Biology 1650 - The Unity of Life - Lab Practical 2 - Frieders
1/106
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
107 Terms
Physiology
The study of how the body and its parts work or function
Active transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane using ATP energy
Passive transport
the movement of substances across a cell membrane using thermal energy
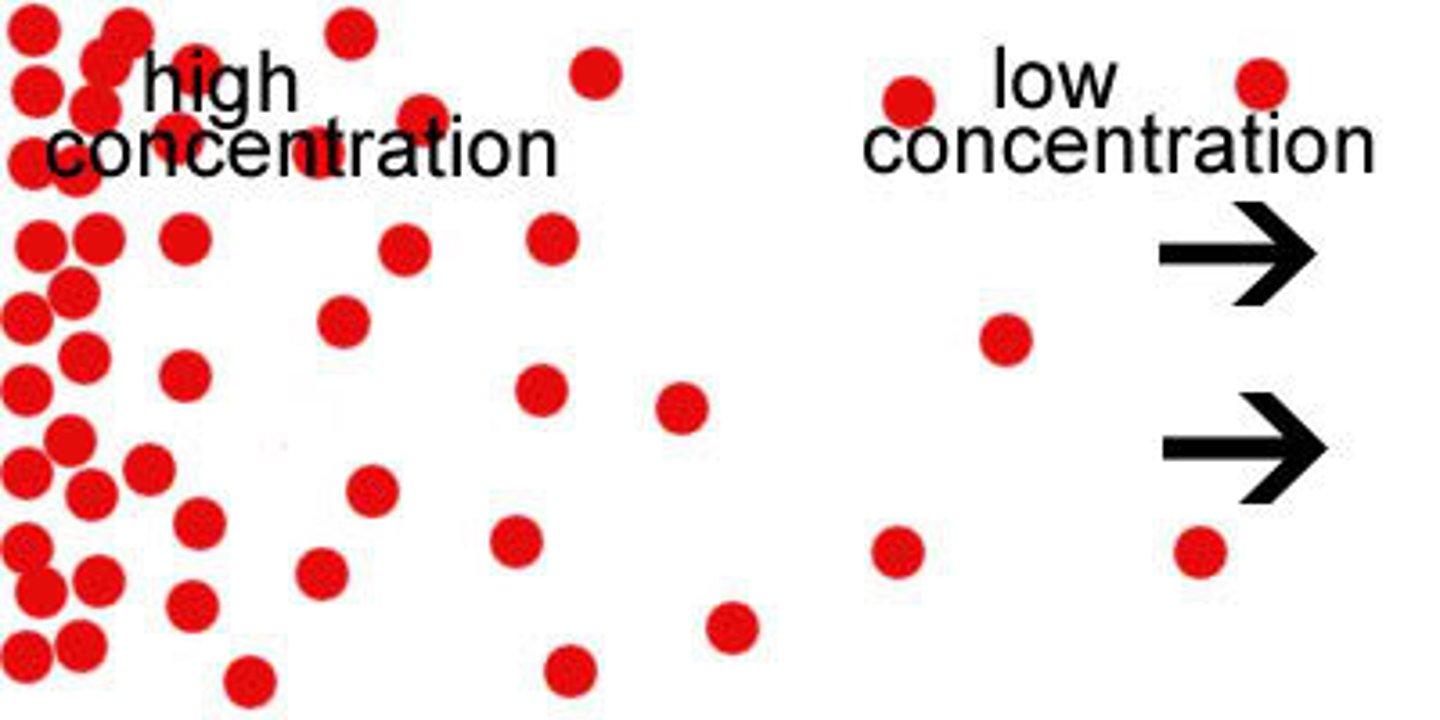
Diffusion
the process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Osmosis
Diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane
Net movement
Molecules moving from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration
Equilibrium
A state of balance (even)
Molecule of interest
When more than one atom, particle, or molecule is diffusing at the same time, but we are only concerned about or only focused on the movement of one of those
Solvent
In a solution, the substance in which the solute dissolves. (Water)
Solutes
Substance dissolved in a solution (Other atoms or molecules)
Solution
A mixture that forms when one substance dissolves another.
Dissolve
the process that takes a place when a solvent is mixed with at solute to make a solution.
Biological membranes
semi-permeable membranes that help maintain homeostasis in the cell
Semi-permeable
Membranes that allow some substances through but not others
What is Science?
A way of thinking, using a systematic method of studying the natural world
What is Biology?
The scientific study of living organisms and biological knowledge (facts and theories)
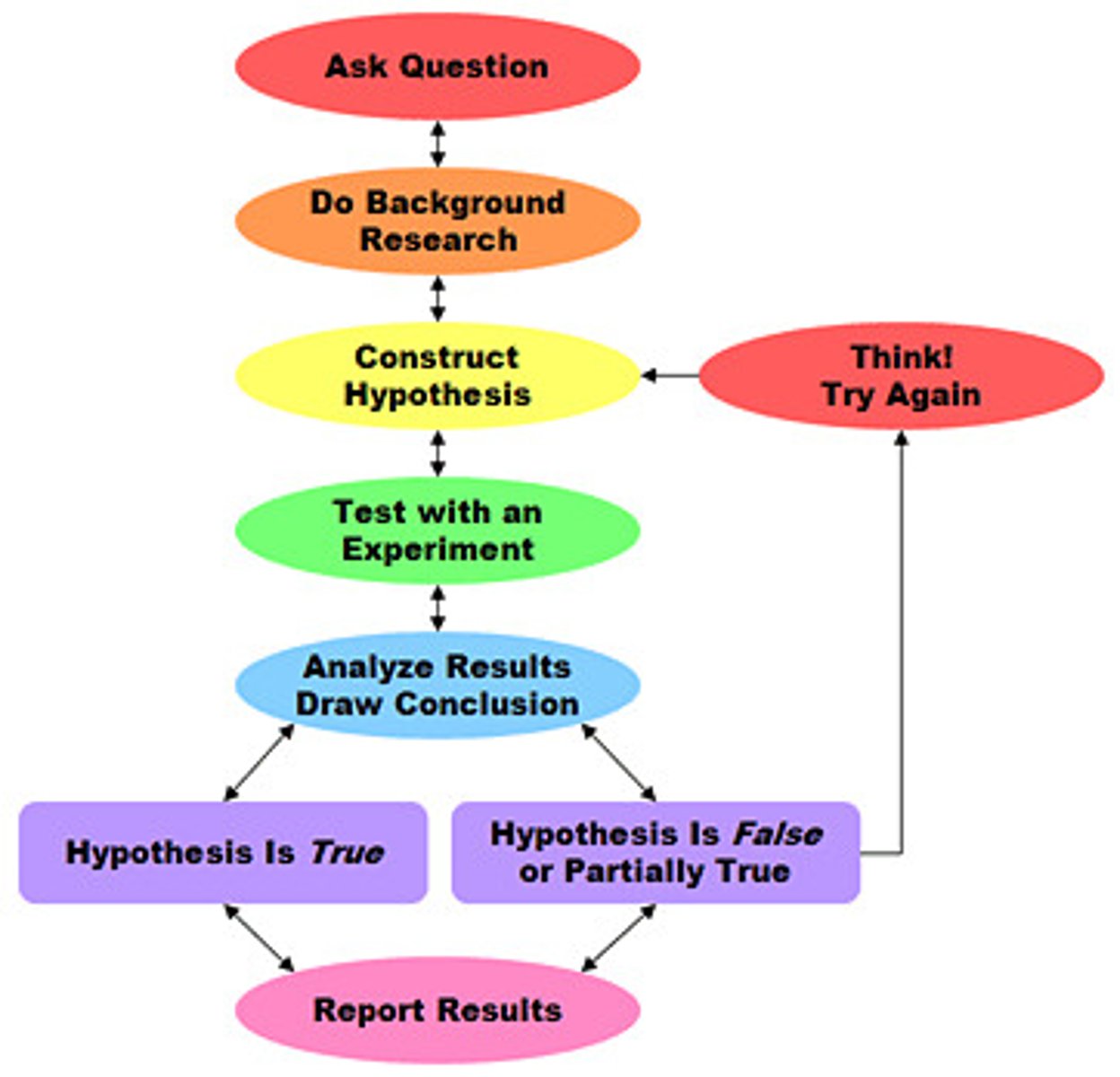
What is the Scientific Method?
A logical, systematic approach to the solution of a scientific problem through testing ideas
Qualitative Observation
An observation that is described using your 5 senses.

Quantitative Observation
An observation that is measurable such as amount, height, length, weight etc.

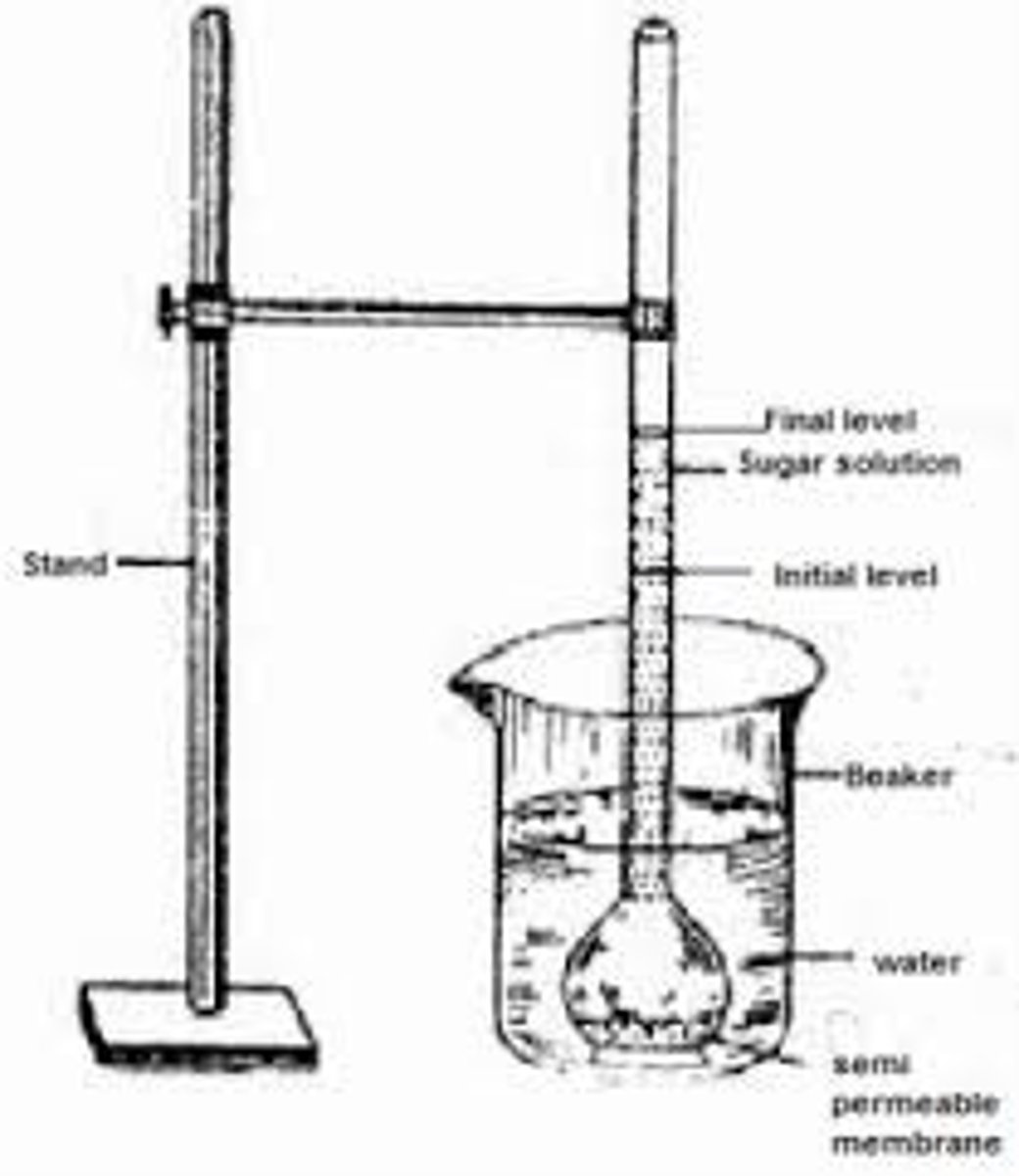
Osmometer
A scientific instrument consisting of a hollow glass tube with a bulbous base that is used for measuring osmotic pressure
Dark Karo Syrup
A concentrated sucrose solution

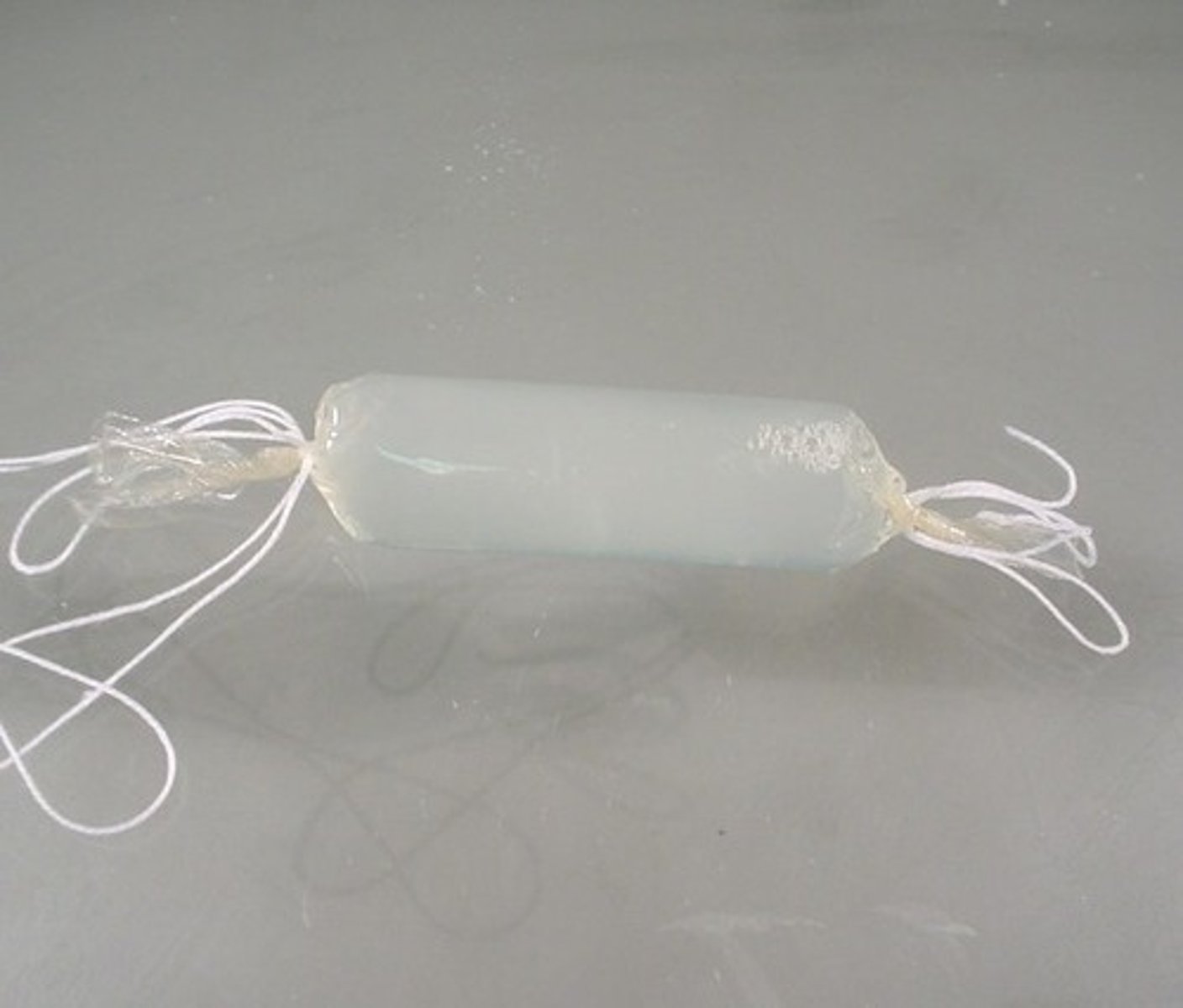
dialysis tubing
tests osmosis using a partially permeable membrane to separate substances

Concentration gradient
difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another
Molecular motion
The motion of the particles and atoms found in matter
Hypothesis
A testbale prediction based on previous knowledge that provides a possible explanation or solution
Null Hypothesis
no difference between groups
Alternate Hypothesis
Hypothesis that the proposed explanation for observations does have an effect
Raw data
The original data as it was collected.
Summary data
descriptive statistics computed from the raw data of an experiment, including the measures of central tendency and variability
control
In an experiment, the standard that is used for comparison
Replicates
multiple subjects that receive either the same experimental treatment or the same control treatment
Data collection
capturing and gathering all data necessary to complete the processing of transactions
Research question
A question that can be answered by an experiment or series of experiments
Constant
A value that does not change
Thermal energy
Heat energy
Hypertonic
when comparing two solutions, the solution with the greater concentration of solutes
Isotonic
when the concentration of two solutions is the same
Hypotonic
Having a lower concentration of solute than another solution
Transpiration
Evaporation of water from the leaves of a plant
Mean
Average
Metabolism
All of the chemical reactions that occur within an organism
Range
the difference between the highest and lowest scores in a distribution
Enzymes
Catalysts for chemical reactions in living things
Digestion
Enzymatic breakdown of a molecule into its smaller subunits, and it occurs in all living organisms.
ATP
(adenosine triphosphate) main energy source that cells use for most of their work
Cellular energy
needed by cells to to work; found in ATP; stored in chemical bonds; released when chemical bonds are broken
Glucose
the form of sugar that circulates in the blood and provides the major source of energy for body tissues
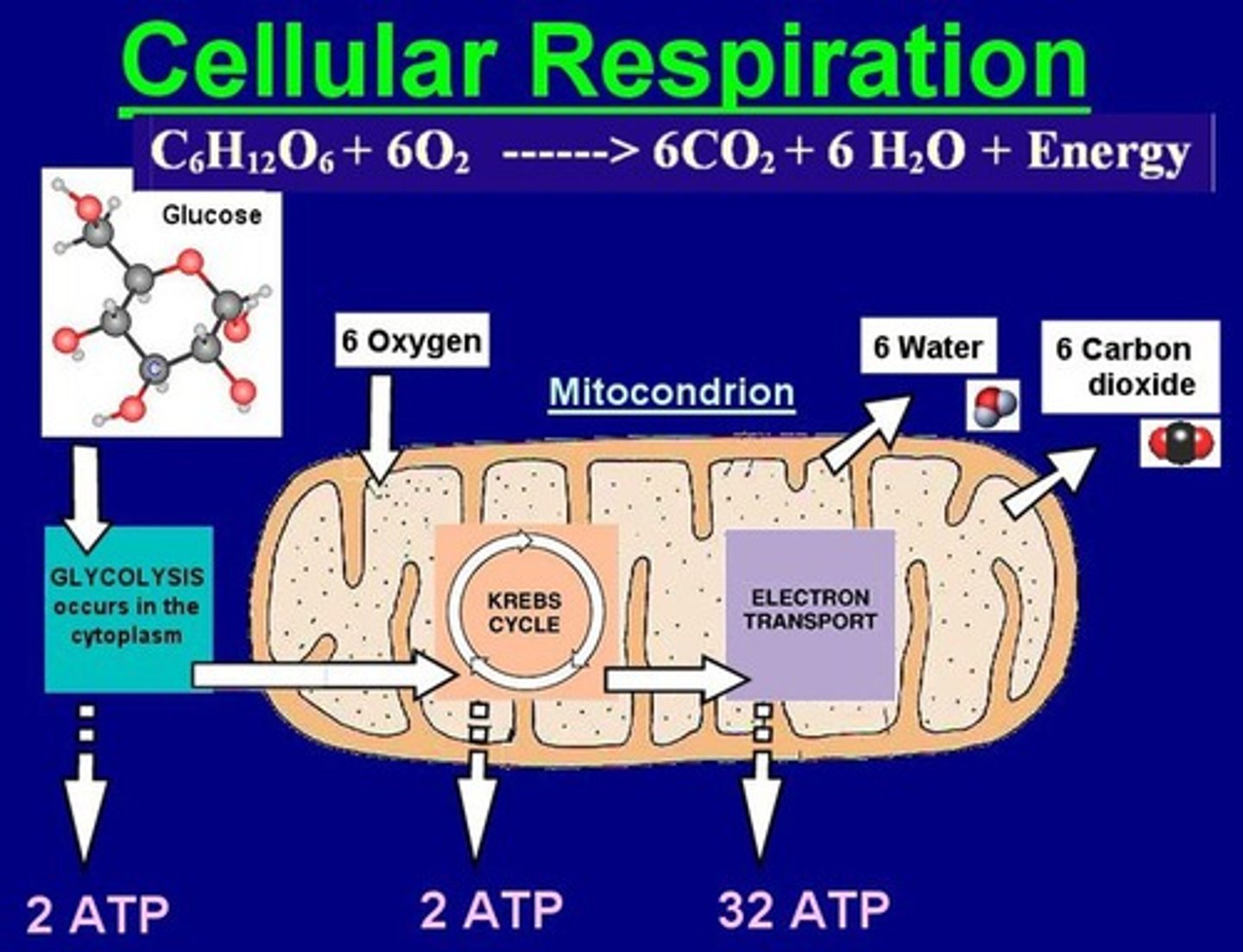
Aerobic cellular respiration
the process by which cells use oxygen to obtain usable energy from an energy source ( Glucose + 6O2 -> 6H2O + ~36ATP )
Glucose
C6H12O6
Alcohol Fermentation Equation
glucose --> ethanol + carbon dioxide + 2 ATP
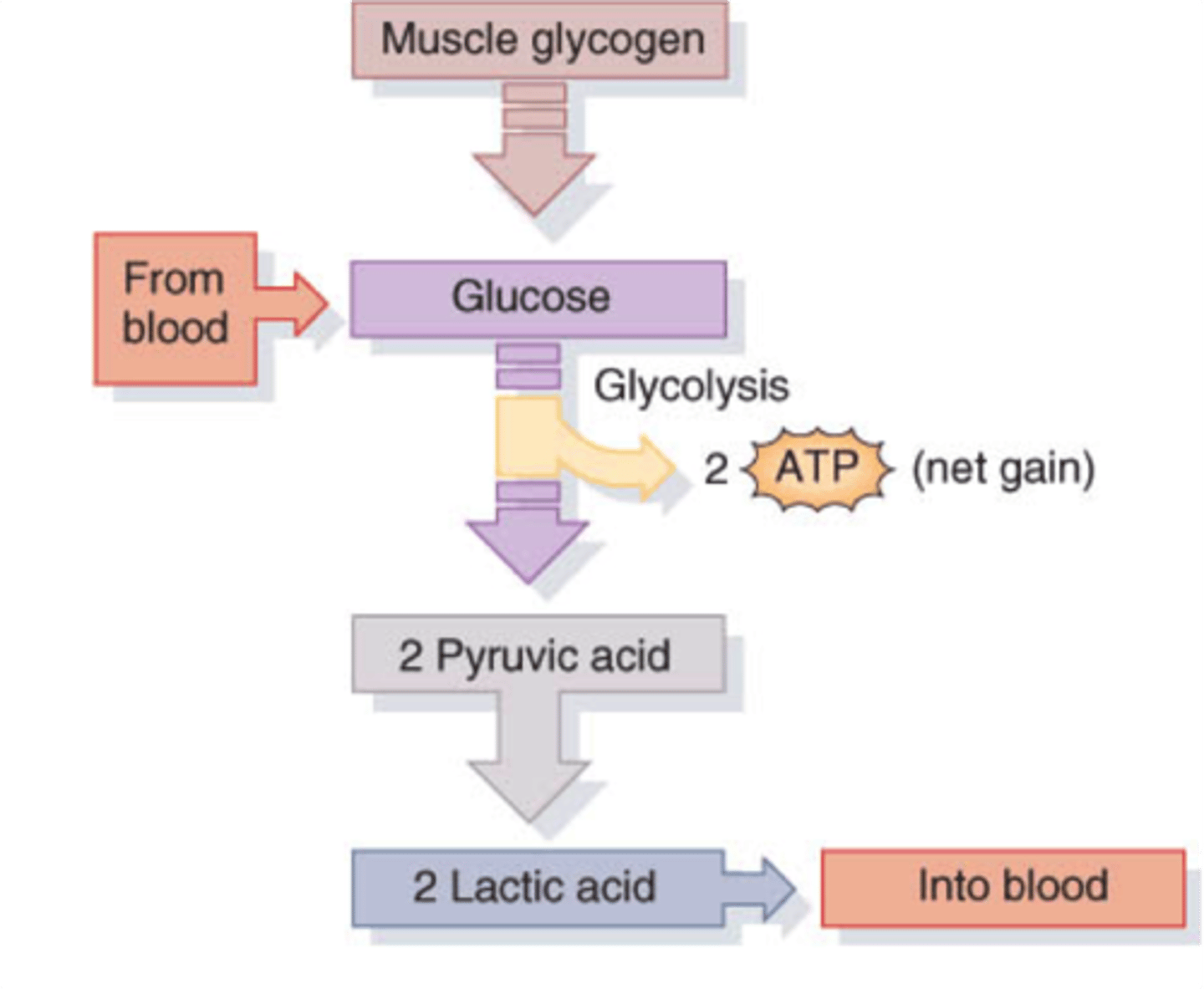
Lactic Acid Fermentation
glucose --> lactic acid + 2 ATP
Sucrose Synthase
Builds sucrose
Sucrase
Breaks down sucrose
Catalysts
Substances that speed up chemical reactions
Lactaid
lactase enzyme

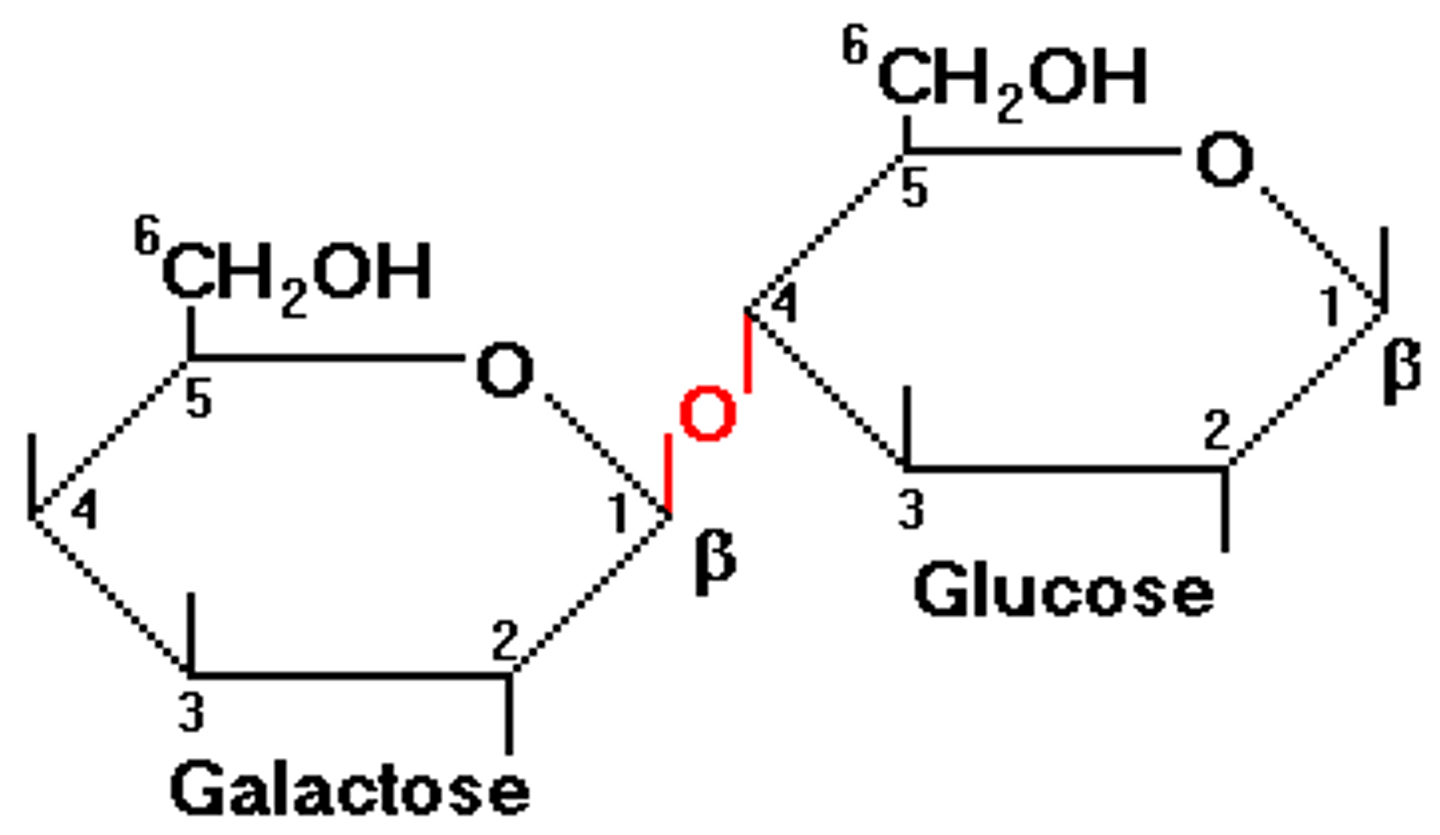
Lactose
glucose + galactose
Indicator
A chemical that changes color in the presence of the substance it reacts with
What do Enzymes do?
1. Aid in digestion
2. Break down fats, proteins, and carbohydrates
------------------------------------
3. Building muscle
4. Nerve function
5. Get rid of toxins
6. Breathing
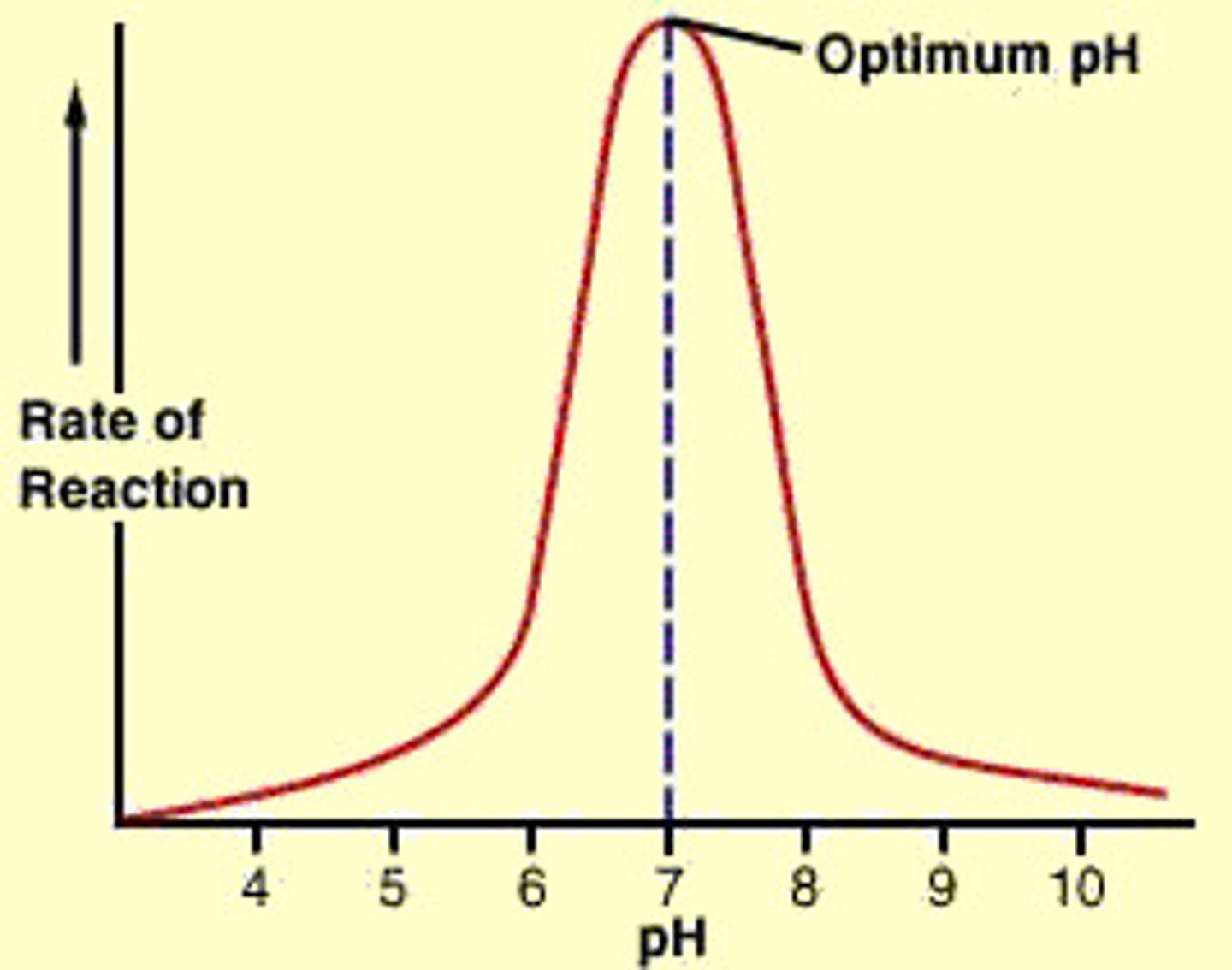
Enzymes & PH level
Enzymes are sensitive to acidity and alkalinity. They don't work properly if an environment is too acidic or basic. For example, an enzyme in the stomach called pepsin breaks down proteins. If your stomach doesn't have enough acid, pepsin can't function optimally
Enzymes & Temperature
Enzymes work best when your body temperature is normal, about 98.6°F (37°C). As temperature increases, enzyme reactions increase. But if the temperature gets too high, the enzyme stops working. That's why a high fever can disrupt bodily functions.
Final products of alcohol fermentation
Ethanol, CO2, and ATP
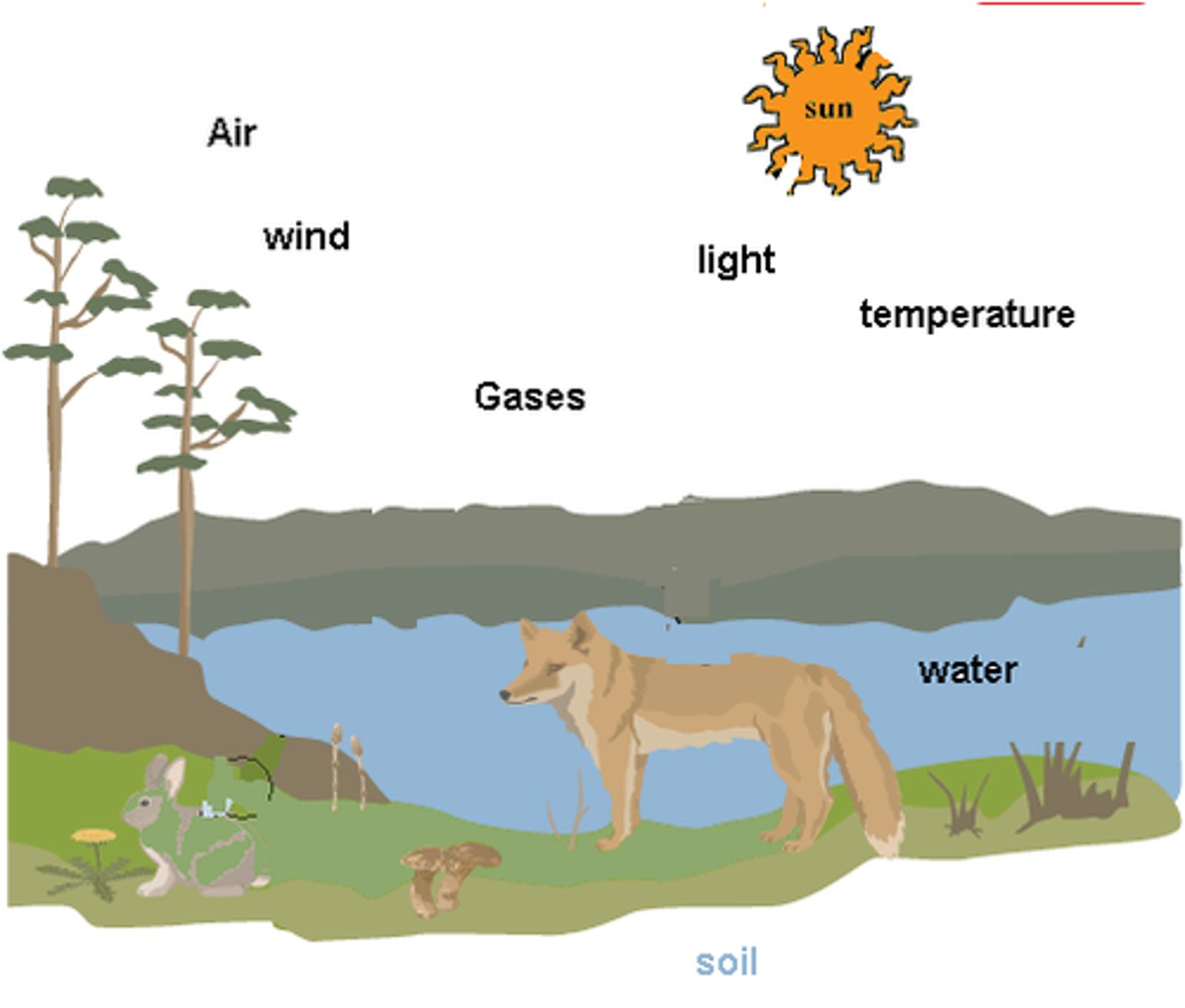
Abiotic factors
Nonliving components of environment.
Anaerobic cellular respiration
the process by which cells obtain energy from an energy source without using oxygen
Respiration
The chemical process organisms use to release the energy from food, which typically involves the consumption of oxygen and the release of carbon dioxide.
Photosynthesis and Respiration
Respiration releases energy, making it the chemical reverse of photosynthesis. Photosynthesis and respiration are also connected ecologically because the vast majority of organisms use the oxygen produced by photosynthesis for respiration.
Anaerobic cellular respiration is done by who/what?
Some bacteria and archaea
Fermentation
Fermentation is a anaerobic (non-oxygen-requiring) pathway for breaking down glucose, one that's performed by many types of organisms and cells
PRACTICE: Why would a snake not survive in the Himalayas?
imagine that someone picks up one of these desert-adapted snakes and places it on a snowy peak in the Himalayas. The Himalayas lack the abiotic factors—like an arid climate and loose soil—that the snake is adapted to, and the snake likely will not be able to survive.

Positive reaction
Turns blue-black in the presence of starch (ex: sucrose)
Negative reaction
Remains amber brown (ex: water)

Equation for aerobic cellular respiration
Glucose + 6 O2 → 6 CO2 + 6 H2O + ~ 36 ATP

Yeast
eukaryotic unicellular fungi
Why do some organisms make starch?
Serves as a stored energy source, to be digested into glucose later
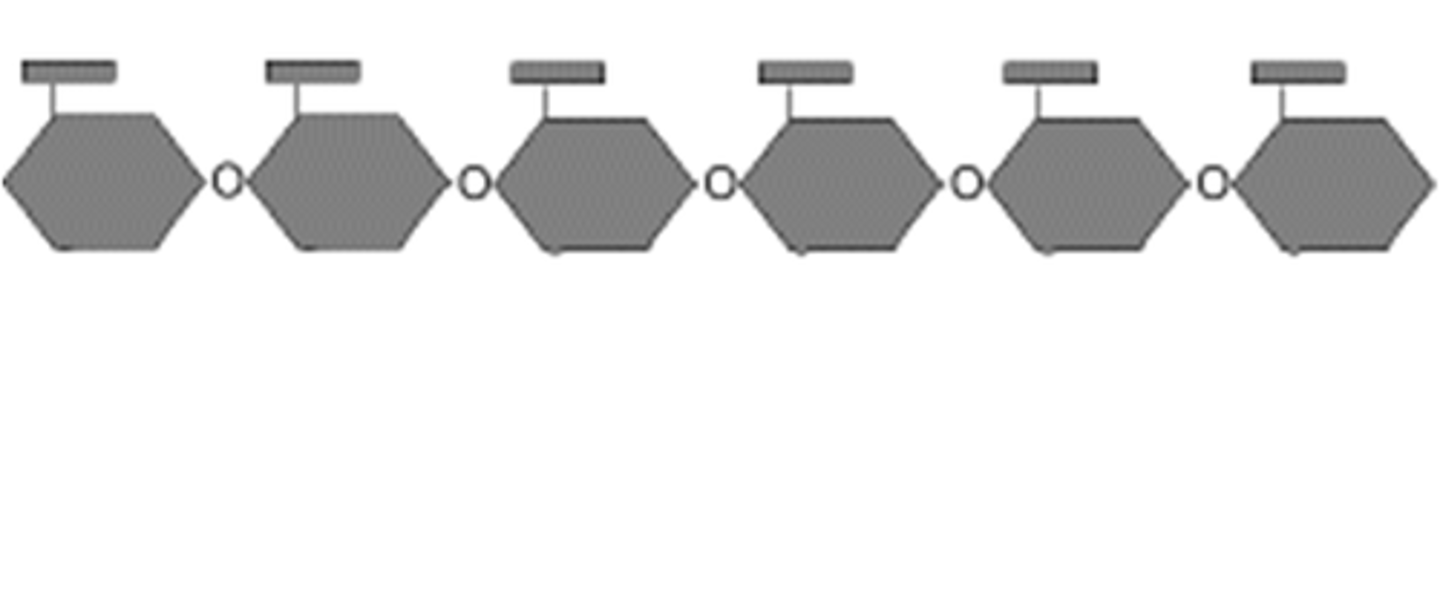
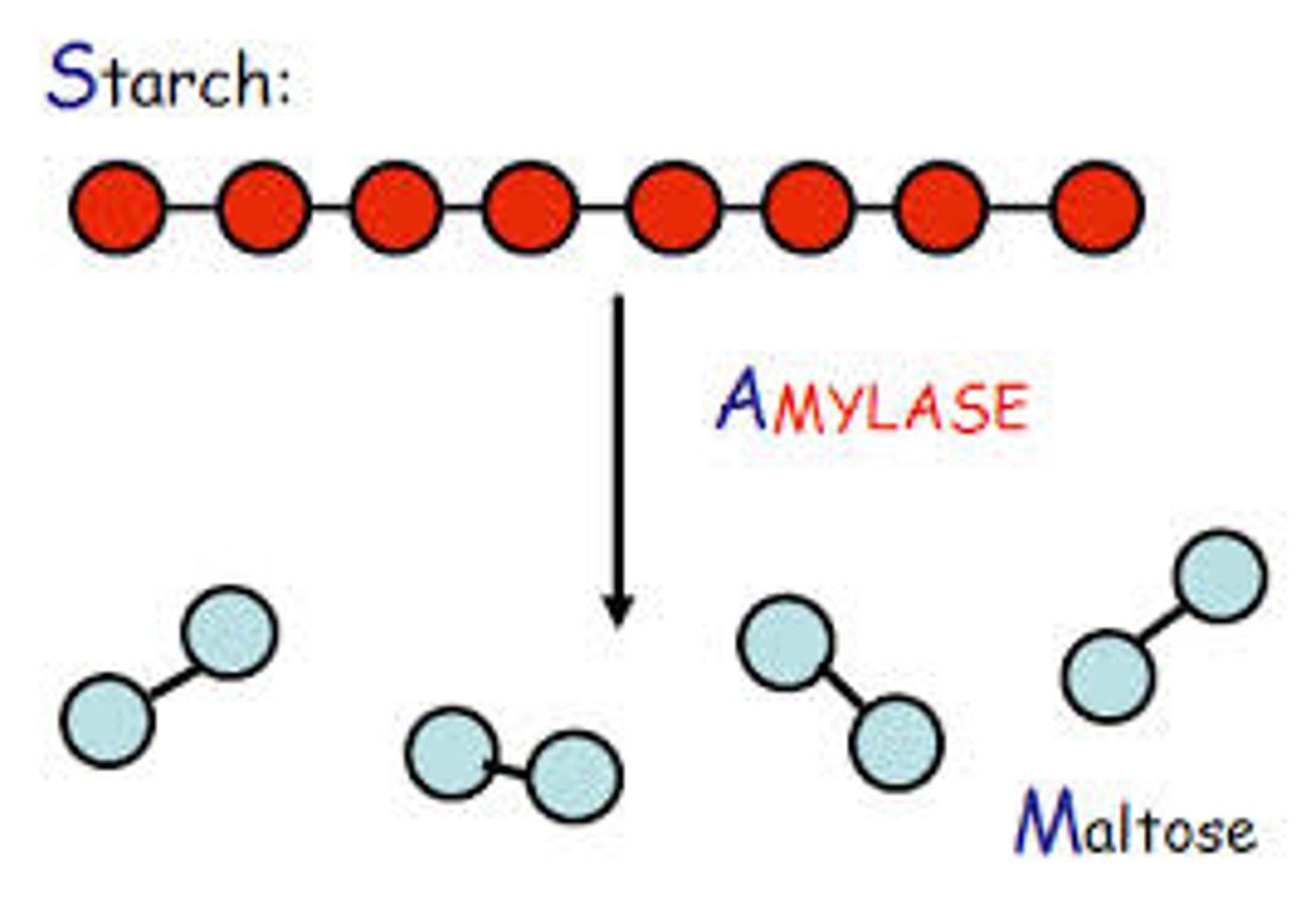
Amylase
An enzyme that digests starch (a polysaccharide or complex carbohydrate) down into simple sugars such as glucose &/or maltose
Why are replicates important?
Important to account for variation among organisms and to ensure accuracy

Week 7: Fermentation Lab
1. What were the independent variables
The different sugar sources (+ H2O)
Week 7: Fermentation Lab
2. What were the dependent variables
Height of CO2 (mm of gas produced)
Week 7: Fermentation Lab
3. Constants in this experiment (name at least 3)
1. Temperature
2. Amount of yeast
3. Amount of sugar
4. Species of yeast
5. Same size fermentation tubes
Same kind of water in solutions
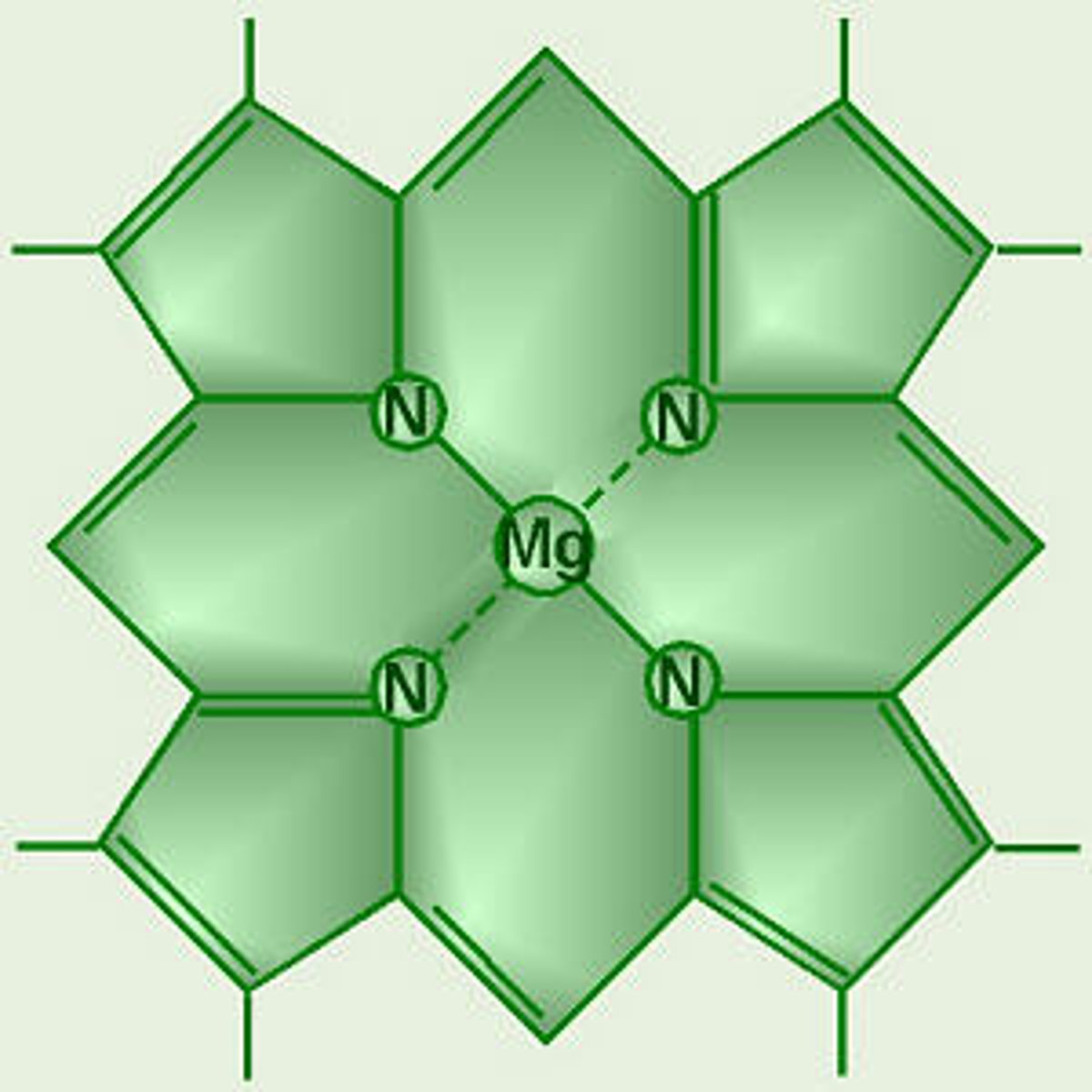
Pigment
A colored chemical compound that absorbs light, producing color.

Chlorophyll
A green pigment found in the chloroplasts of plants, algae, and some bacteria
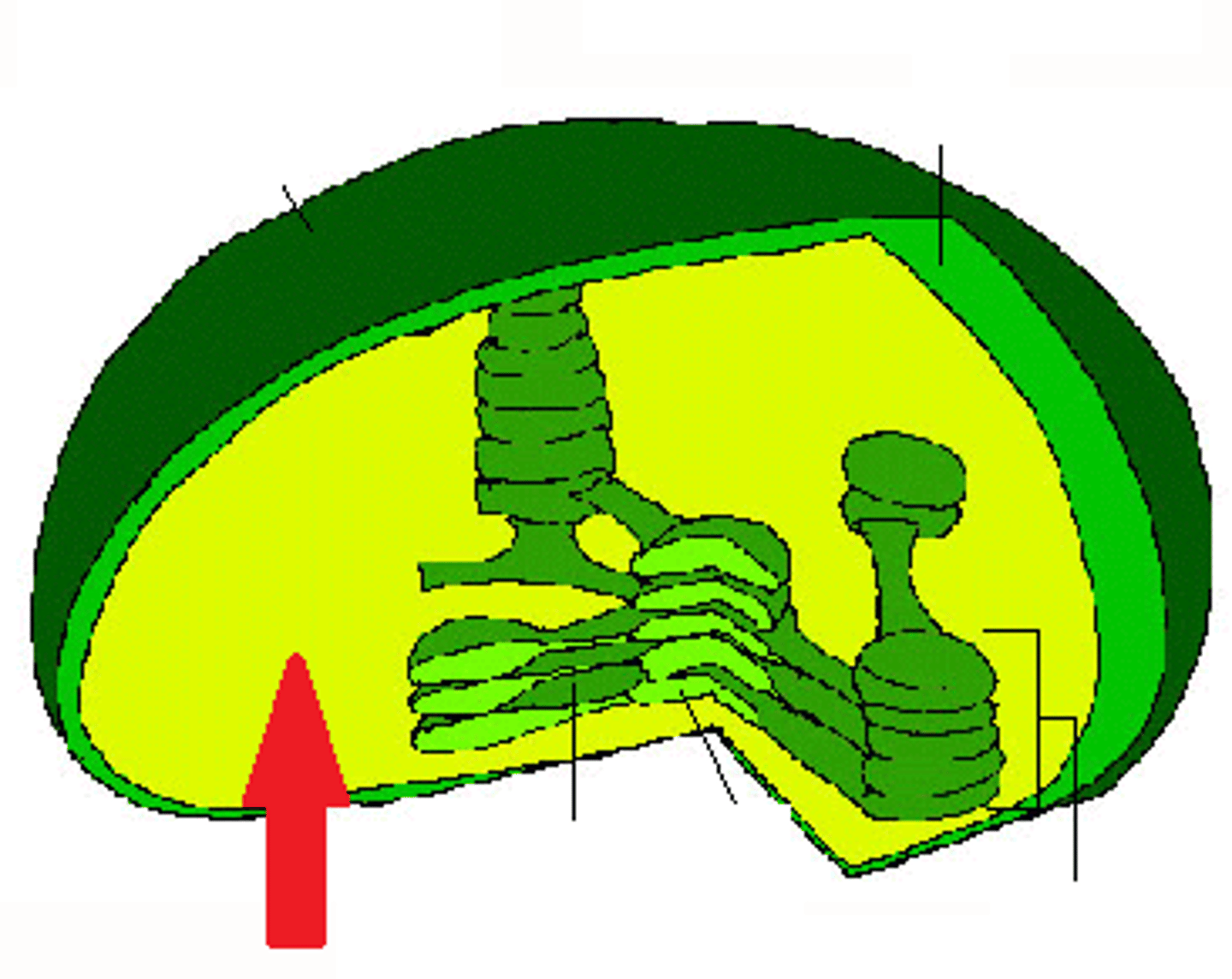
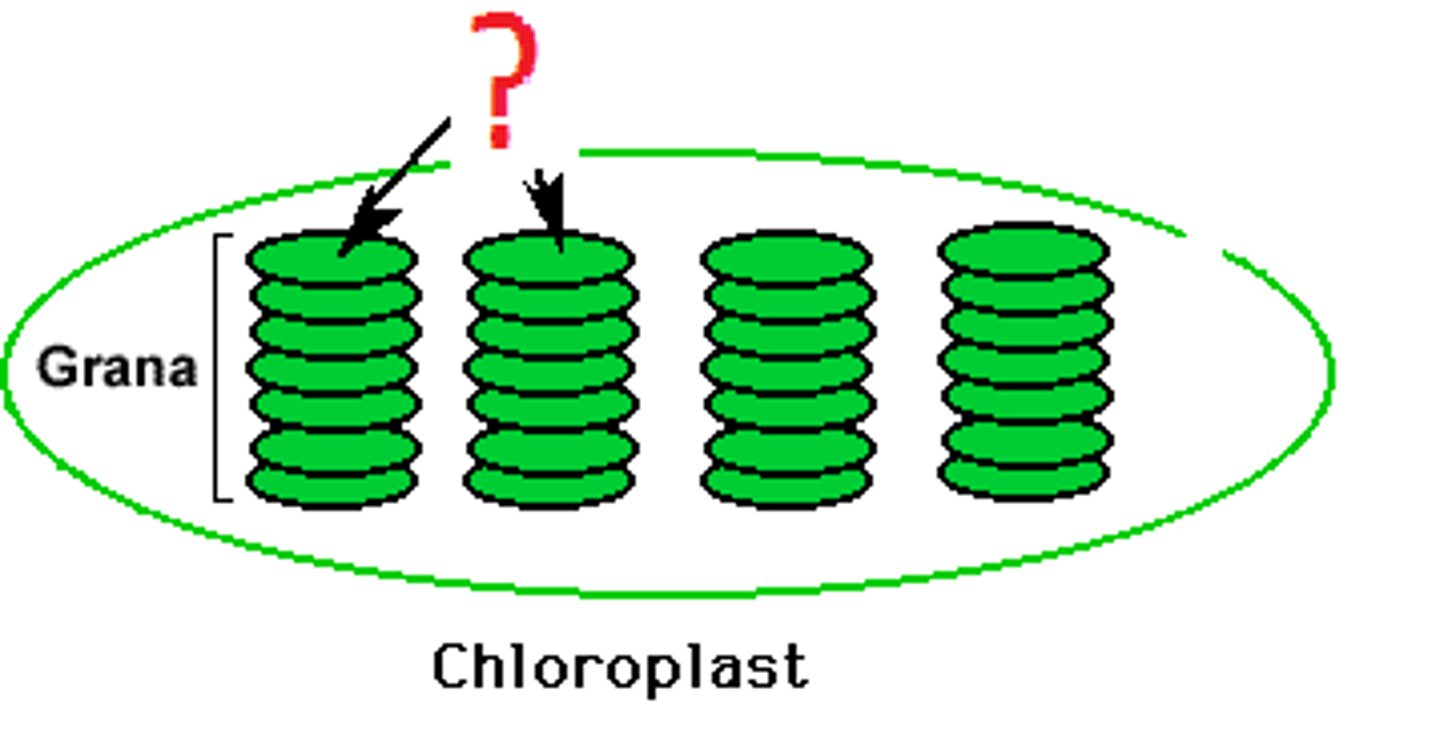
Stroma
fluid portion of the chloroplast; outside of the thylakoids
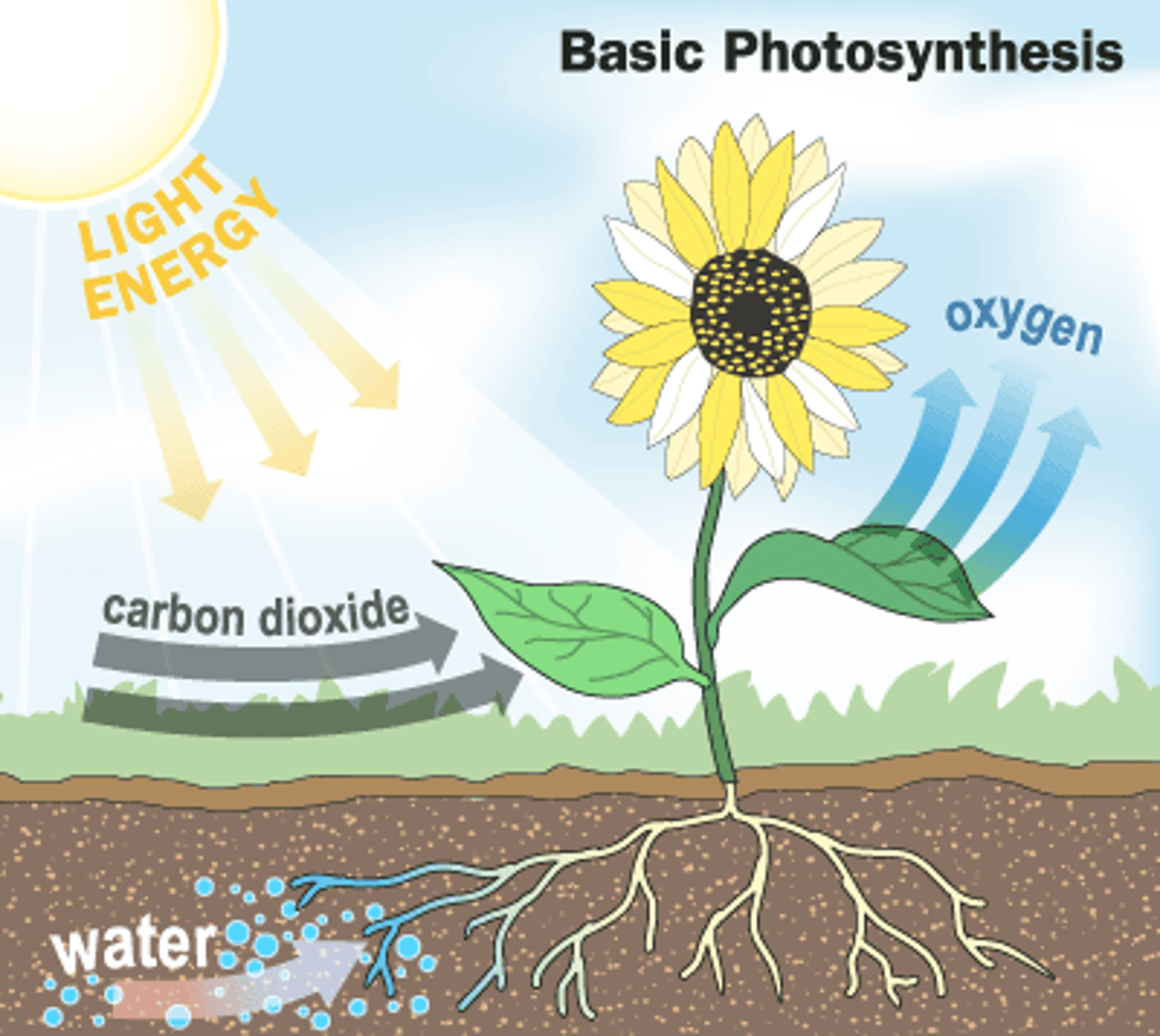
Photosynthesis equation
6CO2 + 6H2O + light energy --> C6H12O6 + 6O2
Thylakoid
A membrane system found within chloroplasts that contains the components for photosynthesis
Absorption spectrum
The range of a pigment's ability to absorb various wavelengths of light.
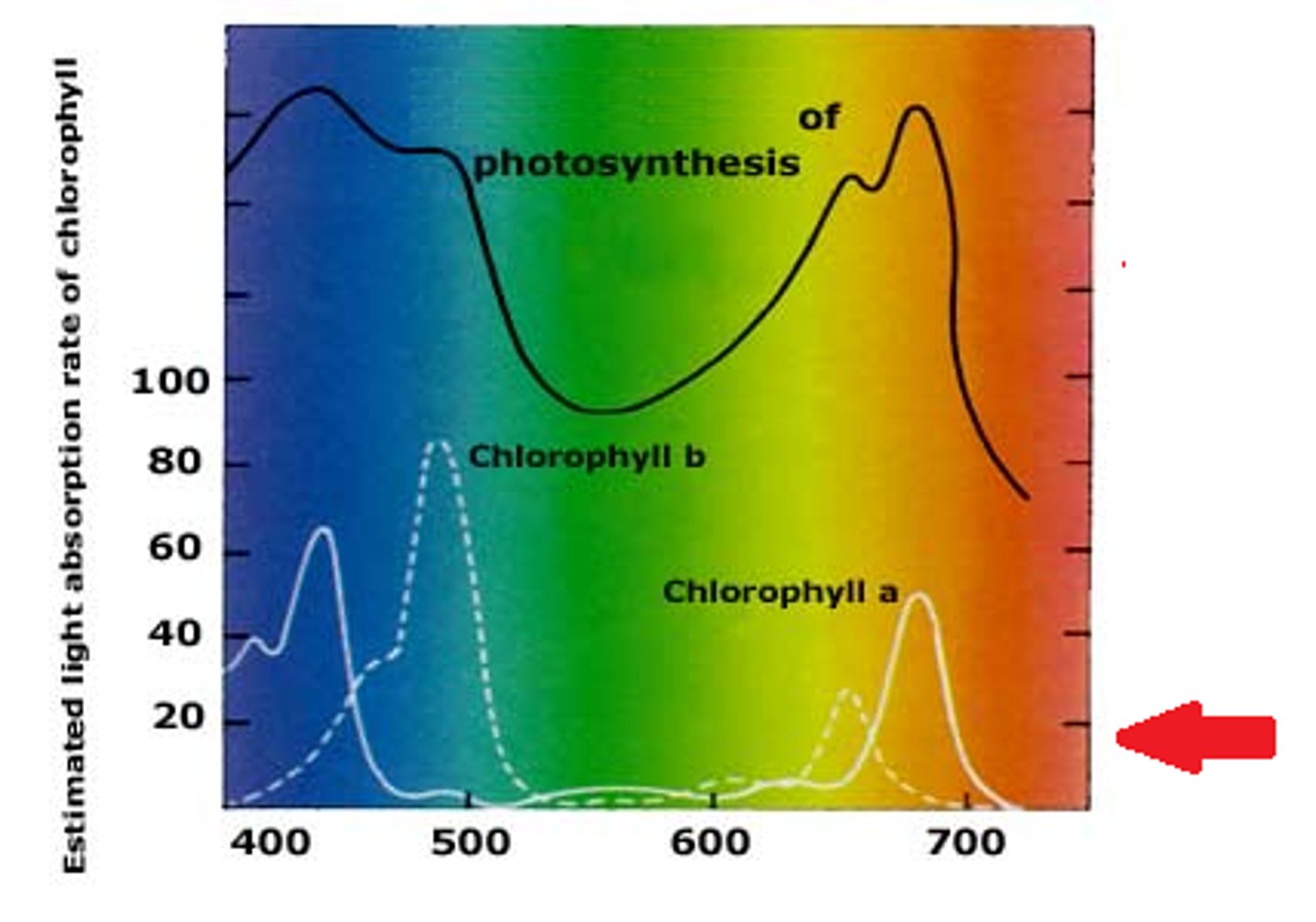
Chlorophyll a
primary pigment, involved in the light reactions, blue/green pigment
Chlorophyll b
accessory pigment that absorbs blue and red-orange light and consequently has a yellowish-green tint
chromatography paper
an absorbent paper that will take in the non polar solvent and it's dissolved pigments
What do enzymes do?
speed up chemical reactions by lowering activation energy
How do enzymes help in digestion?
Enzymes cut proteins into amino acids that the body can use.
What are some Metabolic enzymes functions?
1. Proteolysis
2. Digestion
3. Cellular respiration
4. Energy storage
5. Transcription
6. Respond to the environment.
Abiotic variables examples
1. Temperature
2. lighting
3. precipitation
4. timing
5. evolution
6. species interactions
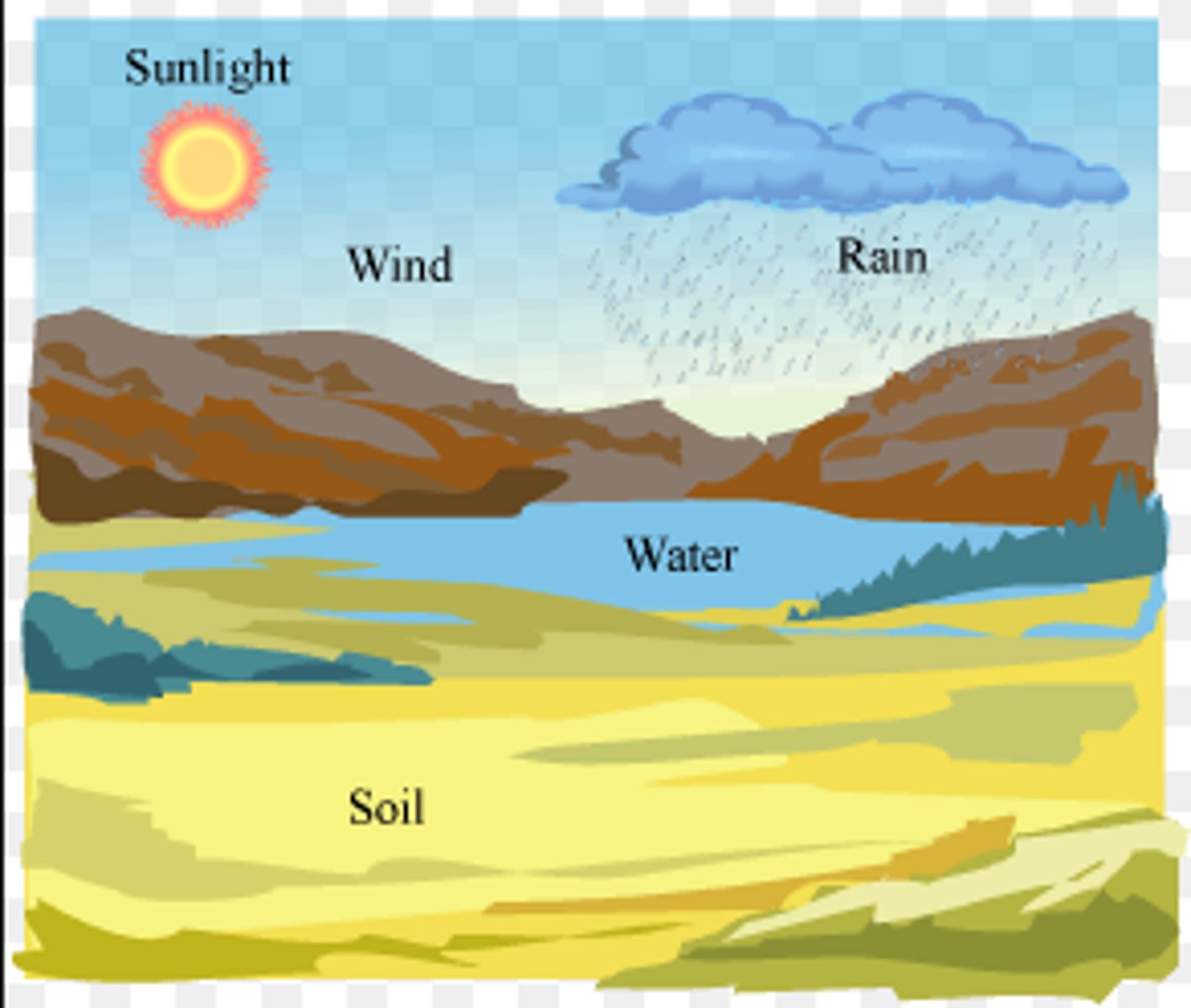
How do abiotic factors influence ecosystems?
Abiotic factors influence the types of species that can occupy an ecosystem and certain abiotic environmental factors can affect the chemical reactions of respiration, including the availability of oxygen and nutrients.
Similarities between photosynthesis and aerobic cellular respiration?
1. Membranes
2. Phosphorylation
3. ATP Synthase
4. Redox reaction
5. Electron Transport Chain
Aerobic cellular respiration differences (compared to Photosyn.)
1. Mitochondria in Eukaryotes
2. All living organisms
3. Requires carbohydrates
4. Catabolic
Photosynthesis differences (compared to ACR)
1. Chloroplasts in Eukaryotes
2. Photoautotrophs only
3. Photophosphorylation
4. Photolysis
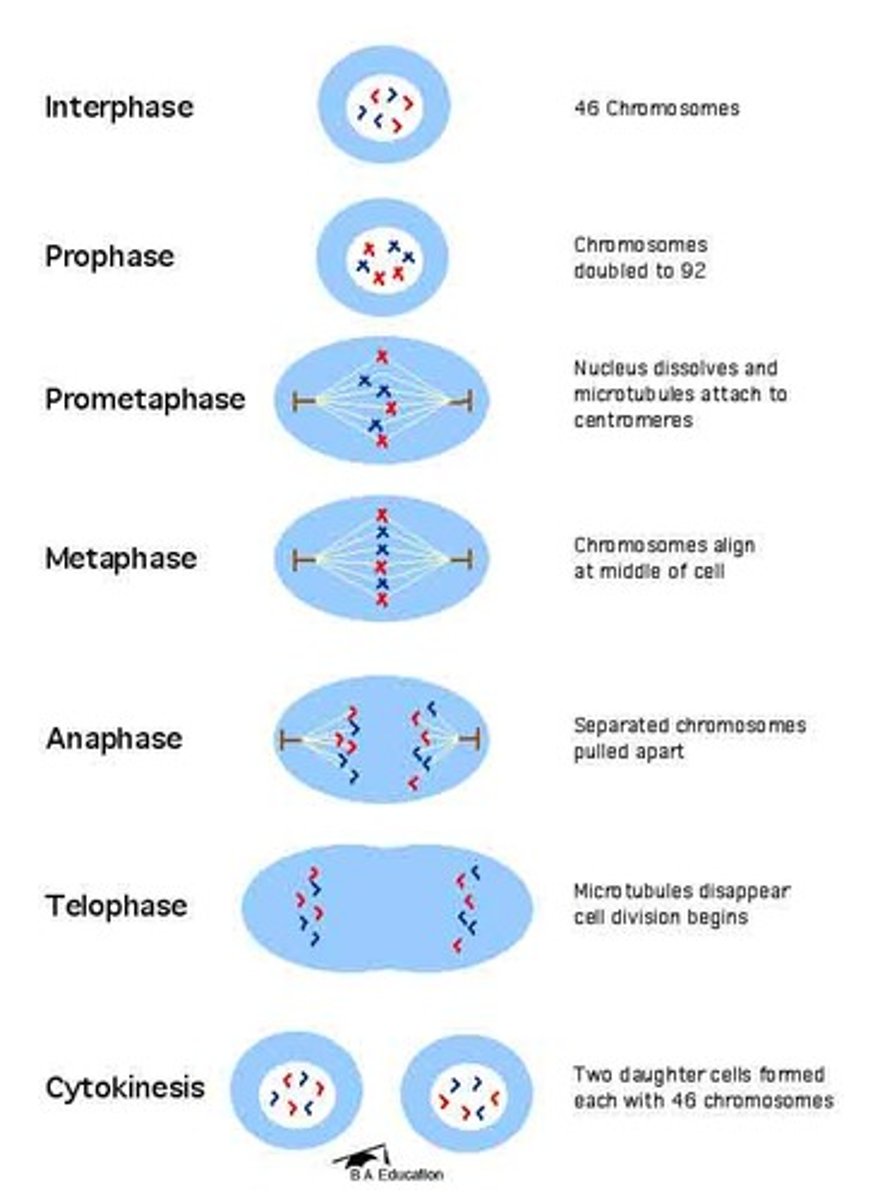
Dividing eukaryotic cell cycle:
1. Interphase
2. Nuclear Division
3. Cytokinesis
Mitotic cell division
One parent cell divides into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to each other with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
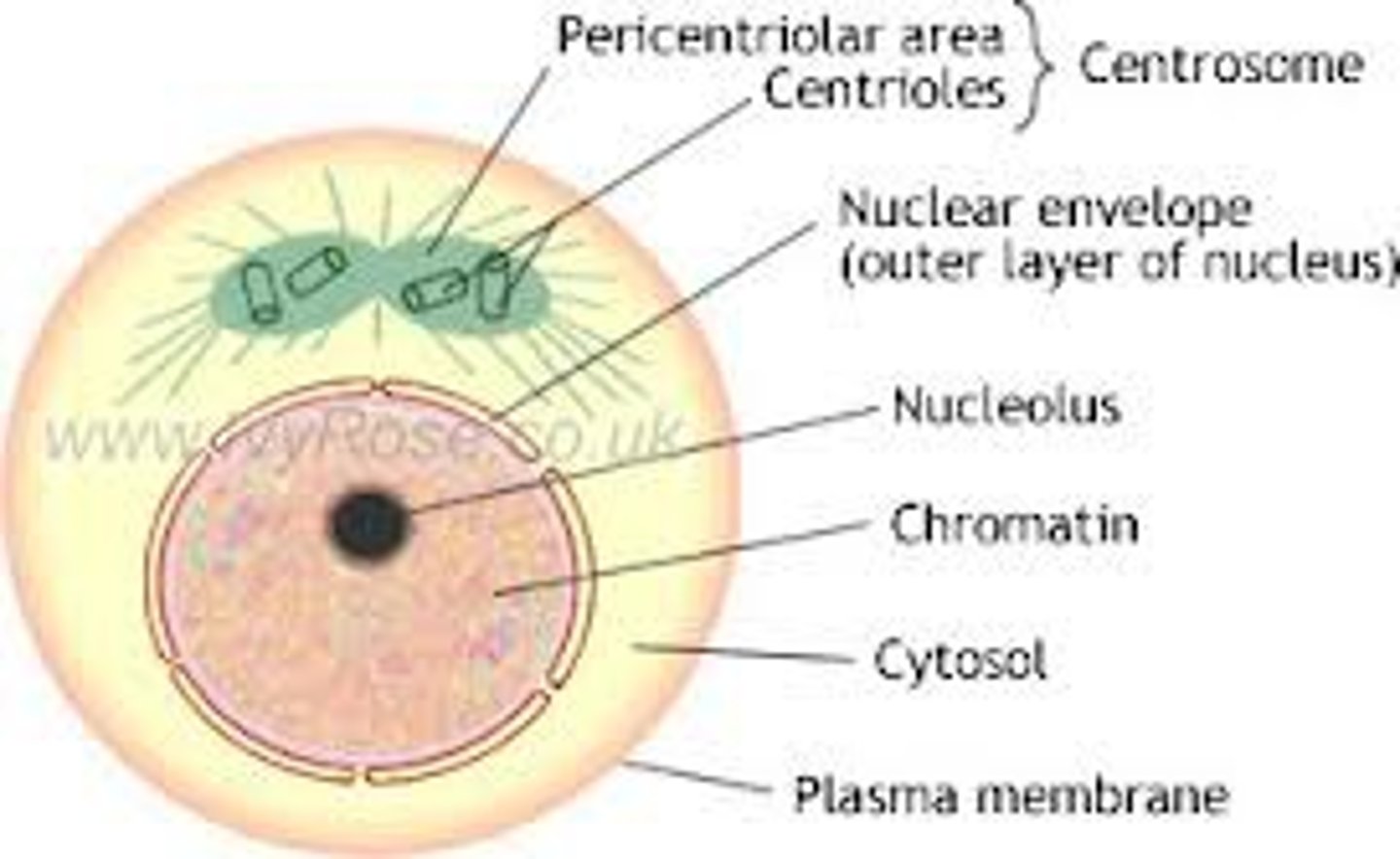
Interphase
Period of the cell cycle between cell divisions
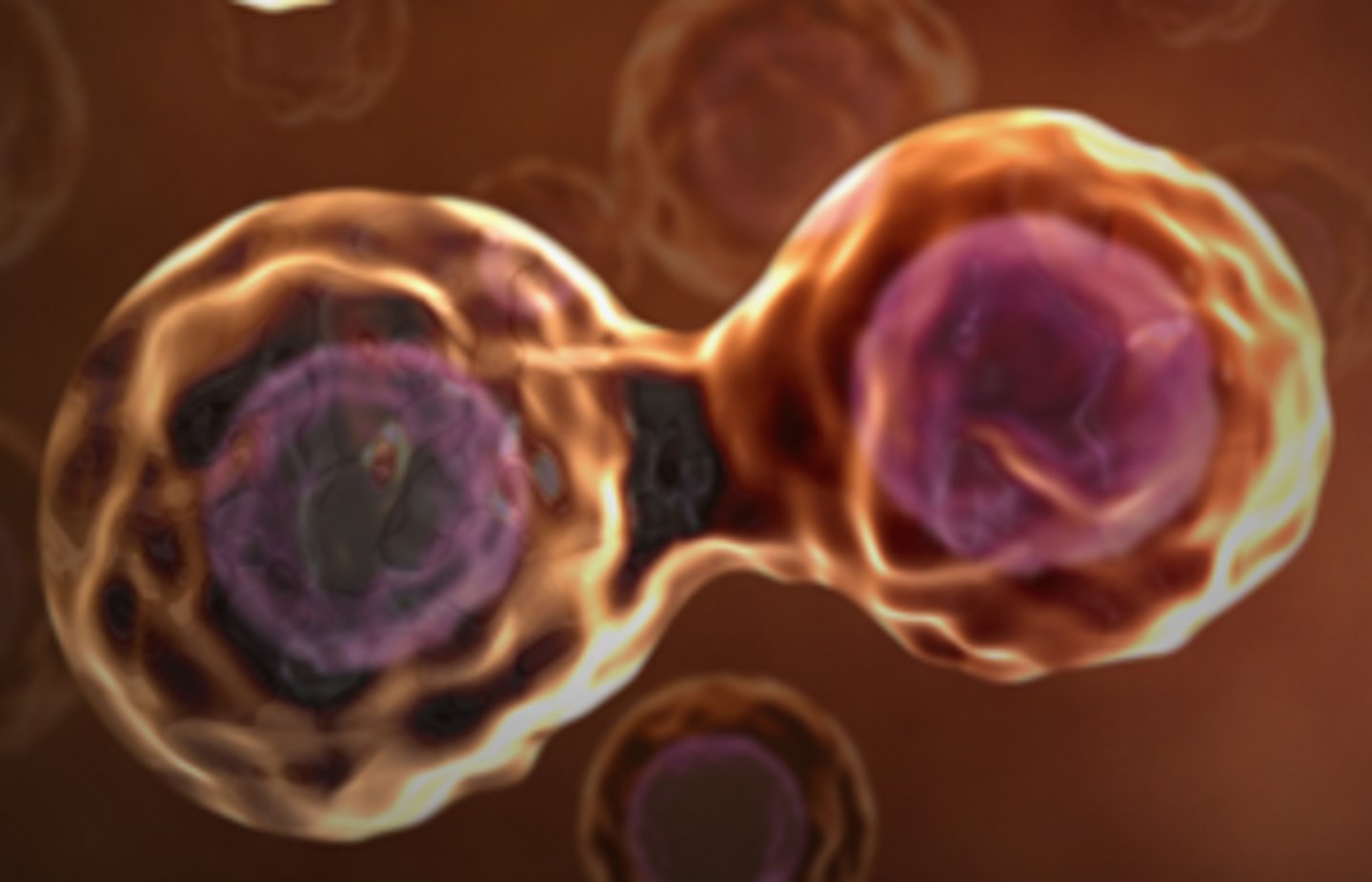
Cell division
Process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
Mitosis vs. Meiosis
Mitosis: one division forming 2 identical cells (clones)
Meiosis: two divisions forming 4 genetically different cells