Physics: Midterm
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
How kilometers are there in 40,000 meters?
40
How many mega hertz in 55,000,000 hertz?
55 MHz
What is the approximate rate of sound traveling 22 cm in 540 µsec?
410 m/sec
(convert units to base)
What is 1/5 in percentage?
20%
How many microseconds are there in 10 seconds?
10,000,000
The vertical axis of a graph is called?
y - axis
What is the reciprocal of 1,000?
0.001
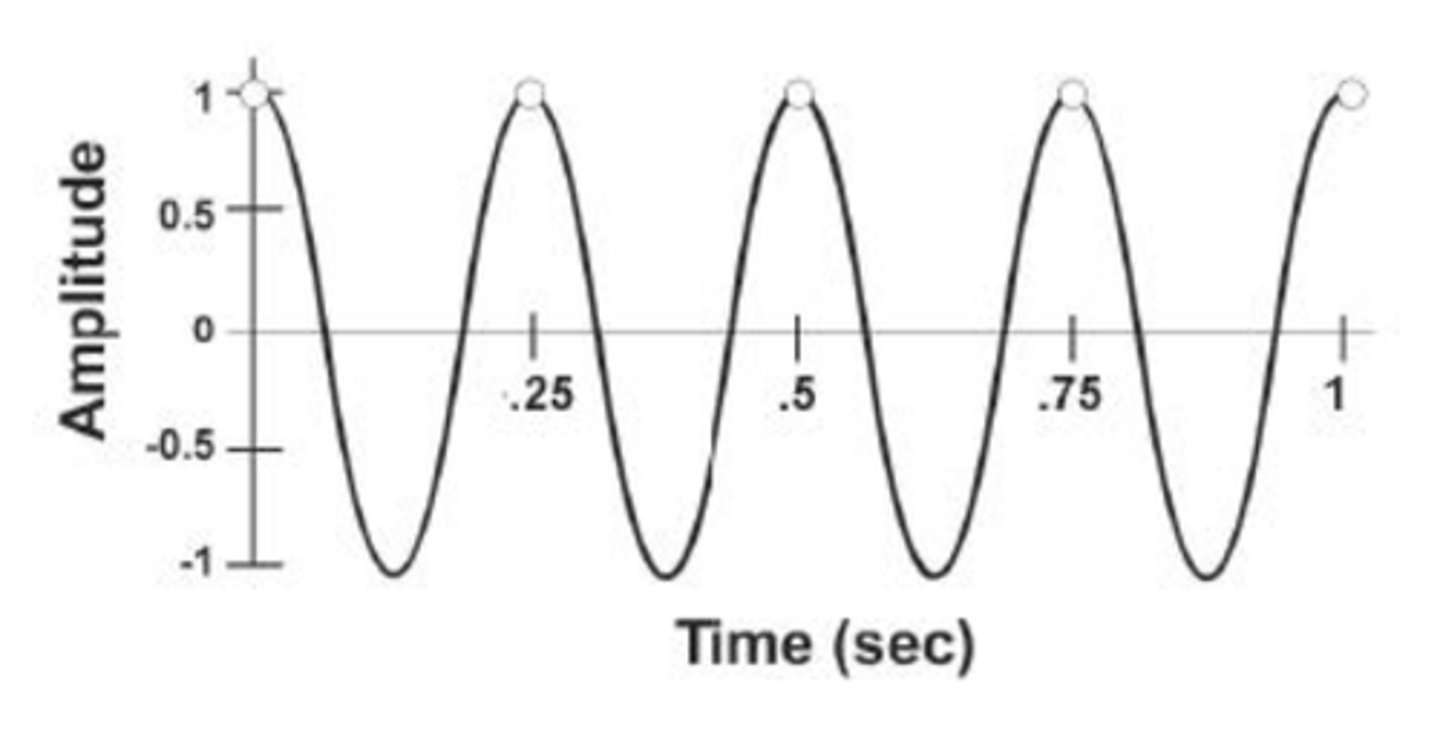
What is the frequency?
4 Hz
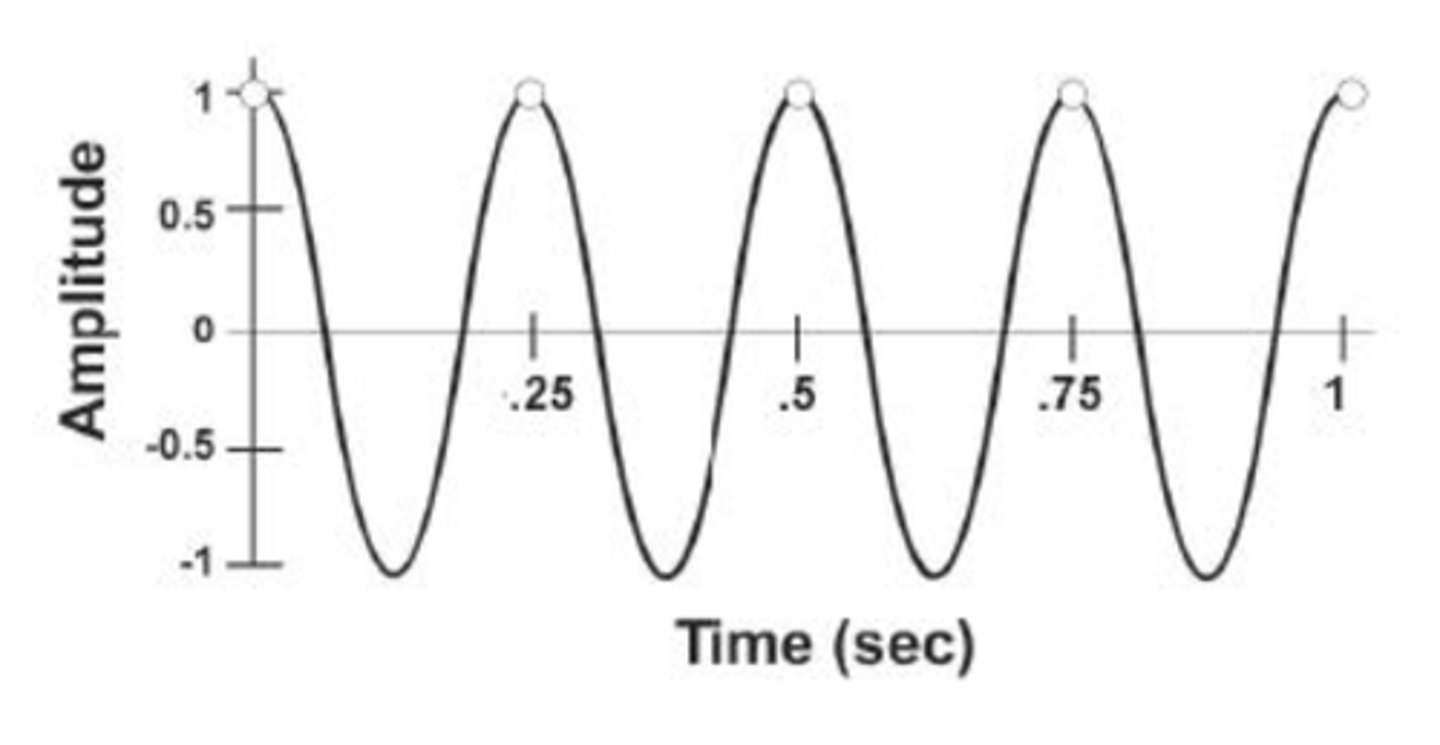
What is the cosine of 60 degrees?
0.5
B = r(w)^3
k
Using the equation above, if the variable w increases by a factor of 3 how will B change?
increase by a factor of 27
Period and frequency are
reciprocals of each other
Define Acoustic Variables
There are four different measurable quantities of the medium that change with the interaction of the wave propagation.
Pressure
Density
Particle Motion
Temperature
Calculate the wavelength of a 7 MHz wave traveling thru soft tissue:
0.22 mm
We will expect areas of rarefaction along the path of the wave to be
low pressure
What is the relationship of pulse duration and pulse length?
directly
What units are used to describe attenuation?
decibels
Which of the following describes the characteristics of a sound wave?
mechanical, longitudinal
What happens to the period of the wave as it propagates into a medium?
remains the same
The intensity of the beam is calculated by
Power/area
Which of the following are acoustic variables?
Pressure
Temperature
Motion of particles in a wave
Density
You increase the depth from 8 cm to 10 cm. What affect will this have on the duty factor of the transducer?
decreases the duty factor
To calculate the spatial pulse length we need to know two things:
number of cycles in the pulse and the wavelength
Calculate the amount of attenuation of a 10 MHz beam imaging a kidney at a depth of 8 cm (assume soft tissue rate):
80 dB
Assuming the beam is passing from medium 1 to medium 2 and the speeds of the tissues are the same but their impedance are different. What do we know about the angles of reflection and transmission?
angle of incidence = angle of reflection = angle of transmission
When tissues have more similar acoustic impedance we can predict:
(regarding transmission & reflection)
there will be more transmission and less reflection
Edge shadowing is an example of reflection. T/F
False; refraction
What causes signal enhancement distal to a cyst?
weak attenuation by cyst
Which mode is most likely to have the highest bandwidth?
B-mode
Reflection will occur when there is a difference in
the acoustic impedance of 2 different media
What does a 3 dB change in value of intensity mean?
the value has doubled
What determines the resonant frequency of an imaging transducer?
Thickness of the crystal element
Which type of transducer permits electronic focusing in the elevation direction?
3 dimensional transducer
Define frequency of an ultrasound wave.
number of pressure oscillations per unit time
How can lateral resolution be improved?
reduce beam width
What term describes the ratio of time that a transducer is actively generating ultrasound energy?
Duty factor
What transmit focus method is used in linear array transducers?
Time delay to excite crystal elements
Which of the following is most likelly to improve axial spatial resolution in B-mode imaging?
Changing from a 3 MHz to a 5 MHz imaging transducer
How long does it take to image an aorta at a depth of 8 cm?
104 µsec
For best axial resolution we would want to use:
high frequency and a short SPL
The technique of phasing is used to
steer the beam
focus the beam
What term describes the reflection of ultrasound at large, smooth interfaces?
specular
Which wave parameter is unchanged as ultrasound is transmitted through an interface composed of soft tissue and fat?
frequency
Refraction will occur only if
the angle of incidence is not equal to 0 and there is a change in tissue velocities (different propagation speeds)
What factor(s) control PRP?
the speed of the medium
Which of the following below is a job of the beamformer?
phasing and steering the beam
Color Doppler displays the __________ velocity of blood flow.
average
What equation governs refraction artifact?
Snell's
What happens to the intensity of a beam if the beam area is doubled?
it's decreased by a factor of 2
What determines the period of an ultrasound wave?
the transducer
How many microseconds are there in 10 seconds?
10,000,000
What happens to the period of the wave as it propagates into a medium?
remains the same
As an ultrasound wave travels through the body, its amplitude usually:
decreases
What is the propagation speed of a 5 MHz sound wave in soft tissue?
1.54 mm/μsec
Which is the best description of how sound propagates?
Particles of medium move back and forth in the same direction as wave propagation direction
Units used to measure intensity are:
Watts/meters squared
The resonance frequency of a transducer depends on the
thickness of the piezoelectric element
Lateral resolution is determined by
beam width
Which design feature of the transducer improves the transmission of acoustic energy into tissue?
matching layer
What information is presented in the A-mode display?
echo signal strength and depth of origin
Which component has the highest dynamic range?
received signal
Which adjustment can increase the frame rate in B-mode imaging?
decrease the scan area
Which signal processing technique converts the radio frequency signal to a video format?
demodulation
Applying compression to a signal coming back from the patient will
decrease the number of shades of gray visualized
How many shades of gray can be represented by a monitor with a bit depth of 8?
256
A zoom box is placed over a portion of the image and displayed. The resolution in the zoom box does not appear to improve (in fact, the image looks quite pixilated). Which type of zoom was more likely employed?
read zoom
This ultrasound technique is used to improve Signal to Noise Ratio (SNR)
averaging
The brightness of each pixel displayed in the 2D image is directly proportional to the
amplitude of the signal reflection
Axial resolution is measured in units of
distance
For optimal image we expect a _______ signal to noise ratio.
high
Explain how crystal oscillation occurs
Alternating electricity is applied to the crystal
*The crystal expands and contracts
*Oscillates/resonates
*Creating a pressure/sound mechanical wave
*If there is not too much acoustic impedance mismatch there will be transmission of the sound into the medium
Compare operating frequency of CW and PW
CW operating frequency is equal to the drive voltage
*PW = Ccrystal/2 x thickness
The more cycles there are in the pulse, the_____is the numerical value of the range resolution.
greater
Snell's Law determines:
presence and amount of refraction
Describe how elevational resolution changes at different depth
It is best at the focus and decreases farther
Refraction
Takes place due to:_change in propagation velocity_Angle of incidence not equal 0
*It causes ____lateral_______displacement of structures beyond an interface.
Name four wave characteristics and parameters that we must be able to measure or calculate:
Frequency
Period
Wavelength
C
Amplitude
Calculate the duty factor if the pulse duration is 4.5msec and the pulse repetition is 12.5 msec?
36%
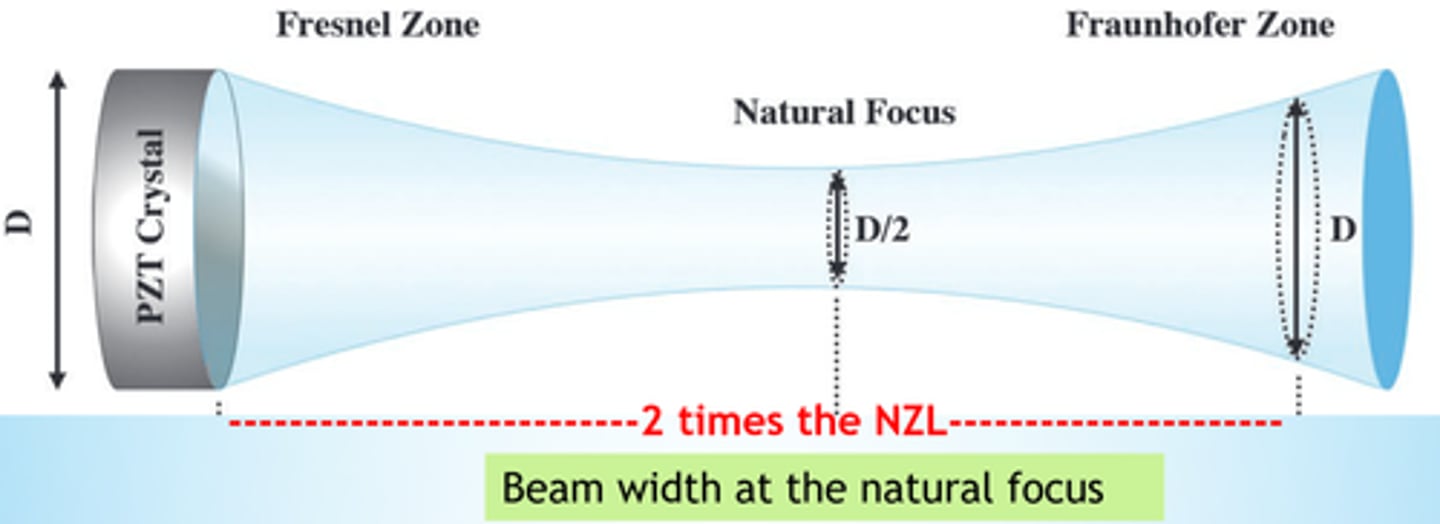
Describe the distance from the crystal to a depth where the beam is the original width
NZL x 2
Can the pulse duration be increased without affect the pulse repetition frequency or pulse repetition period?
Absolutely
If you double the operating frequency how does the natural focus length change?
NZL = D2 x f o/6
Just doubles the depth of the natural focal depth
Describe Averaging and Signal to Noise Ratio
By taking multiple measurements and averaging them, the random noise tends to cancel out, leaving a clearer signal.
Acoustic Impedance is equal to:
c x ρ
(rayls)
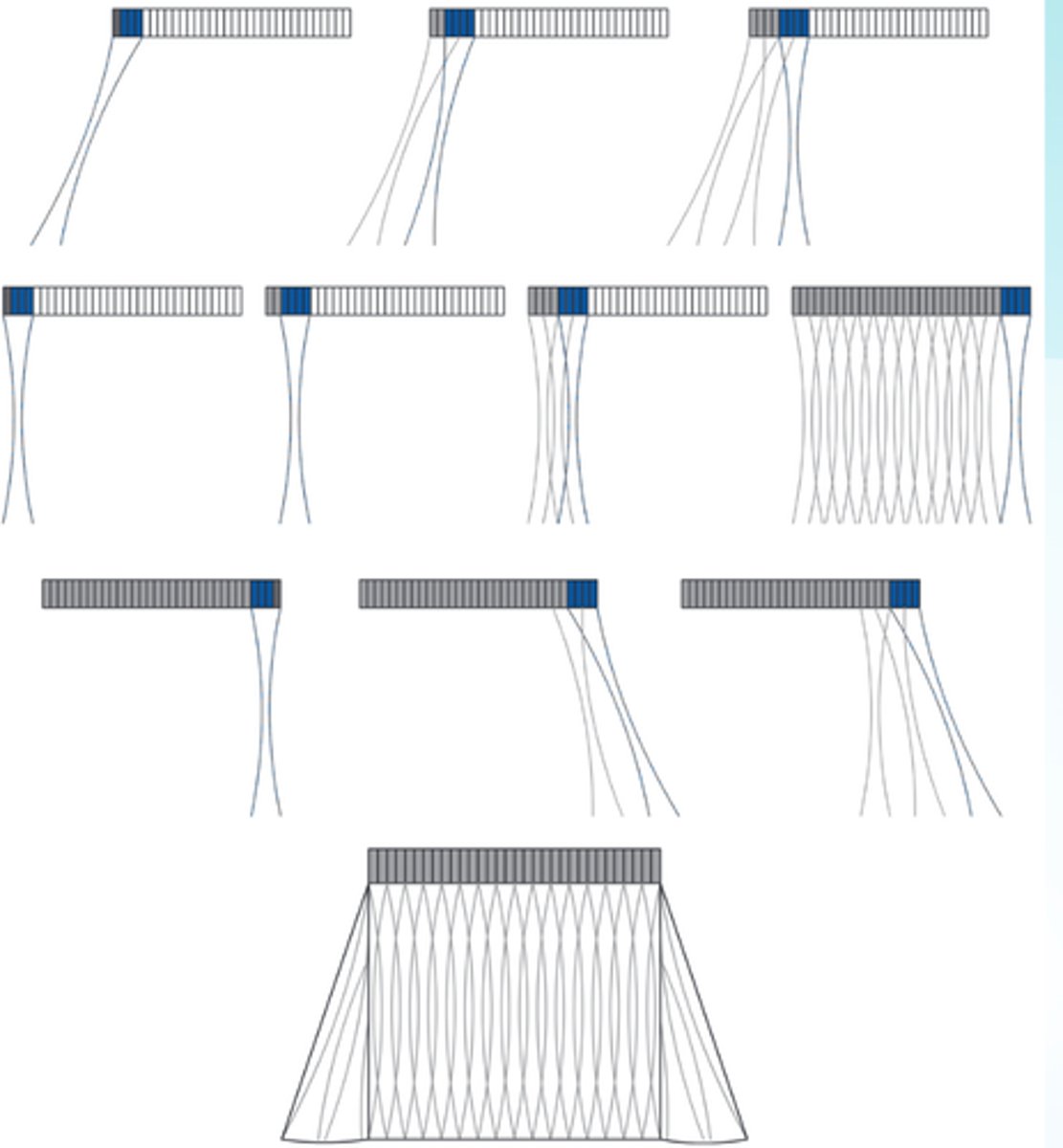
Sequencing with phased array
How is this image steered/produced?
Which of the following will not change if you change the transducer's frequency?
speed of a sound
How is the near zone length affected if the diameter of the crystal is increased by three times?
Increase by factor of 9
NZL=D^2 x Fop/6
Use formula to describe how applying backing material helps improve axial resolution
Axial resolution = SPL/2
SPL = λ x # of cycles in a pulse
The shorter the pulse length the better the axial resolution. Backing material shortens the pulses.
What is the thickness of a matching layer if the frequency is 6MHz?
λ/4
λ = c/f = 1540 m/sec x 6 MHzλ = 257 μm
Thickness of matching layer = 64.25 μm
Describe the focal region
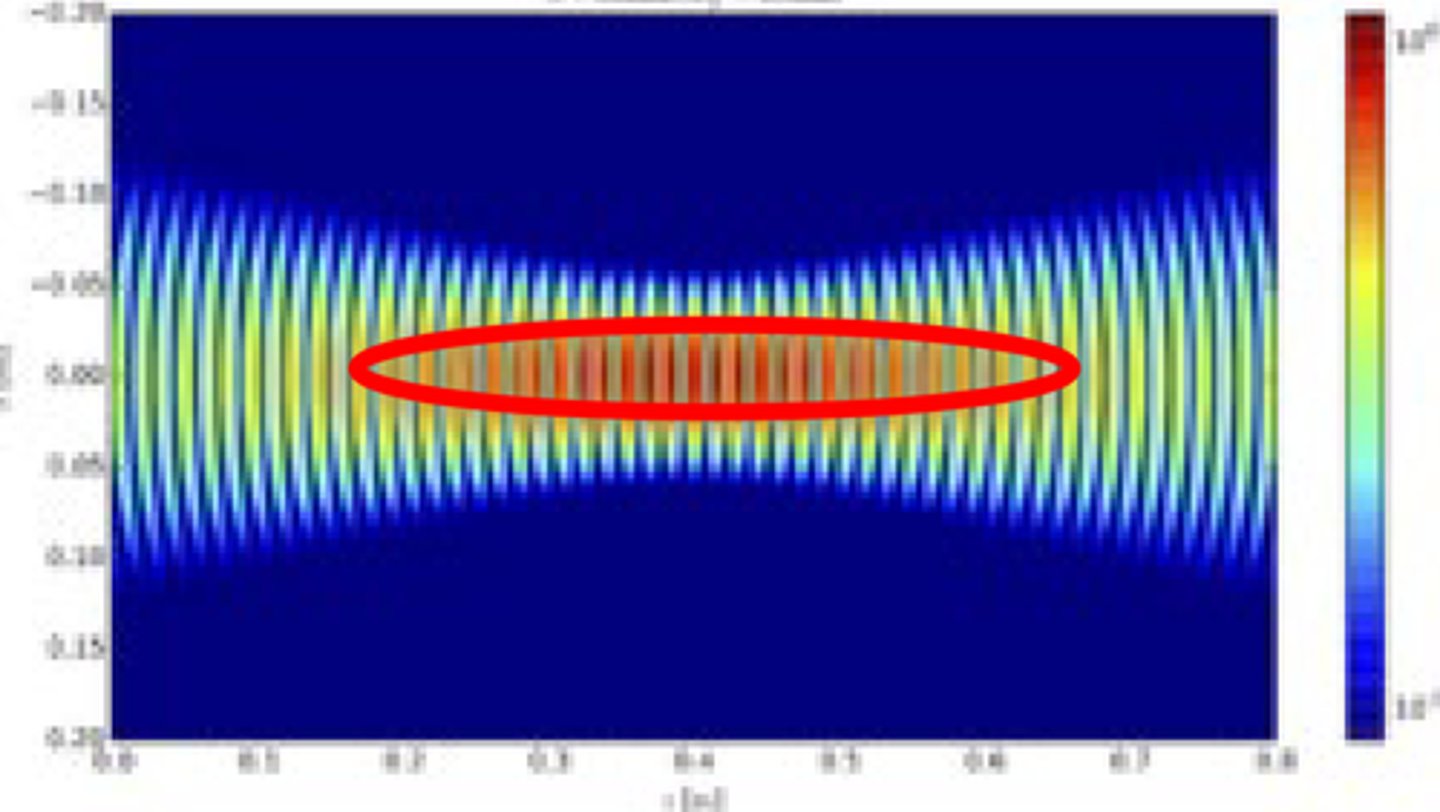
What is % reflection at a tissue interface,Z1 = 24 MRaylsZ2 = 12 MRayls
11% Reflection and 89%Transmission
Definition of Power?
The amount of work being performed
Power is measured in what units?
Watts or joules/second
Amplitude is measured in what units?
Volts Or could be dB
How are power and amplitude related?
Power = Amplitude^2
What are the change in dB if the power is increased by 10?
dB = 10
Name the four acoustic variables that can change in the presence of a sound wave
Pressure
Density
Temperature
Particle motion
If the difference in acoustic impedance between two media becomes more alike will the amount of transmission increase or decrease?
increase
Lateral resolution does not depend on
Dampening
If the PRP is 143 μsec what is the PRF? (in kHz)
PRF=1/PRP
0.007 MHz or 7 kHz
It is not. The crystal placement allow broader window of view
How is this transducer steered?
Can I increase the frequency of the transducer and not affect the PRP?
YES, it has nothing to do with PRP
PRP=depth x 13usec