NUR 317 Exam 3 - Coronary Artery Disease and Acute Coronary Syndrome
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Cardiovascular disease is the __ cause of death in the United States
#1 (leading)
Coronary artery disease (CAD)
Most common CVD
Asymptomatic CAD
Chronic stable angina (chest pain)
Acture coronary syndrome (ACS)
Unstable angina (UA) or myocardial infarction (MI)
Atherosclerosis
“Hardening of arteries”
Begins as soft deposits of fat that harden with age
Major cause of CAD
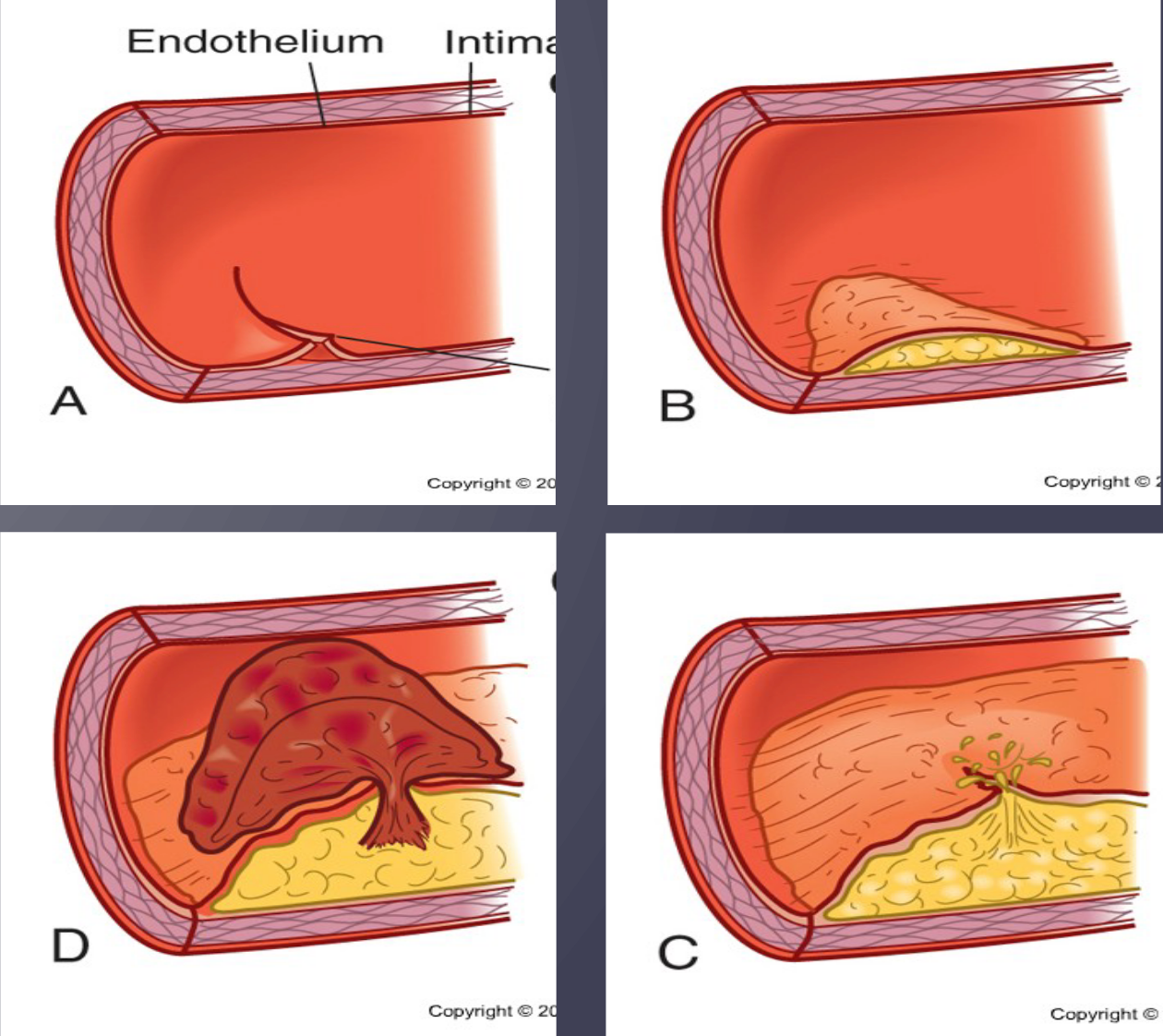
Atherosclerosis endothelium
Intact endothelium is normally nonreactive
Damage causes localized inflammatory response
C-reactive protein (CRP)
Nonspecific marker of inflammation
Increased in many patients with CAD
Chronic exposure to CRP triggers the rupture of plaques
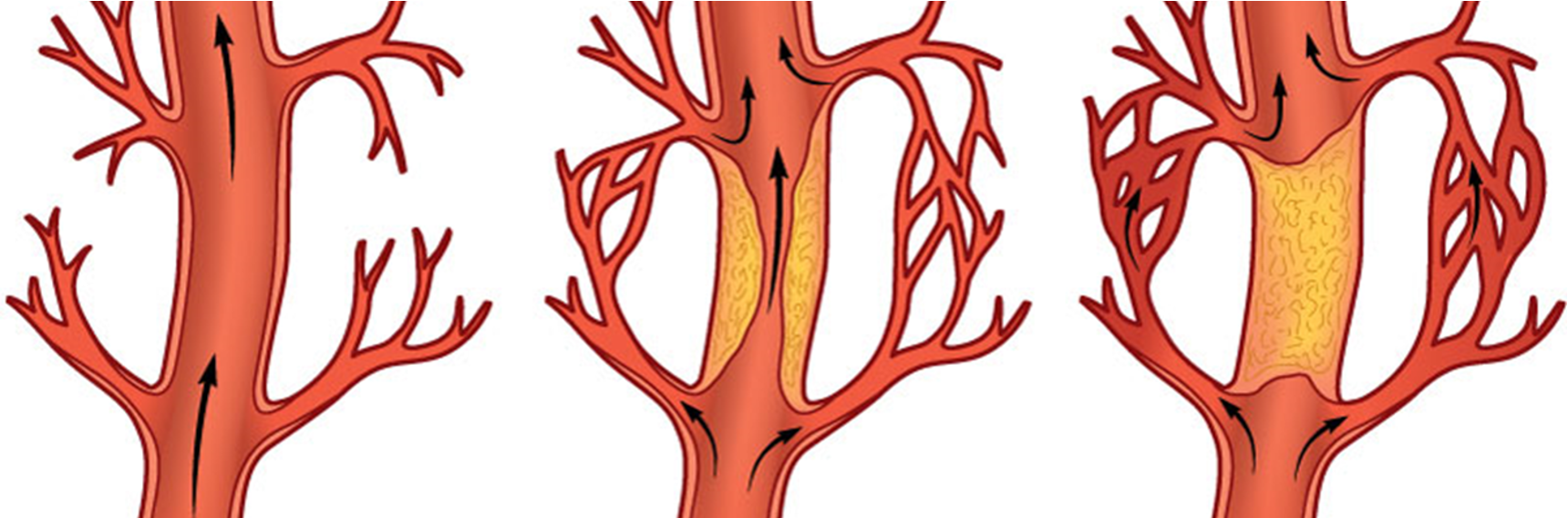
Collateral circulation
A network of small blood vessels that develop in response to a blockage or narrowing (stenosis) of a larger artery or vein
These vessels provide an alternative pathway for blood to flow, bypassing the obstruction and delivering oxygen and nutrients to the affected tissues
Coronary artery disease non-modifable risk factors
Age
Gender
Ethnicity
Family history
Genetic predisposition
Coronary artery disease modifable risk factors
Elevated serum lipids
Elevated BP
Tobacco use
Physical inactivity
Obesity
Diabetes
Metabolic syndrome
Psychologic states
Elevated homocysteine level
Substance use
Elevated serum lipids - risk factors for coronary artery disease
Cholesterol >200 mg/dL
Triglycerides >150 mg/dL
HDL <40 mg/dL
LDL >130 mg/dL
Promoting health equity
Ethnic consideration
White males: highest mortality from CAD
Native Americans: die earlier than expected
Gerontology Consideration
Assess for readiness for enhanced learning
Symptoms are determined to be a result of CAD not “normal aging”
Need to modify guidelines for physical activity
Cardiac primary prevention: nutritional therapy
Goal: lower LDL cholesterol
Decrease saturated fat and cholesterol
Increase complex carbohydrates and fiber
Increase intake of Omega-3 fatty acids
Limit alcohol use
Limit red meats, full-fat dairy, processed foods
Cardiac primary prevention: activity
Goal: get moving
Track activity
30 minutes at least 5 days per week
Increase weight training (2 days a week)
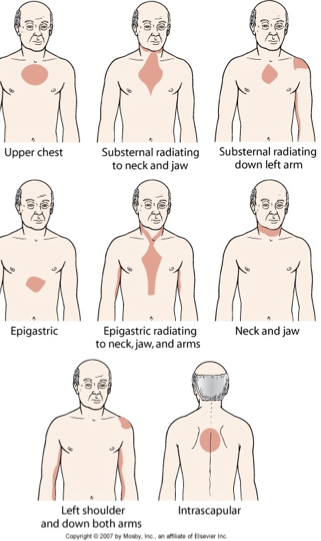
Chronic stable angina
Angina is the clinical manifestation of reversible cardiac ischemia
Characteristics
Chest pain that occurs intermittently over long period of time
Same pattern of onset, duration and intensity
Pain at rest is unusual
Diagnostic studies
Chest x-ray
12-lead ECG
Laboratory studies
Echocardiogram
Exercise stress test
Coronary CT angiography
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization
Cardiac catheterization - “gold standard” to identify and localize CAD
Visualize blockages (diagnostic)
Open blockages (interventional)
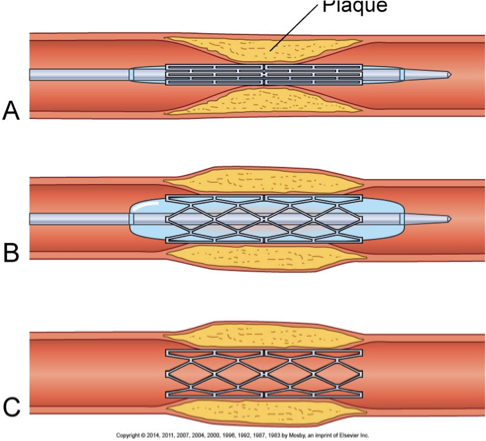
Percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
Balloon angioplasty
Acute coronary syndrome
A medical emergency caused by a sudden decrease in blood flow to the heart muscle
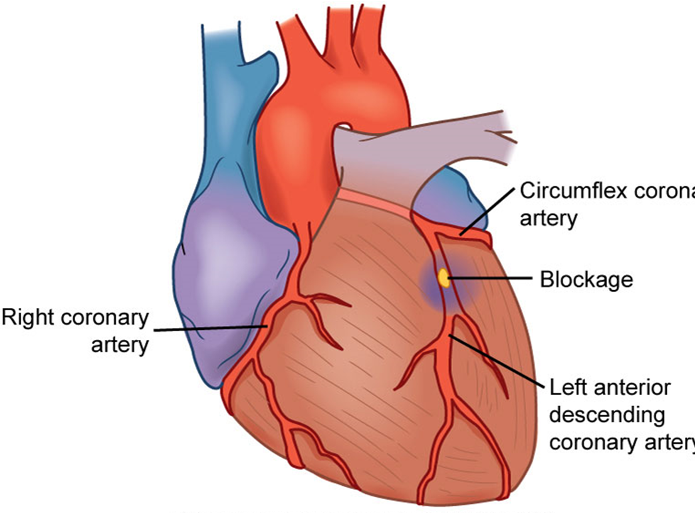
Acute coronary syndrome etiology
Deterioration of once stable plaque
Rupture
Platelet aggregation
Thrombus
Partial occlusion of coronary artery
Unstable angina or NSTEMI
Total occlusion of coronary artery
STEMI
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina
New in onset
Occurs at rest
Increase in frequency, duration, or with less effort
Pain last > 10 minures
Needs immediate treatment
Symptoms in women often under-recognized
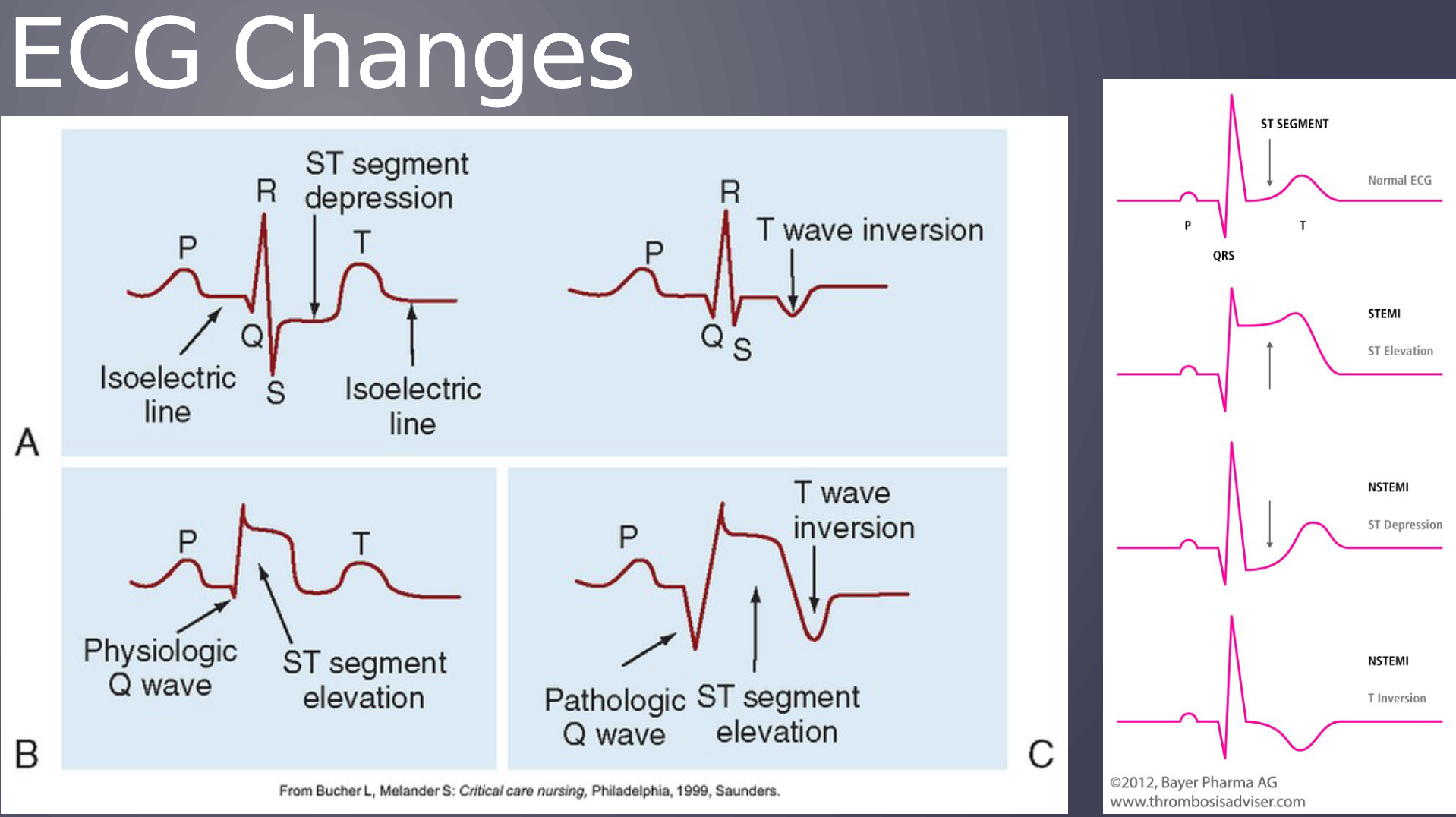
ECG changes
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina - pain
Severe chest pain not relieved by rest, position change, or nitrate administration
Often occurs in early morning
Atypical in women, elderly
No pain if cardiac neuropathy (diabetes)
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina - sympathetic nervous system stimulation
Release of catecholamines
Diaphoresis
Increased HR and BP
Vasoconstriction of peripheral blood vessels
Skin: ashen, clammy, and/or cool to touch
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina - cardiovascular
Initially, increased HR and BP, then decreased BP (secondary to decrease in CO)
Decreased renal perfusion leads to decreased urine output
Crackles
Jugular venous distention
Abnormal heart sounds
S3 or S4
New murmur
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina - nausea and vomiting
Reflex stimulation of the vomiting center by severe pain
Vasovagal reflex
Clinical manifestations of unstable angina - fever
Up to 100.4° F (38° C) in first 24-48 hours
Systemic inflammatory process caused by heart cell death
Unstable angina and myocardial infarction diagnostic studies
Detailed health history
12-lead ECG
Serum cardiac biomarkers
Coronary angiography
Pharmacologic stress testing
Unstable angina ECG changes
Unstable angina treatment
A:
Antiplatelet/anticoagulant therapy
Antianginal therapy
ACE inihibitor/ARB
B:
Beta blocker
BP control
C:
Cigarette smoking cessation
Cholesterol management
Calcium channel blocker
Cardiac rehab
D:
Diet/weight management
Diabetes management
Depression screening
E:
Education
Exercise
F:
Flu vaccine
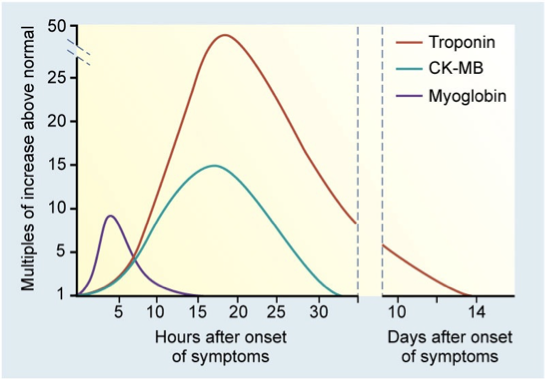
Serum cardiac biomarkers after myocardial infarction
Acute coronary syndrome treatment priorities
Initial interventions
12-lead ECG
Upright position
Oxygen – keep O2 sat > 93%
IV access
Nitroglycerin (SL) and ASA (chewable)
Statin
Morphine
Acute coronary syndrome treatment
Ongoing monitoring
Treat dysrhythmias
Frequent vital sign monitoring
Bed rest/limited activity for 12–24 hours
UA or NSTEMI
Dual antiplatelet therapy and heparin
Cardiac catheterization with PCI once stable
Acute coronary syndrome treatment - emergent percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI)
Treatment of choice for confirmed STEMI
Goal: 90 minutes door to cath lab
Balloon angioplasty + stent(s)
Many advantages over CABG
Acute coronary syndrome treatment - thrombolytic therapy
Only for patients with a STEMI
Agencies that do not have cardiac catheterization resources
Given IV within 30 minutes of arrival to the ED
Patient selection critical
Acute coronary syndrome treatment - CABG
Nursing:
24-48 hr ICU
Hemodynamic monitoring
Arterial line
Chest tubes
ECG monitoring
Pacing wires
Endotracheal tube
Urinary catheter
Nasogastric tube
Complication:
Bleeding, dysrhythmias, pain, DVT prevention, inflammation
Acute coronary syndrome nursing goals
Relief of pain
Preservation of heart muscle
Effective coping with illness-associated anxiety
Resumption of sexual activity
Participation in a rehabiliatation plan
Health promotion
Cardiac delegation
UAP
VS
I&O’s
Assist with meals, toileting
Report complications
LPN
May handle stable patient
Cannot administer thrombolytic medications
Sudden cardiac death (SCD)
Unexpected death from cardiac causes
Occurs within 1 hour of symptom onset
Dysrhythmia (e.g., VT, VF) causes disruption in cardiac function, resulting in loss of CO and cerebral blood flow
If survive, increased risk of another event due to electrical instability from scarred muscle
Psychosocial Adaptation
Brush with death”, “time bomb” mentality, anger, depression
Additional issues: driving restrictions, change in occupation