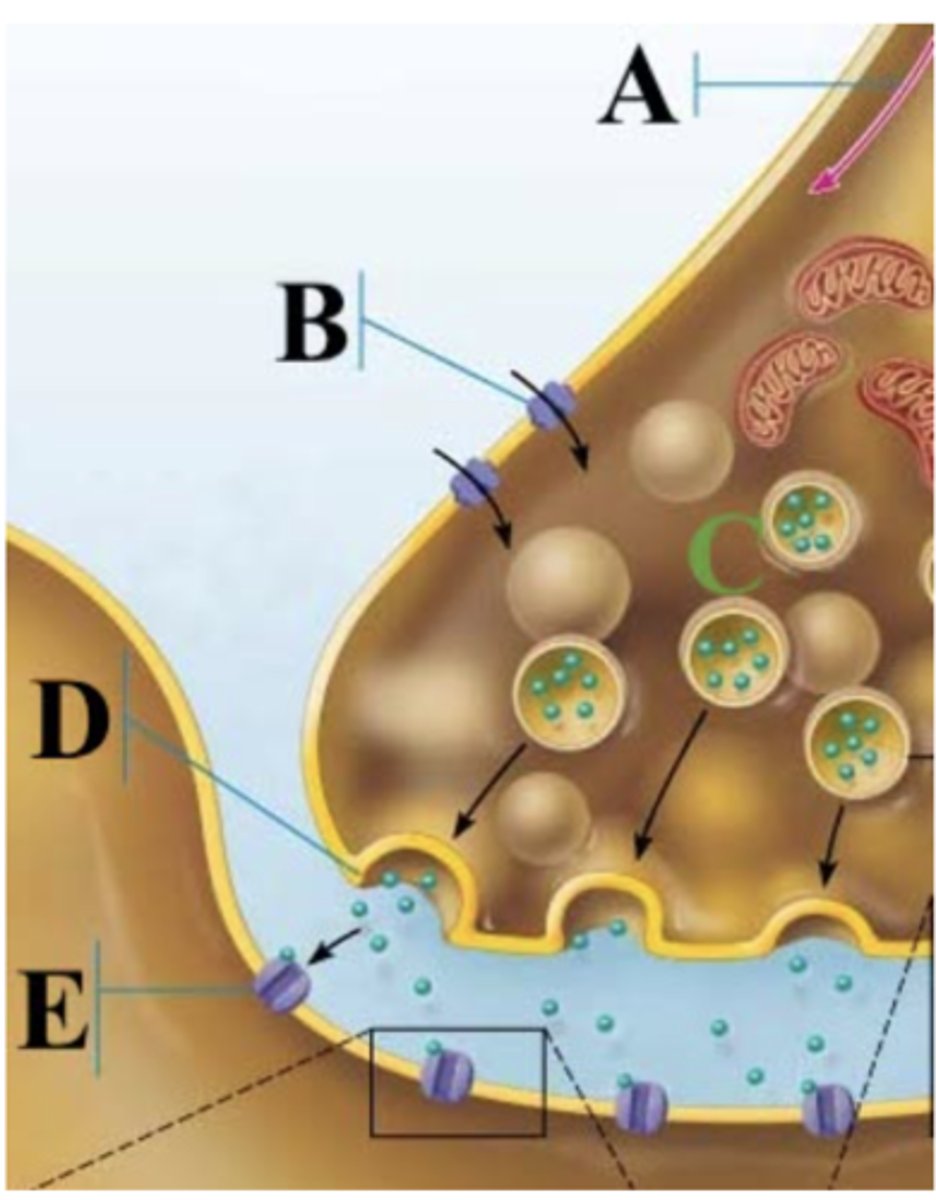
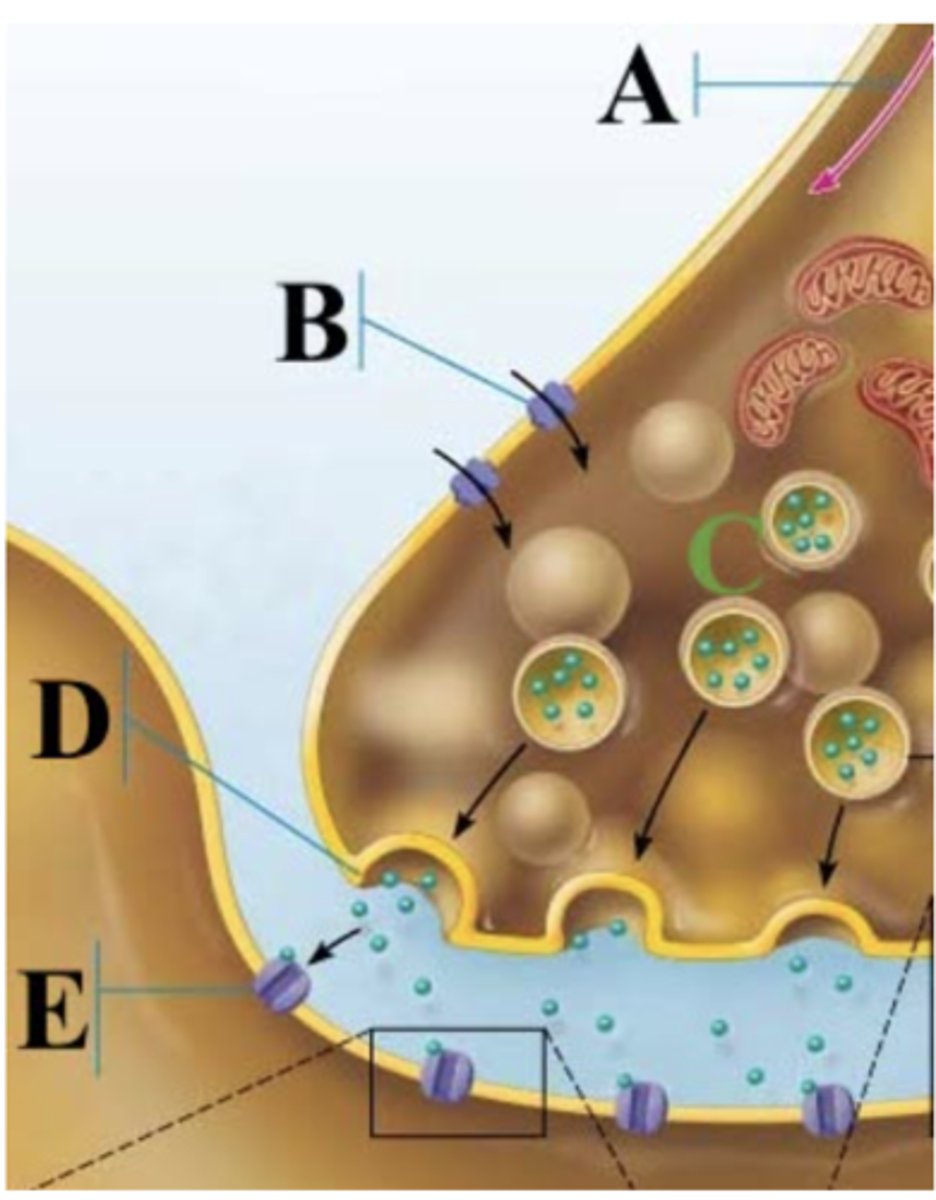
Which part of the image shows a chemically gated ion channel?
E
Which channel is B?
Chemically gated channel
One incoming axon triggers responses in ever-increasing numbers farther and farther along the circuit.
Diverging circuit
Put the typical serial processing of a reflex arc in order from the initial stimulus
1. Receptor detection
2. Sensory neuron firing
3. Interneuron signaling
4. Motor neuron signaling
5. Effector activated
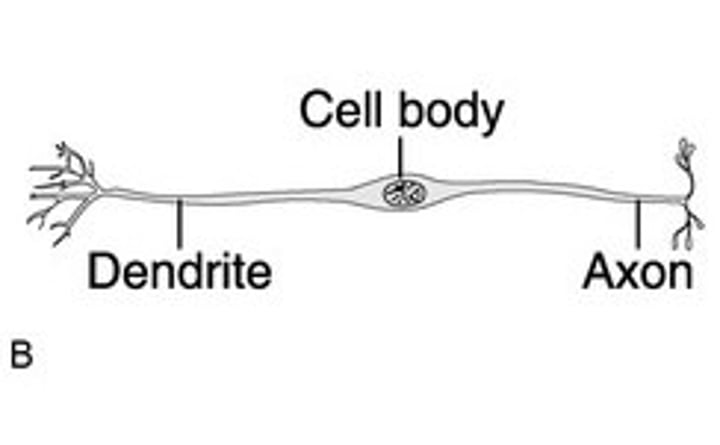
Receives stimuli
Dendrites
Nerve impulses leading to the brain carry information about cool temperatures on the skin. The nerve fibers sending these signals will most likely belong to which division o the nervous system?
Sensory (afferent) divison
The specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in the membrane permeability
Repolarization
Which neuron is multipolar?
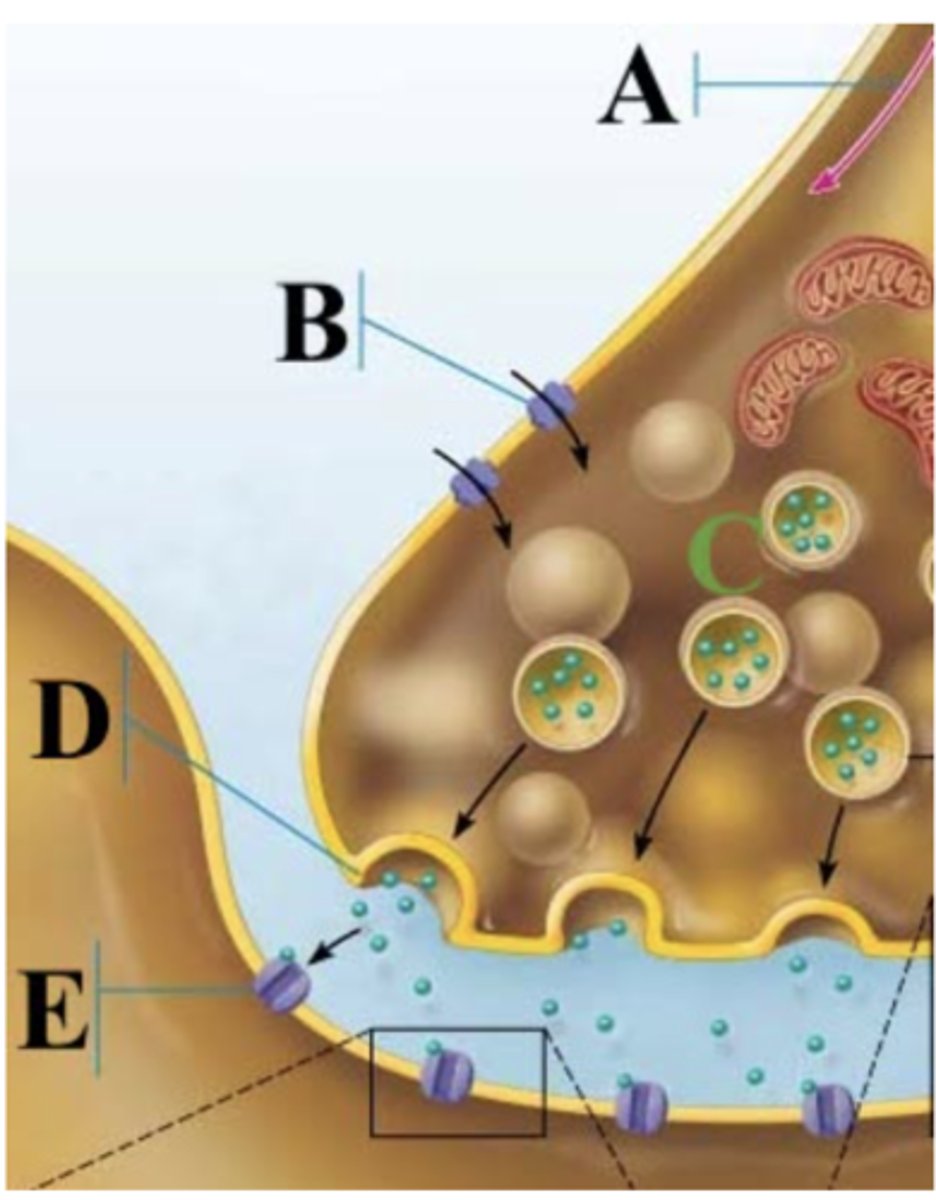
Which part of the image shows calcium ions?
B
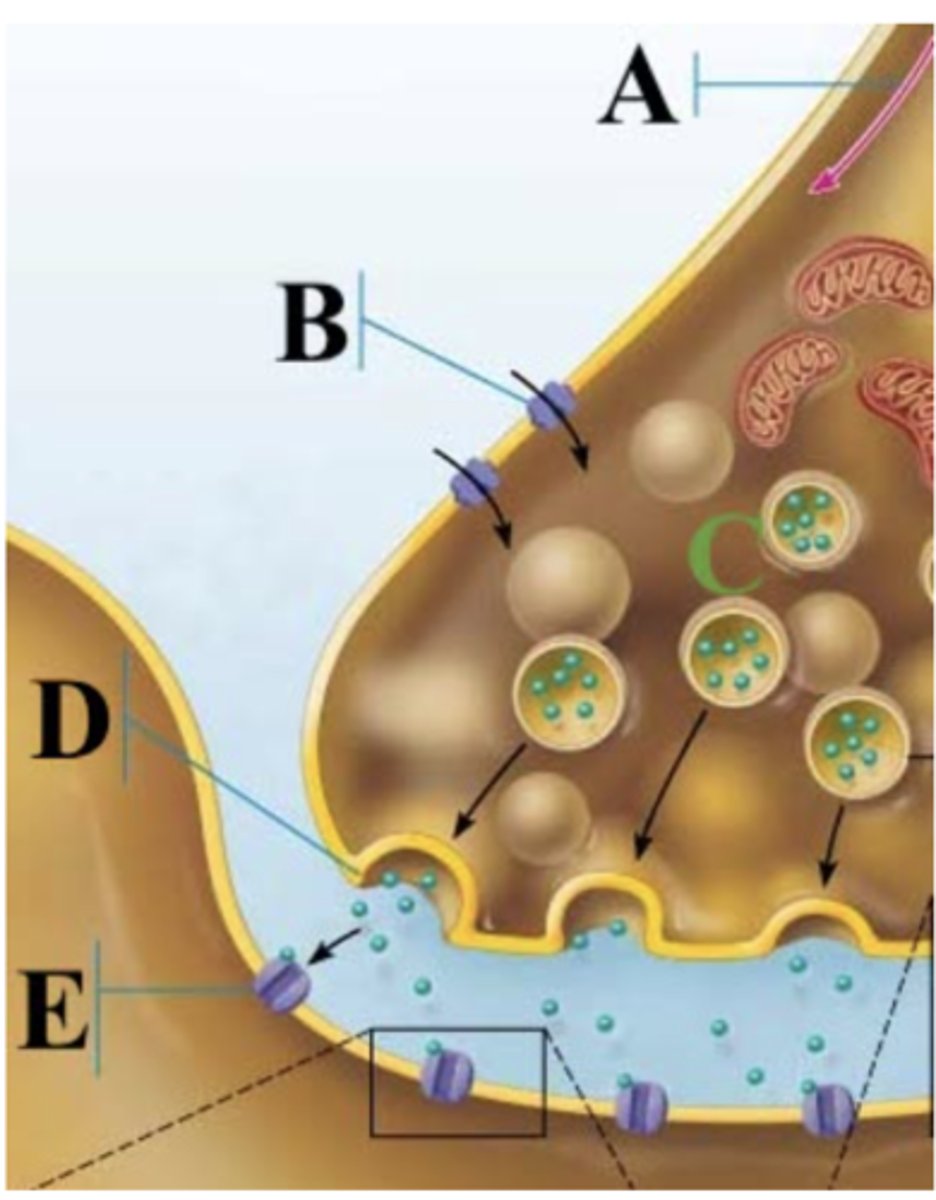
Which part of the image shows a synaptic vesicles?
C
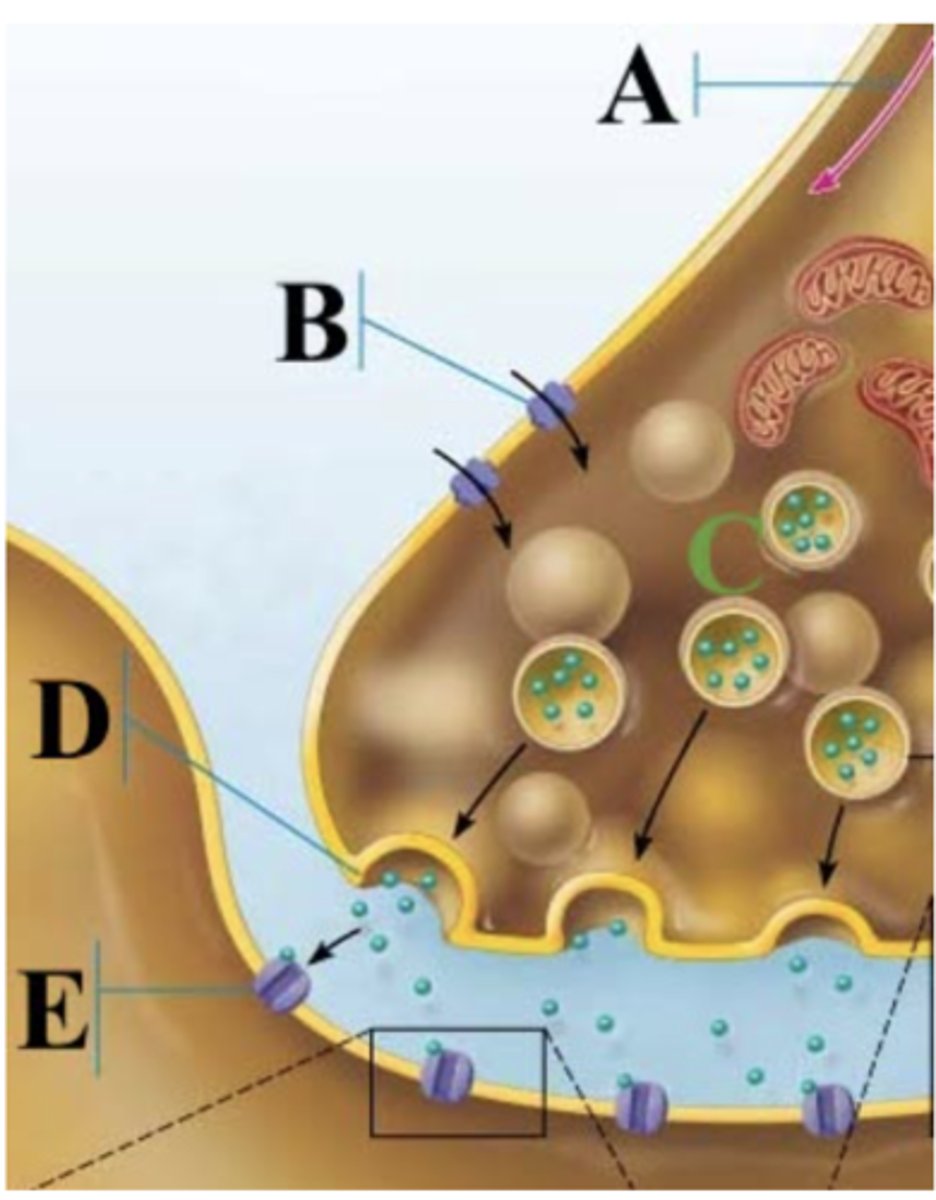
At which stage is the Na+/K+ pump working most to restore membrane potential?
D
Nerve impulses leading to the skeletal muscle carry information to direct movement. The nerve fibers sending these signals will most likely belong to which division of the nervous system?
Somatic nervous system
Which part of the image shows the action potential?
A
At which stage are both sodium and potassium channels closing?
D (repolarization)
Processes all input information
Cell body
Which channel is a?
Voltage gated channel
These cells in the CNS have cilia that move in order to circulate cerebrospinal fluid
Ependymal cells
Which part of the image shows calcium ions?
B
At which stage is the K+ channel open?
C (depolarization)
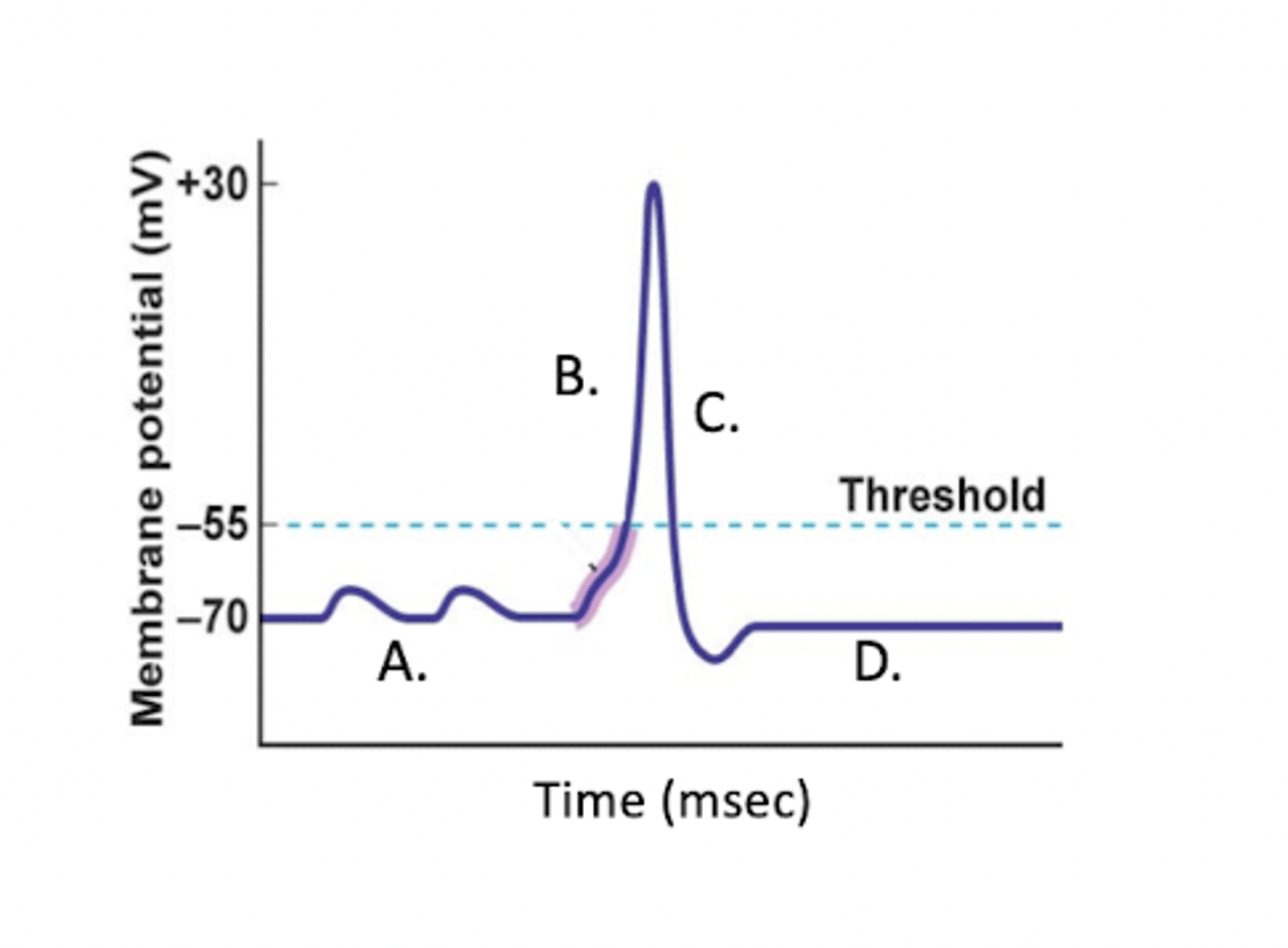
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open
depolarization
When a neurotransmitter like acetylcholine is acting in an excitatory manner which of the following is likely a result of the acetylcholine acting on the post synaptic cell?
Chemically gated sodium channels will open
Area where nerve impulse is generated.
Axon of hillock
Which part of the image shows the presynaptic membrane?
D
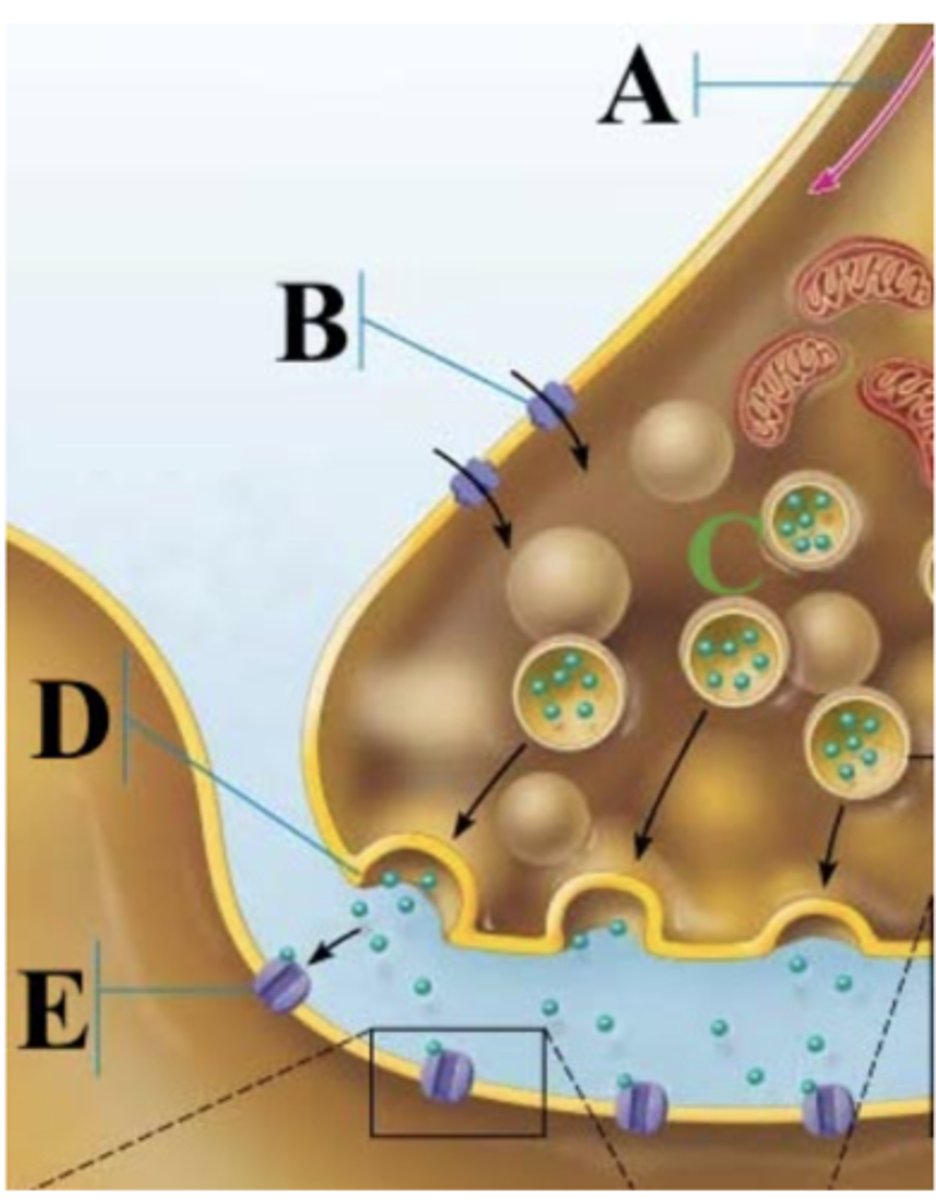
When a neurotransmitter like GABA is acting in an inhibitory manner which of the following is likely a result of the GABA acting on the postsynaptic cell?
Hyperpolarization of the postsynaptic cell membrane
The specific period during which potassium ions diffuse out of the neuron due to a change in membrane permeability
Repolarization
Which neuron is a sensory neuron found in a reflex arc?
unipolar (B)
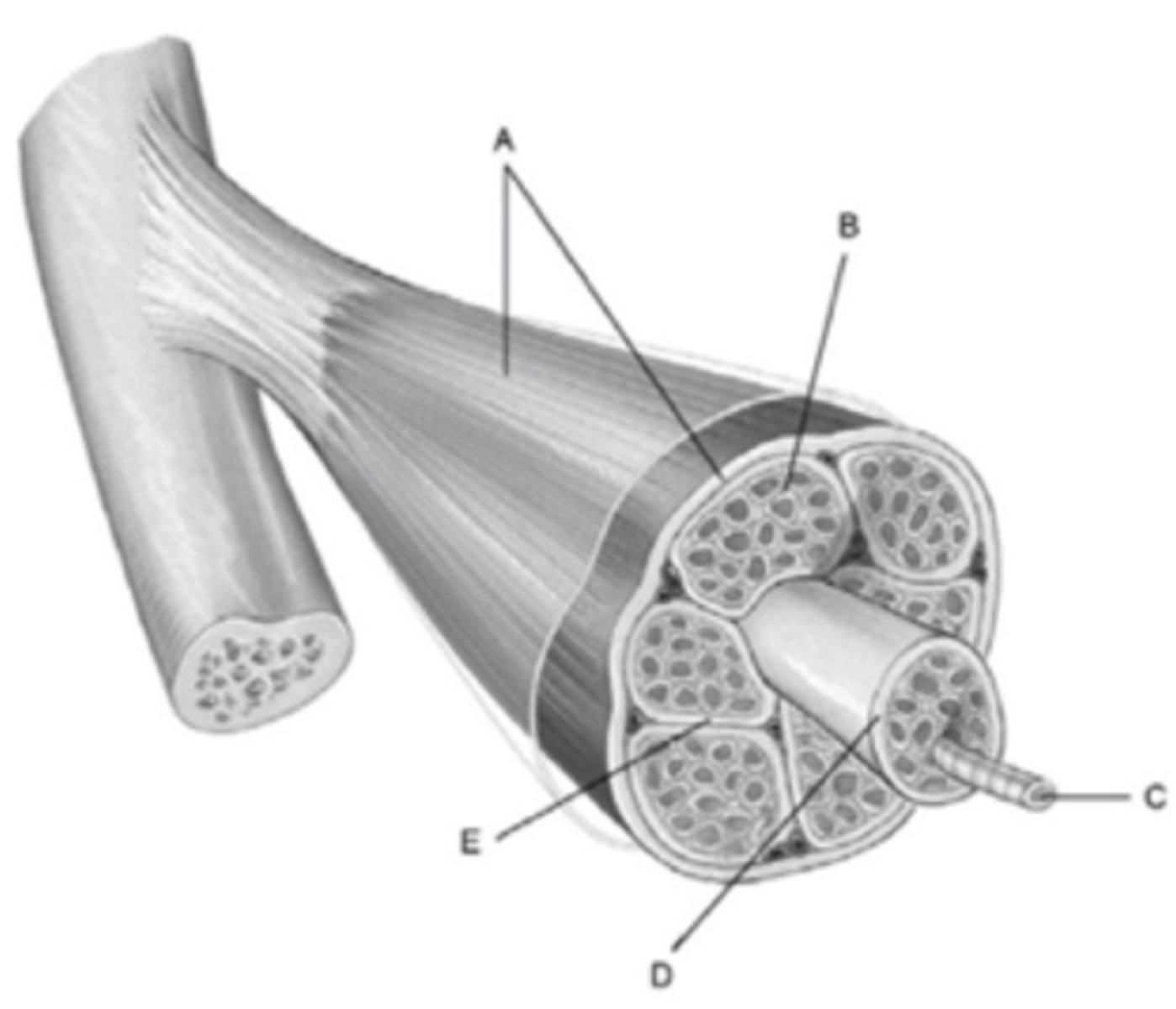
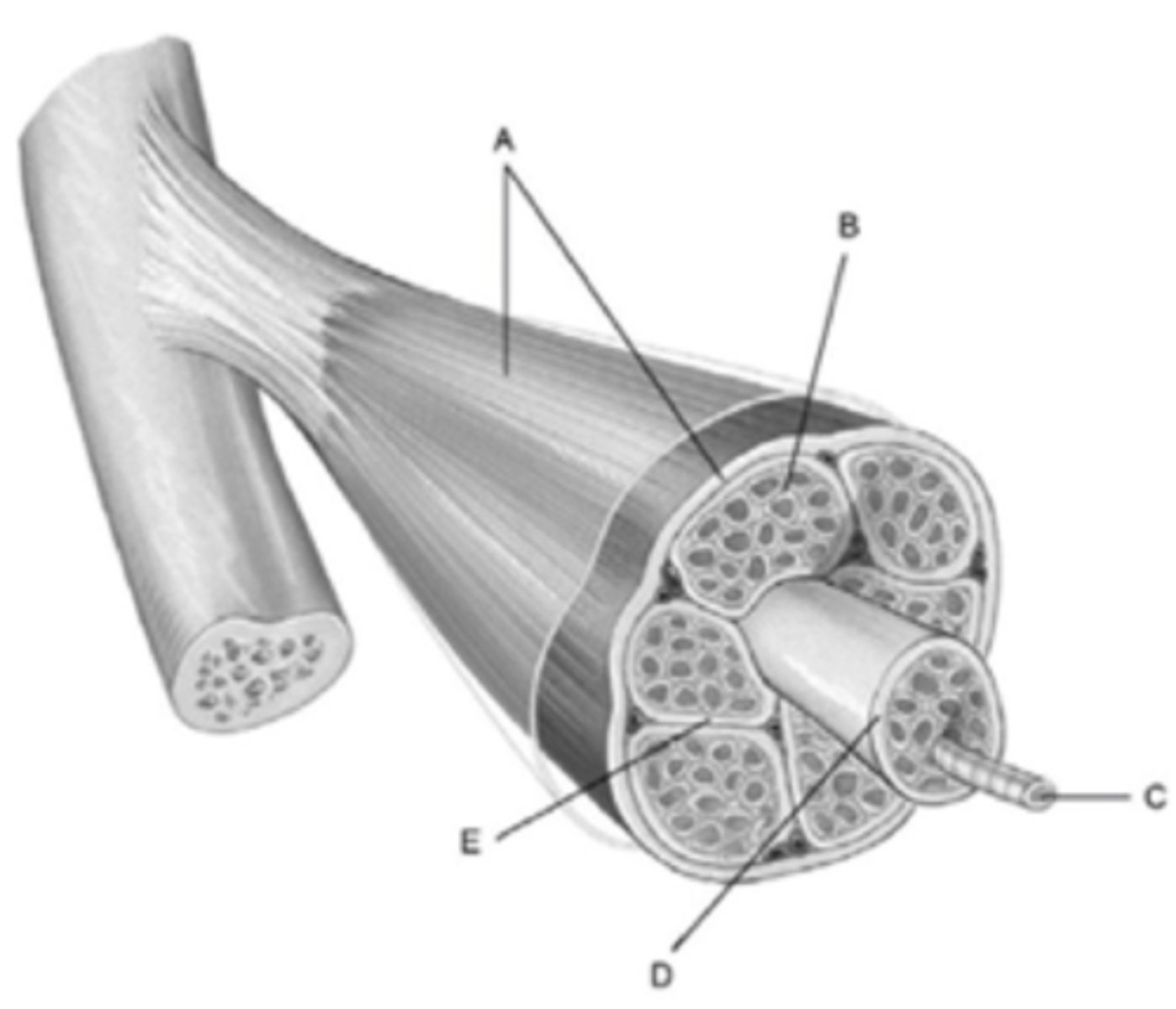
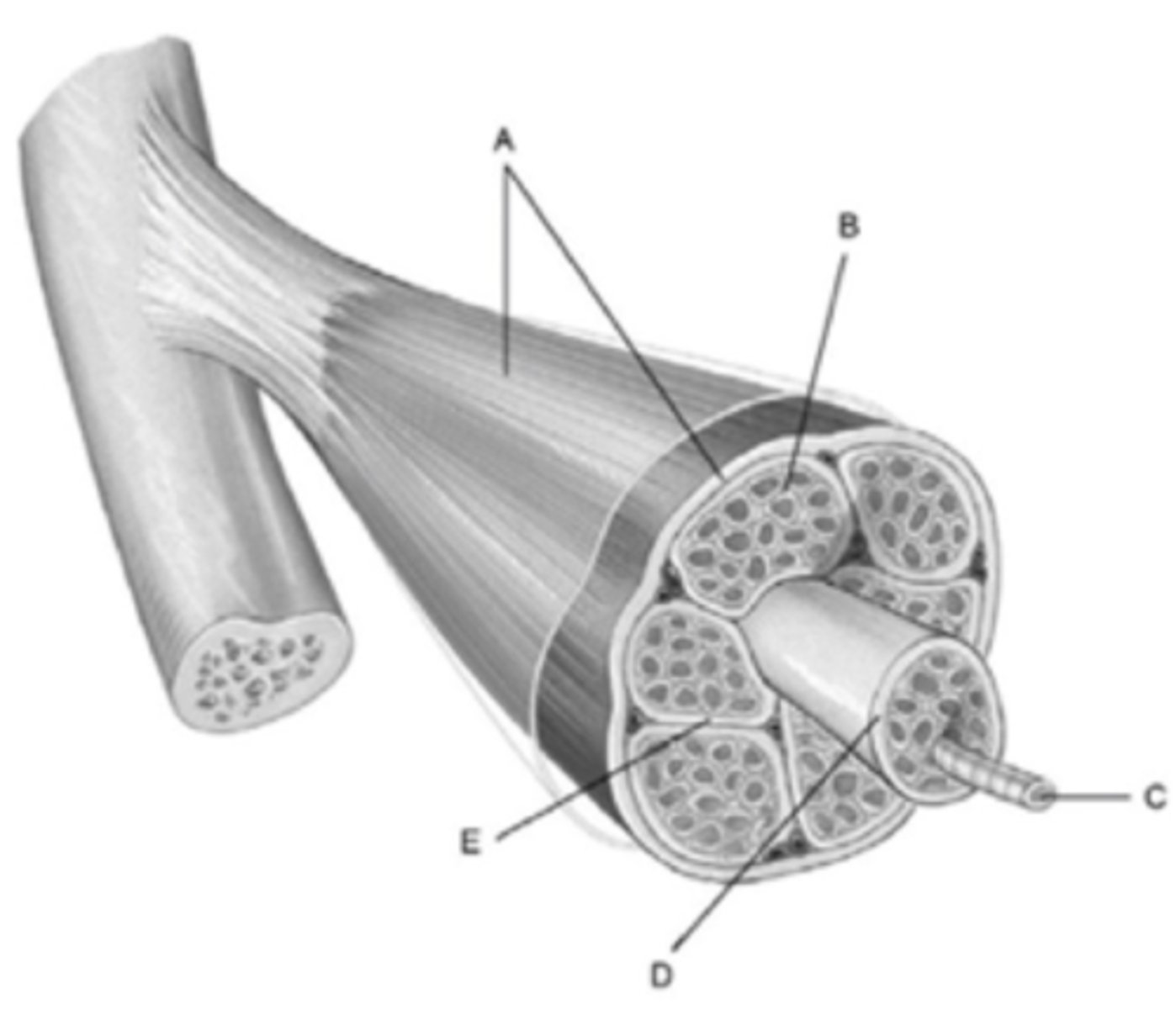
What membrane is labeled b?
Endomysium
Which process requires ATP?
1. Sodium being removed from cytoplasm
2. Release Acetylcholine from synaptic vesicles
3. Myosin releasing form actin
4. Calcium storage in Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
5. Reloading myosin head into active position
What pairs up with troponin proteins to form a complex that blocks muscle contractions?
Tropomyosin
The ___ is a modified form of endoplasmic reticulum that stores and releases calcium ions when a muscle contracts
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
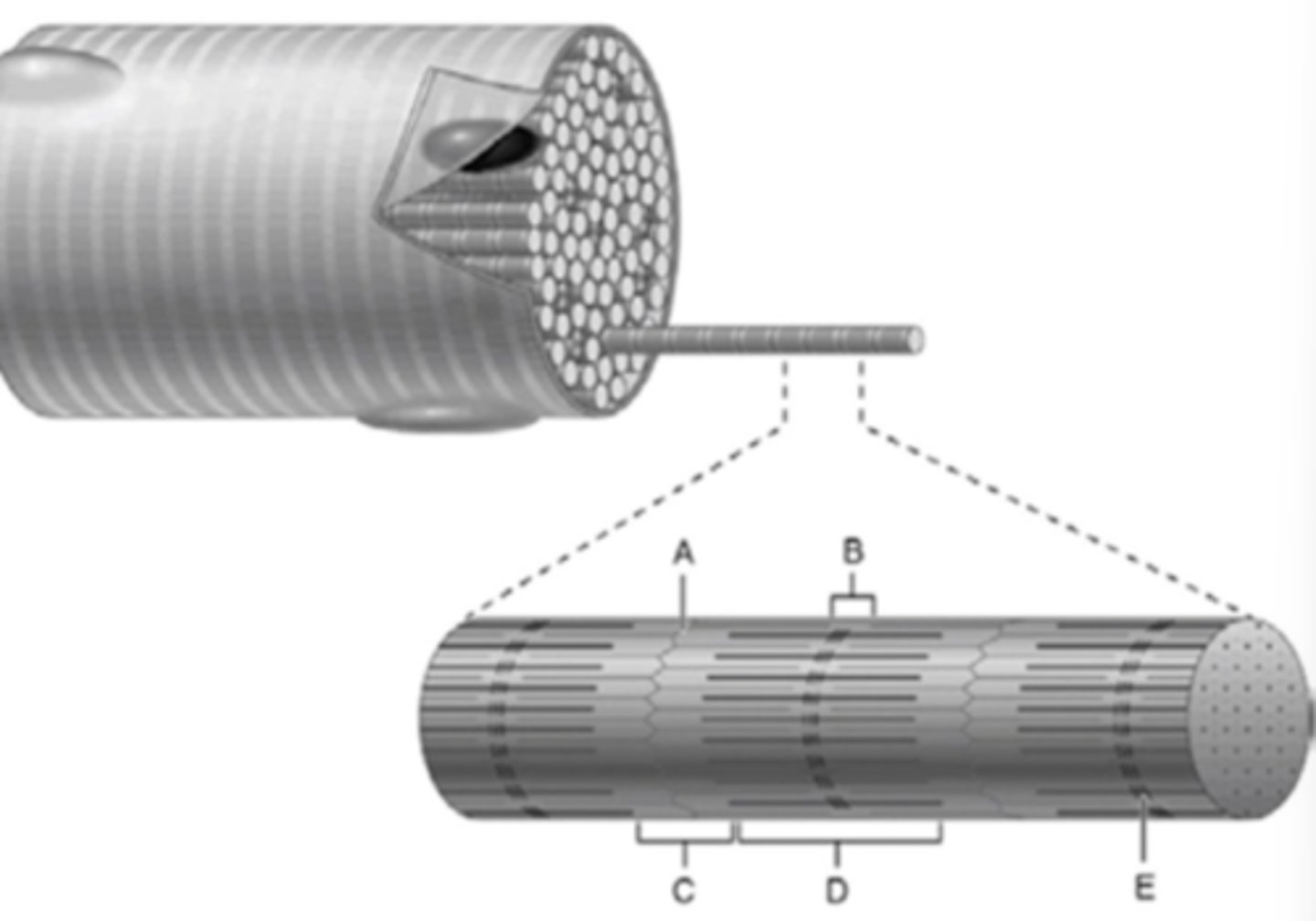
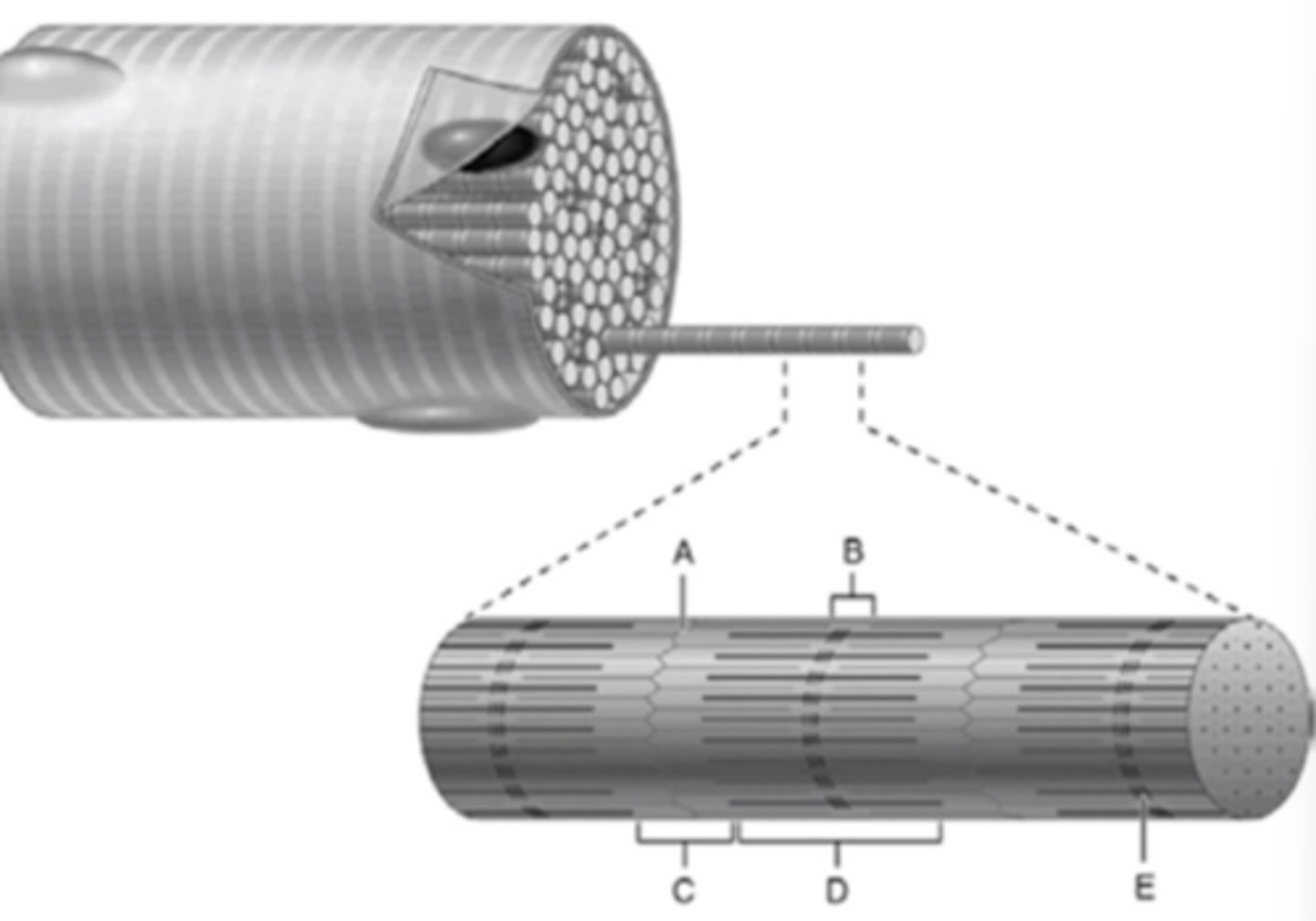
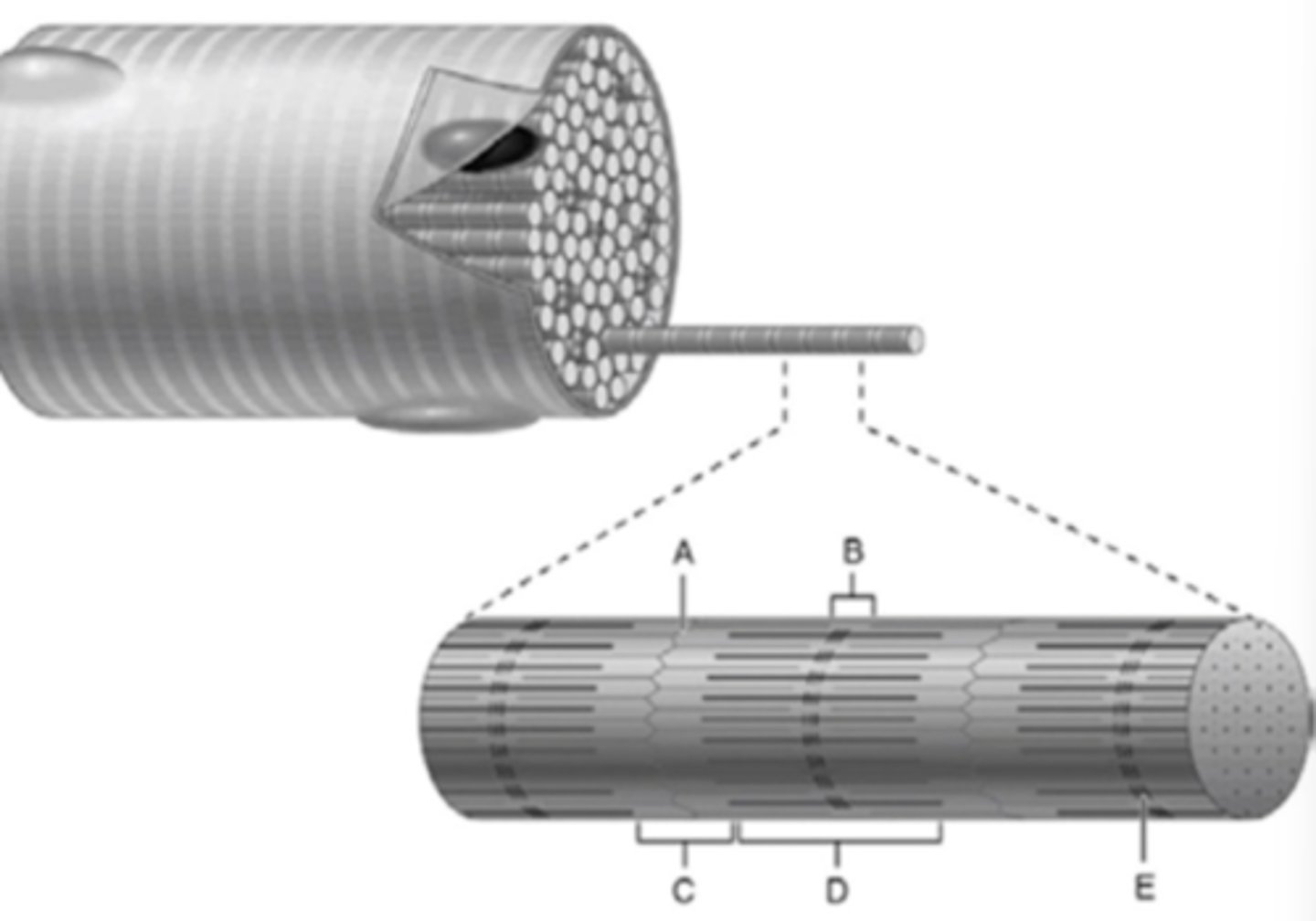
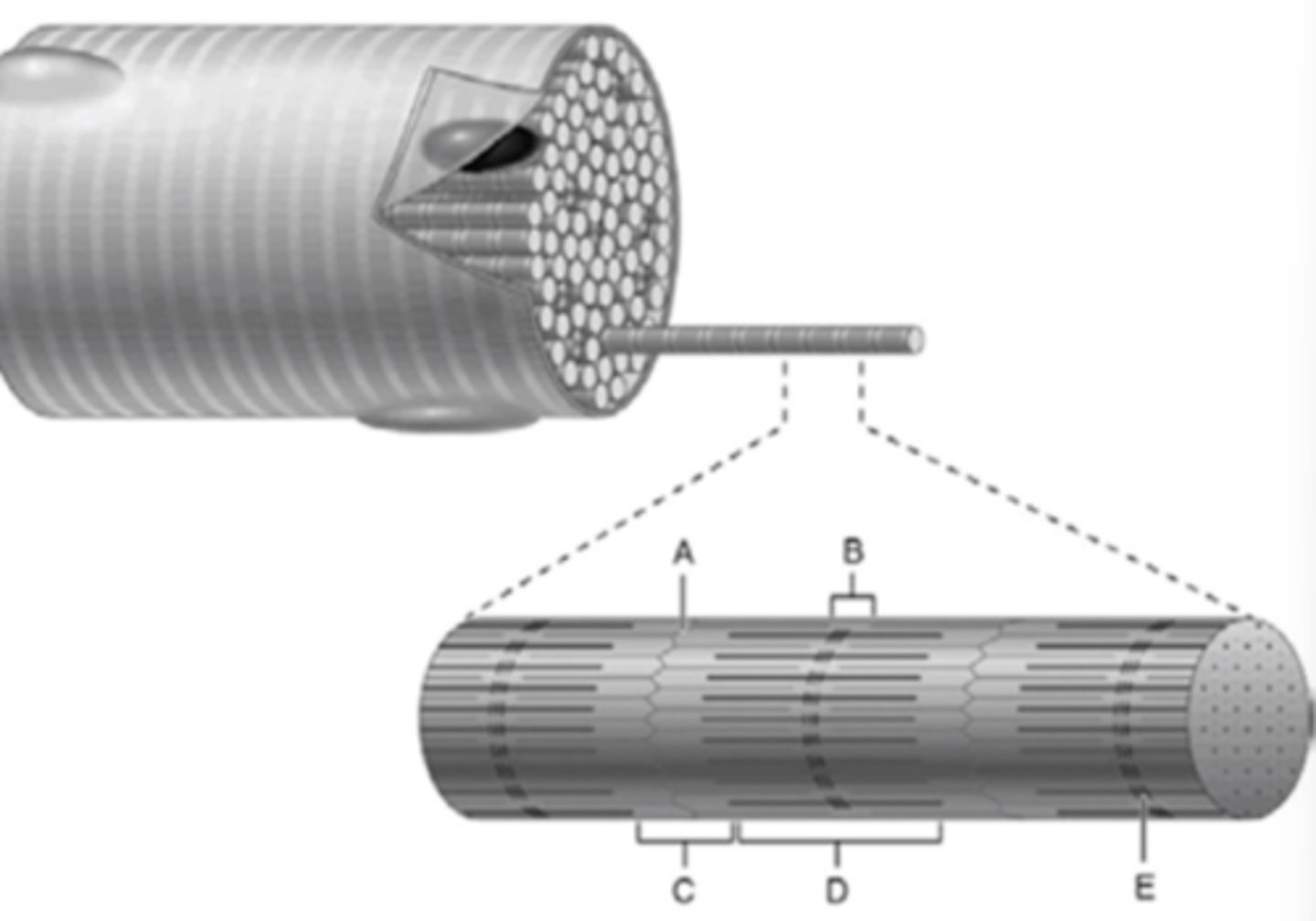
What part of a myofibril is E?
M Line
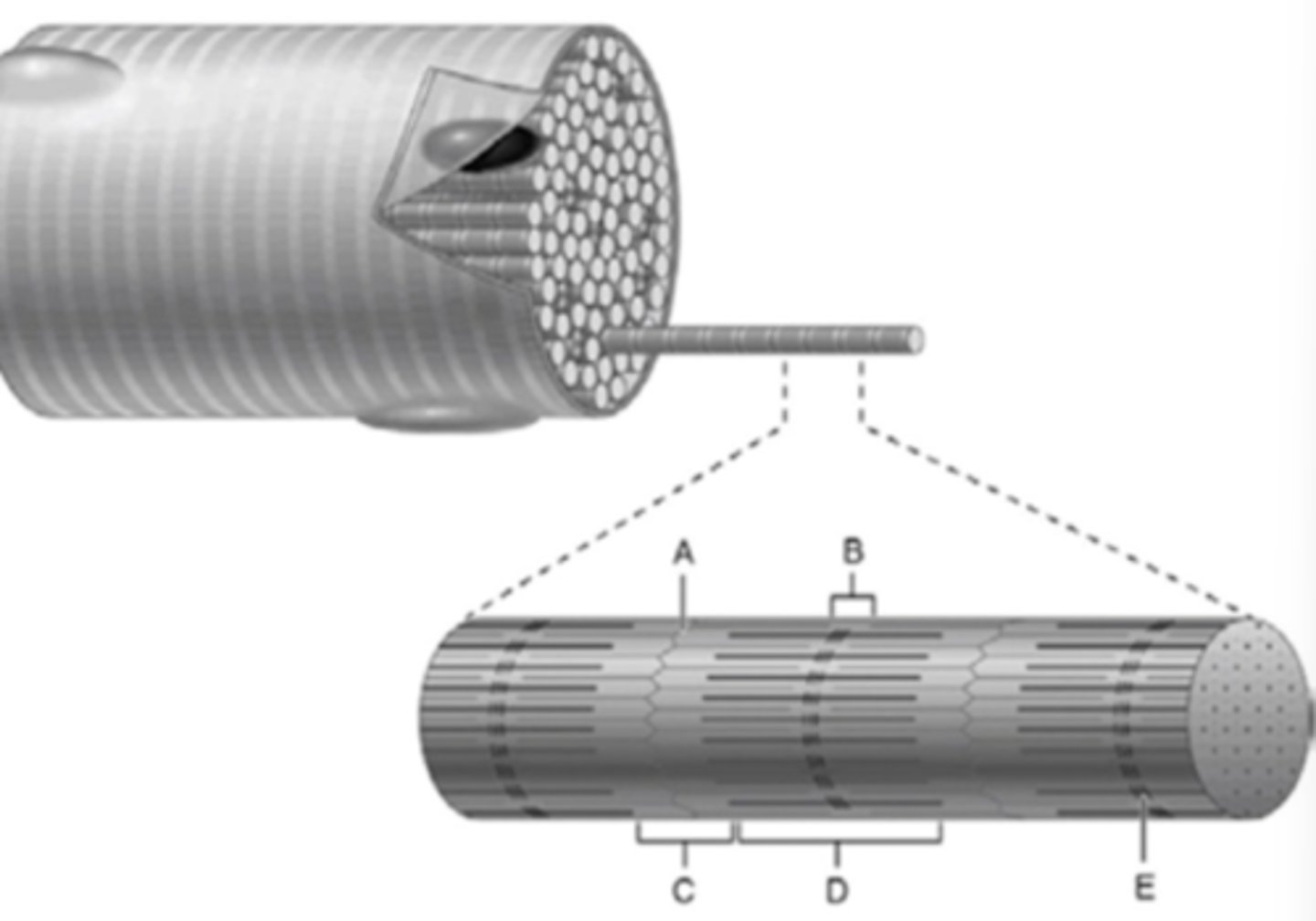
What part of a myofibril is C?
I Band
Describe what should have been observed after adding activating solution to muscle sample
Before adding the activating solution, the muscle sample was long and relaxed. After adding the activating solution, there was a lot of movement in a very short amount of time. It was noted that the muscle sample appeared to have shrunk, losing its length. It was very hard to see specifically what was happening, but after doing some research, there were a few things that happened that were too fast to catch. The first was that the I bands shortened, pulling the Z discs closer to the M line. The second was noticing that there was no longer a H zone - it completely disappeared. The last was realizing that the A bands had moved closer to each other, even though their length had not changed. That was due to the I bands shortening.
Define a sarcomere
The distance from one Z disc to the next z disc
At which stage of the contraction cycle will a muscle cell remain in after death?
myosin will be attached to actin and unable to release
Define I-Band in a sarcomere
Part of sarcomere with only actin
What part of the myofibril is B?
H Zone
___ are the proteins that appear as dark bands that mark the ends of the sarcomeres
Z lines
A rapid, very brief muscle contraction
muscle twitch
Muscle fibers designed for rapid and powerful responses
fast twitch muscle fibers
Calcium binds to this protein to initiate a contraction
Troponin
Protein that makes up the thin myofilament
Tropomyosin
Binds to troponin in the sarcomere to initiate muscle contraction
Calcium Ions
Covers the myosin-binding sites on actin
tropomyosin
Functions in the attachment of muscle to bone
tendons
Delivers the signals from the motor neuron to every sarcomere of the muscle cell
T tubules
Muscle fibers that are designed for endurance, contract slowly, and have a steady supply of energy
Slow twitch muscle fibers
Protein that makes up the thick myofilament
myosin
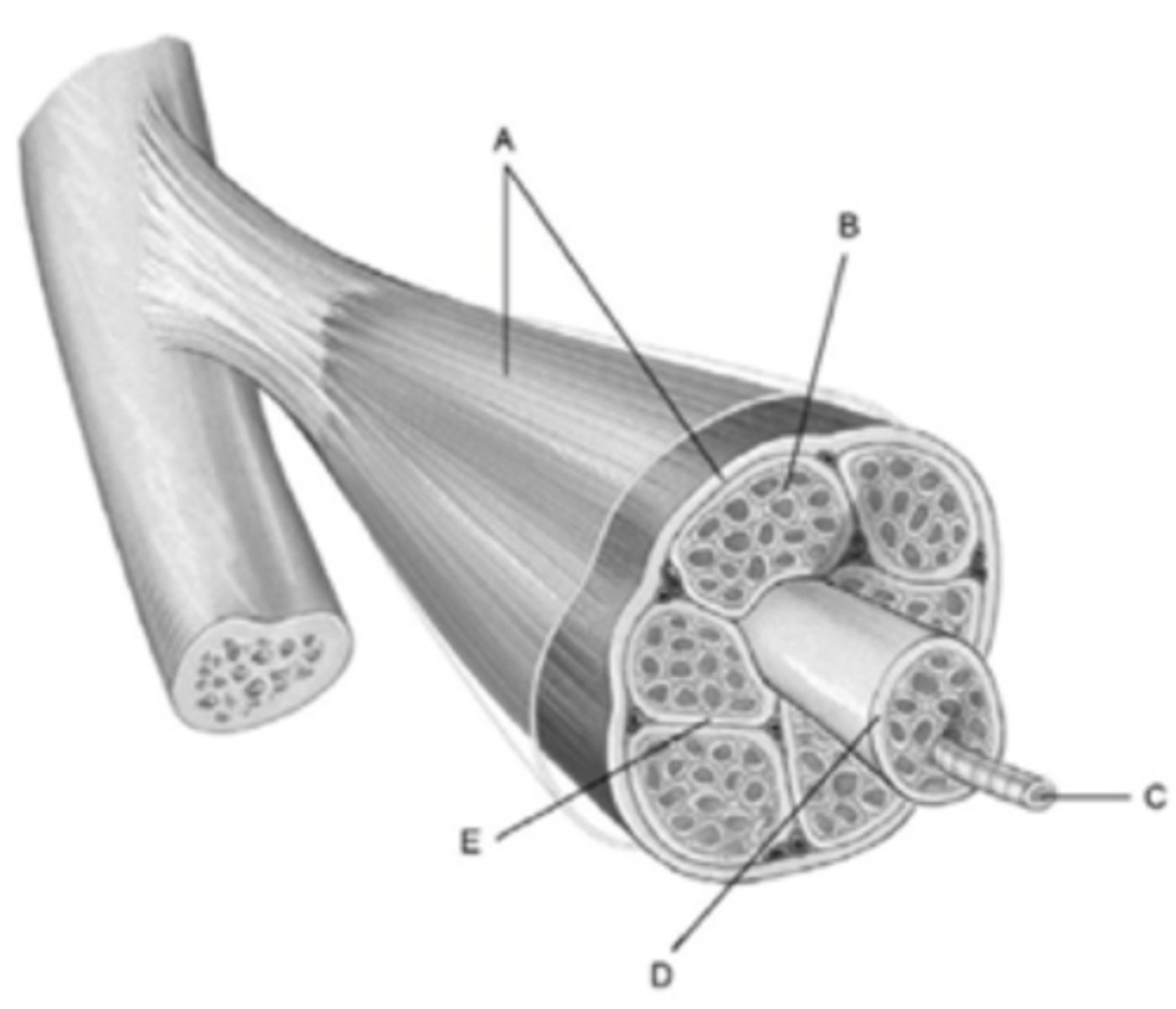
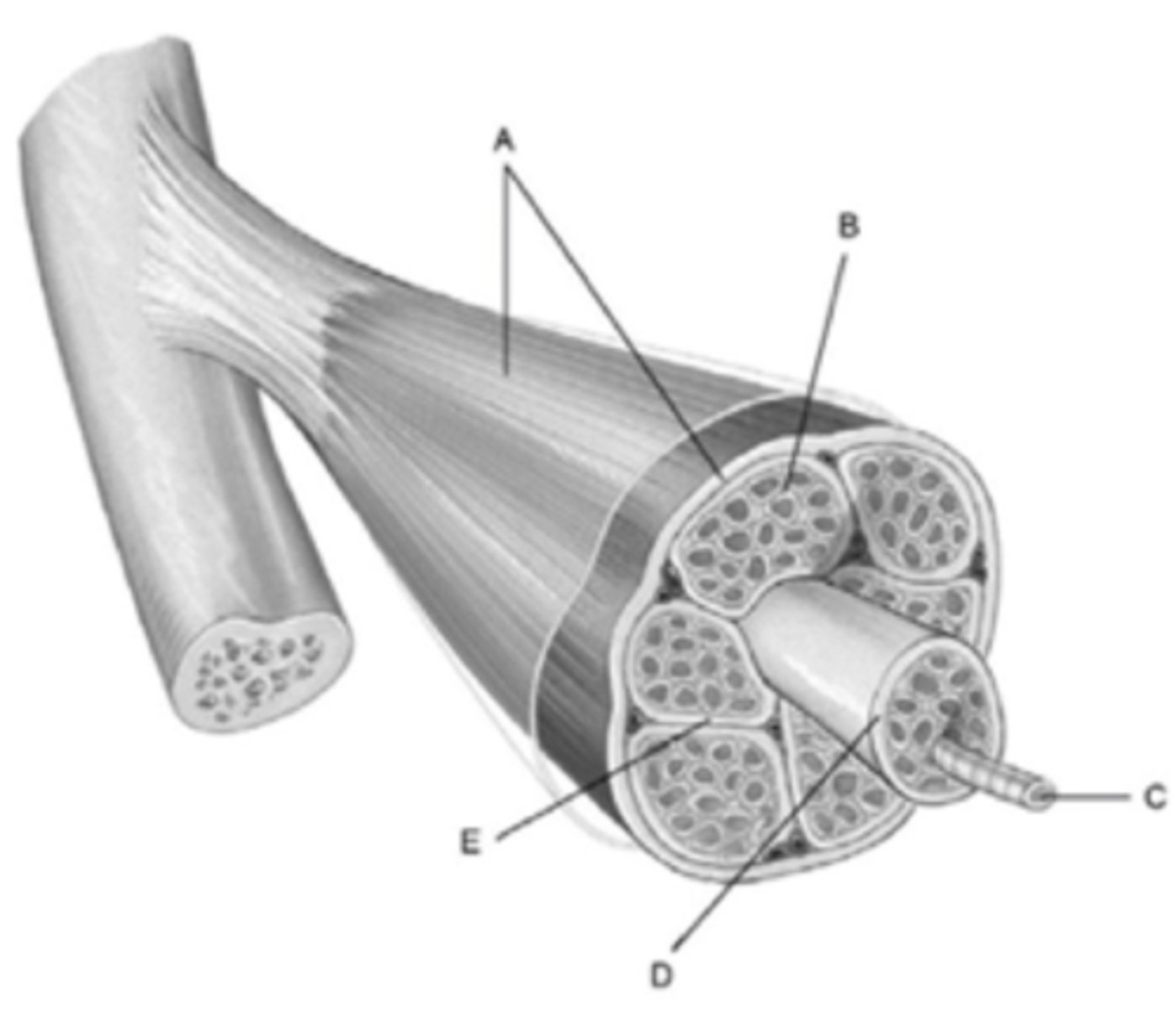
What structure is labeled D
Fascicle
Define the M line in a sarcomere
The center point where all myosin is bound together
What membrane is labeled A?
Epimysium
Propose what would happen to a sarcomere if ATP runs out, as in after death?
Each thick filament is composed of multiple myosin heads, which means that multiple cross-bridges form and break continuously during muscle contraction. Knowing this, it is extremely important for an abundance of ATP to be present in order to keep skeletal muscles healthy and working properly. Without ATP, it would be impossible for the myosin heads to detach from the actin-binding sites, which would leave the cross-bridges intact. This would mean that the muscles are fully contracted, leaving them stuck and stiff. This is known as rigor mortis - the muscles freeze and remain in the position that the person died in, making it extremely hard to reposition that person's body
Which of these structures is part of a muscle cell's plasma membrane that delivers signals to the sarcomere?
T tubule
Which of these junctions represents the connection between the tip of a neuron and a skeletal muscle cell from which acetylcholine diffuses?
neuromuscular
What part of the myofibril is D?
A band
Define the A band in a sarcomere
Part of a sarcomere that incudes myosin from one end to the other
What structure is labeled C?
muscle fiber
Define the Z disc in a sarcomere
the center point where all actin is bound together
What protein makes up the thin filament?
actin
A bundle of muscle cells is called a
fascicle
What part of the myofibril is A?
z- disc
What components are needed during a muscle contraction?
Troponin, Myosin, Sodium entering cell, Calcium, ATP, Actin, Acetylcholine
What membrane is labeled E?
Perimysium
During a muscle contraction which band should not be changed in size?
A band
What does calcium bind to in a sarcomere?
troponin
The arrangement of muscles so that the action of one muscle is the opposite to that of its partner is referred to as ____
antagonistic
What covers up the actin binding sites?
Tropomyosin
What protein pulls on tropomyosin to expose actin binding sites?
Troponin
During muscle contraction which band should be reduced in size?
I band
Which of the following are protein filaments that function in muscle contraction and are shaped like a golf club with two heads?
myosin filaments
Which process does NOT require ATP?
1. Opening of sodium gates on a muscle cell
2. Closing of sodium gates on muscle cell
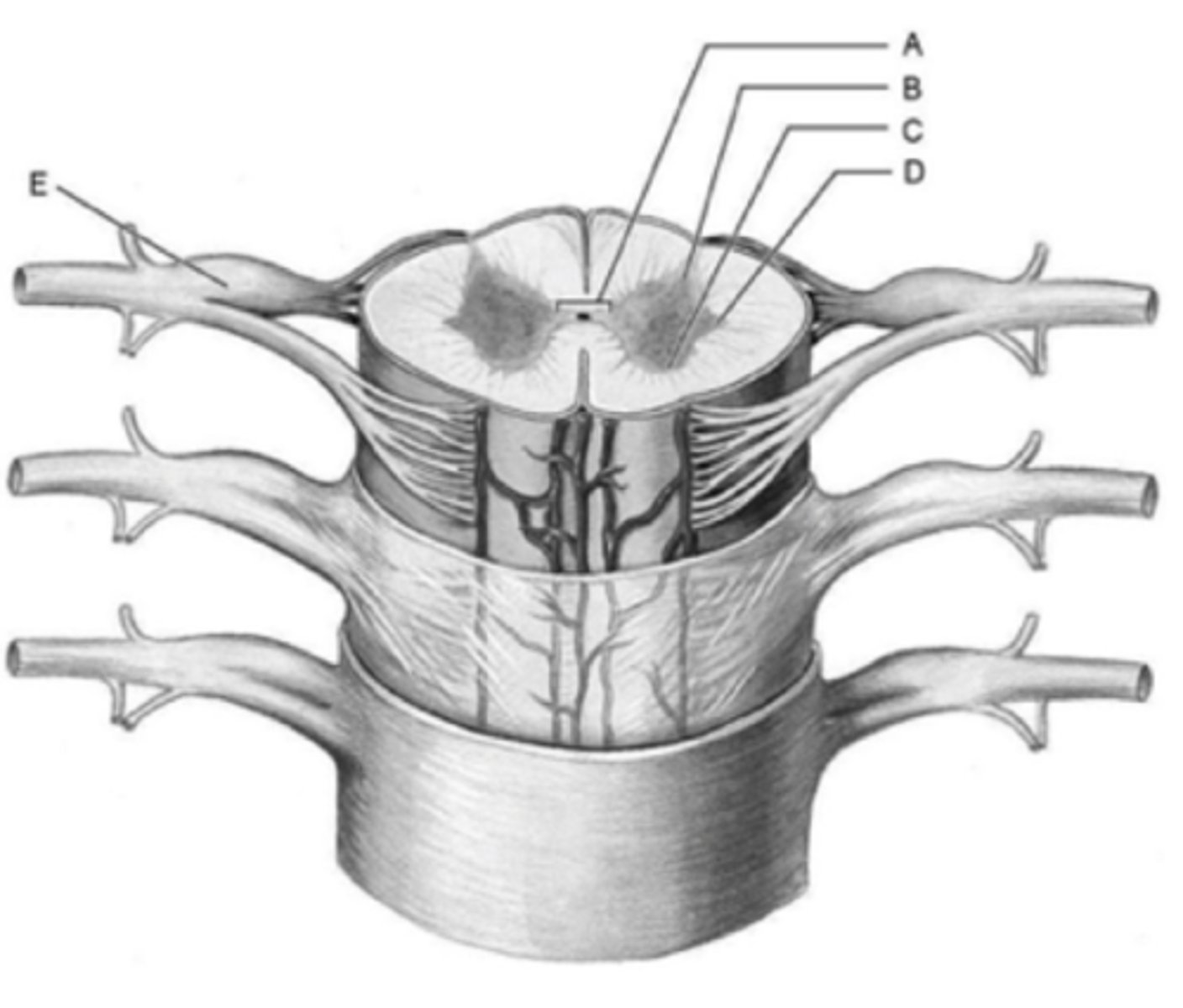
Interneurons receiving input from sensory neurons are located in the ________.
dorsal (posterior) horn
Which area that encloses the central canal
A
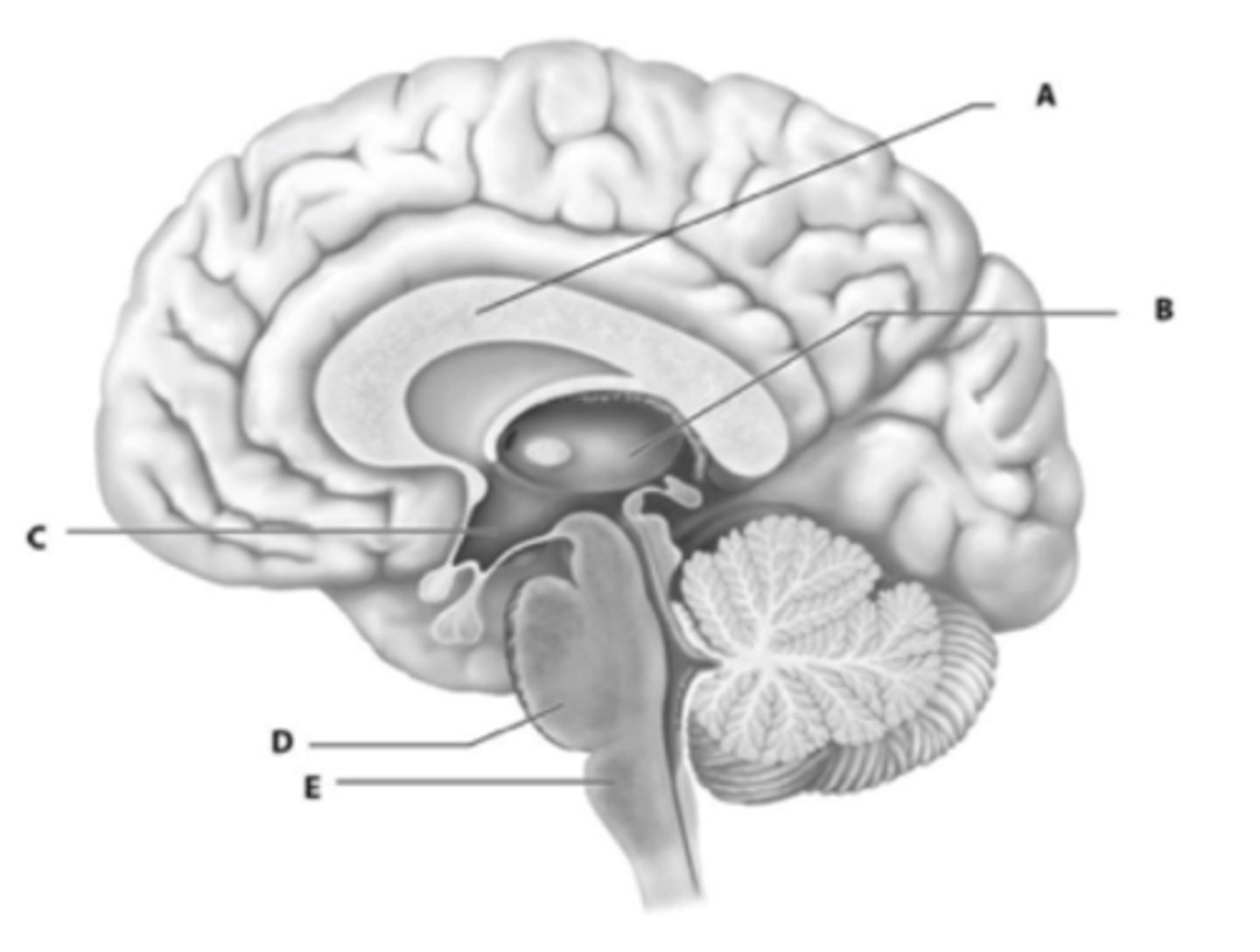
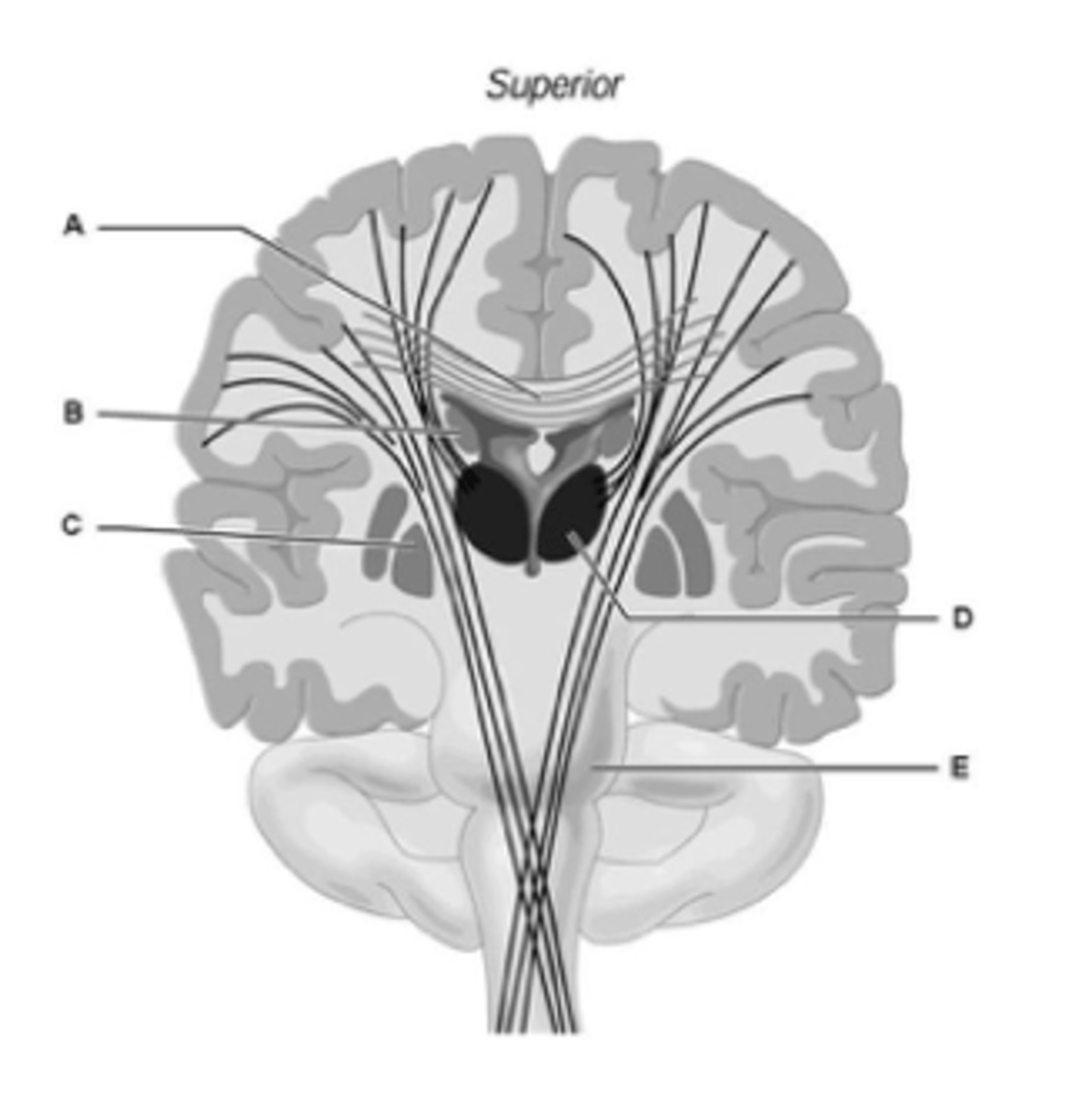
Where are the white fiber tracts connecting the two hemispheres?
A
The corpora quadrigemina are found in the _____.
midbrain
What letter shows the hypothalamus?
C
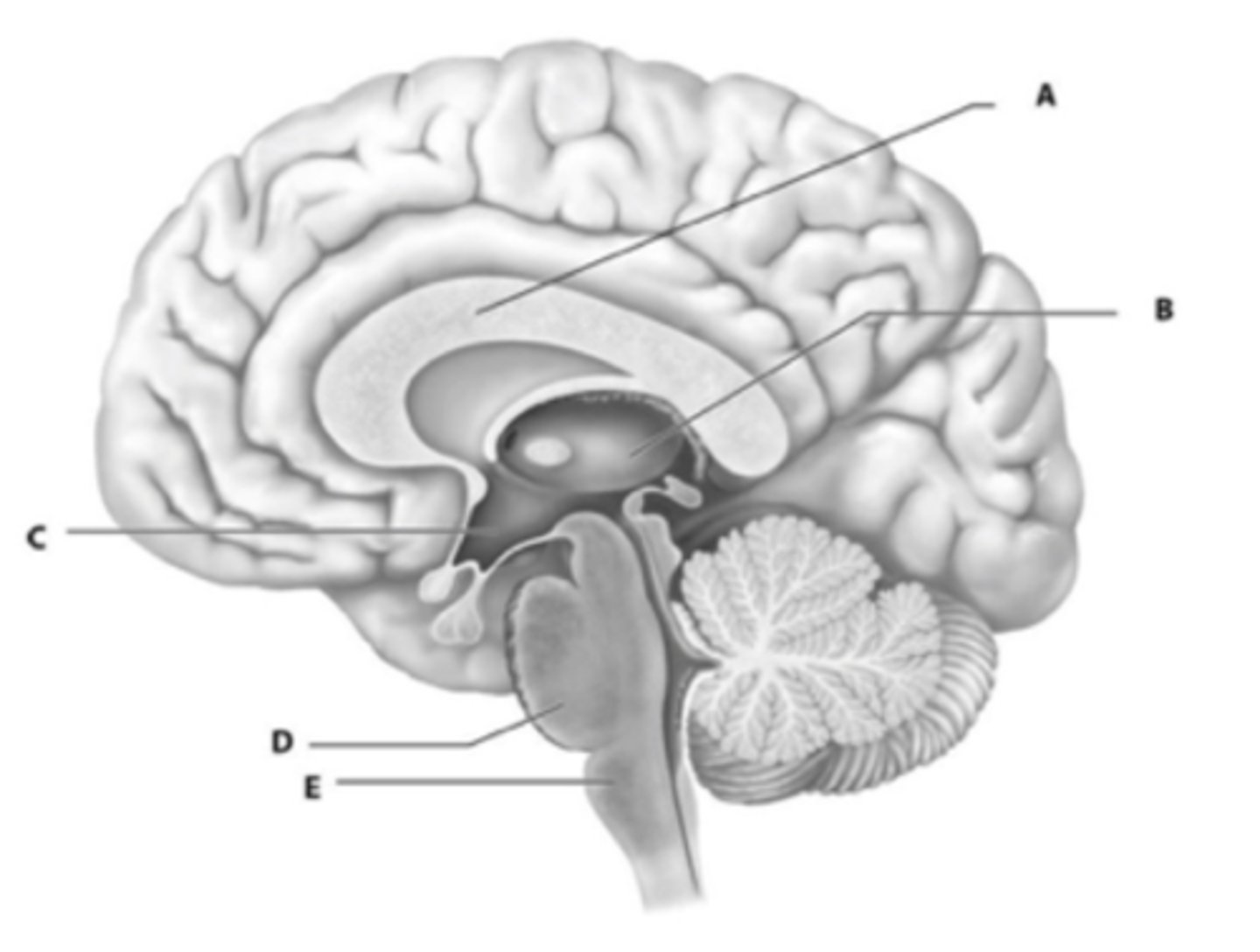
The brain area just anterior to the precentral gyrus that selects and sequences basic motor movements into more complex tasks.
Premotor cortex
What type of cells line the ventricles of the brain?
ependymal cell
This area on the extreme posterior of the occipital lobe receives visual information that originates on the retina of the eye
primary visual cortex
The _____ includes the thalamus, hypothalamus and epithalamus
diencephalon
The brain area that regulates activities that control the state of wakefulness or alertness of the cerebral cortex is the _____
reticular formation
What structure is C?
Globus pallidus
Visual centers for the control of heart rate, respiration and blood pressure are located in the ______
medulla oblongata