pathology exam 1
1/1247
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1248 Terms
ID
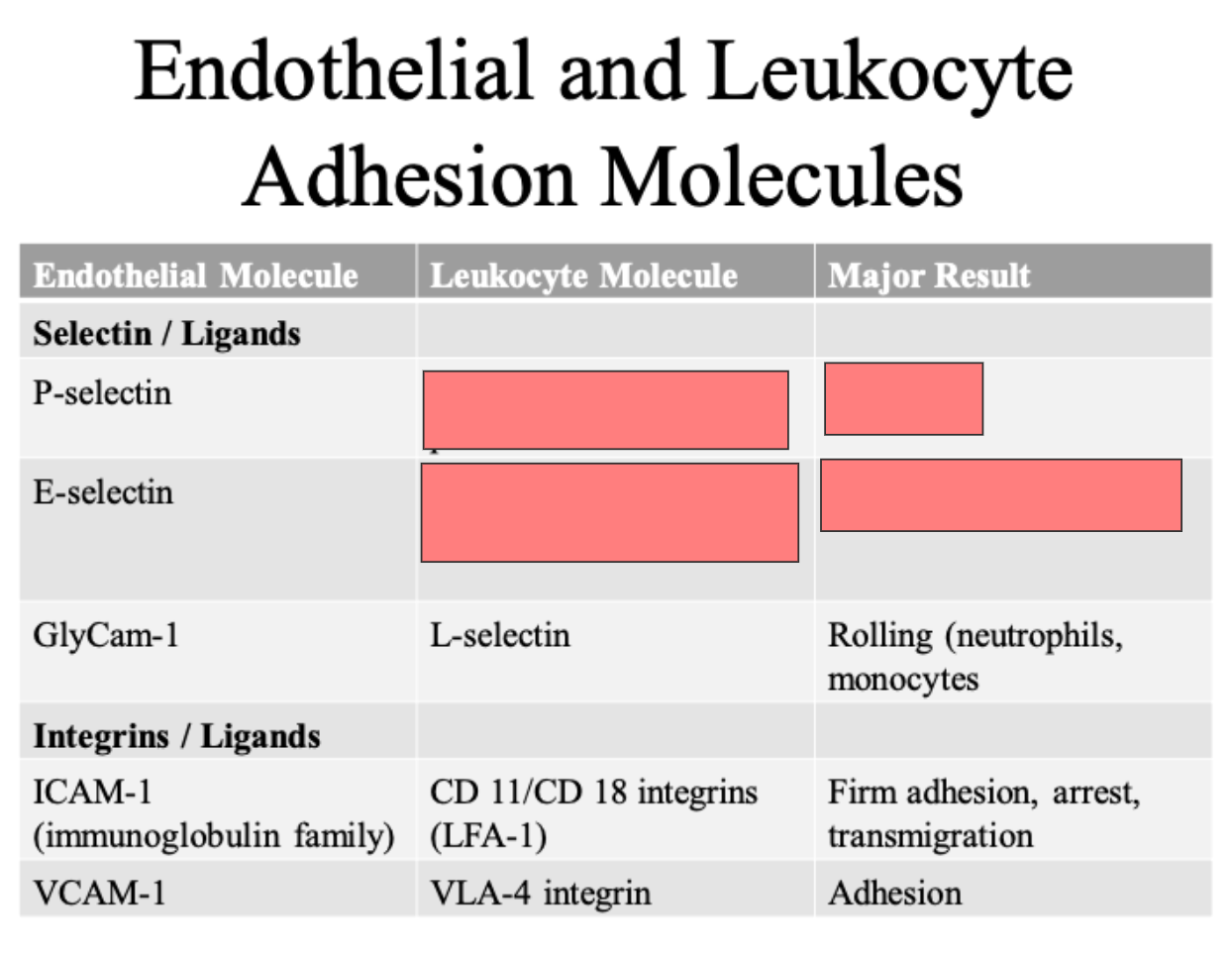
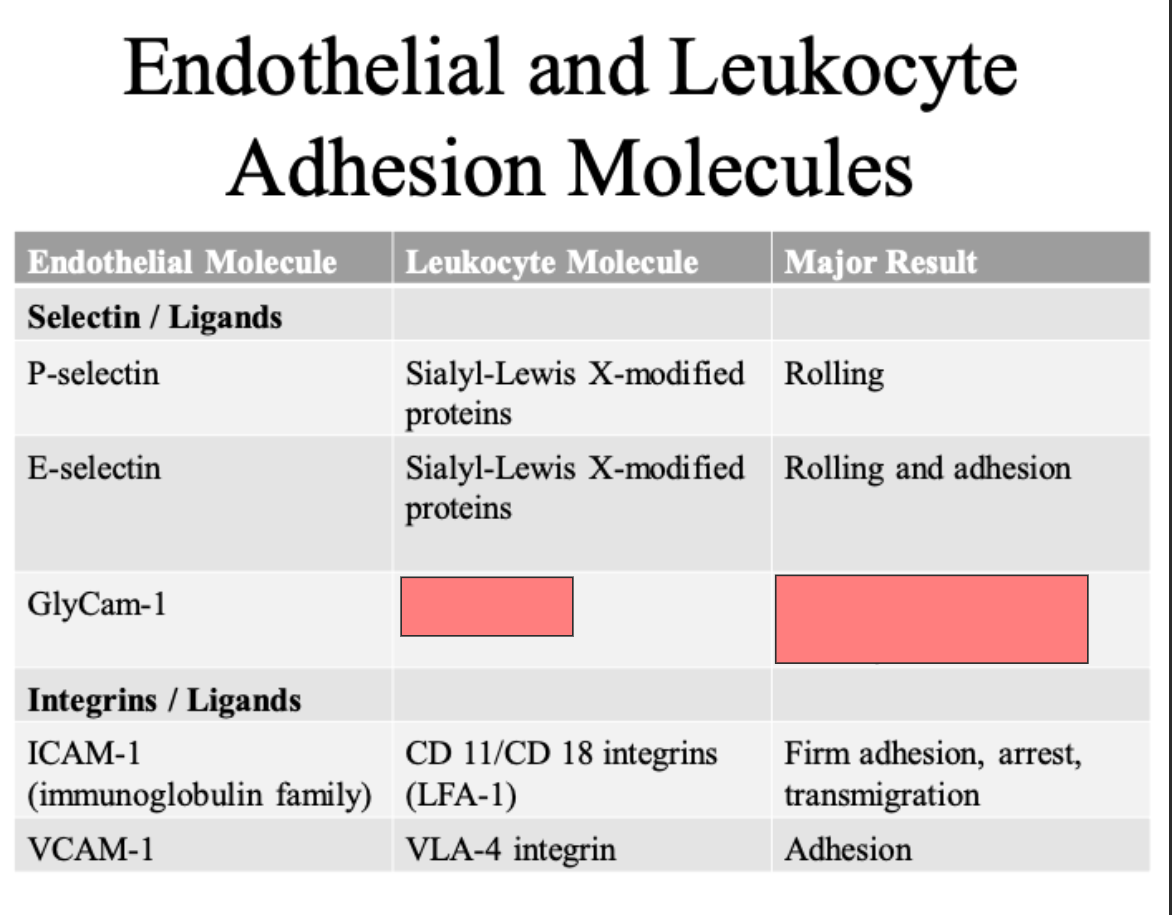
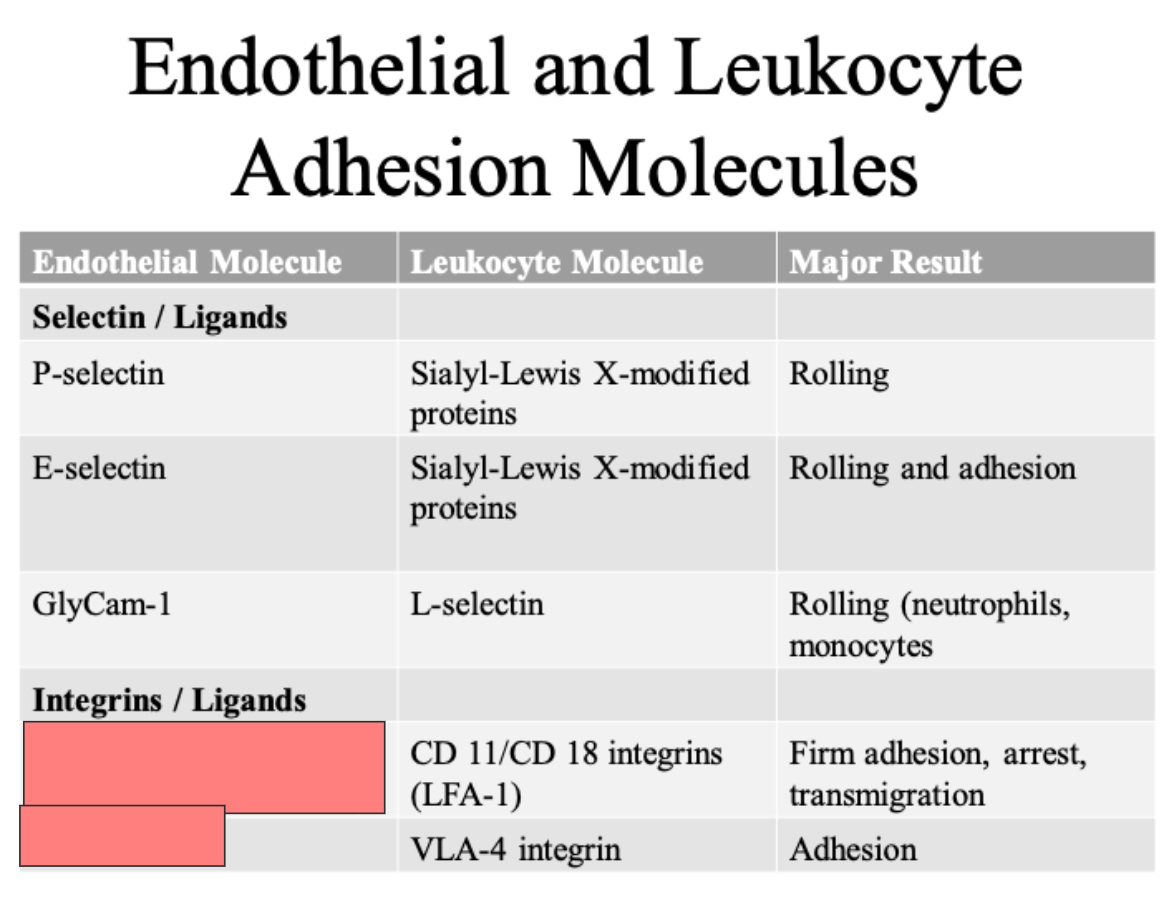
Lialyl lewis X modified proteins
rolling
Lialyl lewis X modified proteins
Rolling and adhesion
ID
L selectin
Rolling (neutrophils, monocytes)
ID
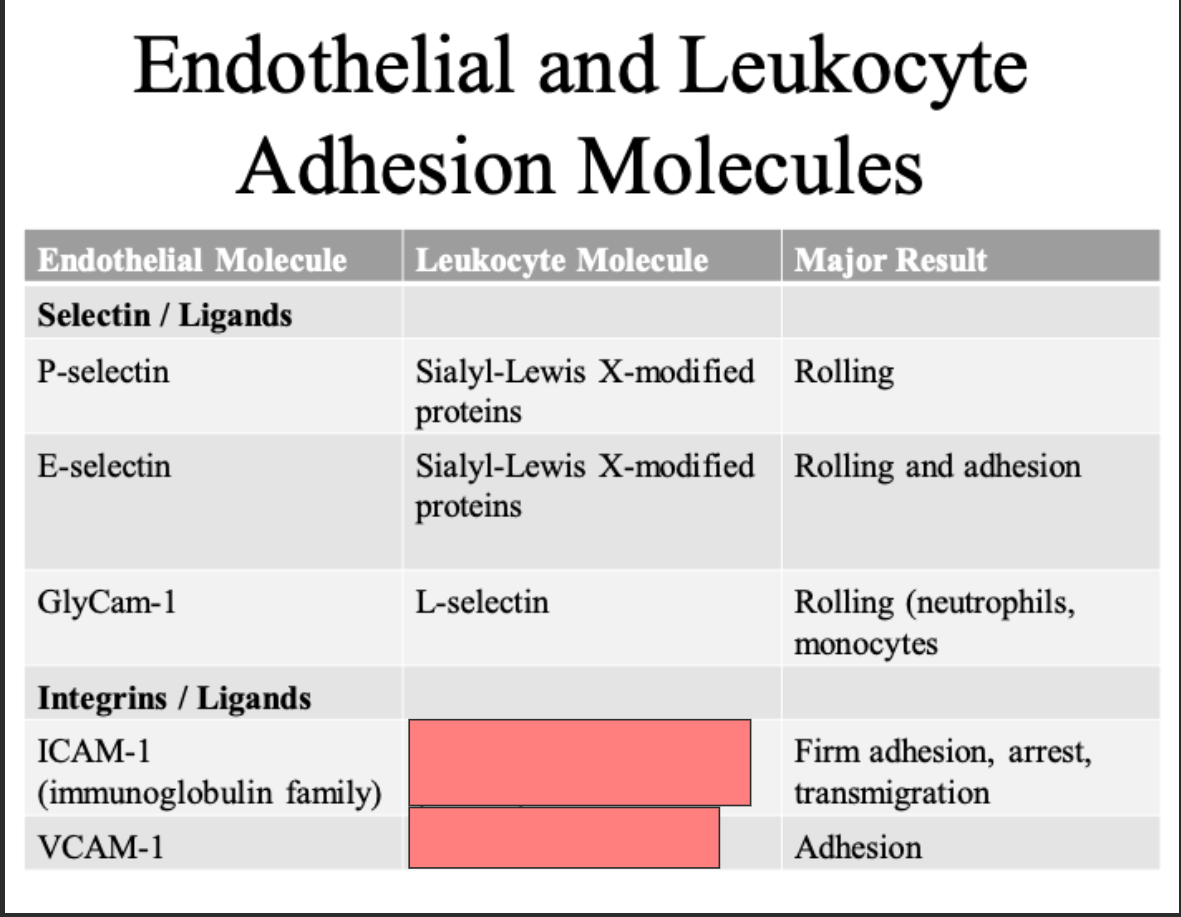
ICAM 1
VCAM 1
ID
CLUB DANCE 11/CD 18 integrins LFA 1
VLA 4 integrin
ID
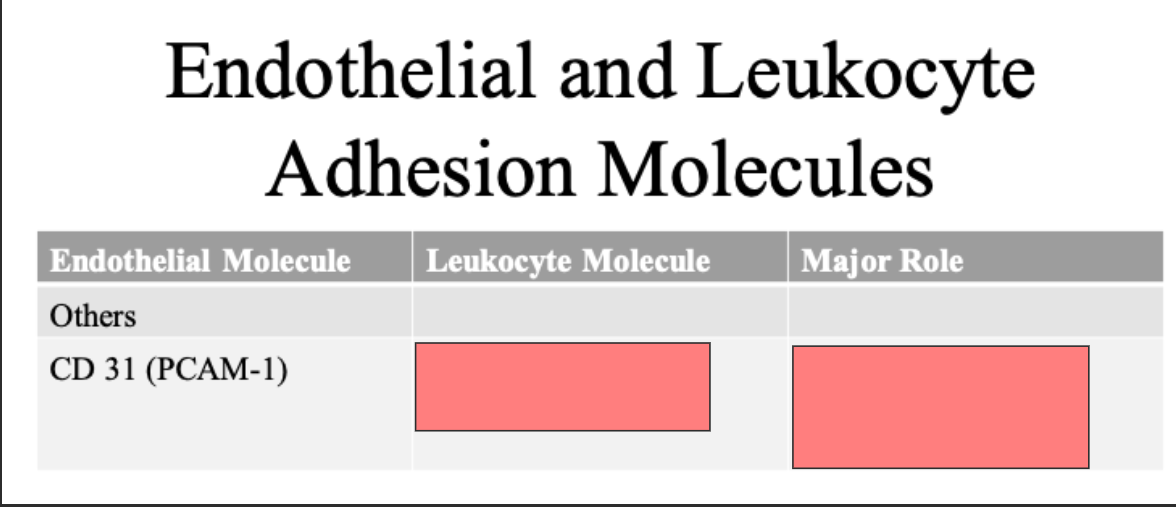
CLUB DANCE 31 homotypic interaction
transmission of leukocytes through endothelium
Extra 1
Homotypic interaction -- binds to itself (on both the endothelial and leukocyte molecule)
ID
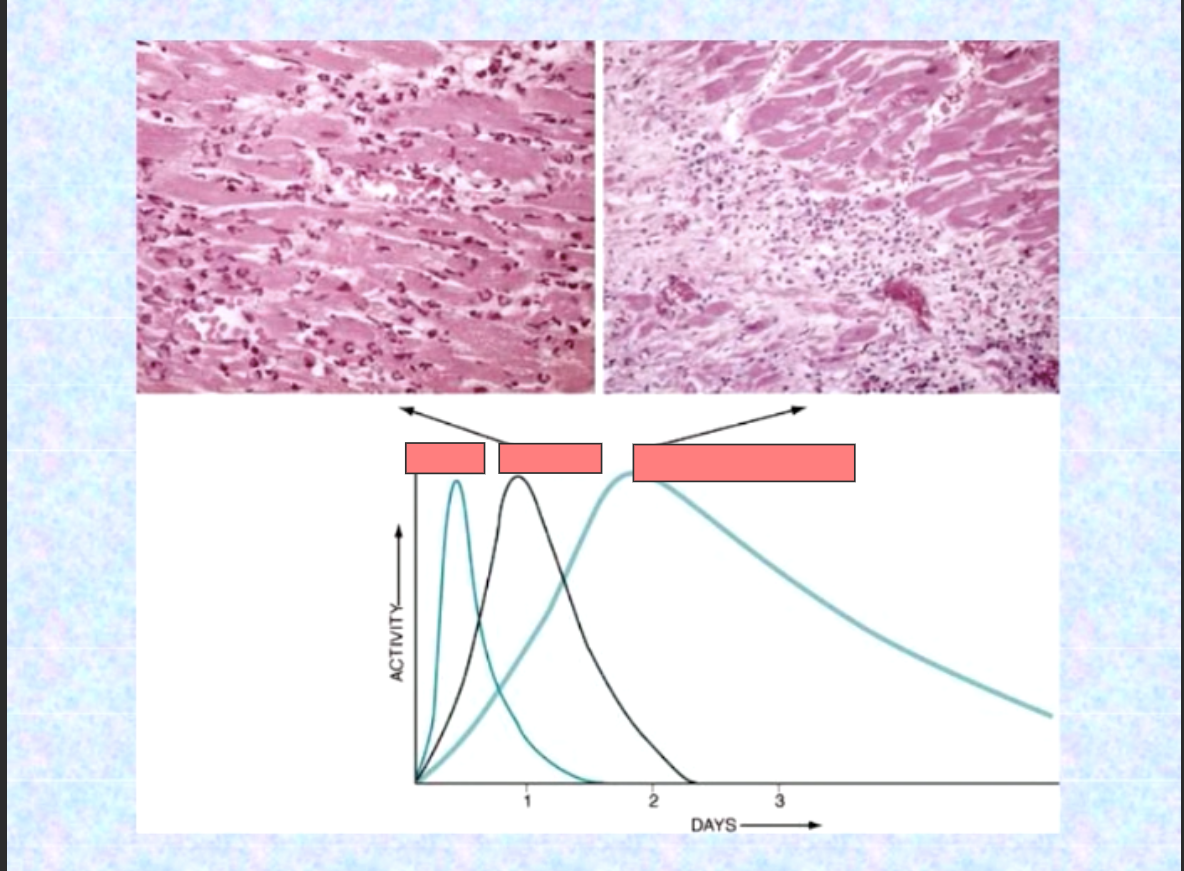
Edema
neutrophils
monocyte/macrophage
ID
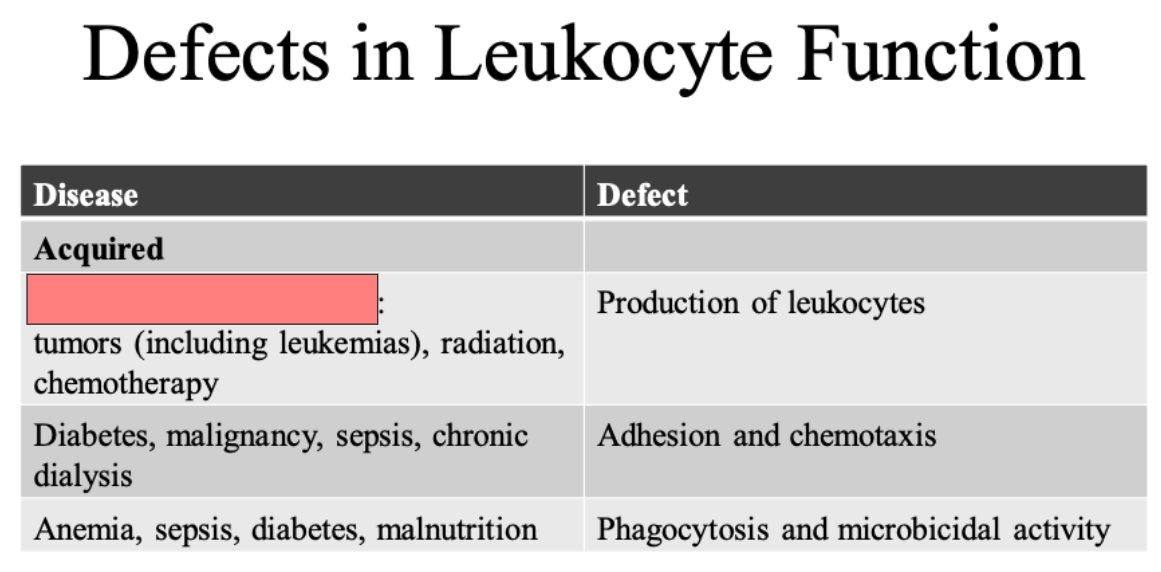
Bone marrow suppression
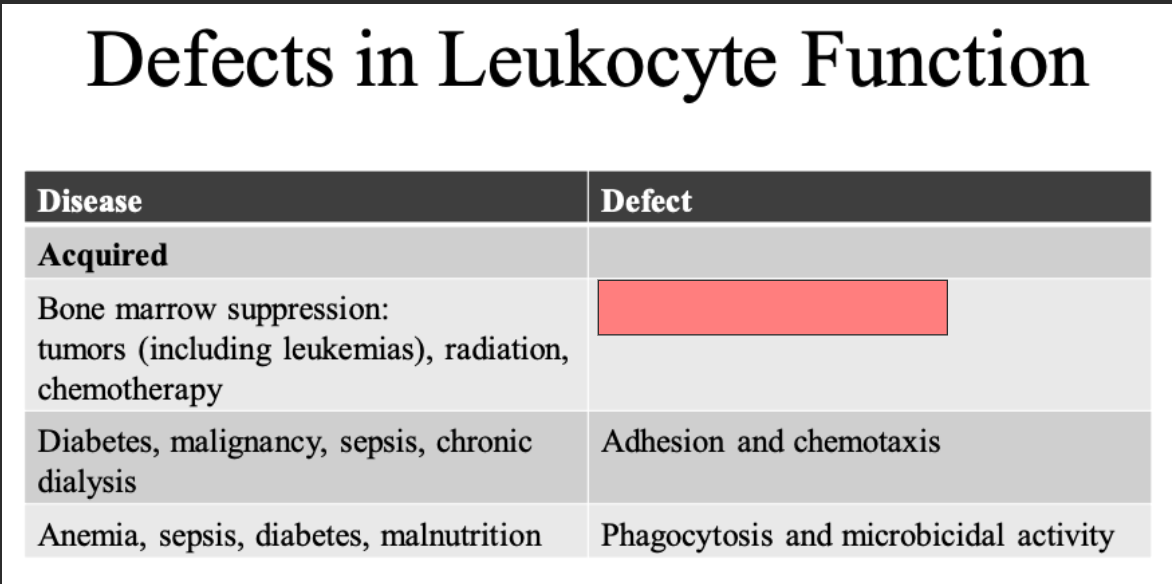
ID
Produuction of leukocytes
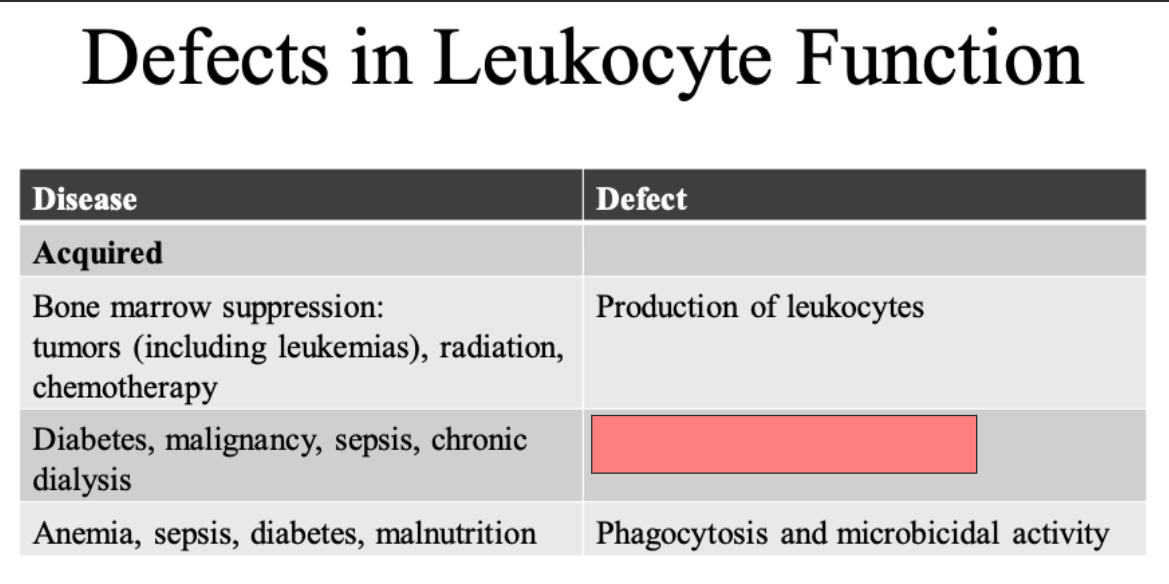
ID
Adhesion and chemotaxis
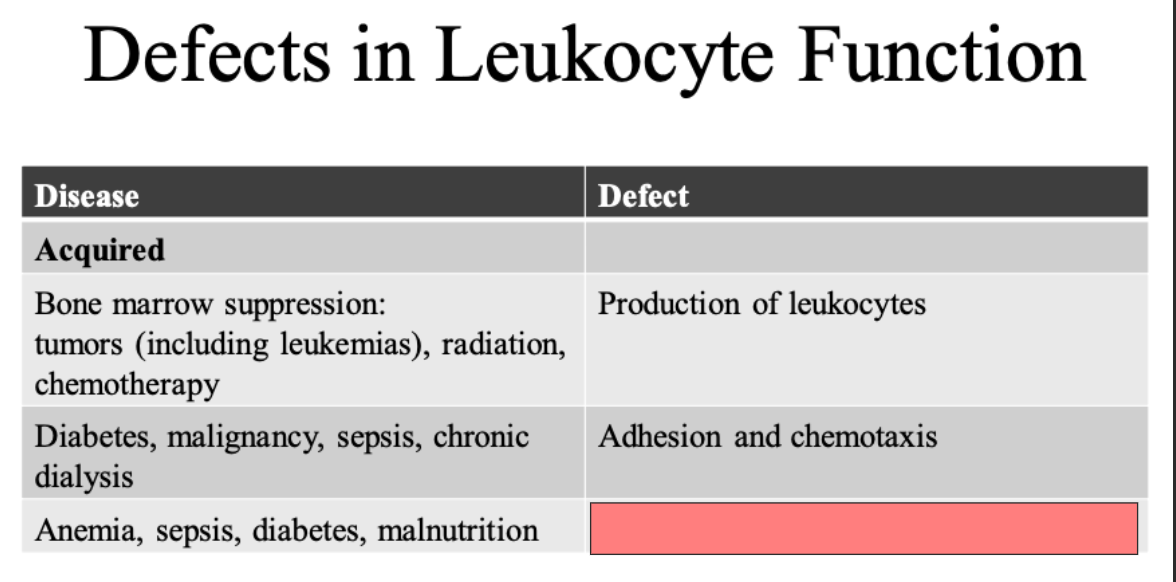
ID
Phagocytosis and microbial activity
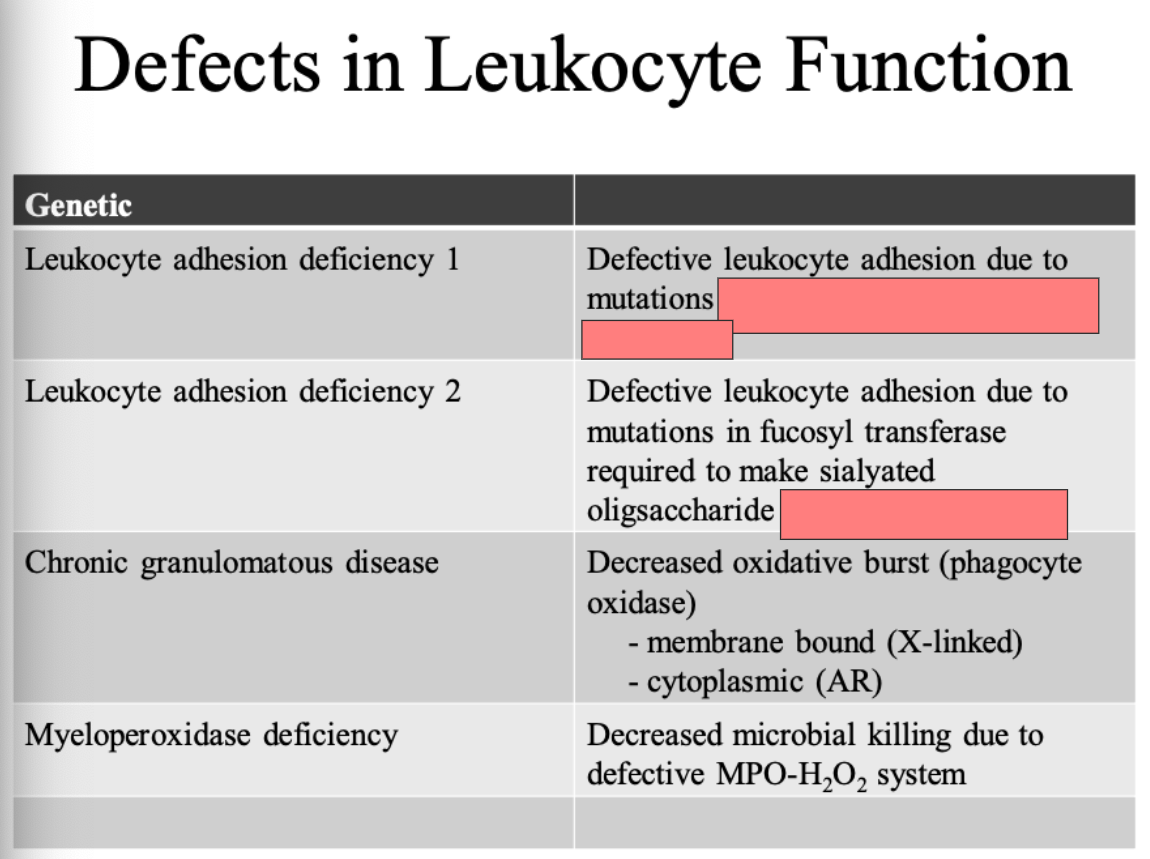
ID
in b chain of CD 11/CD 18 integrins
Selectin receptor
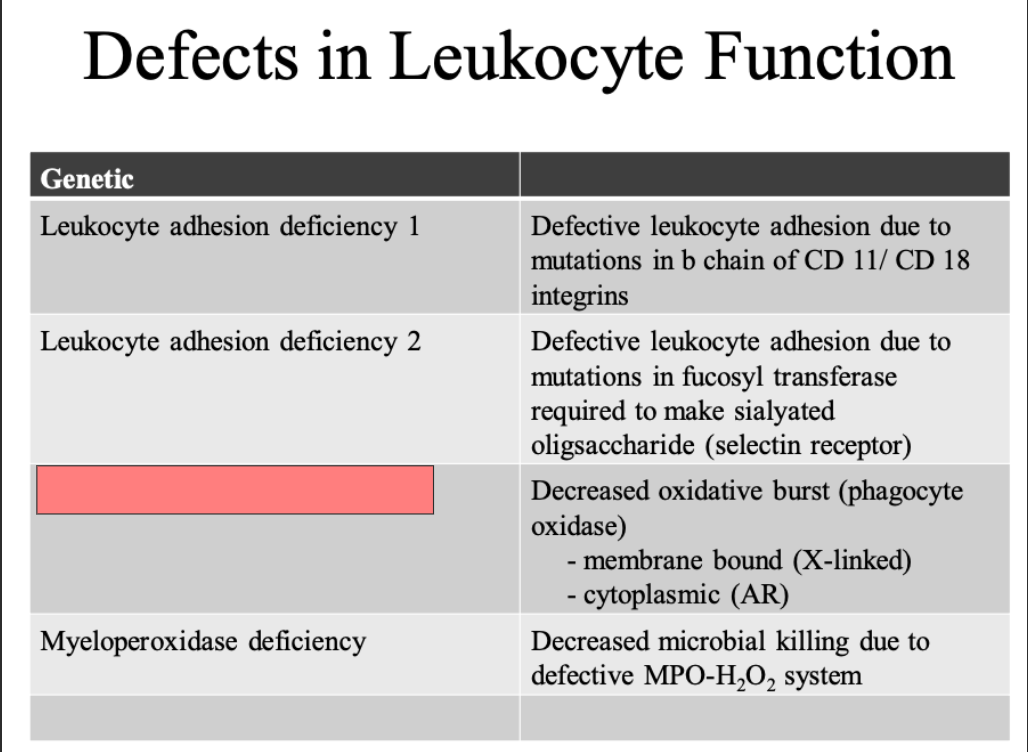
ID
Chronic granulomatous disease
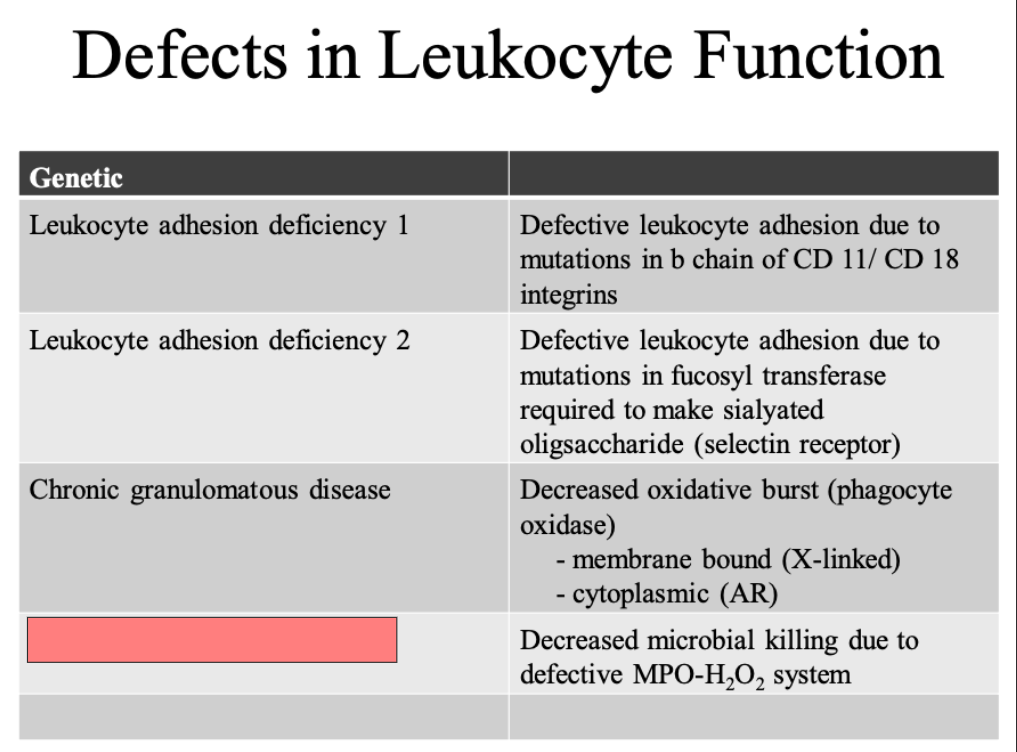
ID
Myeloperoxidase dificiency
Acute Inflammation
Stimuli
Infectious agents
Physical agents (like trauma or foreign bodies)
Chemical agents
Immunologic reactions
[...] (surprising stimuli for me
Necrotic tissue
Acute Inflammation
[...]: excess interstitial or serous cavity fluid
Edema
Acute Inflammation
[...]
inflammatory exudate rich in leukocytes and cellular debris
[...]
inflammatory exudate with a high protein content (SG > 1.020)
[...]
extravascular fluid with a low protein content (SG < 1.012)
Purulent Exudate
Exudate
Transudate
Acute Inflammation
Purulent Exudate
inflammatory exudate rich in leukocytes and cellular debris
Exudate
inflammatory exudate with a [high or low] protein content (SG > 1.020)
Transudate
extravascular fluid with a [high or low] protein content (SG < 1.012)
high
low
Acute Inflammation: immediate and early response to injury or infection
Major components
Vascular
[...]
[...]
Cellular
Emigration of leukocytes (from circulating in blood)
Accumulation of leukocytes at site of injury
Vasodilation
Increased vascular permeability (due to structural changes)
Acute Inflammation: immediate and early response to injury or infection
Major components
Vascular
Vasodilation
Increased vascular permeability (due to structural changes)
Cellular
[...]
[...]
Emigration of leukocytes (from circulating in blood)
Accumulation of leukocytes at site of injury
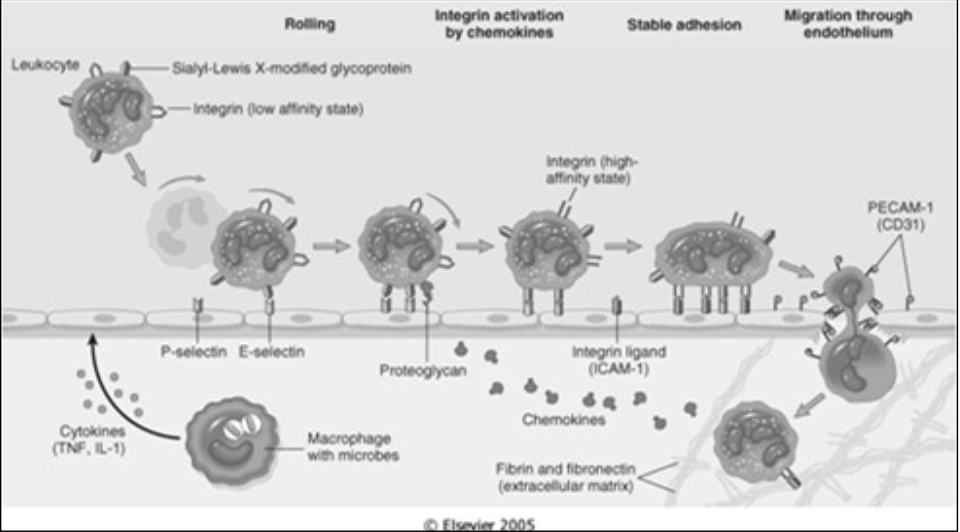
Adhesion & Transmigration
Determined by binding of [...] (complementary adhesion molecules on the leukocyte cell surface)
integrins
Integrins interact with their ligands on endothelial cells
Expression (intensity) is influenced by chemokines (chemical mediators)
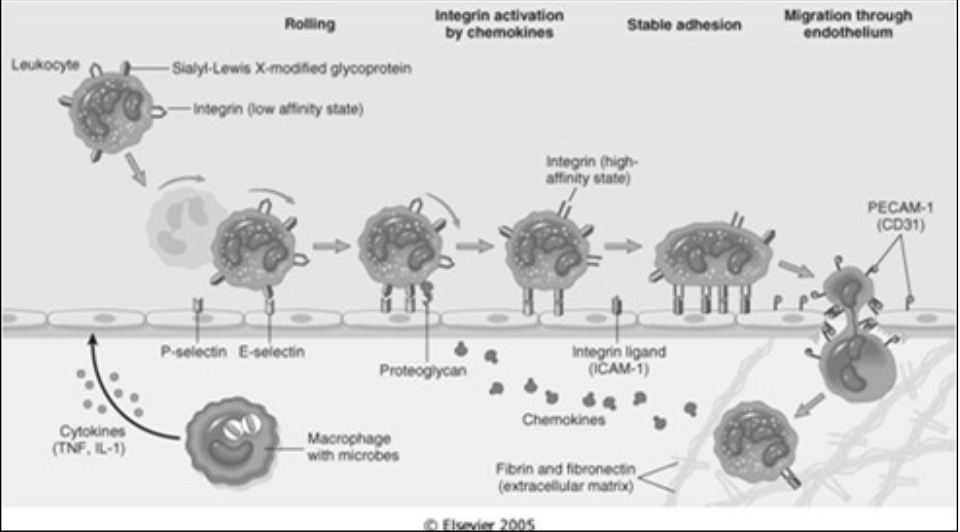
Adhesion Molecules – belong to four molecular families
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
Selectins
Immunoglobulins
Integrins
Mucin-like glycoproteins
![<p>Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber</p><ul><li><p>Changes<br></p><ul><li><p>Transient <span><strong>[vasoconstriction or vasodilation]</strong></span> (lasting seconds)</p></li><li><p><span><strong>[vasoconstriction or vasodilation]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span>Increased</span> vascular permeability</p></li><li><p>Results in edema (can be a palpable mass aka tumor)</p></li><li><p>Slowing of circulation</p></li><li><p>Leukocyte margination </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/d88e9b20-a339-448f-b54d-42708c0768fc.png)
Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber
Changes
Transient [vasoconstriction or vasodilation] (lasting seconds)
[vasoconstriction or vasodilation]
Increased vascular permeability
Results in edema (can be a palpable mass aka tumor)
Slowing of circulation
Leukocyte margination
vasoconstriction
Vasodilation
![<p>Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber</p><ul><li><p>Changes<br></p><ul><li><p>Transient <span>vasoconstriction</span> (lasting seconds)</p></li><li><p><span>Vasodilation</span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[increased or decreased]</strong></span> vascular permeability</p></li><li><p>Results in edema (can be a palpable mass aka tumor)</p></li><li><p>Slowing of circulation</p></li><li><p>Leukocyte margination </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/534a8192-5787-4b4f-93fb-4b7c9b670c8d.png)
Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber
Changes
Transient vasoconstriction (lasting seconds)
Vasodilation
[increased or decreased] vascular permeability
Results in edema (can be a palpable mass aka tumor)
Slowing of circulation
Leukocyte margination
Increased
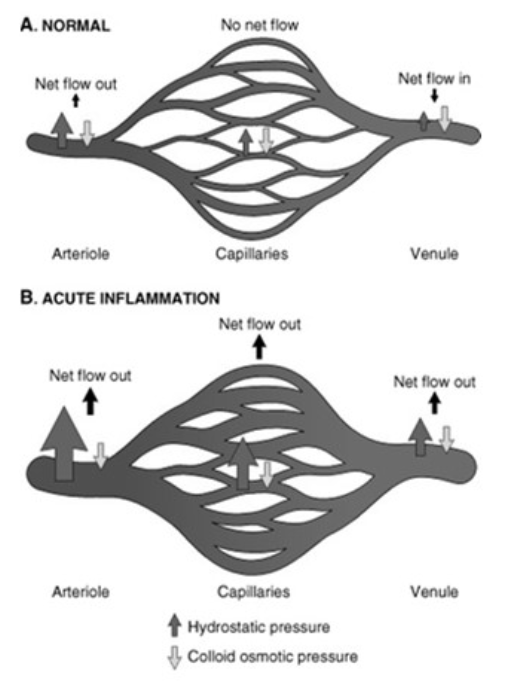
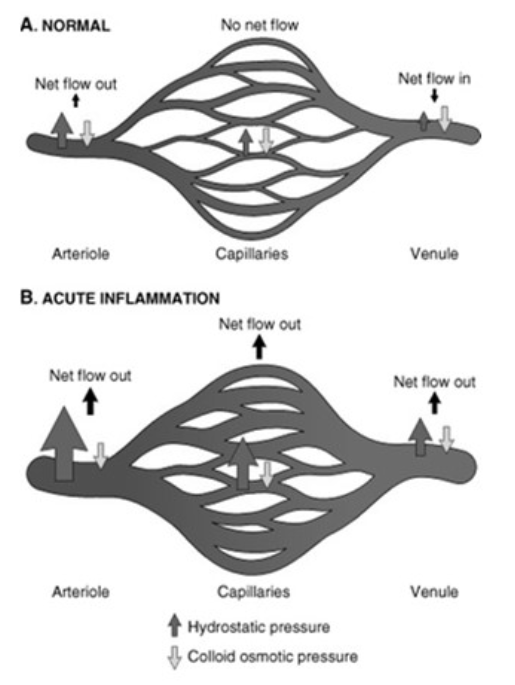
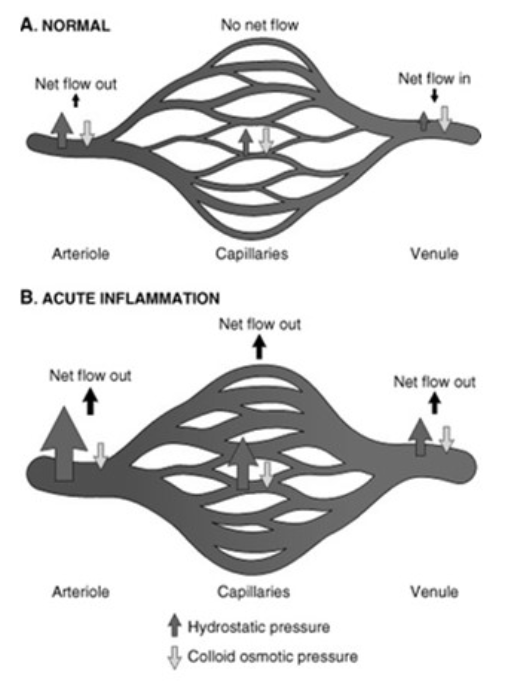
![<p>Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber</p><ul><li><p>Physiology<br></p><ul><li><p>During acute inflammation, net flow is <span><strong>[in or out]</strong></span> in the arteriole, capillaries and venules due to <span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/8595f586-0f21-4819-b361-e1b9614bd583.png)
Changes in Vascular Flow and Caliber
Physiology
During acute inflammation, net flow is [in or out] in the arteriole, capillaries and venules due to [...]
out
increased hydrostatic pressure
Chemical Mediators of Inflammation
From [...] or [...]
Function as [...]
Short lived
May act on just one target cell or on a few
Potential for harmful effects
plasma or produced locally
amplifiers
Chemotaxis
Exogenous
[...]
Endogenous
Components of the complement system
Products of the lipoxygenase pathway
Cytokines
Bacterial products
Chemotaxis
Exogenous
Bacterial products
Endogenous
[...]
[...]
[...]
Components of the complement system
Products of the lipoxygenase pathway
Cytokines
Function of Adhesion Molecule
Expression of E Selectin
Caused by
[...]
[...]
[...]
TNF
IL-1
Chemokines
Function of Adhesion Molecule
Redistribution of P selectin to the cell surface
[...] bodies are distributed to the site of injury
Caused by
Histamine
Thrombin
Platelet Activating Factor (PAF)
Weibel-Palade
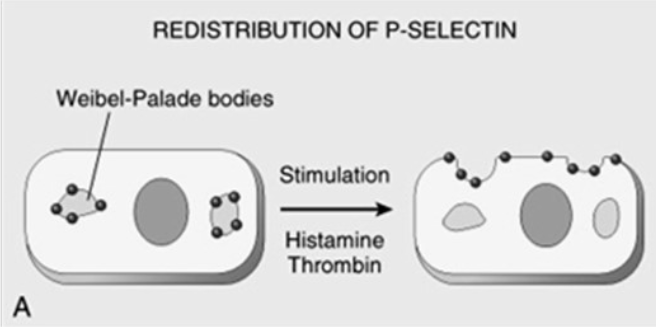
![<p>Function of Adhesion Molecule</p><ul><li><p>Redistribution of P selectin to the cell surface<br></p><ul><li><p><span>Weibel-Palade</span> bodies are distributed to the site of injury</p></li><li><p>Caused by</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li><li><p><span><strong>[...]</strong></span></p></li></ul></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/6864cc22-beae-4acc-aa11-ab0985a751f2.png)
Function of Adhesion Molecule
Redistribution of P selectin to the cell surface
Weibel-Palade bodies are distributed to the site of injury
Caused by
[...]
[...]
[...]
Histamine
Thrombin
Platelet Activating Factor (PAF)
Function of Adhesion Molecule
VCAM-1 and ICAM-1 Expression
Caused by:
[...]
[...]
TNF
IL-1
Function of chemotactic agents
Leukocyte activation
Causes:
Production of [...] (causing amplification of the inflammatory reaction)
Degranulation, secretion of lysosomal enzyme & the oxygen burst
Modulation of leukocyte adhesion molecules
arachidonic acid metabolites
Function of chemotactic agents
[...]
[...] activation
Locomotion along a chemical gradient
Leukocyte
Historical Highlights
Clinical Features
Rubor = [...]
Tumor = [...]
Calor = [...]
Dolor = [...]
Functio Laesa = [...]
Redness
Mass
Warmth
Pain
loss of function
Inflammation: Overview
Attempts to eliminate [...] as well as cleaning up [...]
Goal of inflammation
Host cells of defense normally circulate in blood. Inflammation tries to bring them to the site of damage
the initial cause of cellular injury
necrotic cells and tissue
Integrins
Normally in a [high or low]-affinity form on the leukocyte surface
Becomes activated when leukocytes are activated by chemokines
Integrins do not bind to their ligands until the leukocyte is activated
Other cytokines activate endothelial cells, increasing their expression of ligands for integrins
low
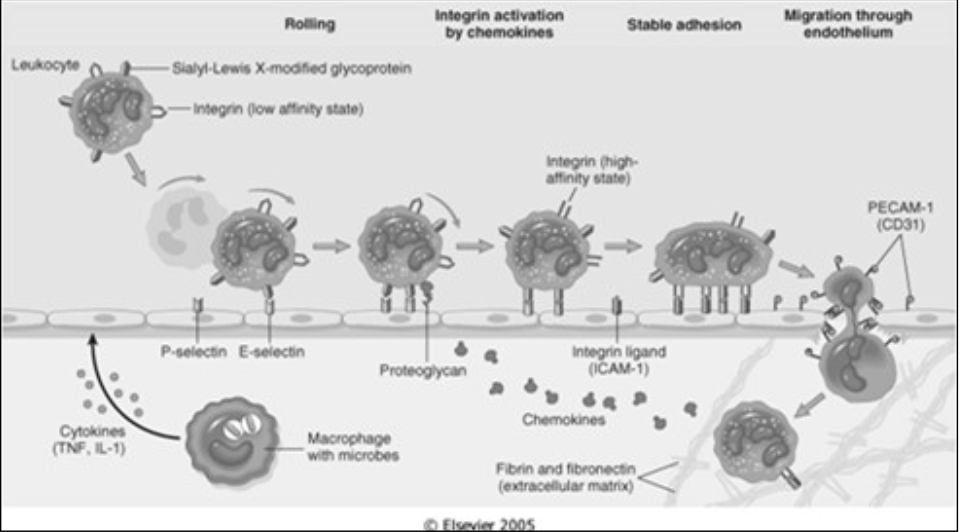
Integrins
Normally in a low-affinity form on the leukocyte surface
Becomes activated when [what happens?]
Integrins do not bind to their ligands until the leukocyte is activated
Other cytokines activate endothelial cells, increasing their expression of ligands for integrins
leukocytes are activated by chemokines
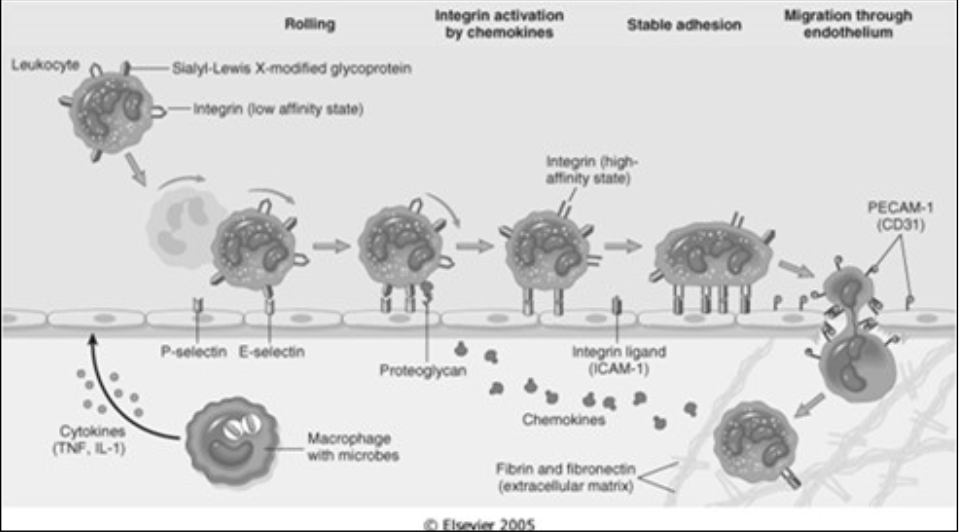
Leukocyte activation
Stimuli for activation
[...]
[...]
[...]
Microbes
Products of necrotic cells
Mediators
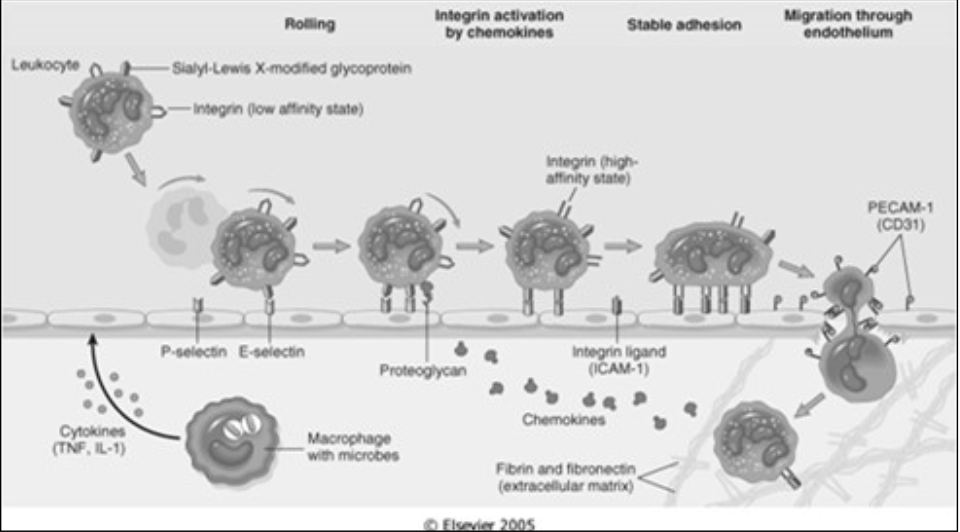
Location of adhesion molecules
[Where are the following located?]
P-selectin
E-selectin
Endothelial Cells
![<p>Location of adhesion molecules</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Where are the following located?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>L-Selectin</p></li><li><p>VLA integrins</p></li><li><p>LFA </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/b0d9f3ac-20ad-4c69-8262-53b5abab142d.png)
Location of adhesion molecules
[Where are the following located?]
L-Selectin
VLA integrins
LFA
Leukocyte
![<p>Location of adhesion molecules</p><ul><li><p><span><strong>[Where are the following located?]</strong></span><br></p><ul><li><p>P-Selectin </p></li></ul></li></ul><p></p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/3ff33b51-762b-4da2-a0ca-c231fc48d6e8.png)
Location of adhesion molecules
[Where are the following located?]
P-Selectin
Platelets
Location of adhesion molecules
[Where are the following located?]
ICAM-1
VCAM-1
GlyCam-1
PECAM (CD31)
Endothelial Cells
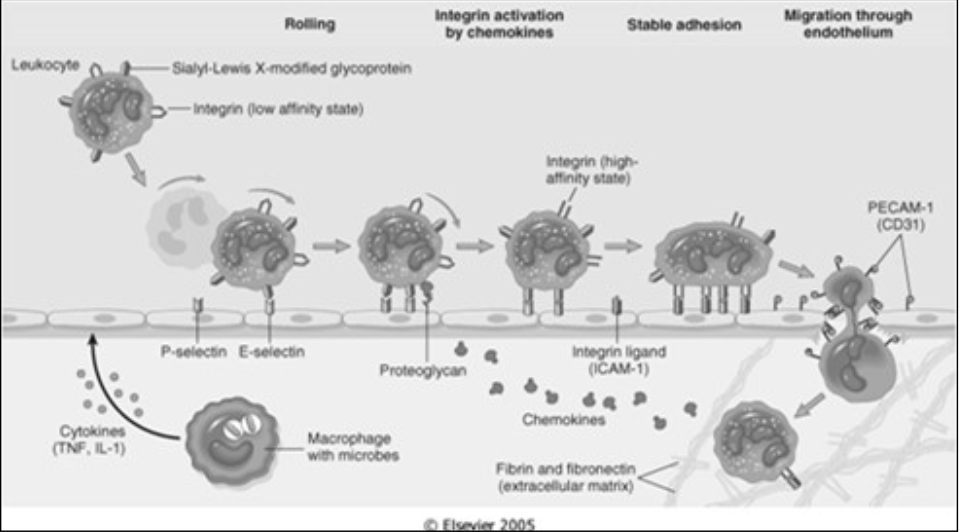
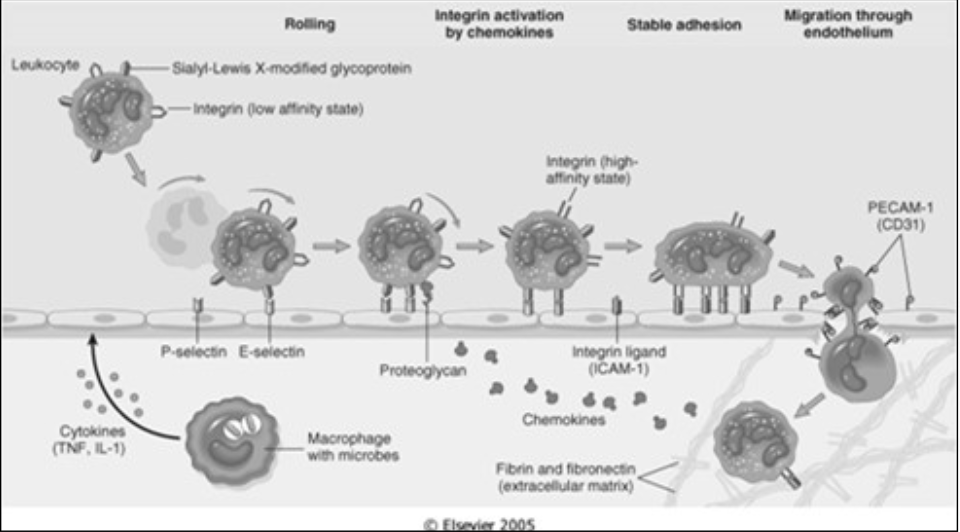
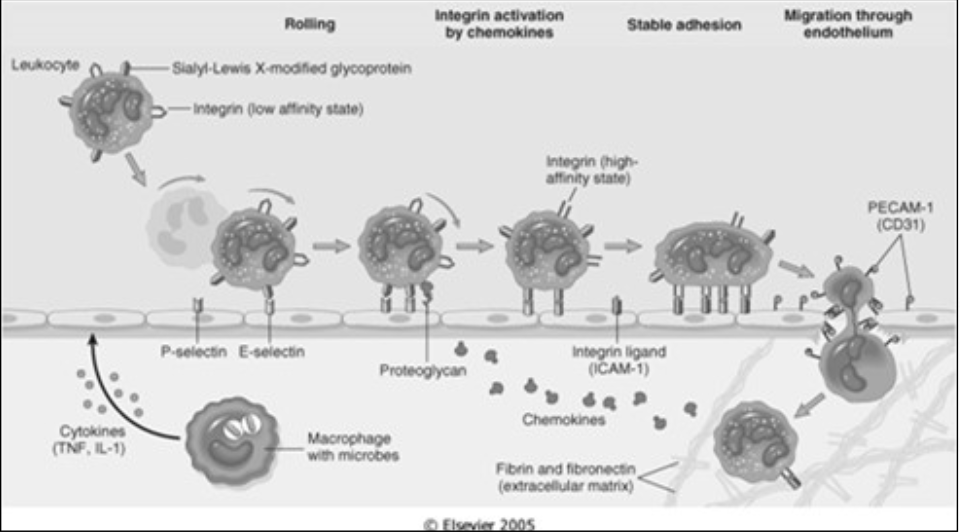
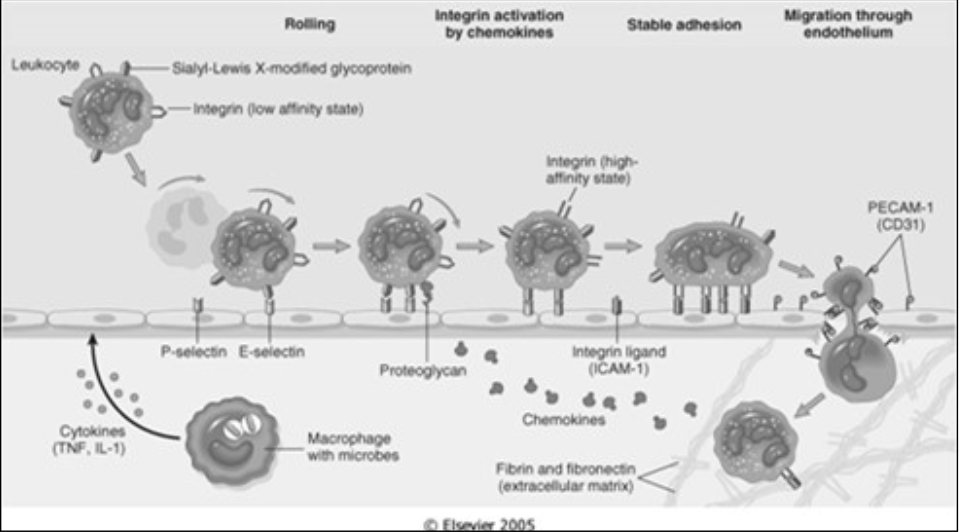
Margination and Rolling
Leukocytes forced against the vascular walls [where] due to flow dynamics
post-capillary venules
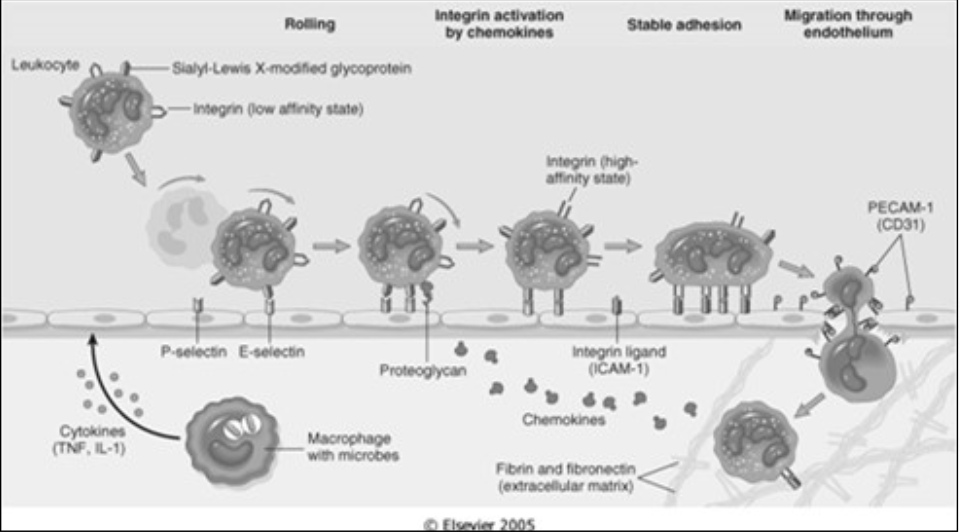
Margination and Rolling
Rolling
Leukocytes roll along the vessel wall and transiently stick to the vessel (low adherence)
Mediated by [...]
selectins (an adhesion molecule)
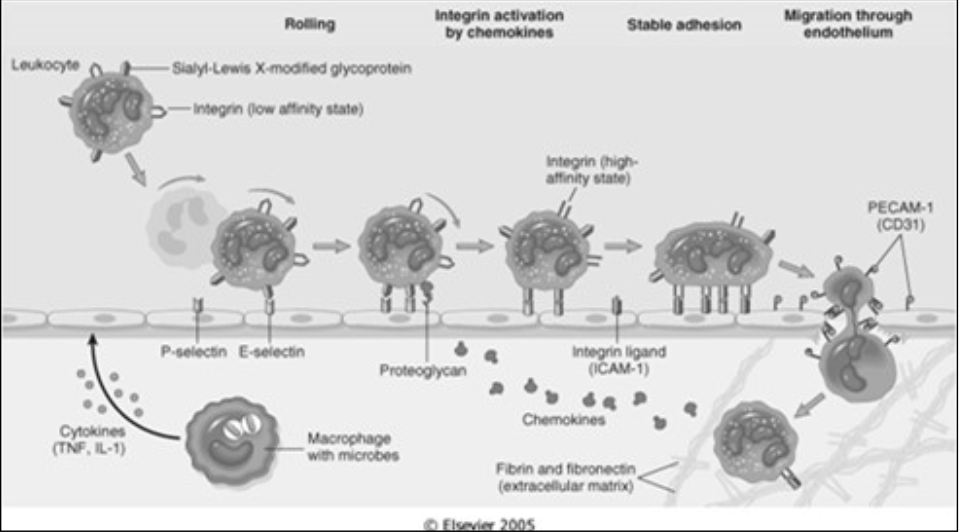
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Direct Endothelial Injury
Where:
[...]
Why:
[...]
arterioles, capillaries, and venules (basically everywhere)
Toxins, burns, chemicals
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Forms [...] due to:
[...]
Where: in venules
Why: vasoactive mediators (primarily histamine and leukotrienes)
[...]
Where: mostly in venules but also capillaries
Why:
Cytokines (IL-1 & TNF)
Hypoxia
gaps
Endothelial cell contraction
Cytoskeletal reorganization
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Forms gaps due to:
Endothelial cell contraction
Where: [...]
Why: [...]
Cytoskeletal reorganization
Where: mostly in venules but also capillaries
Why:
Cytokines (IL-1 & TNF)
Hypoxia
in venules
vasoactive mediators (primarily histamine and leukotrienes)
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Forms gaps due to:
Endothelial cell contraction
Where: in venules
Why: vasoactive mediators (primarily histamine and leukotrienes)
Cytoskeletal reorganization
Where: [...]
Why:
[...]
[...]
mostly in venules but also capillaries
Cytokines (IL-1 & TNF)
Hypoxia
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Increased transcytosis -- cell takes up fluid on one side and releases it on the other side
Where: [...]
Why: [...]
venules
VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor)
Mechanisms of Vascular Leakage in acute inflammation
Leukocytes dependent injury aka friendly fire
Where: mostly in [...] but also in [...]
When: [...]
venules
pulmonary capillaries
late response (takes days)
NOD-like Receptors
Capase-1
Function
[...]
cleaves precursor form of inflammatory IL-1b into its active form of IL-1
IL-1 is an important mediator of leukocyte recruitment
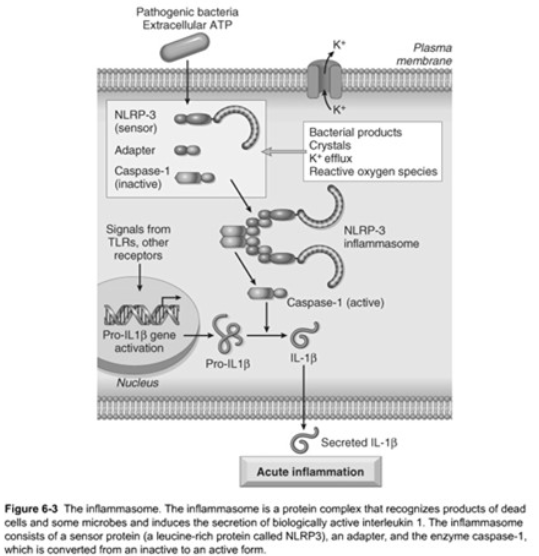
NOD-like Receptors
Receptors signal via the [...]
inflammasome
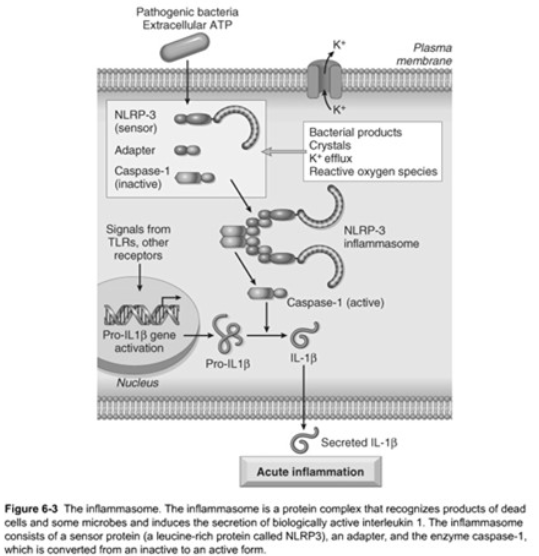
NOD-like Receptors
The inflammasome is a multi-protein cytoplasmic complex
Triggering of the inflammasome results in activation of [...]
capase-1
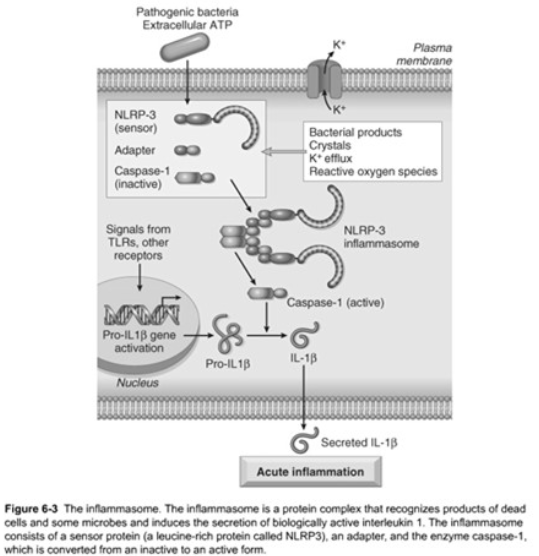
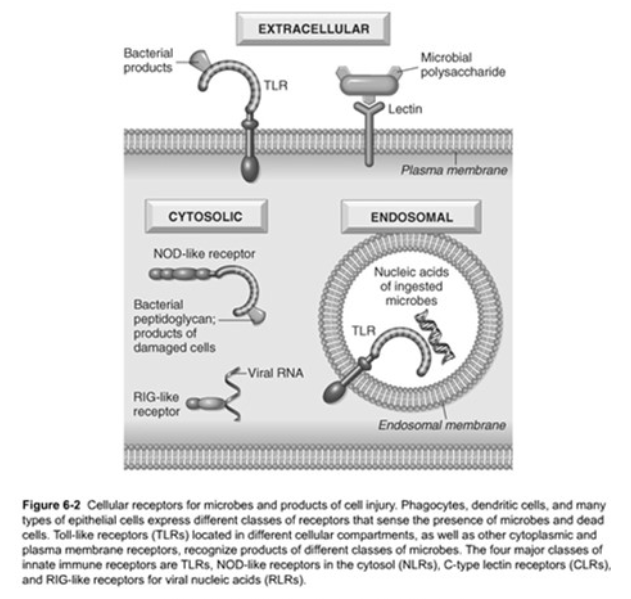
Pattern Recognition Sensors
Phagocytes, dendritic cells, and epithelial cells express receptors
Four major classes of receptors
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...] for viral nucleic acids
TLRs
NOD-like Receptors (NLRs)
C-type Lectic Receptors
RIG-like receptors (RLRs)
Phagocytosis
Engulfment
One step if
[...]
More steps required if:
[...]
Triggered by binding of the opsonized particle to the Fc portion of IgG
Binding to C3 receptors alone
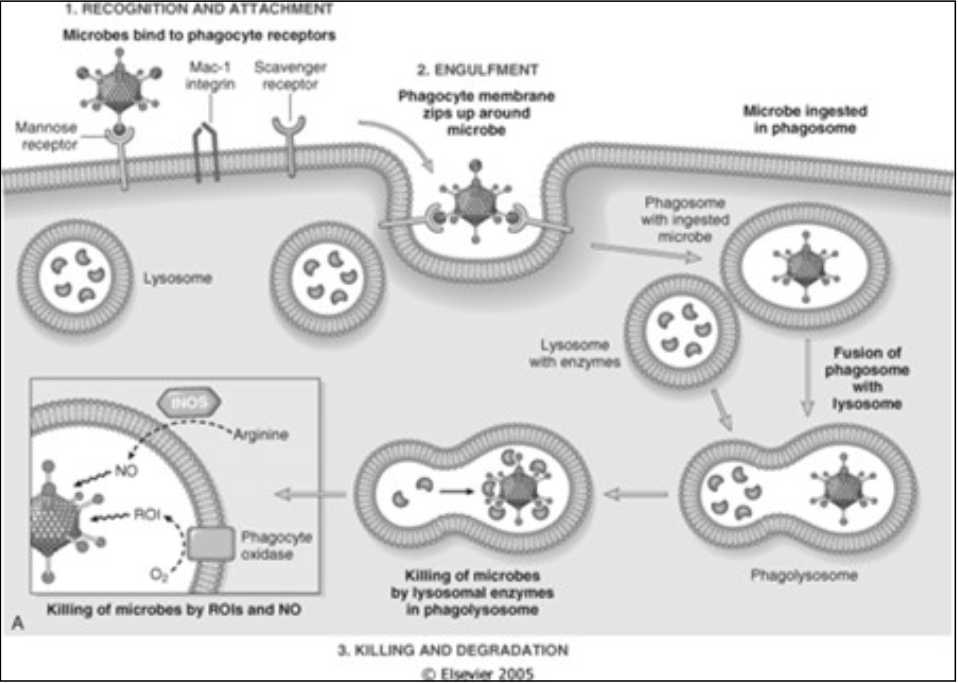
Phagocytosis
Killing or degradation
Two mechanisms
Oxygen dependent
[...]
Oxygen independent
BPIP (bactericidal permeability increasing protein)
Lactoferrin
Lysozyme
Major basic protein
Defensins
Oxidase
Phagocytosis
Killing or degradation
Two mechanisms
Oxygen dependent
Oxidase
Oxygen independent
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
BPIP (bactericidal permeability increasing protein)
Lactoferrin
Lysozyme
Major basic protein
Defensins
Phagocytosis
Recognition and attachment
Via [...]
Fc portion of IgG
C3b (and C3bi – its inactive form)
Collectins
opsonins
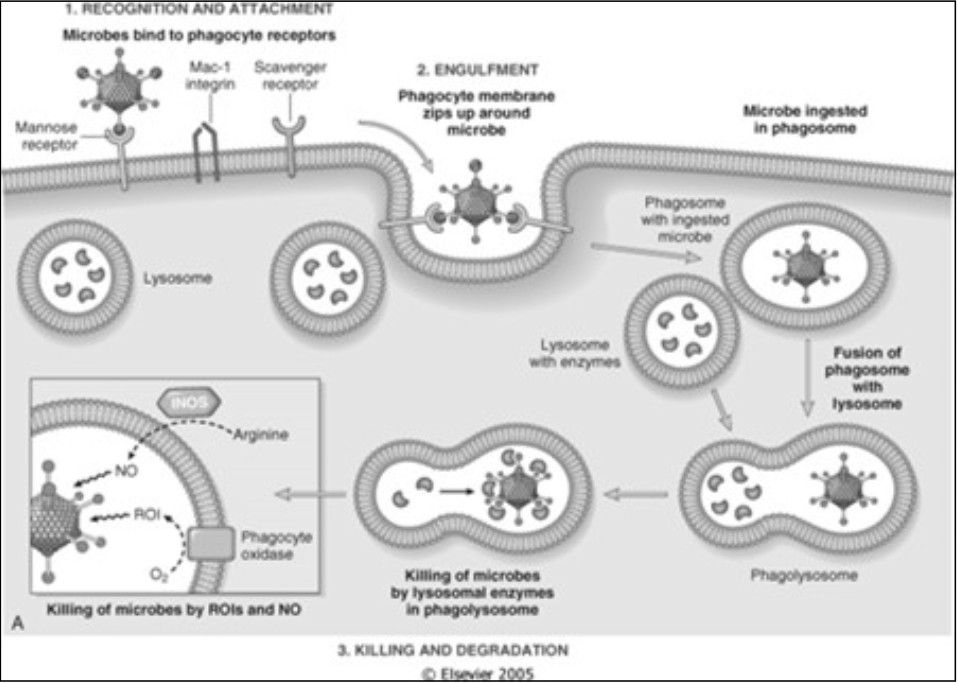
Phagocytosis
Recognition and attachment
Via opsonins
[...]
[...]
[...]
Fc portion of IgG
C3b (and C3bi – its inactive form)
Collectins
Phagocytosis
Three distinct steps
[...]
Microbes bind to phagocyte receptors
[...]
Phagocyte membrane zips up around microbe
Microbe is ingested in phagosome
Fusion of phagosome with lysosome
[...]
by lysosomal enzymes in phagolysosomes
by ROIs and NO
Recognition and attachment
Engulfment
Killing or degradation
Recruitment of Inflammatory Cells
Leukocytes must be stopped and brought to the site of injury from normal circulation
Cellular Events (in order)
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
[...]
Margination
Adherence
Transmigration
Chemotaxis and Leukocyte activation
Phagocytosis
Response of Lymphatic Vessels (to deal with edema)
Lymph flow is [increased or decreased] during inflammation
Leukocytes, cell debris, and microbes are drained to lymph nodes (where we start making antibodies and recognizing them)
increased
Response of Lymphatic Vessels (to deal with edema)
[...] – lymphatic vessels getting secondarily inflamed
[...] – draining lymph nodes become inflamed
Lymphangitis
Lymphadenitis
Terminating the Acute Inflammatory Response
Tight controls are needed
Short half-lives of chemical mediators
Inflammation simultaneously triggers a variety of stop signals
Switch from pro-inflammatory leukotrienes to [...]
[...] (anti-inflammatory)
[...]
anti-inflammatory lipoxins
Liberation of TGF-b from macrophages
Neural impulses (cholinergic) inhibit production of TNF in macrophages
[...]
Locomotion along a chemical gradient
Induce a response in all granulocytes, monocytes and, to a degree, lymphocytes
Can be endogenous (produced by us) or exogenous (produced by debris or bacteria)
Chemotaxis
Chemotaxis
Locomotion along a chemical gradient
Induce a response in all granulocytes, monocytes and, to a degree, [...]
Can be endogenous (produced by us) or exogenous (produced by debris or bacteria)
lymphocytes
[...]
Present on leukocyte surface
Are transmembrane heterodimeric glycoproteins that also function as cell receptors for extracellular matrix
Integrins
[...]
Due to phagolysosome leaking its products into the extracellular space
Includes:
Lysosomal enzymes
Oxygen-derived active metabolites
Products of arachidonic acid metabolism
Leukocyte-Induced Tissue Injury
Leukocyte-Induced Tissue Injury
Due to phagolysosome leaking its products into the extracellular space
Includes:
[...]
[...]
[...]
Lysosomal enzymes
Oxygen-derived active metabolites
Products of arachidonic acid metabolism
[...]
High concentration of antimicrobial substances at sites of infection to prevent the spread of microbes
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
[...]
It’s an extracellular fibrillar network produced by neutrophils in response to infectious pathogens and inflammatory cytokines
Infectious pathogens – bacteria or fungi
Inflammatory mediators – chemokines, cytokines, complement, and ROS
Contain a framework of nuclear chromatin with embedded granule protein
Neutrophil Extracellular Traps (NETs)
[...] Receptors & the Inflammasome
Cytosolic receptors
Function – recognizes a wide variety of substances
Products of necrotic cells (uric acid and released ATP)
Ion disturbances
Some microbial products
NOD-like
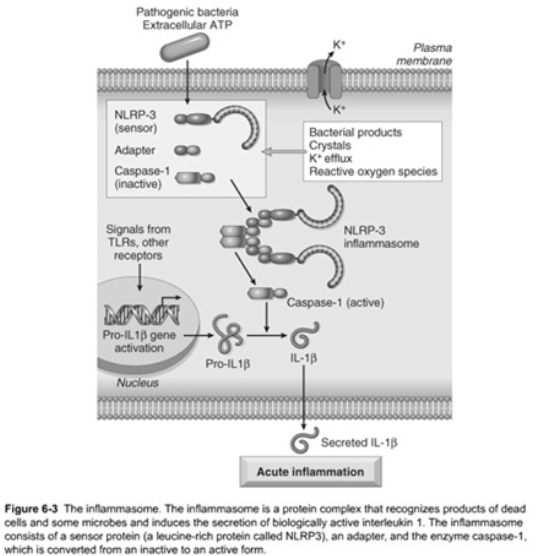
NOD-like Receptors & the Inflammasome
Cytosolic receptors
Function – recognizes a wide variety of substances
Products of [...]
[...]
Some [...]
necrotic cells (uric acid and released ATP)
Ion disturbances
microbial products
[...]
Receptor that is expressed on leukocytes and endothelium
Mediates rolling
Contains an extracellular domain that binds to sugars
Normally in low levels on endothelial cells
Up-regulated by specific mediators
Makes sure binding of leukocytes are restricted to site of injury
Selectins
Selectins
Receptor that is expressed on leukocytes and endothelium
Mediates rolling
Contains an extracellular domain that binds to sugars
Normally in [high or low] levels on endothelial cells
Up-regulated by specific mediators
Makes sure binding of leukocytes are restricted to site of injury
low
[...]
Function – Microbial sensors
Recognizes products of bacteria (endotoxin, bacterial DNA, and other pathogens)
Located in the plasma membrane and endosomes
Complemented by:
Cytoplasmic and membrane molecules
Other families that recognize microbial products
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
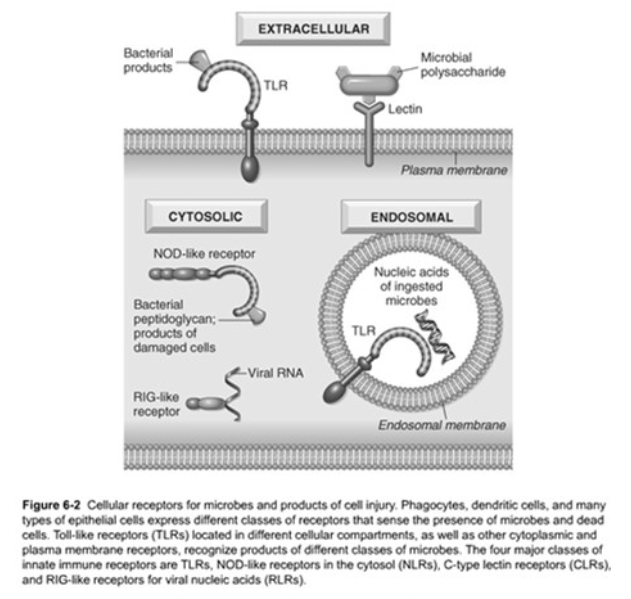
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Function – [...]
Recognizes products of [...]
Located in the plasma membrane and endosomes
Complemented by:
Cytoplasmic and membrane molecules
Other families that recognize microbial products
Microbial sensors
bacteria (endotoxin, bacterial DNA, and other pathogens)
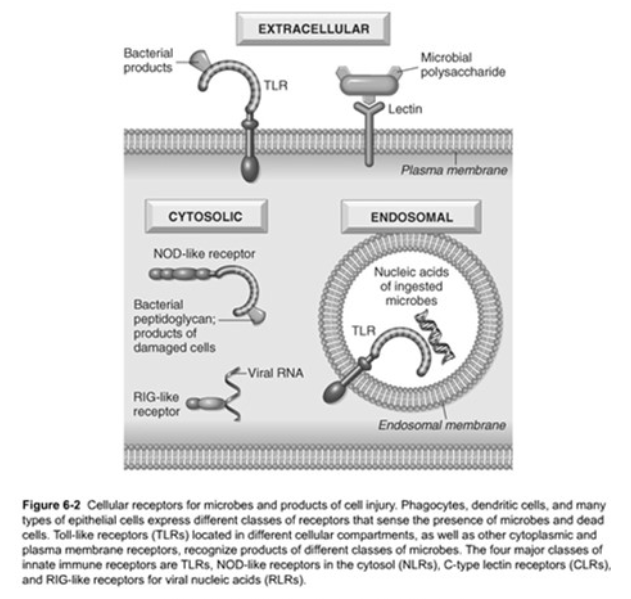
Toll-like Receptors (TLRs)
Function – Microbial sensors
Recognizes products of bacteria (endotoxin, bacterial DNA, and other pathogens)
Located in the [...] and [...]
Complemented by:
Cytoplasmic and membrane molecules
Other families that recognize microbial products
plasma membrane
endosomes
[...]
Migration of leukocytes through vessel wall via space in between cells at intercellular junctions
Mediated by PECAM-1 (aka CD31)
Transmigration
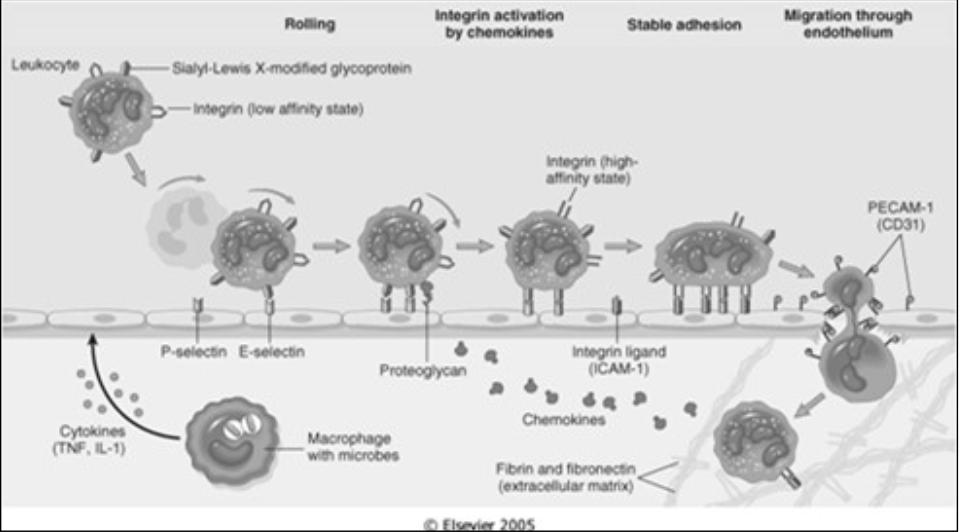
Transmigration
Migration of leukocytes through vessel wall via space in between cells at intercellular junctions
Mediated by [...]
PECAM-1 (aka CD31)
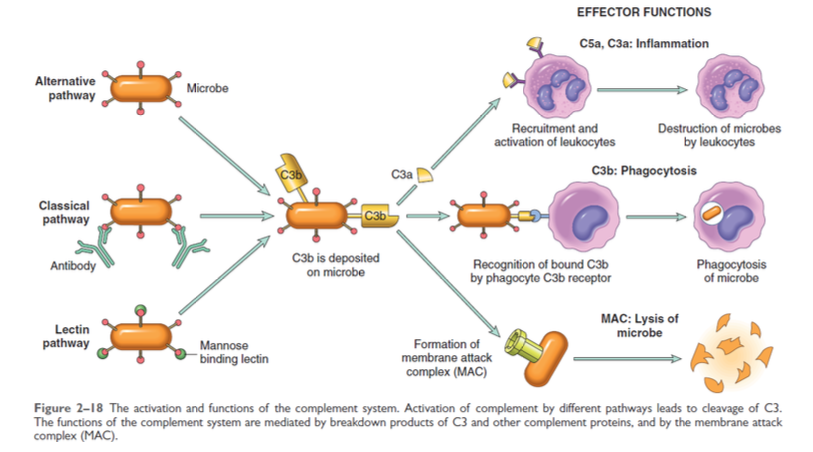
Complement System
All pathways converge on C3 and cause a splitting of C3
[...] – attaches to microbe
[...] goes on to work on [...] which splits again
[...] – attaches and goes to C6-C9→MAC
[...] – goes into blood stream→ trigger mast cell degranulation
[...] – goes off into bloodstream → trigger mast cell degranulation
C3b
C3b
C5
C5b
C5a
C3a
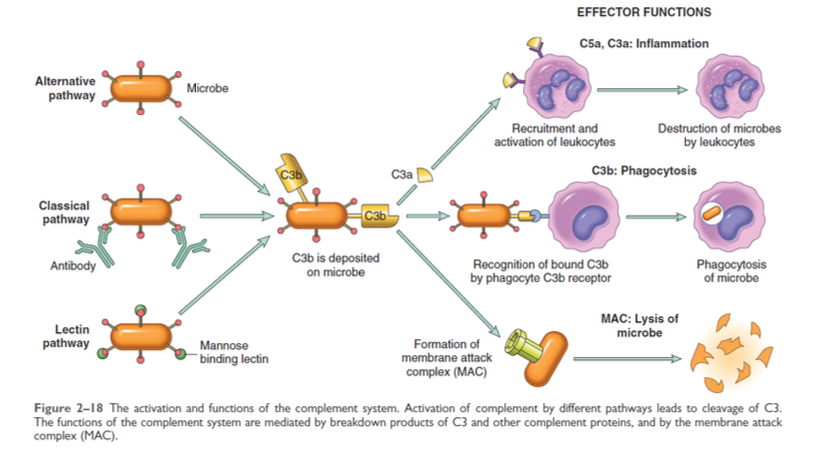
Complement System
All pathways converge on C3 and cause a splitting of C3
C3b – attaches to microbe
C3b goes on to work on C5 which splits again
C5b – attaches and goes to C6-C9→[...]
C5a – goes into blood stream→ trigger mast cell degranulation
C3a – goes off into bloodstream → trigger mast cell degranulation
MAC
Complement System
20 plasma proteases
Source of vasoactive mediators
Important role in immunity
Present in the plasma in an inactive form but sequentially activated by three independent pathways
Classical Pathway
activated by [...]
Alternate Pathway
activated by [...]
Lectin Pathway
activated by [...]
IgG / IgM (memory cells, 2nd line of defense)
surface molecules - microbes (1st line of defense)
MBL binding to mannose on microorganisms
Anti-Inflammatory Mechanisms
Mediators are short-lived and destroyed by degrative enzymes
Counteractive measures
[...]
[...]
[...]
Down-regulate the responses of activated macrophages
[...]
Lipoxins
Complement regulatory proteins
IL-10
TGF-b
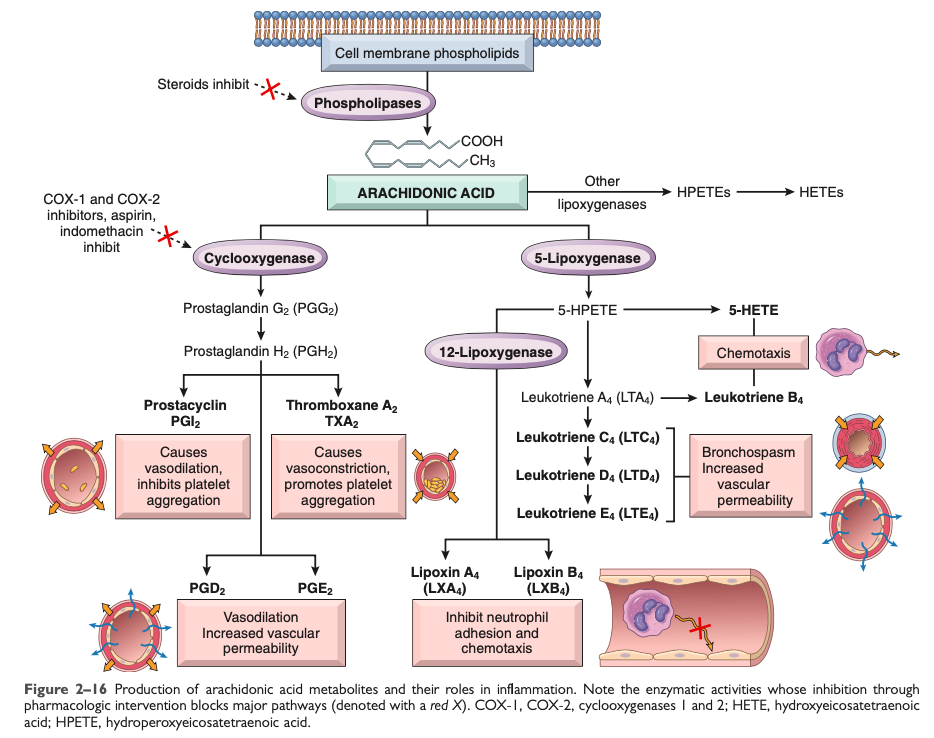
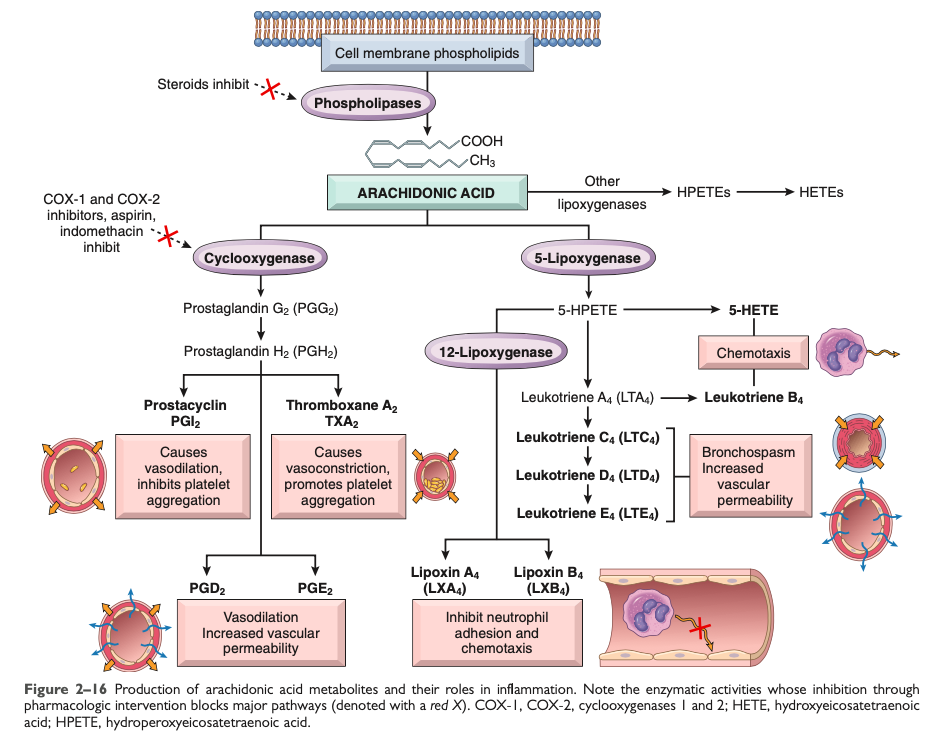
Arachidonic Acid Metabolites
[Which] pathway is active even when you take NSAIDs
5-Lipoxygenase
Cells of Chronic Inflammation
Two major pathways of macrophage activation
Classically activated (M1)
Produced by:
[...]
[what kind of cytokines?]
Microbicidal
Alternative macrophage activation (M2)
Activated by
[what kind of cytokines?]
[specifically?]
[specifically?]
NOT microbicidal – principle role is in tissue repair
Microbial products
Cytokines (IFN-g)
cytokines other than IFN-g
IL-13
IL-4
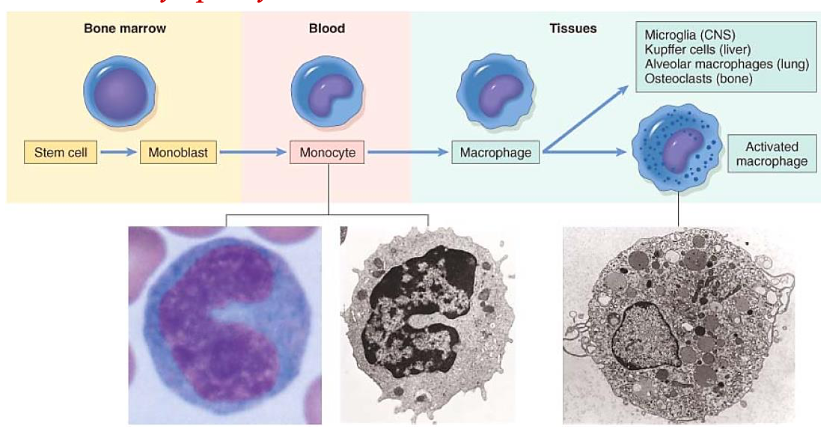
Cells of Chronic Inflammation
Two major pathways of macrophage activation
Classically activated (M1)
Produced by:
Microbial products
Cytokines (IFN-g)
[Is it microbicidal?]
Alternative macrophage activation (M2)
Activated by
cytokines other than IFN-g
IL-13
IL-4
[Is it microbicidal?]
Microbicidal
NOT microbicidal – principle role is in tissue repair
Chemokines
Classified into four group, but the two major groups:
[...]
Act primarily on neutrophils
[...]
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
Macrophage inflammatory protein – 1a
CXC chemokines
CC chemokines
Chemokines
Classified into four group, but the two major groups:
CXC chemokines
Act primarily on [...]
CC chemokines
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
Macrophage inflammatory protein – 1a
neutrophils
Chemokines
Classified into four group, but the two major groups:
CXC chemokines
Act primarily on neutrophils
CC chemokines
[...]
[...]
Monocyte chemoattractant protein-1
Macrophage inflammatory protein – 1a
Chemokines
Family of small (8 to 10 kDa) structurally related proteins
Act primarily as a [...] for different subset of leukocytes
chemoattractant
Chemokines
Mediate their activities by binding to specific G protein coupled receptors on target cells
[...] & [...]
Important in binding and entry of HIV into cells
CXCR4 & CCR5
Chronic Inflammation
Characteristics
Prolonged duration
Tissue destruction
Repair – involving [...] and [...]
Active inflammation involving [what type of] cells
angiogenesis and fibrosis
mononuclear
Scar formation; tissue will not return to normal
mononuclear cells -- macrophages, lymphocytes, plasma cells
Chronic Inflammation
Histologic Features
Infiltration with mononuclear cells
[...]
[...]
[...] cells
Tissue destruction
Attempts at healing by connective tissue replacement of damaged tissue via:
Angiogenesis
Fibrosis
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Plasma
Chronic Inflammation
Histologic Features
Infiltration with mononuclear cells
Macrophages
Lymphocytes
Plasma cells
Tissue destruction
Attempts at healing by connective tissue replacement of damaged tissue via:
[...]
[...]
Angiogenesis
Fibrosis
Clotting System
[...]
Increases vascular permeability
Increases leukocyte emigration
Factor Xa
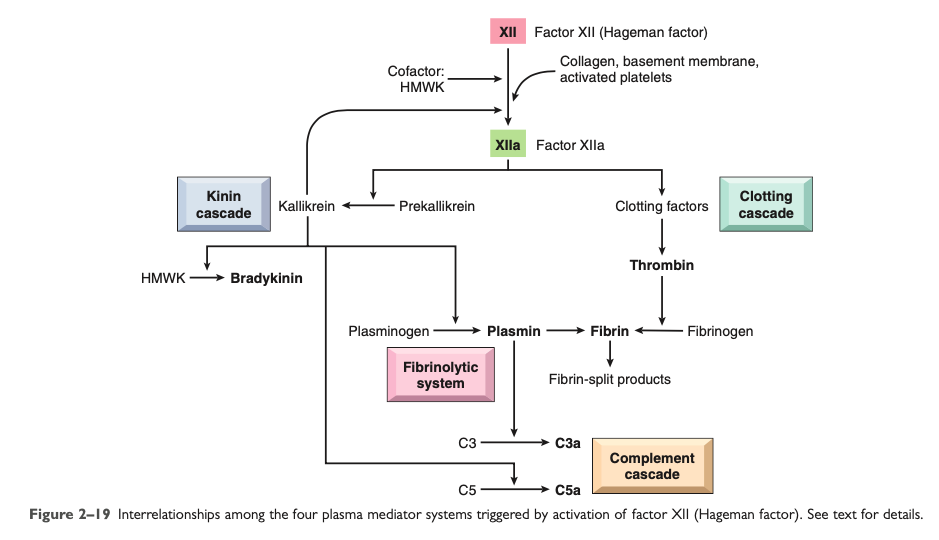
Clotting System
[...]
Activates kinin cascade
Factor XIIa
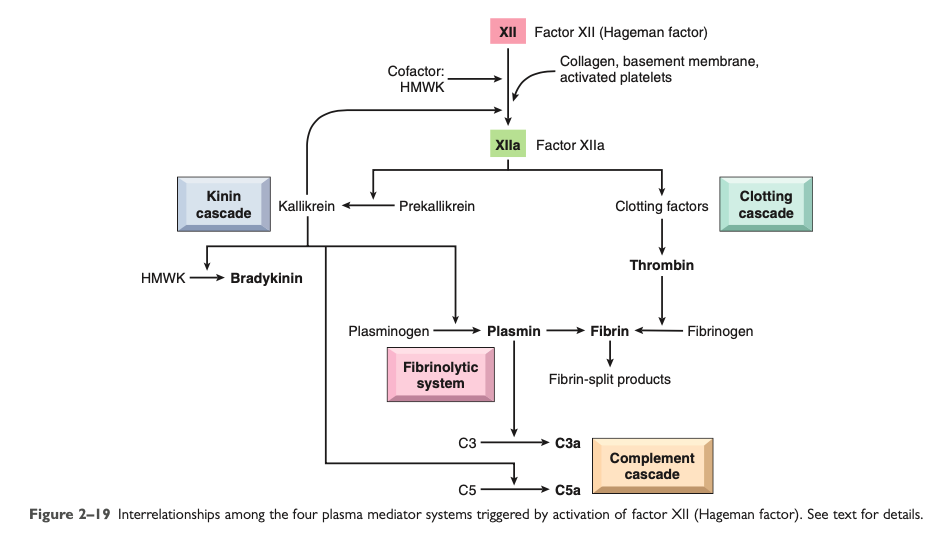
Clotting System
[...]
Increased leukocyte adhesion and fibroblast proliferation
During the formation of the fibrin clot, fibrinopeptides are formed which increase vascular permeability and chemotaxis
Thrombin
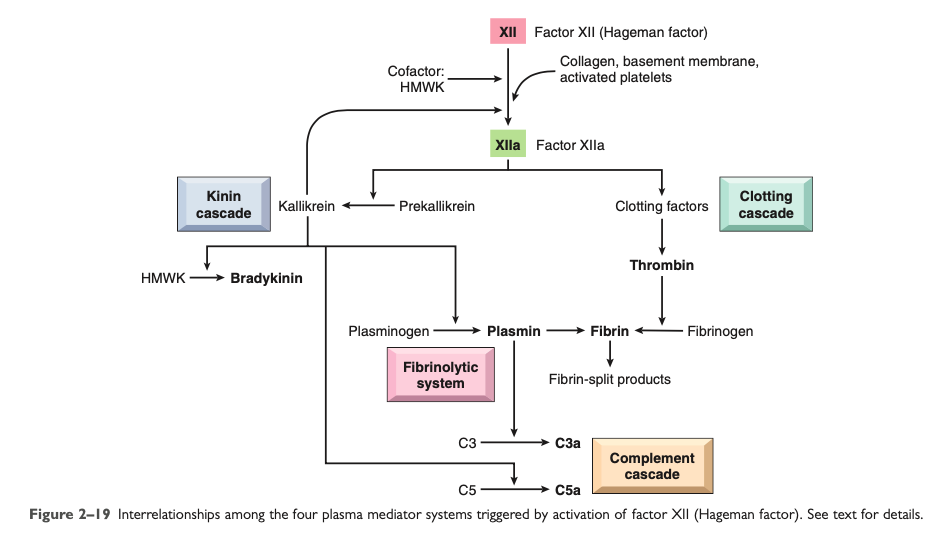
Clotting System
Thrombin
Increased leukocyte adhesion and fibroblast proliferation
During the formation of the fibrin clot, [...] are formed which increase vascular permeability and chemotaxis
fibrinopeptides
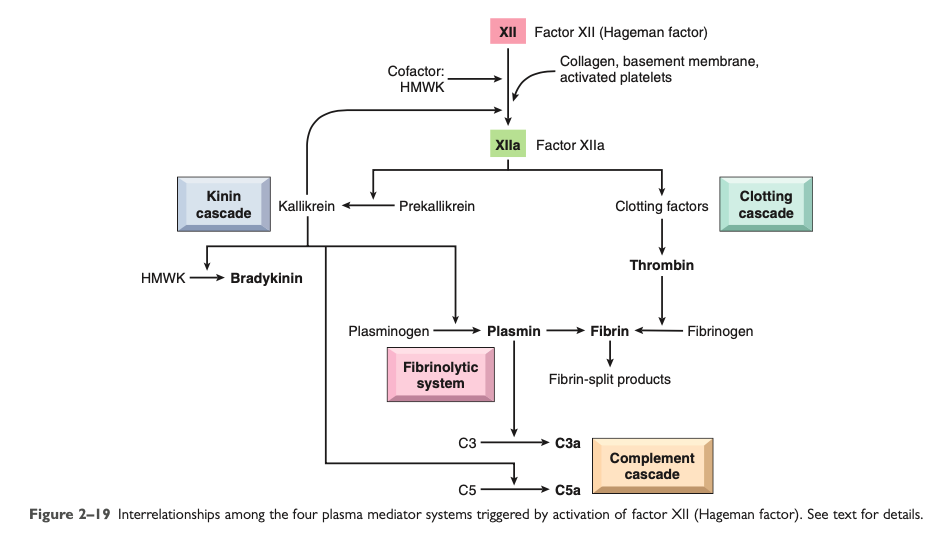
Complement System
Anaphylatoxins
C5a
Activates the [...] pathway of arachidonic acid metabolism
[major function?]
lipoxygenase
Chemotactic factor